ENT + Ophthalmology
1/180
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
181 Terms
Embryonic development of head + neck structures
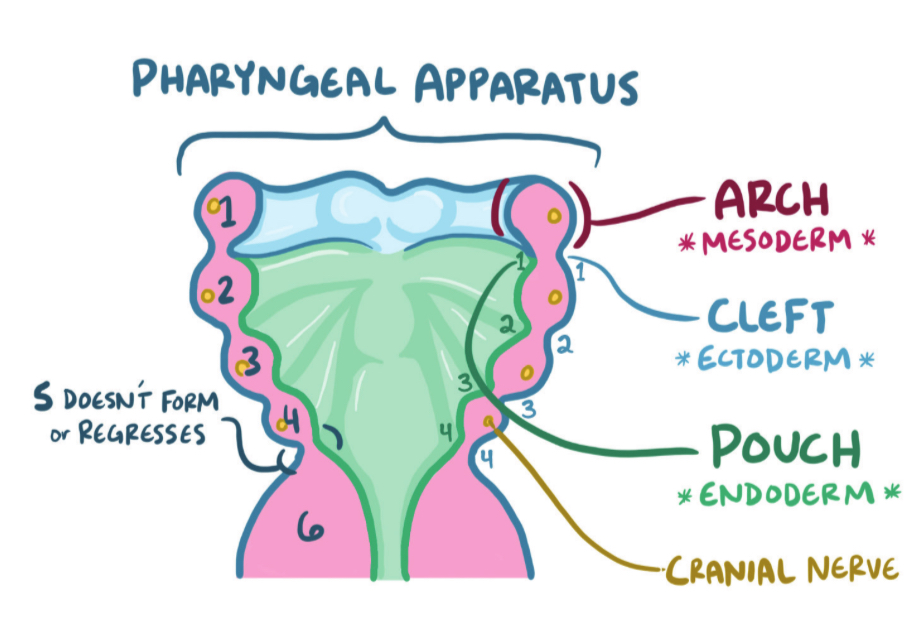
Week 4: pharyngeal apparatus forms
6 arches + cranial nerves → separated by 4 clefts
5th regresses early
Outer ectoderm lining, mesenchyme core, inner endoderm lining
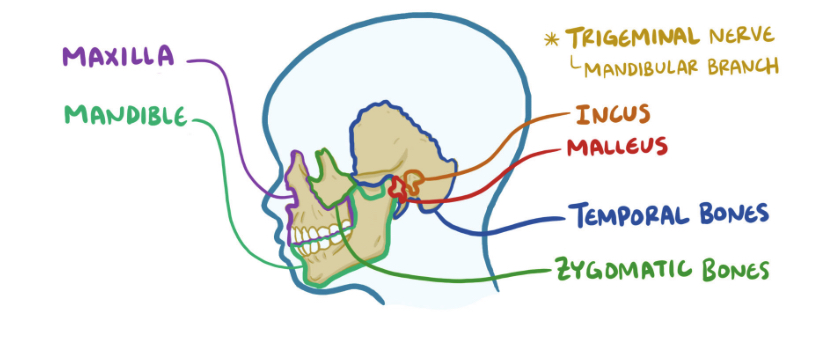
What bones arise from 1st pharyngeal arch
maxilla
Mandible
Incus
Malleus
Temporal
Zygomatic
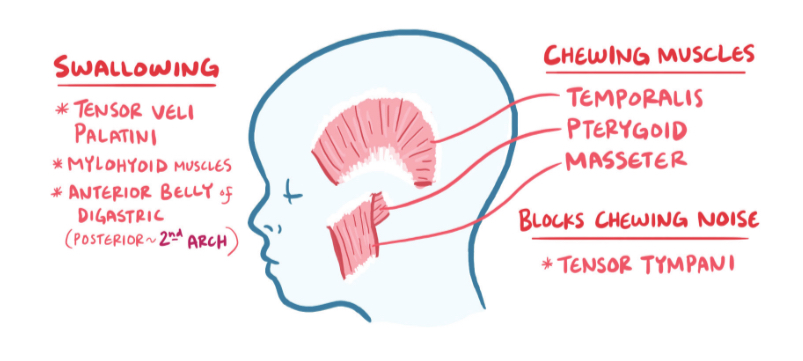
Muscles arising from 1st pharyngeal arch (+innervation)
temporalis
Pterygoid
Masseter
Tensor tympani
Mylohyoid
Anterior belly of digastric
Innervated by trigeminal n. (V3)
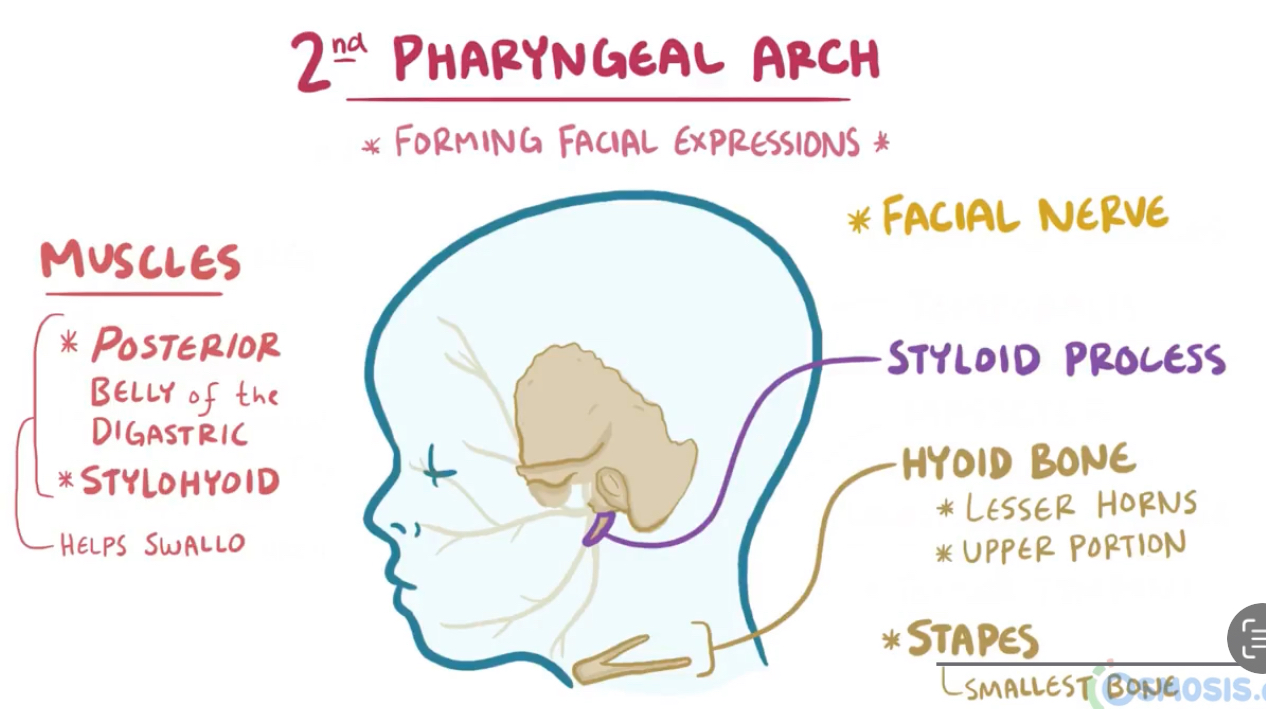
Structures arising from 2nd pharyngeal arch + innervation
Hyoid (upper portion + lesser horns)
Stapes + stapedius
Posterior belly of digastric
Stylohyoid
Innervated by facial nerve
Structures arising from 3rd pharyngeal arch + innervation
Hyoid
Stylopharyngeus m.
Innervated by glossopharyngeal nerve (IX)
Structures arising from 4th pharyngeal arches + innervation
levator palatini
Pharyngeal constrictors
Cricothyroid m.
Innervated by vagus n. (Sup. laryngeal branch)
Structures arising from 6th pharyngeal arch + innervation
Intrisinc muscles of larynx
Innervated vagus n. (Recurrent laryngeal branch)
Structures arising from 1st pharyngeal cleft + pouch
Form ear:
Cleft → external acoustic meatus + tympanic membrane
Pouch → middle ear + eustachian tube
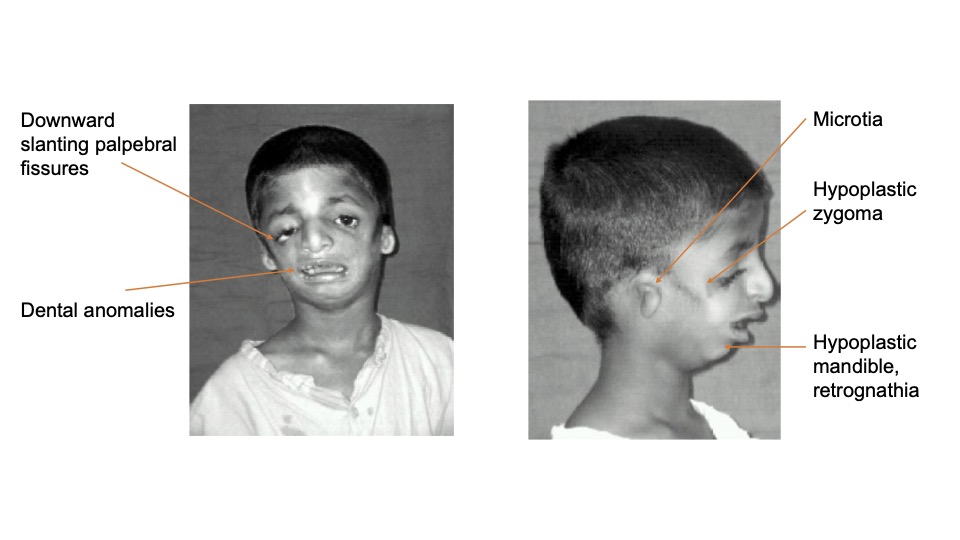
What is first arch syndrome
Congenital disorders caused by failure of neural crest cells to migrate into first pharyngeal arch
treacher-collins syndrome
Pierre-robin sequence
Development of palate (week 6-12)
intermaxillary segment → primary palate
Maxillary prominences → 2 palatine shelves (secondary palate)
All fuse together
Palate deformities
Congenital malformations due to improper fusion of facial bones + associated tissues
cleft lip = gap or separation in upper lip, anterior deformity
Cleft palate = can exist in hard or soft palate, uvula typically split
Layers of scalp superficial to deep (SCALP)
Skin
Connective tissue (dense) → blood vessels
Aponeurosis
Loose connective tissue
Periosteum
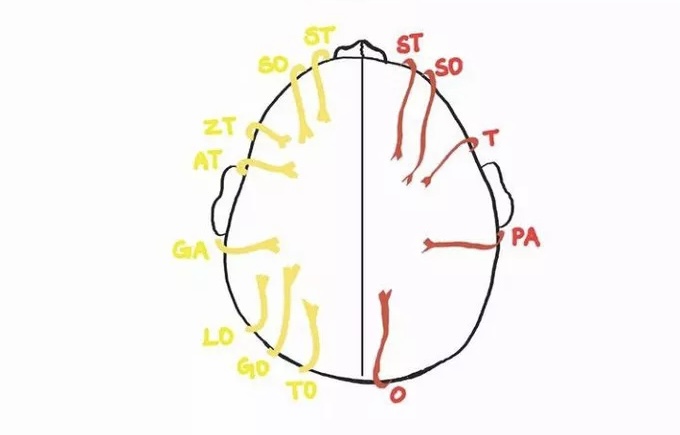
Scalp blood supply
Supratrochlear (ICA)
Supraorbital (ICA)
Superficial temporal
Posterior auricular
Occipital
Branches of external carotid artery
superior thyroid
Ascending pharyngeal
Lingual
Facial
Occipital
Posterior auricular
Maxillary
Superficial temporal
Venous drainage of head + neck
superficial v. = external jugular v → subclavian v.
Deep v. = internal jugular v → subclavian → brachiocephalic v.
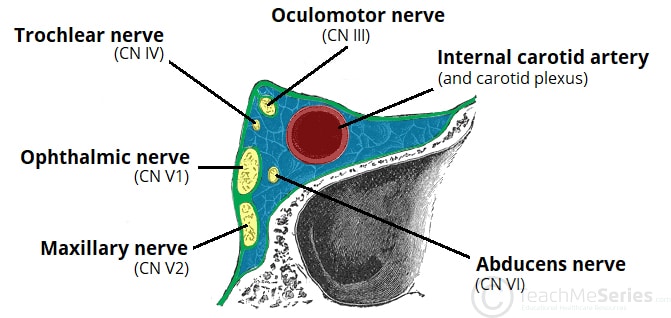
Cavernous sinus contents + significance
Plexus of thin walled veins on upper surface of sphenoid sinus → superior + inferior ophthalmic veins drain inside
ICA
Oculomotor n.
Trochlear n.
Abducens n.
Trigeminal V1+2
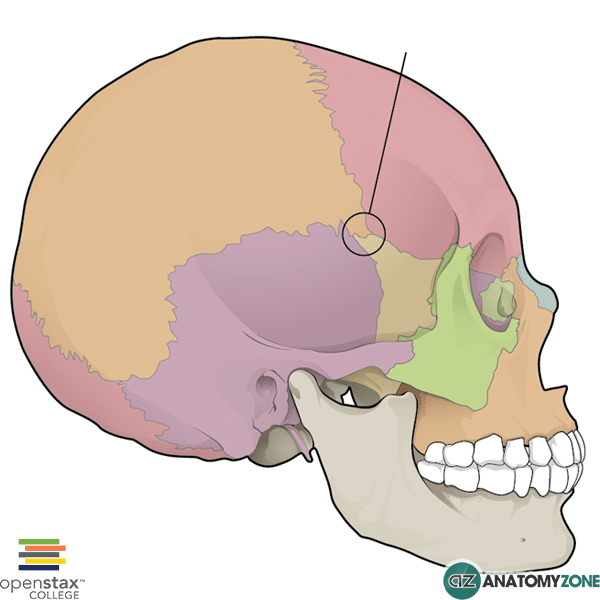
Thinnest part of cranium + significance
Pterion → frontal, sphenoid, parietal + temporal bones
Likely fracture site
Middle meningeal artery injured (foramen spinosum) = extradural haematoma (compression of cerebral cortex)
Tri-lamina structure of cranium
outer compact bone plate
Diploe spongy bone (reduces weight)
Inner compact bone plate
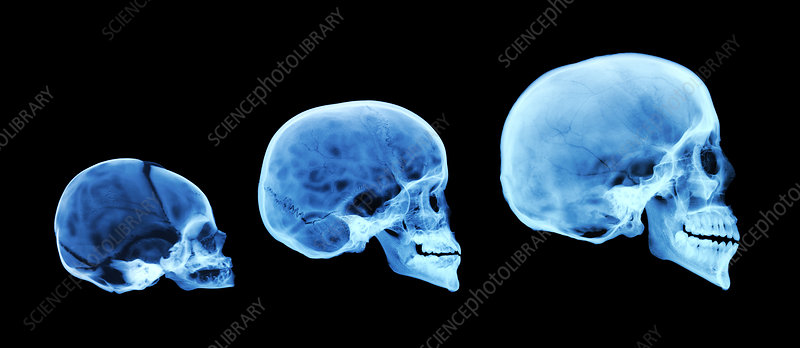
How does a newborn skull differ from an adult
sutures not fused → gaps = anterior + posterior fontanelle (more mobile)
Neurocranium + viscerocranium ratio 8:1 (adult 2:1)
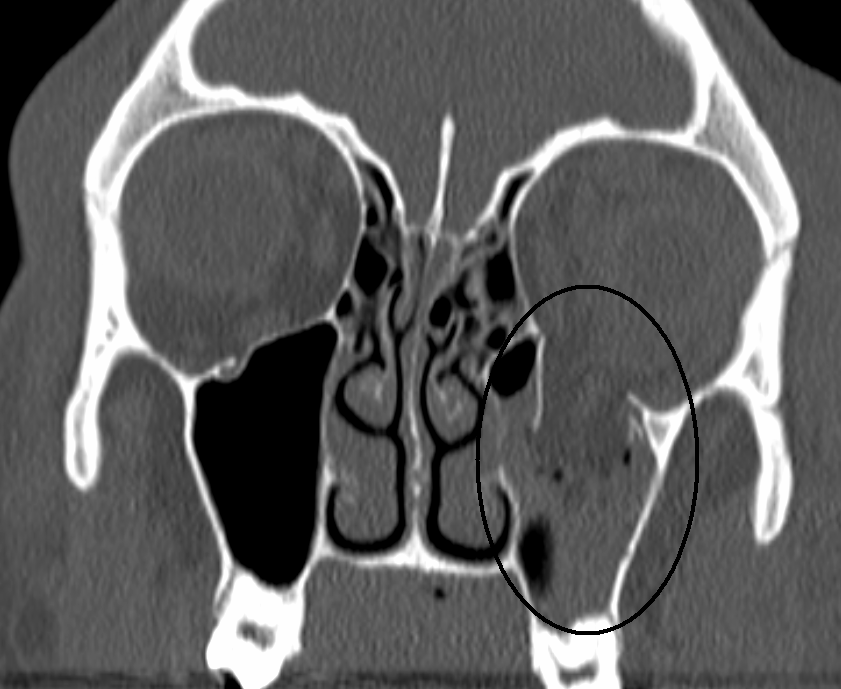
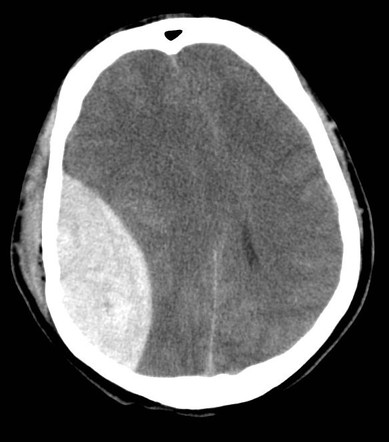
What is shown
Orbital blow-out fracture → risk of damage to infraorbital nerve
May show black eyebrow sign + tear drop
Orbital rim → risk of damage to supratrochlear n
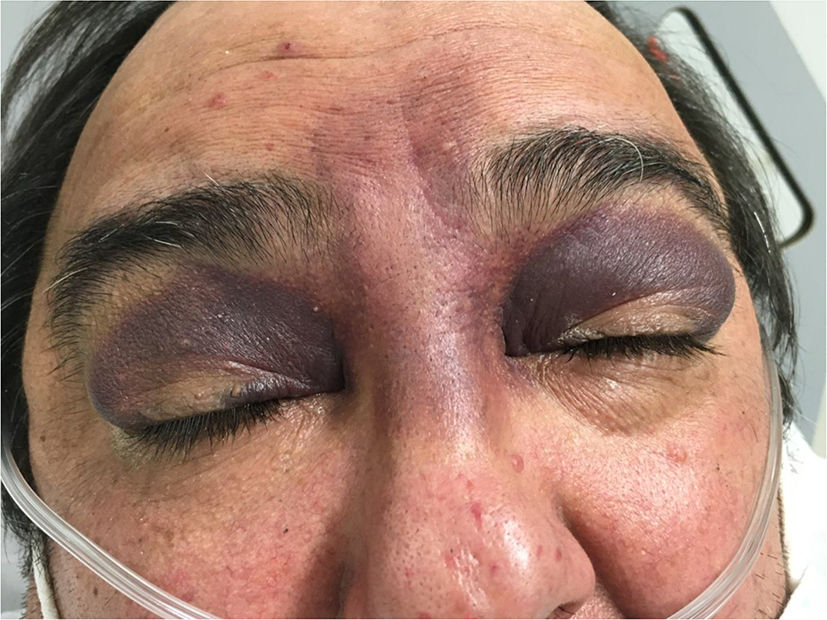
Anterior fossa skull base fracture clinical presentations
Periorbital ecchymosis
Halo sign (in CSF)
Partial/total loss of vision/scent
Eye movement defects
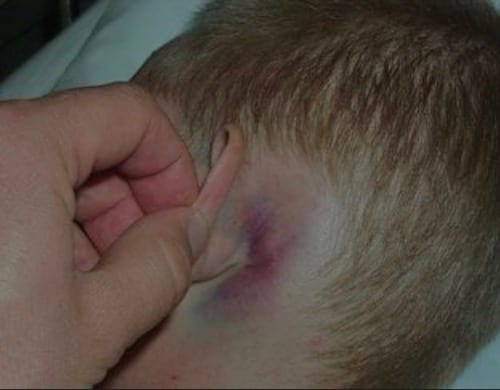
Middle fossa skull base fracture clinical presentations
Battle sign
Hearing loss
Carotid a. Damage
Balances issues
Atypical cervical vertebrae
C1 (atlas): no body or spinous process
C2 (axis): odontoid process
C7: no bifid spinous process (vertebral prominence)
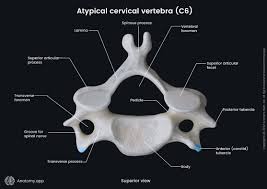
Features of typical cervical vertebrae (C3-6)
Bifid spinous process
Triangular foramen
Uncinate process
Smallest vertebrae
Transverse foramen in transverse process
Cervical vertebrae fractures
C1 (atlas) → Jefferson’s, head first fall
C2 (axis) → Hangman’s, neck hyperextension - more critical
Layers of fascia in neck
skin + subcutaneous fat
Superficial fascia → platysma m. (Involve in facial expressions innervated by CN VII)
Deep fascia → investing, pretracheal + prevertebral
Forms carotid sheath (common + internal carotid artery, internal jugular vein + vagus nerve)
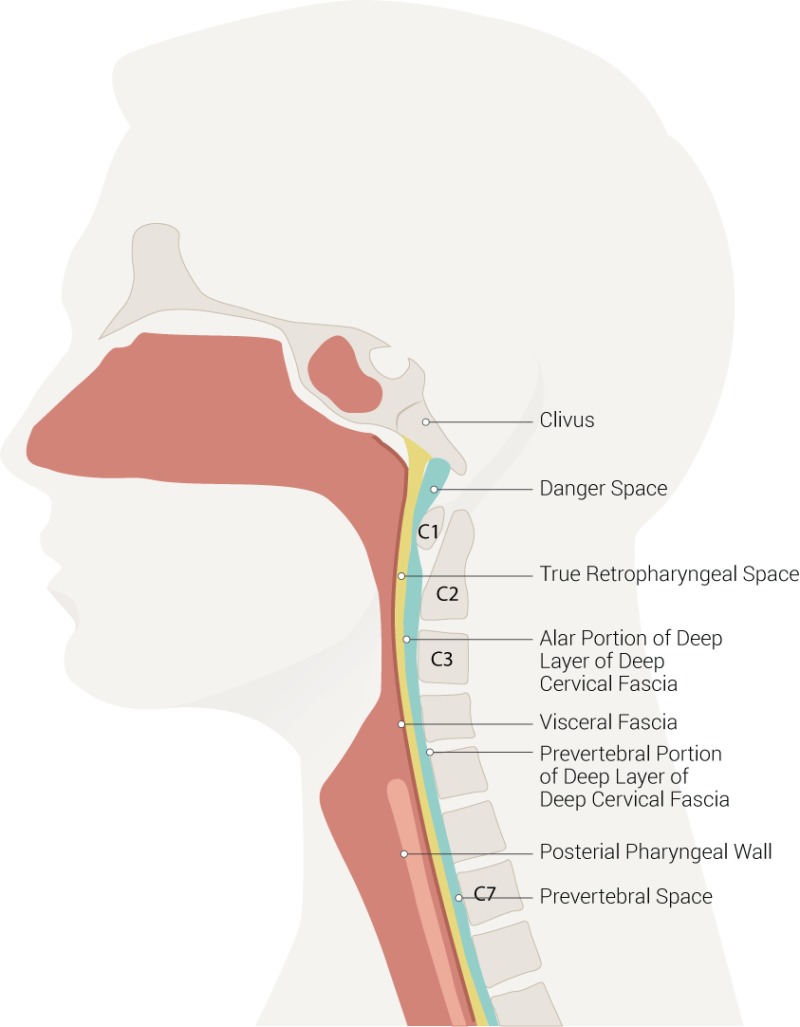
Fascial spaces in neck + significance
pretracheal
Retropharyngeal (alar fascia splits true + danger space)
Prevertebral
Deep neck space infections → can spread to mediastinum/pericardium
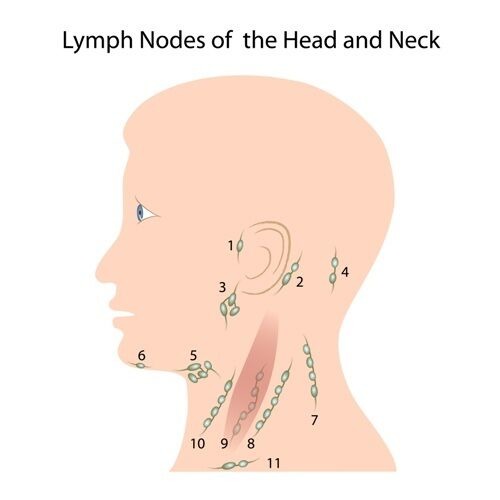
Superficial/regional lymph nodes
Receive lymph from scalp, face + neck
Occipital → occipital scalp
Mastoid → posterior neck, upper ear + lateral scalp
Preauricular + parotid → temporal scalp + lateral face
Submental → chin + lower lip
Submandibular → face between eye + mouth
Buccal → nose + cheek
Superficial cervical → anterior neck
Deep lymph nodes
Located close to internal jugular veins under sternocleidomastoid
prelaryngeal
Pretracheal
Paratracheal
Retropharyngeal
Jugulo-digastric/tonsillar (superior deep node)
Jugulo-omohyoid (inferior deep node)
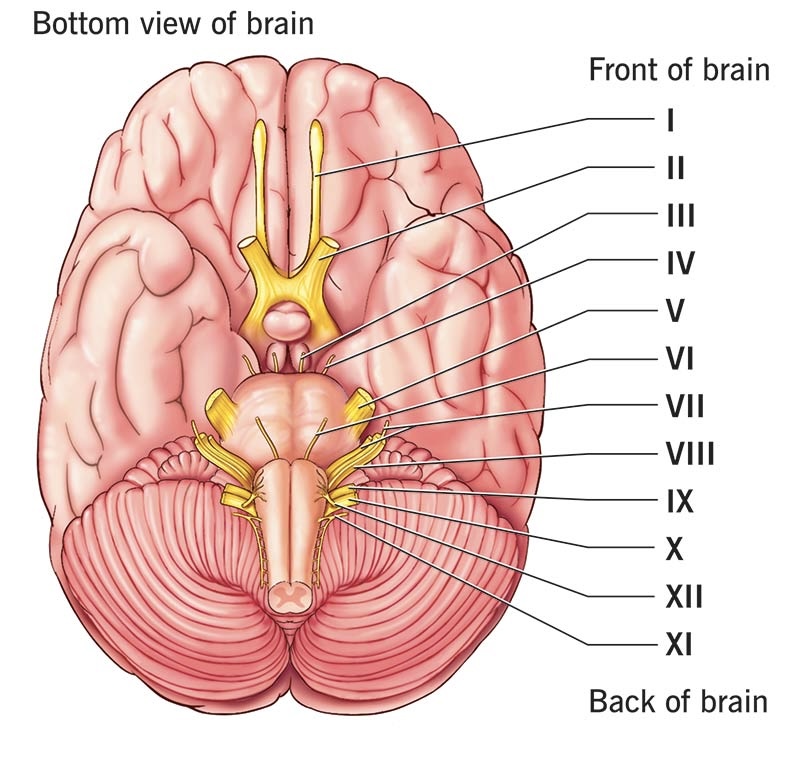
Name the 12 cranial nerves (PNS)
olfactory
Optic
Oculomotor
Trochlear
Trigeminal
Abducens
Facial
Vestibulocochlear
Glossopharyngeal
Vagus
Accessory
Hypoglossal
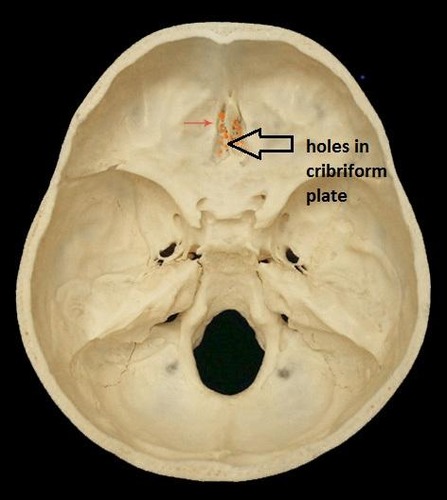
CN I: olfactory
Function: Sensory → smell
Arises from primary olfactory cortex
exits through cribriform plate(ethmoid bone)
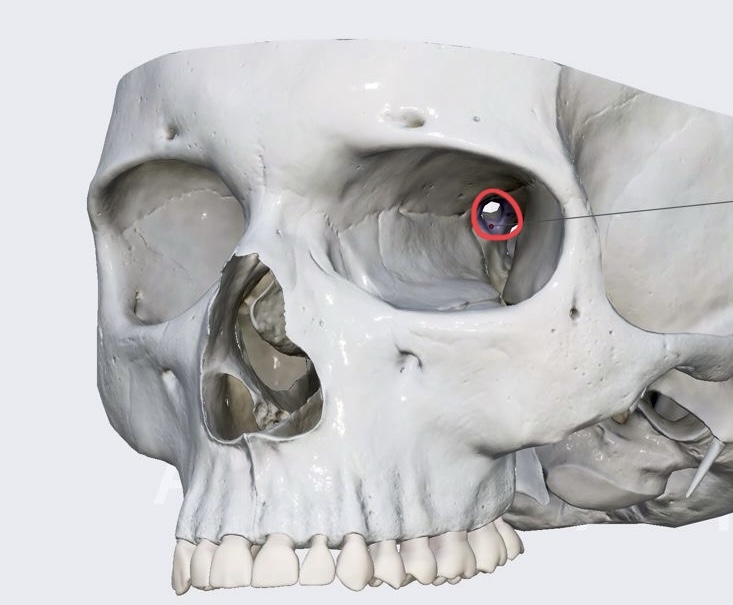
CN II: optic
function: Sensory → vision
Arises from retinas
exits through optic canal
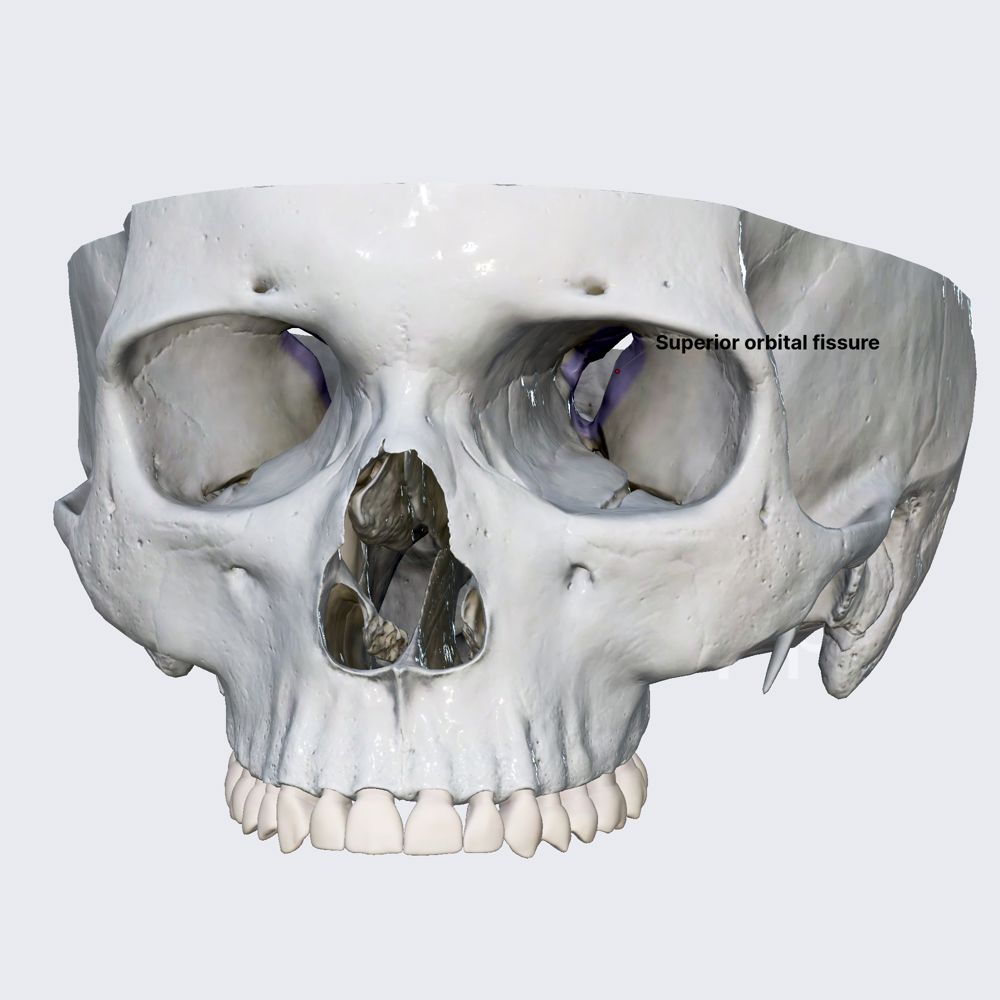
CN III: oculomotor
function: Motor → extraorbital muscles+ eyelid elevation
Arises from ventral midbrain
exits superior orbital fissure
CN IV: trochlear
function: motor → superior oblique m.
Arises from dorsal midbrain
Exits from Superior orbital fissure
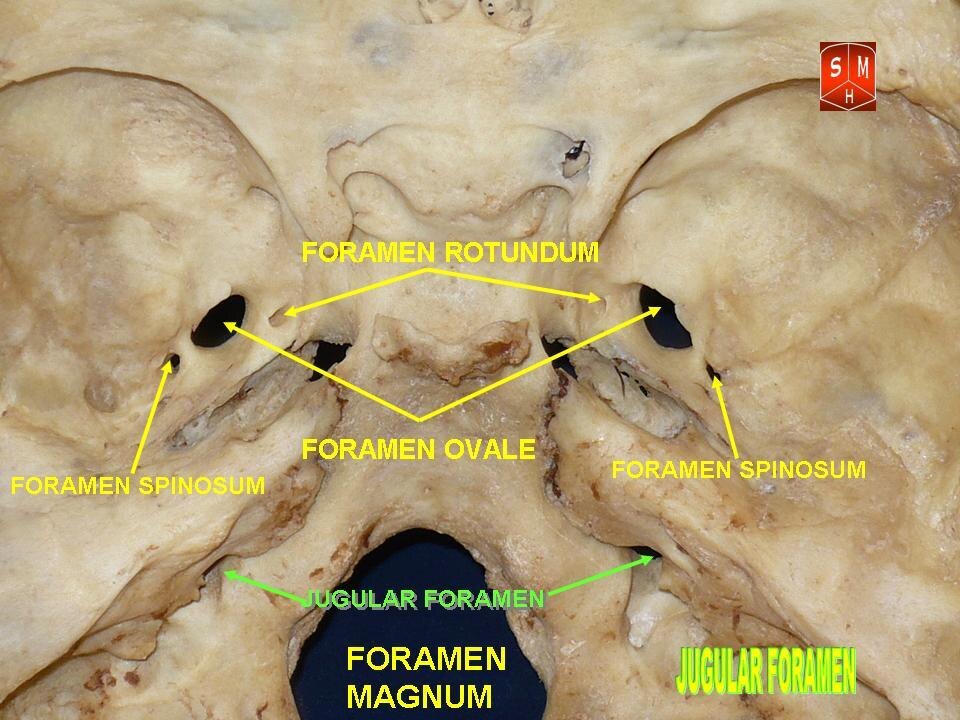
CN V: Trigeminal
Function: sensory + motor → splits into 3 branches at trigeminal ganglion
Arises from Pons
V1 opthalmic - superior orbital fissure
V2 maxillary - foramen rotundum
V3 mandibular - foramen ovale
CN VI: abducens
Function: motor → lateral rectus
Arises from Pons
Exits superior orbital fissure
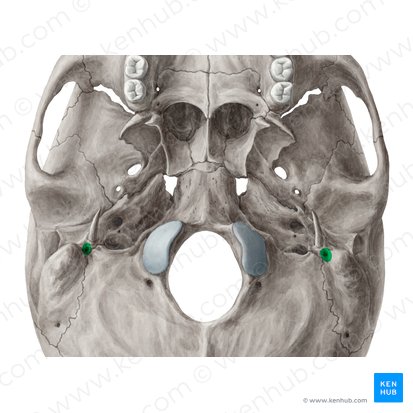
CN VII: Facial
function: sensory + motor → facial expression, anterior 2/3 tongue, lacrimal+salivary glands, stapedius m. (ear)
Arises from pons → internal acoustic meatus
exit stylomastoid foramen
CN VIII: Vestibulocochlear
Function: sensory → 2 branches
vestubular → balance, cochlear → hearing
arises from pons
exits internal acoustic meatus
CN IX: Glossopharyngeal
function: sensory + motor → posterior 1/3 tongue, pharynx + stylopharyngeus
arises from medulla
exits jugular foramen
CN X: Vagus
function: sensory + motor → pharyngeal + laryngeal muscles, PANS innervation
arises from medulla
exits jugular foramen
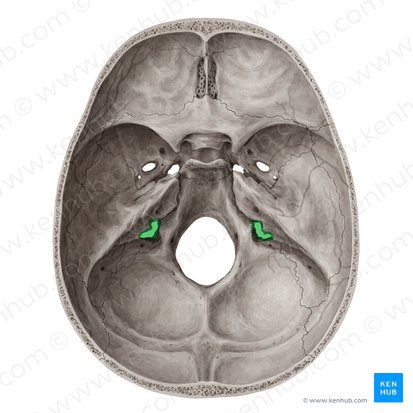
CN XI: Accessory
function: motor → trapezius + sternocleidomastoid m.
arises from spinal cord/medulla
exits jugular foramen
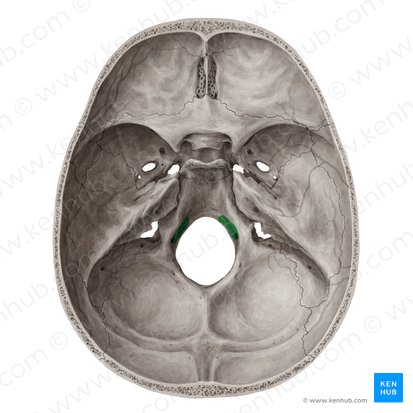
CN XII: Hypoglossal
function: motor → innervates tongue (not palatoglossus)
arises from medulla
exits hypoglossal canal
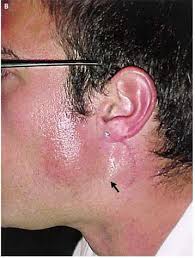
Frey’s syndrome
damaged auriculotemporal n. (branch of V3)
during healing reinnervates sweat gland
sweating instead of salivating + redness whilst eating
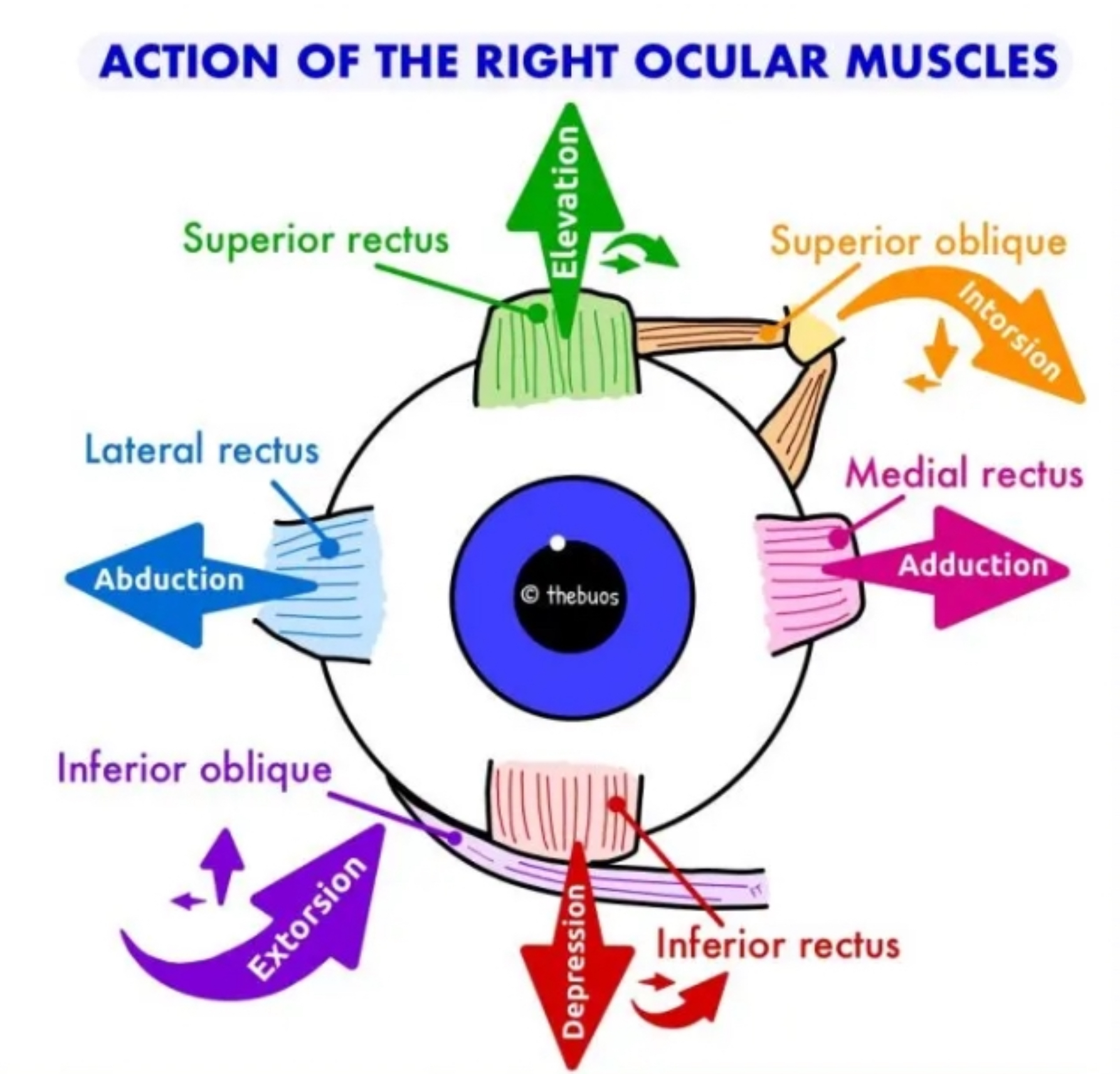
Extra-ocular muscles + functions
superior rectus (III) → elevate, intorsion, adduct
Medial rectus (III) → adduct
Inferior rectus (III) → depress, extort, adduct
Lateral rectus (VI) → abduct
Inferior oblique (III) → extorsion, elevate, abduct
Superior oblique (IV) → intorsion, depress, abduct
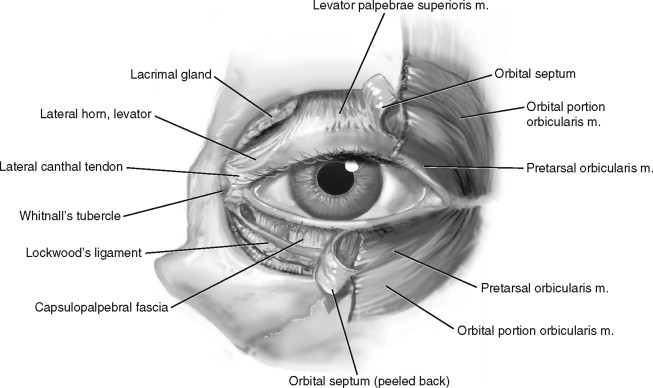
Muscles + nerves involved in opening/closing of eyes
opening: levator palpebrae superioris → occularmotor n.
Closing: oribicularis oculi → facial n.
Attach to inferior + superior tarsal plates
Bell’s palsy pathology
damage to CN VII (facial)
Unilateral facial weakness/paralysis
Lower motor neurone lesion
Typically idiopathic → infection, lyme disease, pregnancy + diabetes RFx
How to differentiate between stroke + Bell’s palsy
stroke: upper neurone lesion = bilateral innervation so forehead sparing (able to move)
BP: lower motor = paralysis of all muscles
Bell’s Palsy clinical presentations (BELLs PAlsy)
Blink reflex abnormal
Ear sensitivity
Loss of taste
Lacrimation → absent/excess
Paralysis
Absent nasolabial fold
Horner’s syndrome
ocularsympathetic palsy → interruption of cervicothoracic sympathetic chain (C8-T2)
Can occur at 1st/2nd/3rd order neurone
Presents w/ ptosis, miosis + anhydrosis
3 layers of eye wall
fibrous: sclera + cornea
Vascular/uvea: pupil, iris, ciliary body, choroid
Neural: retina
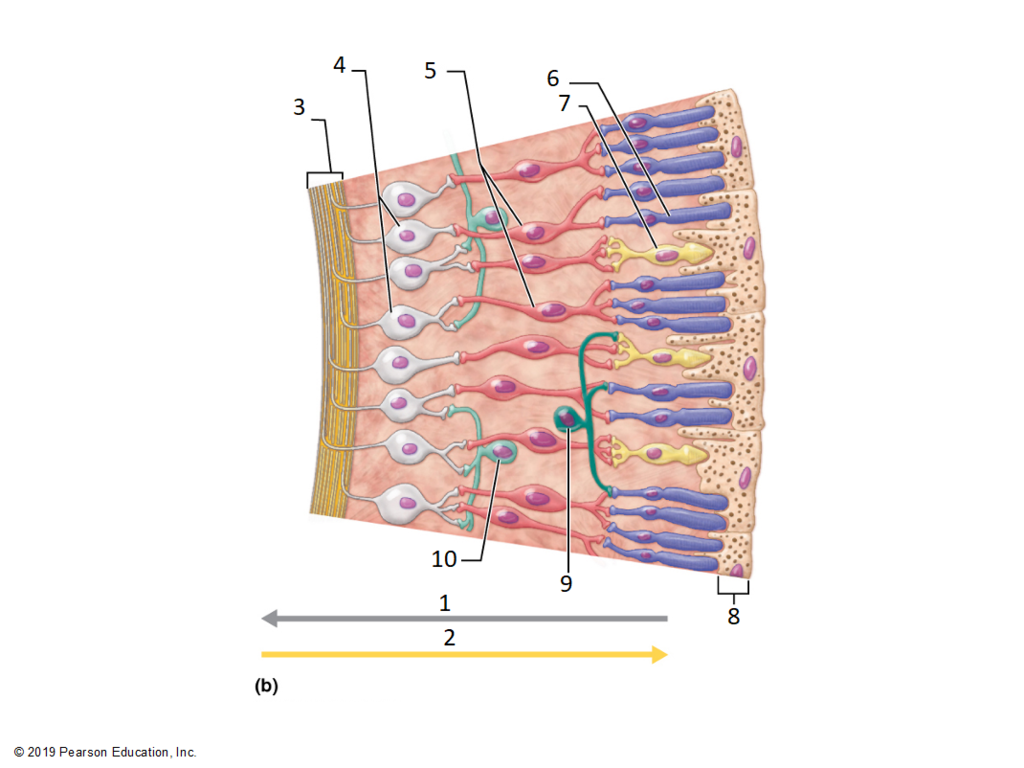
Retinal neurones
Ganglion cell
Bipolar cell
Photoreceptors: cones + rods
Pigment epithelium
photoreceptors
Cones:
concentrated in fovea
highest visual acuity
detect blue, red + green light
Rods:
more numerous
light sensitive → vision in low light
black + white
Contain light-sensitive pigment → rhodopsin
Ocular accommodation
reflex when focusing on a close object after looking far away
ciliary muscle contraction = relaxation of zonular fibres
lens becomes more curved (refractive power increases)
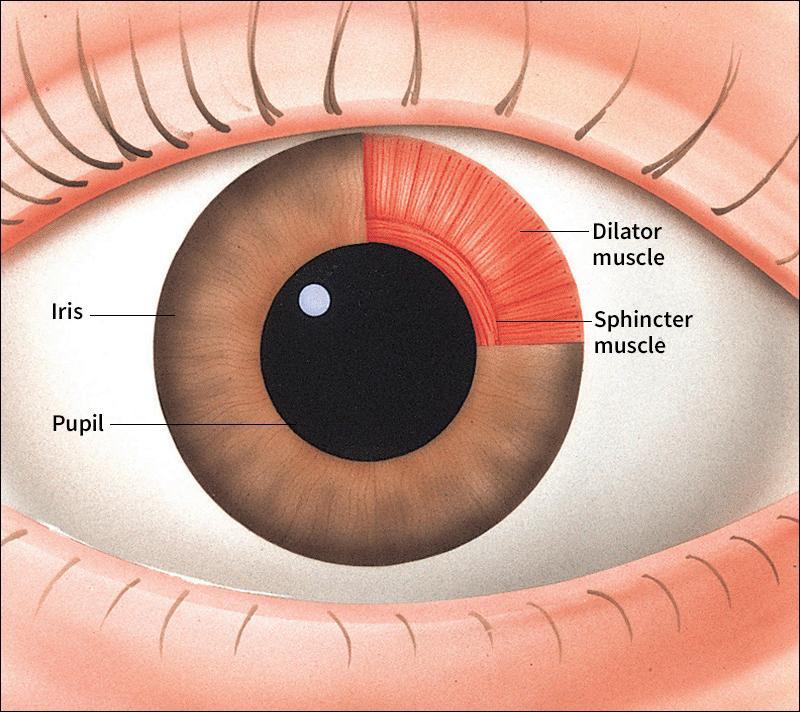
Mechanism of pupil constriction + dilation
Constriction/Miosis: increased light → sphincter pupillae contract
Dilation/mydriasis: decreased light → dilator pupillae contract
Parasympathetic control → CN III
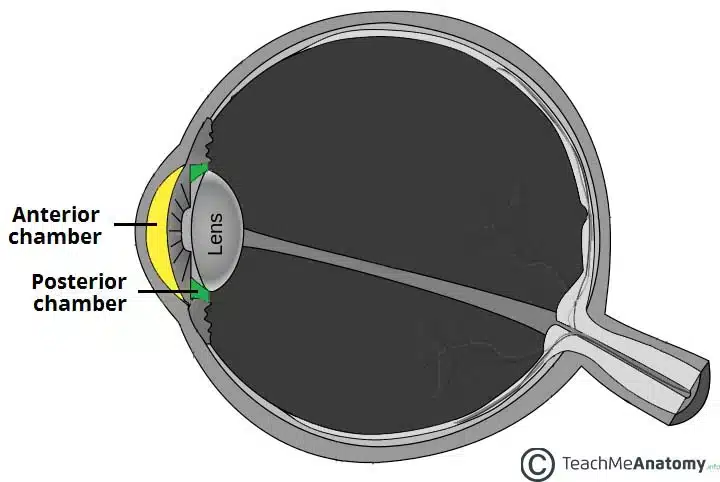
Aqueous humour
produced by ciliary body into posterior chamber → anterior
Drained through trabecular meshwork → canal of schlemm
Maintains intraoccular pressure, provides nutrients, removes waste
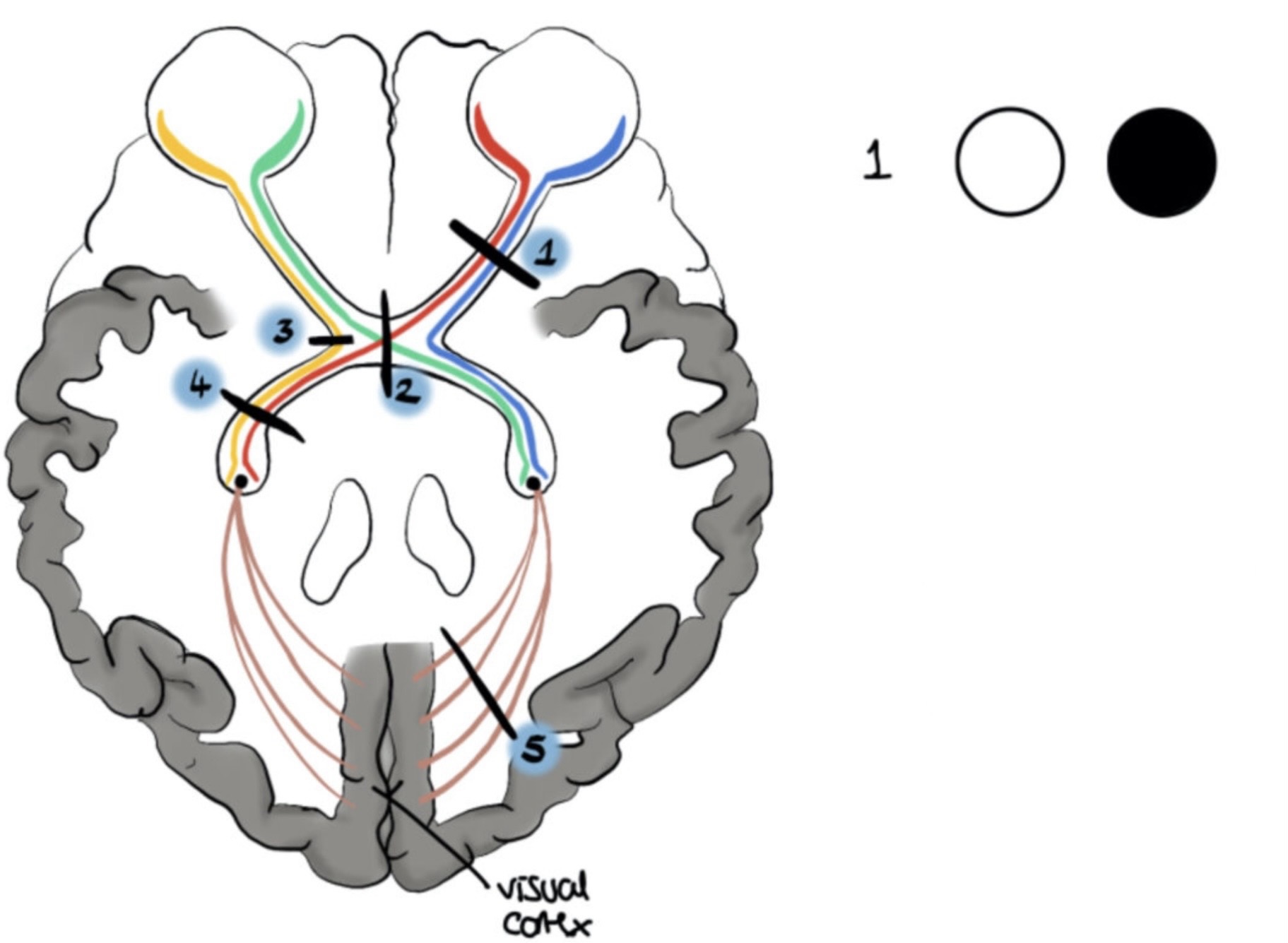
What visual field defect is shown
Total right eye visual loss
Optic nerve lesion → ipsilateral blindness
What visual field defect is shown
Bitemporal hemianopia (Central optic chiasm lesion)
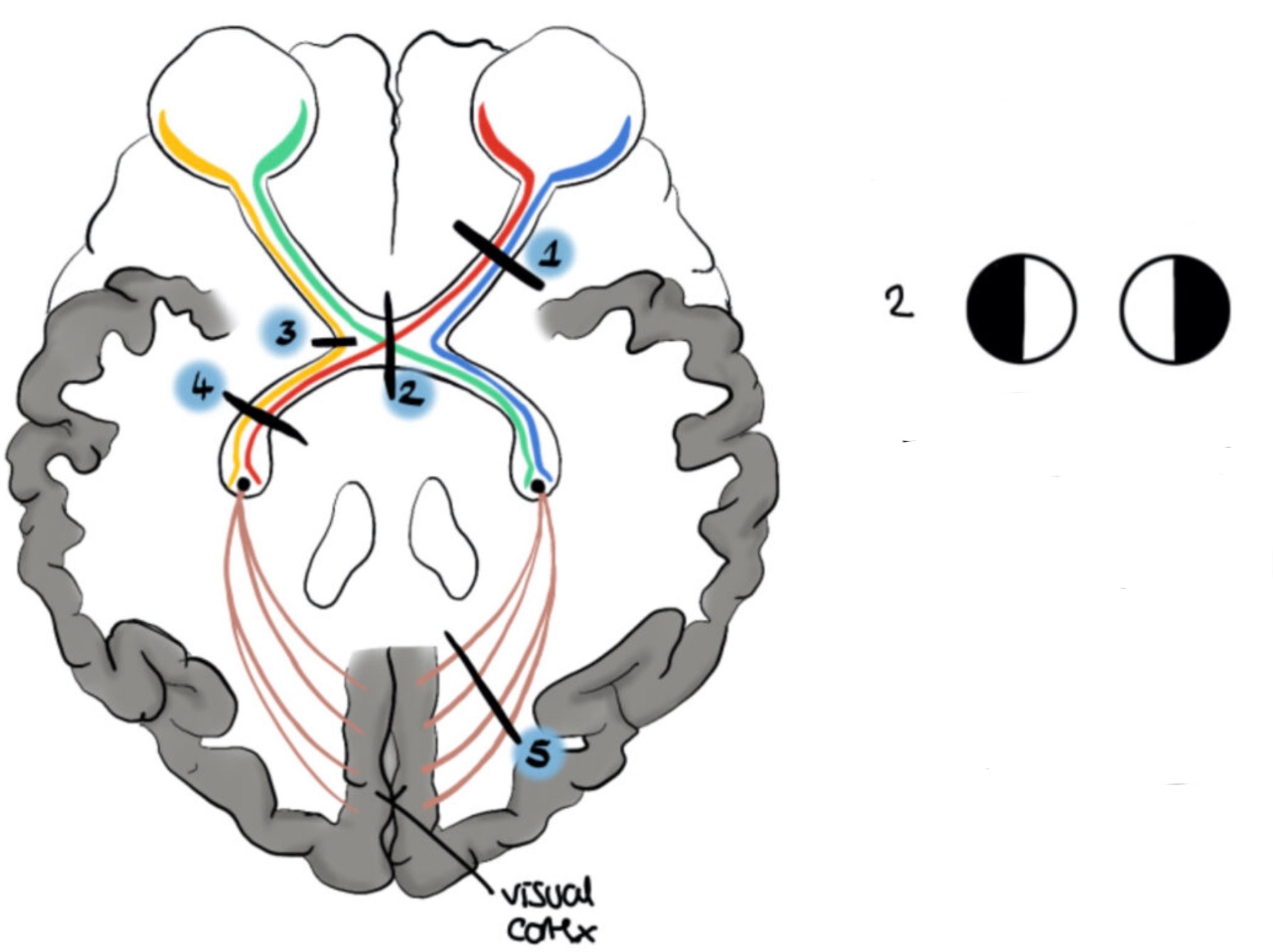
What visual field defect is shown
Left nasal hemianopia (Lateral optic chiasm lesion = ipsilateral)
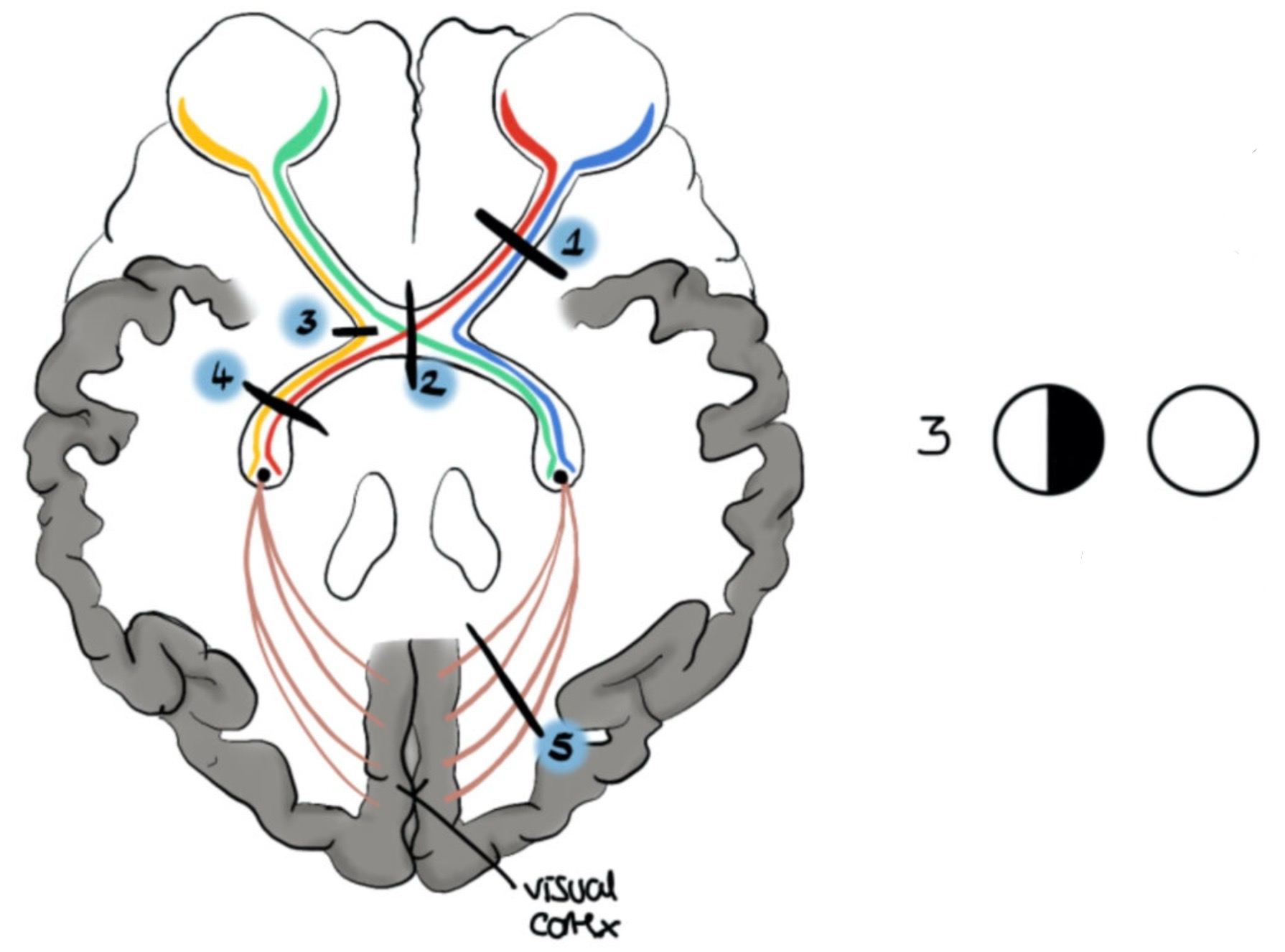
What visual field defect is shown
Right homonymous hemianopia (optic tract lesion = contralateral)
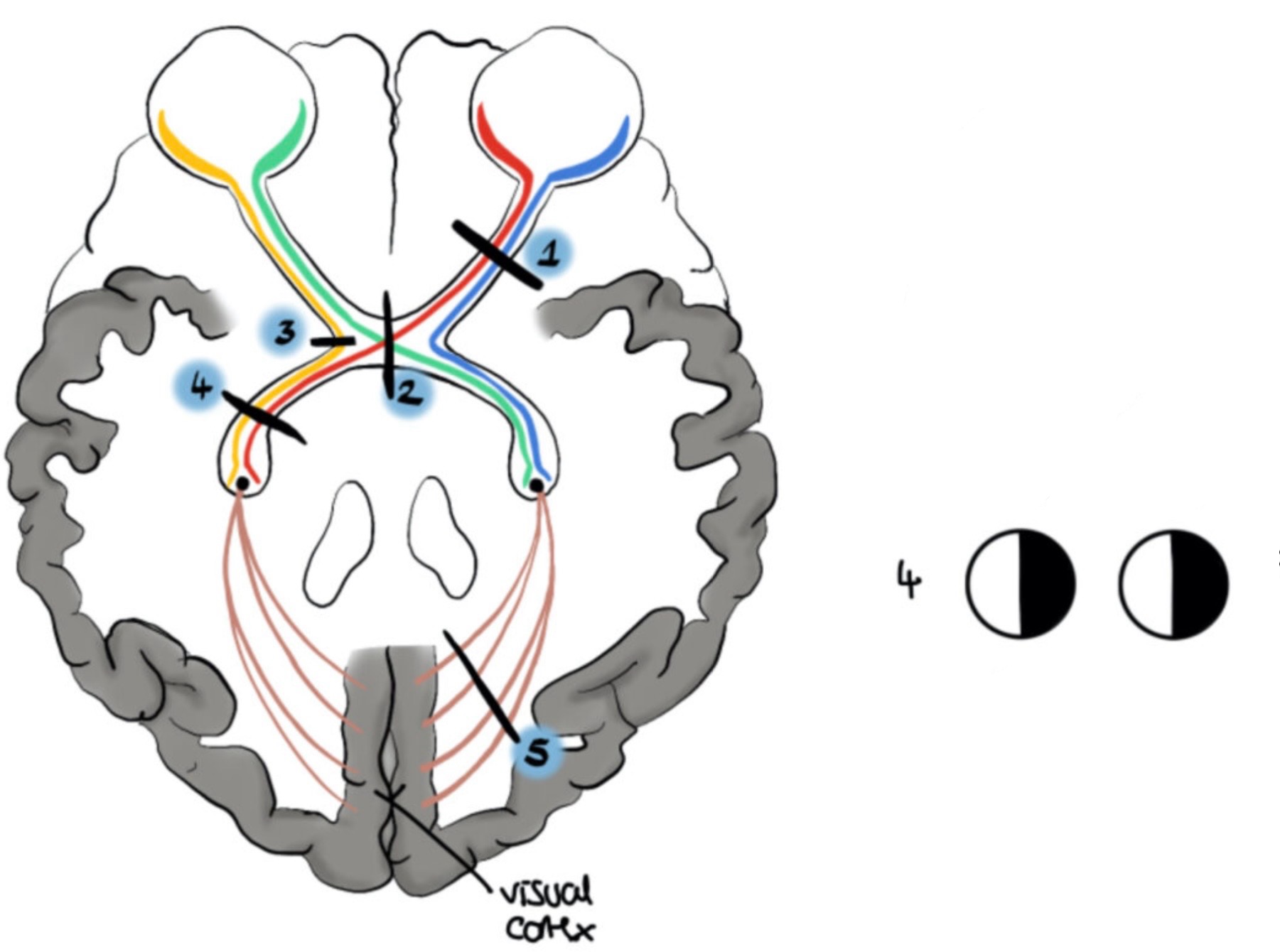
What visual field defect is shown
Left homonymous hemianopia w/ macular sparing (occipital cortex lesion)
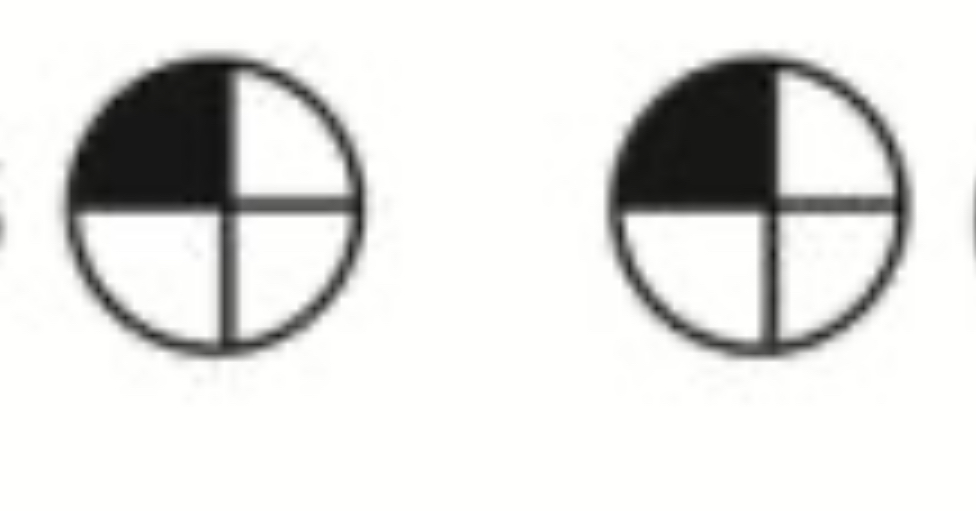
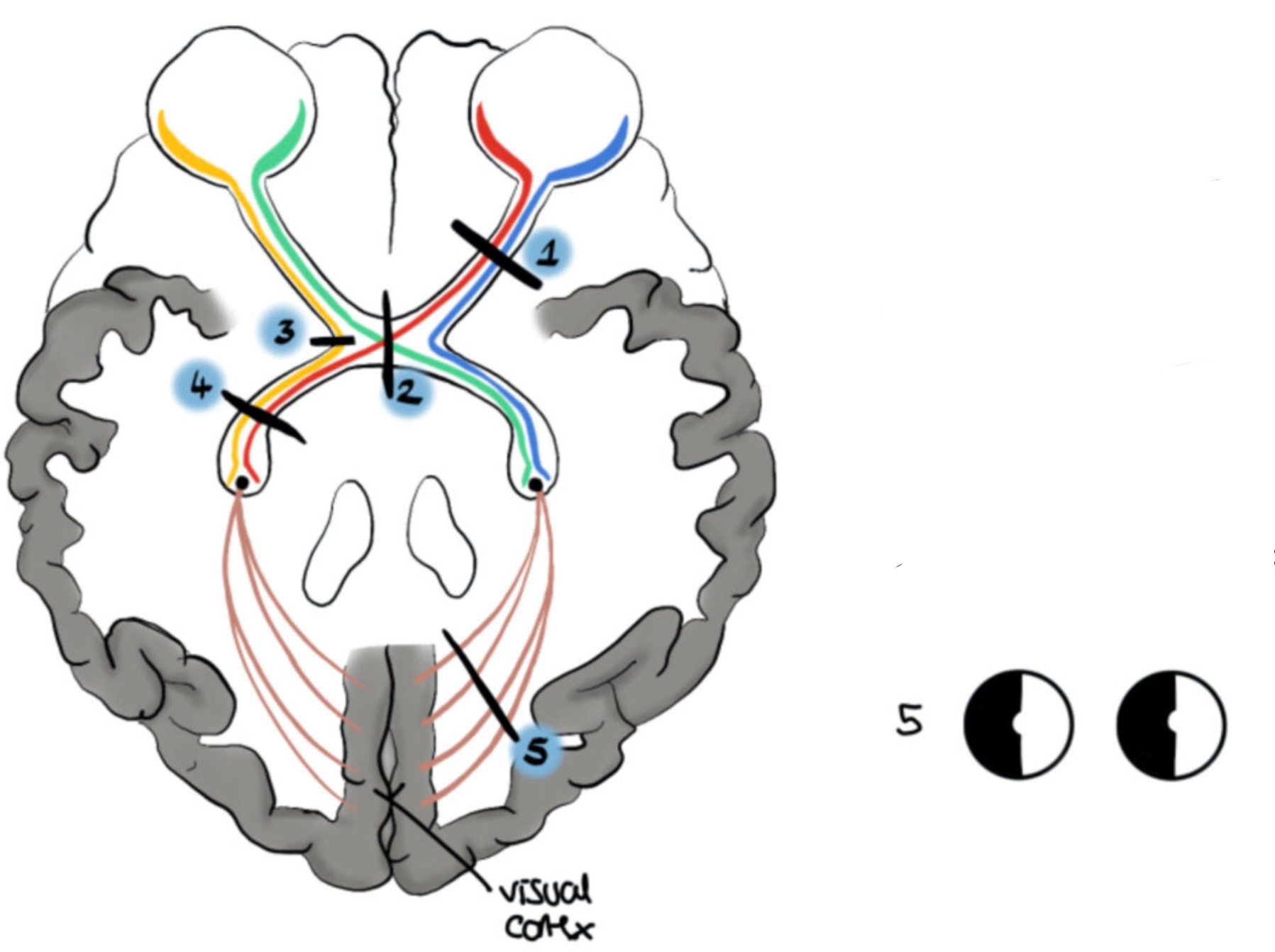
What visual field defect is shown
Left superior homonymous quadrantanopia (optic radiation lesion= contralateral)
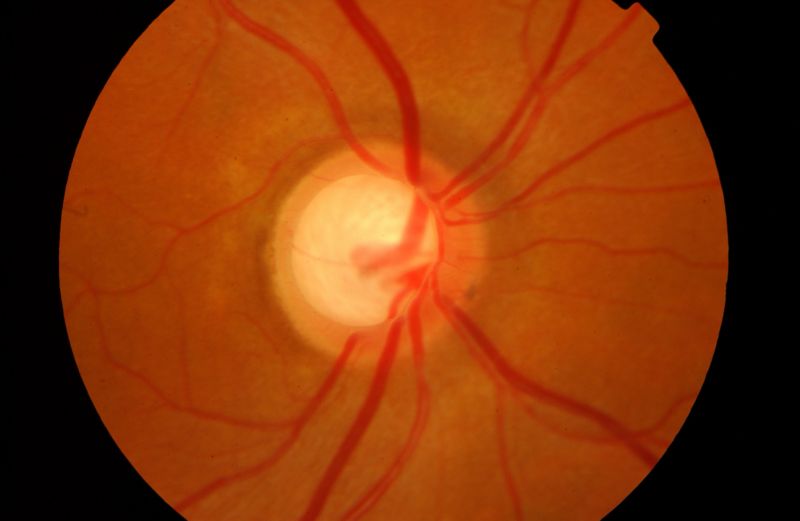
Glaucoma pathology
Impaired aqueous humour drainage = increased anterior chamber pressure
intraocular hypertension damages optic nerve (atrophy) = peripheral visual field loss
loss of ganglion cells = loss of central vision
Glaucoma risk factors
increasing age (>50)
African ethnicity
FHx
Glaucoma clinical presentations
Chronic → asymptomatic, visual field defects
Acute:
Severe eye pain
Redness + corneal oedema
Blurred/reduced vision
Haloes
Fixed mid-dilated pupil
Glaucoma investigations
intracocular pressure (tonometry)
Humphrey perimetry (visual field testing)
Fundoscopy → cupping (optic disk assessment)
Glaucoma management
prostaglandin analogue
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitor
Laser surgery
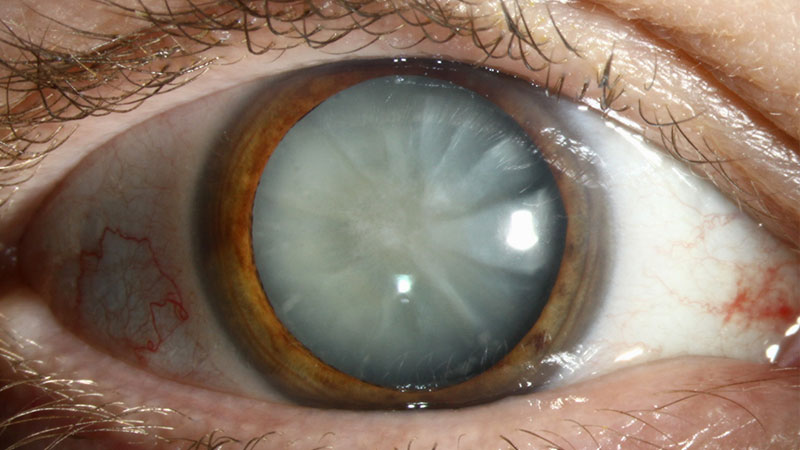
Cataracts pathology
clouding/opacification of lens
Acquired or congenital
Protein deposits on lens = reduced light transmission to retina
Progressive decline
Cataracts risk factors
congenital infections: TORCH
Marfan + alport syndrome
Prolonged glucocorticoid use
Smoking/ excess alcohol
Galactosaemia
Diabetes
How does diabetes + congenital galactosaemia lead to cataracts
excess circulating glucose/galactose
Converted into sorbitol/galactitol + accumulates in lens
Hypertonic environment = lens fibres swell
Fibres rupture (Osmotic cellular injury)
Cataracts clinical presentations
painless visual impairment (bilateral)
Glare
Decrease colour sensitivity
Myopic shift
Cataracts investigations + management
fundoscopy → loss of red reflex
Slit lamp exam
Surgery - lens replacement
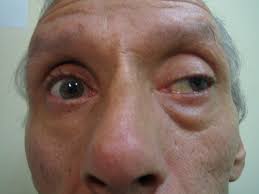
Oculomotor (III) Palsy
Affected eye down + out (lateral rectus + sup. Oblique functional)
mydriasis + ptosis
Diabetic/hypertension microvascular cause, post. Communicating a. Aneurysm, trauma + tumours
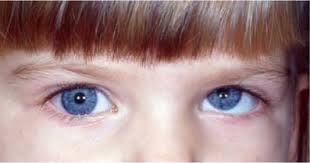
Trochlear (IV) Palsy
superior oblique affected = hypertropia (sits higher)
Head tilted to contralateral side
diplopia looking downwards
Head trauma, microvascular disease, idiopathic
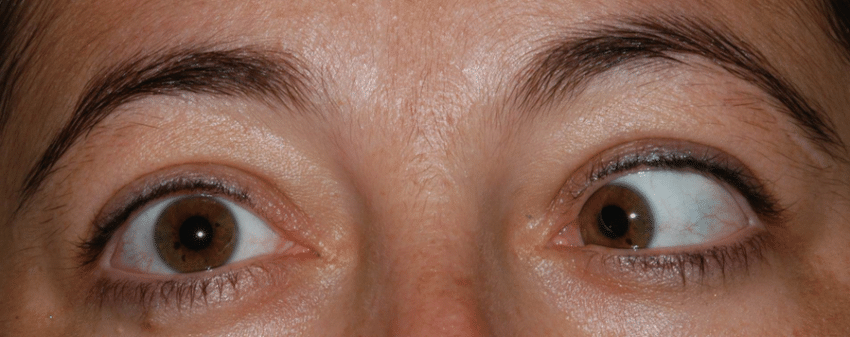
Abducens (VI) Palsy
lateral rectus affected = inability to abduct
Horizontal diplopia + esotropia
Microvascular cause, MS, stroke, tumour
Retinal artery occlusion
Occlusion of central retinal a. (Emergency)
Sudden painless unilateral visual loss
Fundoscopy: pale retina + cherry red spot
High risk in atherosclerosis + giant cell arteritis
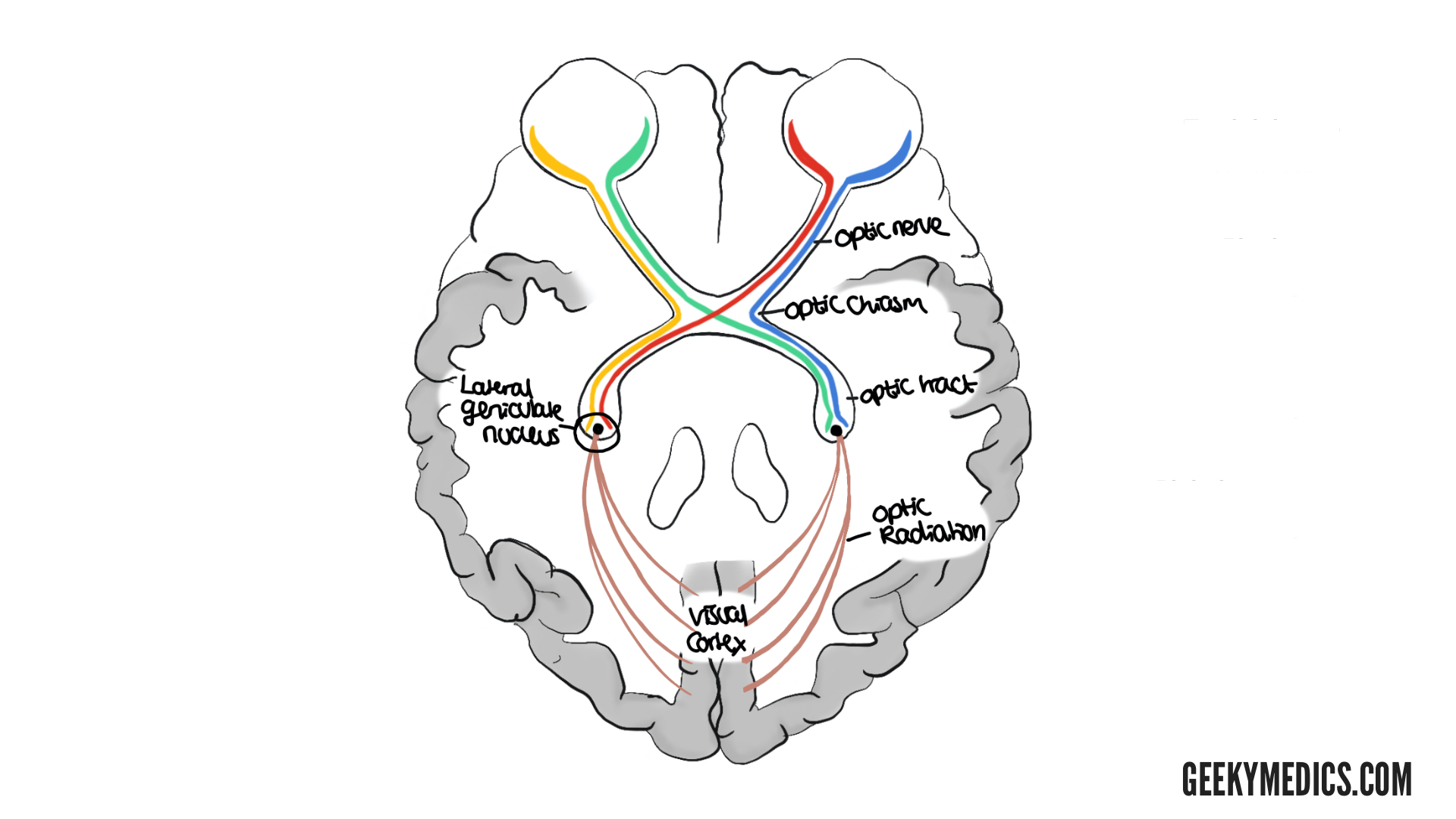
visual pathway
eyes (photoreceptors → bipolar → ganglion)
optic nerve
optic chiasm
lateral geniculate nucleus (thalamus)
optic radiation
visual cortex
myopia
short sightedness → unable to see far away
long eyeball or lens too convex → image in front of retina
corrected with concave lens (neg. diopter)
hypermetropia (hyperopia)
far sightedness → unable to see near
short eyeball or flat lens → image formed behind retina
corrected with convex lens (pos. diopter)
presbyopia
Age related reduction in ability to focus on close objects (failure of accommodation) → Stiff lens + reduced elasticity
Types of hearing loss
conductive: problem w/ sound travelling from environment to inner ear
Sensorineural: problem w/ sensory system or CN VIII so not transferred to primary auditory cortex (temporal gyrus)
Causes of sensorineural hearing loss
presbycusis
Noise exposure
Meniere’s disease
Acoustic neuroma
Labyrinthitis
Causes of conductive hearing loss
ear wax/foreign body
Infection (otitis media/externa)
Effusion
Perforated tympanic membrane
Eustachian tube dysfunction
Medications associated with sensorineural hearing loss (ototoxic)
loop diuretics
Aminoglycoside antibiotics (gentamicin)
Chemotherapy drugs (eg cisplatin)
Weber’s test
Tuning fork place in centre of forehead
normal = sound equal in both ears
Sensorineural = sound louder in normal ear
Conductive = sound louder in affected ear
Rinne’s test
Tuning fork placed at mastoid process (bone conduction) then near ear (air conduction)
normal/positive = air conduction > bone
Negative = bone conduction > air, suggests conductive hearing loss
Presbycusis
age-related hearing loss (sensorineural)
Gradual + symmetrical → high-pitched sounds
Loud noise exposure = key risk factor
Causes: loss of cochlear hair cells or neurones, stria vascularis atrophy or reduced endolymphatic potential
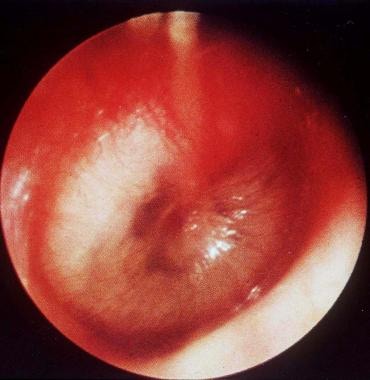
Otitis media pathology, investigation + management
infection + inflammation of middle ear
Often preceded by viral upper respiratory infection (eg rhino-sinusitis)
Otoscopy: red, bulging tympanic membrane
Generally self limiting, analgesia + amoxicillin (pt under 2)
Complication - otitis media w/ effusion (glue ear)
Otitis media common pathogens
streptococcus pneumoniae
Haemophilus influenzae
Moraxella catarrhalis
S. Aureus
Otitis media clinical presentations
otalgia (ear pain)
Fever
Cough/sore throat
Conductive hearing loss
Vertigo/balance issues
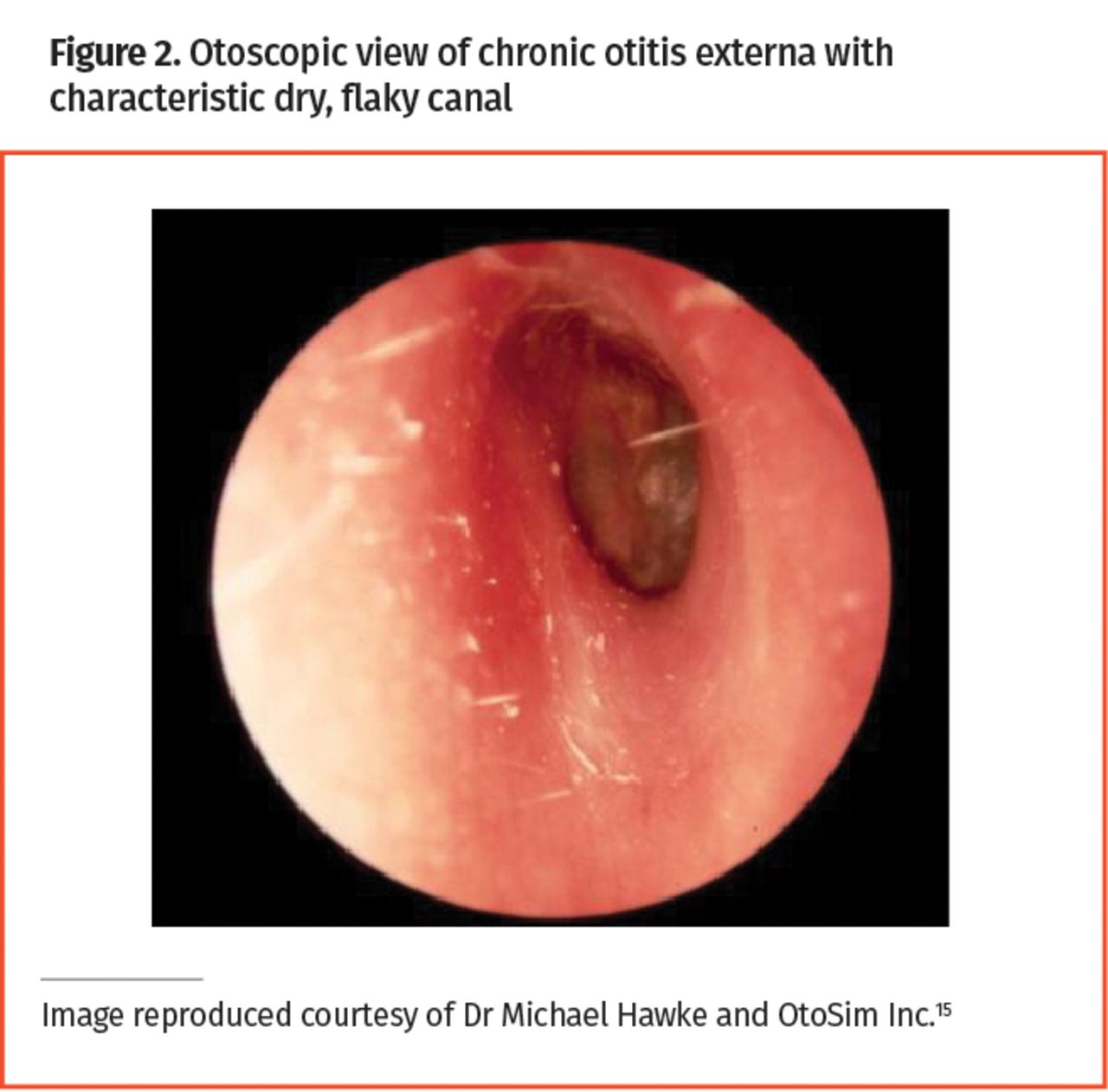
Otitis externa pathology + investigation
infection + inflammation of external ear
Assoc w/ water submersion + cotton bud use
Otoscopy: erythema + oedema of canal, pus/discharge
Otitis externa common pathogens
pseudomonas aeruginosa
Staphylococcus aureus
Fungal → candida, aspergillus
Otitis external clinical presentations
otalgia (ear pain)
Conductive hearing loss
Discharge
Itchiness
Otitis externa management
analgesia
Acetic acid 2% (mild cases)
Moderate: Topical antibiotic + steroid (neomycin, gentamicin)
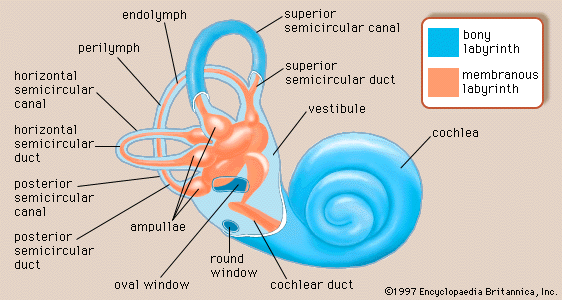
Labyrinthitis Pathology
inflammation of bony labyrinth → semicircular canals, vestibule + cochlear
Typically due to viral upper respiratory tract infection → CMV, mumps, rubella
Bacterial → otitis media or meningitis complication
Labyrinthitis clinical presentations
vertigo (acute onset)
Tinnitus
Hearing loss
Vertigo
Sensation of surroundings spinning
peripheral = problem w/ vestibular system
Central = problem involves brainstem or cerebellum
Common causes of vertigo (VOMITS)
vestibulitis → labyrinthitis or vestibular neuronitis (peripheral)
Ototoxic drugs
Meniere’s disease (peripheral)
Injury to CN VIII
Tumour (Central)
Spin: benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (peripheral)
Vertigo investigations
ear examination
Cerebellar examination
Romberg’s test
HiNTs → head impulse, nystagmus, test of skew
Meniere’s disease pathology
idiopathic inner-ear disorder
Recurrent attacks of vertigo, hearing loss, tinnitus + aural fullness
Assoc. w/ endolymphatic hydrops (high pressure disrupts sensory signals)
Meniere’s disease management
antihistamines
Antiemetic (Prochlorperazine)
Refer to ENT