Fetal Lifespan (study specific development in remnote)
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Anatomy and Physiology
fertilization is key that occurs during week 3 of an average 28-day menstrual cycle
during week 1 & 2
no fertilization yet
egg & follicle matures within the ovary as a result of follicle-stimulating hormone
egg follicle releases estradiol triggers production of luteinizing hormone
leads to release of follicle = ovulation
pre-embryonic period
2 weeks prior to fertilization & continues as the zygote develops at the end of week 4
week 5 = embryonic period
zygote→A single cell that is formed by the joining of two parental cells. This is the first stage of gestation.
gestation→The period of time between conception and birth.
gestational age→is measured from the first day of the client's last menstrual period and describes the weeks of pregnancy.
fetus→The developing offspring in the uterus following the embryonic stage until birth.
embryonic→The stage of develop after implantation occurs through week 10.
zygote
A single cell that is formed by the joining of two parental cells. This is the first stage of gestation.
gestation
The period of time between conception and birth.
gestational age
is measured from the first day of the client's last menstrual period and describes the weeks of pregnancy.
fetus
The developing offspring in the uterus following the embryonic stage until birth.
embryonic
The stage of develop after implantation occurs through week 10.
Embryogenesis
The process of a fertilized ovum developing into an embryo.
begins with the fertilization of the egg
deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)→A molecule that contains genetic information.
there are 23 sets of chromosomes
end of day 5 after fertilization = embryo reaches bastocyst
blastocyst
Stage of embryonic development in which the organism is a mass of cells covered by an outer layer called the trophoblast.
Four Distinct Membranes:
amnion→produces amniotic fluid
chorion→contribues to placental formation
allantois→removes nitrogenous waste production
yolk sac→instrumental in the development of other three membranes; is responsible for providing nutrition & gas exchange before the development of the placenta
surrounded by zona pellucida
zona pellucida→Outer coating of the embryo.
implantation
The blastocyst typically implants into the uterine wall during week 2 of fetal development.
Usually occurs during week 4 of gestation
Ends pre-embryonic period
hCG is detectable
first signs of pregnancy→tender or swollen breasts & fatigue
Week 5 & End of Week 10
embryo tail is gone
developing embryo is called a fetus
body systems begin to develop & structures form
cells continue to multiply & differentiation occurs = cell systems take on specialized functions
teratogen→Anything that negatively affects normal embryonic or fetal development, including medications, illicit drugs, radiation, chemicals, and infections.
blastocyst
Stage of embryonic development in which the organism is a mass of cells covered by an outer layer called the trophoblast.
Four Distinct Membranes:
amnion→produces amniotic fluid
chorion→contribues to placental formation
allantois→removes nitrogenous waste production
yolk sac→instrumental in the development of other three membranes; is responsible for providing nutrition & gas exchange before the development of the placenta
surrounded by zona pellucida
zona pellucida→Outer coating of the embryo.
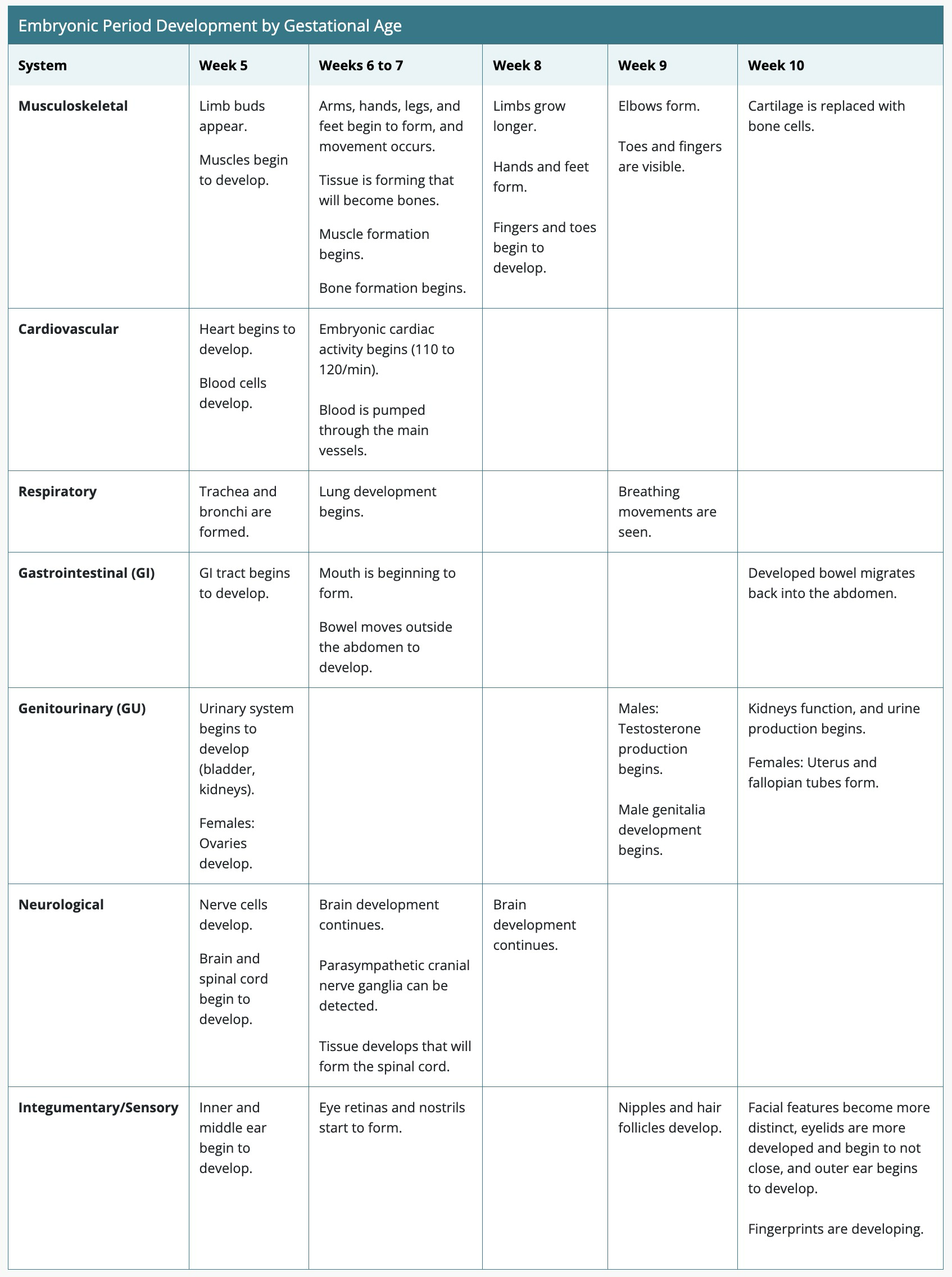
Embryonic Period Development by Gestational Age
Amniotic Fluid
develops early in gestation
initially develops from water in maternal serum, fluid from amniotic cavity, coelomic fluid
week 10 = adds fetal urine then it's fetal urine & secretions from GI systems
skin also becomes keratinized & not be able to absorb or transfer fluids easily
Purposes of Amniotic Fluid
protecting the fetus in event of maternal trauam
provides cushion to protect the umbilical cord from compression
protects fetus from infection
provides nutrients (vitamins, proteins, electrolytes, immunoglobulins)
amniotic fluid index (AFI)
An estimation of the amount of amniotic fluid present in the amniotic sac during pregnancy.
Determine amount of amniotic fluid is too great (polyhydramnios) or too little (oligohydraminios)
amniocentesis
A diagnostic test performed during pregnancy that involves withdrawing amniotic fluid from the amniotic sac to detect chromosomal anomalies or to measure fetal lung maturity.
Placenta
normally located upper portion of uterus
responsible for sustaining pregnancy & has endocrine, immunological, physiological functions
genetic characteristics mirror those of the developing fetus
via maternal blood flow through embryonic capillaries
produces glycogen = source of energy, cholesterol
allows the transfer of gases, hormones, maternal antibodies, nutrition, fetal waste
allows for passage of harmful substances
Umbilical Cord
houses two arteries & single vein that are surrounded & protected by Wharton's jelly (embryonic connective tissue)
average length 50cm-60cm
contains vessels for fetal blood circulation
2 arteries
1 vein
Fetal Circulation
begins on day 22 or 23 when cardiac loop is formed
bypasses the lungs & liver→because the placenta provides the fetus with oxygenation blood & nutrients, removes waste products, and supports fetal circulation
oxygenation takes place via spiral arteries inside the chronic villi (maternal blood provides oxygen & nutrients)
Fetal hemoglobin adapts to lower oxygen environment
Body Systems
Begin developing during embryogenesis, with major organs formed by week 13. Maturation occurs during the fetal period, starting week 11.
Survival Rates: Preterm birth before 23 weeks has low survival; by 27 weeks, survival is about 94%.
Cardiovascular System
Development: First system to form, with a functioning heart by week 5 and visible heartbeat by week 6.
Maturation: Complete by week 37.
regular HR week 6 or 7→110-120
you can hear it by week 4
vein carries it to the baby from the placenta and comes out
babies pH = use arteries
Respiratory System
Development: Trachea and esophagus form by week 5, with lung structures appearing by week 8.
Maturation: Lungs continue developing until birth, with significant milestones at weeks 20 and 24.
Genitourinary System
Development: Urinary tract begins forming week 5, with kidneys producing urine by week 10.
Maturation: Kidneys fully formed by week 32; genital development complete by week 12.
Neurological/Sensory Systems
Development: Neural tube closes week 4, with brain and spinal cord structures forming through weeks 10 to 12.
Maturation: Fetal movements and reflexes develop, with full neurological function by week 29.
Gastrointestinal System
Development: Structures distinguishable by week 5, with significant growth through week 10.
Maturation: Intestinal tract fully functional by week 32, with insulin production starting week 12.
Musculoskeletal System
Development: Bone formation begins weeks 6 to 7, with muscle formation and limb development following.
Maturation: Bones and muscles fully developed by week 37, with blood cell production in bone marrow by weeks 23 to 25.
Remember!
After week 23 = viable
For miscarriage <20 weeks
Fetal death >20 weeks
Abortion verses Intrauterine Fetal Demise
Abortion is a broad term that refers to any pregnancy loss prior to viability, usually around 20 weeks of gestation.
Intrauterine fetal demise (IUFD) classifications will vary somewhat between states and regions, however it is generally classified as a fetal death occurring at or beyond viability (typically around 20 weeks of gestation) or if the fetus weighs 350 g (12.35 oz) to 500 g (17.7 oz) or more. Stillbirth is a therapeutic term that is often used when communicating with clients in reference to IUFD.
Spontaneous Abortion
may occur without warning
miscarriage→term to use when communicating with clients in reference to spontaneous abortions
Complete
When uterine cramping and bleeding occur and an ultrasound reveals the uterus is empty, a complete spontaneous abortion has occurred
Incomplete
Occurs when there is passage of a portion of the uterine contents because of uterine contractions and the cervix being dilated, but the rest of the products of conception remain within the uterus
Inevitable
Is diagnosed when cervical dilation is noted via cervical exam and cramping and vaginal bleeding are present, but there has been no passage of the pregnancy yet, although spontaneous abortion is expected
at 22 weeks
Threatened
Occurs when mild to moderate cramping and vaginal bleeding are present, but the cervix remains closed and an ultrasound shows a viable pregnancy
Missed
Occurs when uterine contractions are not present and the manifestations of pregnancy are still present or may begin to regress, but vaginal bleeding does not occur
The embryo or fetus no longer exhibits signs of life and remains in the uterus
Etiology and Risk Factors
Complete
celiac disease→A chronic immune disorder in which the ingestion of gluten causes inflammation of the intestinal lining.
diabetes, autoimmune disorders, >35 years, history of pregnancy loss, trauam
illicit drugs, smoking, caffeine, alcohol
infections (HIV, vaginitis, syphillis)
Etiology and Risk Factors
Threatened
hyperemesis gravidarum→Nausea and vomiting in pregnancy that is severe and persistent.
placenta previa→Occurs when the placenta partially or completely covers the internal os of the cervix.
advanced maternal age, gestational diabetes, low SES
Etiology and Risk Factors
Missed
maternal age of 30 years and older, BMI greater than 24, embryo or fetus measuring larger or small than expected
Spontaneous Abortion
Clinical Presentation
abdominal cramping
vaginal bleeding
may think menses was late & assume are just having an unusually heavy menstrual period
Lab Testing and Diagnostic Studies
ectopic pregnancy→Implantation of a pregnancy in an area outside the uterus, often occurring in the fallopian tubes.
molar pregnancy→Growth of a nonviable fertilized egg or an overgrowth of trophoblasts, resulting in a nonviable pregnancy.
beta-human chorionic gonadotropin (beta-HCG)
A hormone secreted by the placenta beginning 8 to 10 weeks after conception that can be detected via a blood sample.
3000 mIU/mL
alloimmunization→An immune response to foreign antigens from another person, most commonly occurring after pregnancy or blood transfusion.
erythroblastosis fetalis→Severe edema in the fetus caused by antibodies within maternal circulation if the mother is Rh negative. The antibodies pass through the placenta and react with the fetal antigens, destroying fetal red blood cells.
Ultrasound
hCG Hormone Test
Vaginal Ultrasound & Vaginal Cervical Exam = threatened
Nursing Interventions
Focus on mental health, grieving process, possible planning for future pregnancies
Grief counceling
Contraception information
Managing HTN, maintaining healthy weight, manage substance abuse, stop smoking
Food pantries, support groups
Evaluate depression & anxiety
Treatment
Conservative Treatment: monitoring client for passage of products of conception usually pass products within 8 weeks
Contraindications: maternal anemia, bleeding disorders, maternal infection
Mif, Mis, can expel uterine contents within 3 days & notify provider
dilation and curettage (D&C)→A procedure that expands the uterine cervix to allow for entrance into the uterus in order to perform a procedure (e.g., evacuation of uterine contents, sampling of uterine tissue).
disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)→A condition in which blood clots excessively form in blood vessels. As a result, clotting factors are used up and then bleeding occurs excessively anywhere in the body.
Complications: hypovolemic shock, retained products, excessive bleeding
Induced Abortion
controversial
legally induced completely by a provider to terminate an intrauterine pregnancy that does not result in a live birth
Etiology and Risk Factors
undesired pregnancy, maternal health concerns, fetal congenital anomalies
Cancer treatment (cervical, breast, melanoma, ovarian, thyroid, lymphoma, colorectal)
Medical conditions (severe kidney disease, cardiovascular disease, pulmonary arterial HTN)
Clinical Presentation
desire to end
Lab Testing and Diagnostic Studies
Vagina/Abdominal Ultrasound
Nursing Interventions
Check VS, vaginal bleeding
Postprocedure education
Report signs of infection (increased pain, vaginal bleeding, purulent vaginal discharge, fever)
Treatment
Medication Abortion
Abortion Procedure
Gestation is primary factor
Medication Abortion
safer than surgical
low infection rates
Contraindications:→IUD, ectopic pregnancy, anticoagulant therapy, chronic adrenal failure, poryphyria, hemodynamic instability
porphyria→Disorders that develop as the result of an overaccumulation of porphyrin, a group of compounds that support the hemoglobin in oxygen transport.
Complications
Pain, infection, heavy bleeding
If products do not pass within 24 hrs = report to provider
Surgical or Procedural Abortion
removal of products from uterus by manual vacuum evacuation (bet 4-10 weeks), suction curettage (6-14 weeks), or dilation & extraction (14-24 weeks)
Complications
vasovagal response→The sudden decrease in both heart rate and blood pressure that leads to fainting, often from straining or stress.
heavy bleeding, unsuccessful procedure that requires repeat suction
uterine perforation, infection, sepsis, hemorrhage
Abortion Postprocedure Client Instructions
After an abortion procedure, the client should:
Avoid placing anything in the vagina for 1 week.
Use contraception to prevent unwanted pregnancy.
Keep follow-up appointments.
The client should contact their provider if they experience:
Heavy vaginal bleeding (soaking through two perineal pads in 2 hours).
Passing blood clots larger than a lemon for 2 or more hours.
Continued signs of pregnancy.
A temperature of 38° C (100.4° F) or higher for 24 hours.
Moderate to severe abdominal or back pain.
Vomiting or diarrhea lasting more than 24 hours.
Foul-smelling vaginal discharge.
Nursing Interventions after Abortion
septic shock→A severe localized or systemic infection that is life-threatening and requires immediate medical intervention.
What to expect & what to report
Gather thorough history
Triad manifestations: pain, bleeding, low-grade fever
Nursing Management of a Client Experiencing Abortion Complications
Complete a physical exam, making note of abdominal distension, masses, and severe tenderness or absence of bowel sounds. Inspect the perineum for vaginal bleeding and obvious vaginal injury.
Monitor vital signs, especially a fall in blood pressure, increased heart rate, and increased temperature.
Insert a large-bore intravenous catheter, if needed.
Administer oxygen, if needed.
Accurately monitor vaginal bleeding. When turning the client, note blood collecting on the under pad.
Provide psychological support.
Maintain confidentiality.
Client Teaching Prior to Discharge From the Facility
After discharge, the client should:
Use contraception to avoid future pregnancy.
Complete all prescribed antibiotics.
Increase fluid intake to 64 ounces per day.
Rest for 2 weeks, avoid overexertion, and have no strenuous exercise.
Abstain from alcohol for 48 hours or while taking narcotics.
Avoid putting anything in the vagina for 2 weeks.
Intrauterine Fetal Demise/Stillbirth
18 out of 1000
interchangeable
Etiology and Risk Factors
preeclampsia→A serious complication of pregnancy occurring after 20 weeks of gestation in which aclient's blood pressure value is above 140/90 mm Hg. It can be accompanied by proteinuria, edema, headache, and vision changes. Preeclampsia can become severe, resulting in seizures.
placental abruption→Occurs when the placenta detaches from the uterine wall.
Down syndrome→A genetic condition resulting in an extra chromosome 21 in some or all of the body's cells. It is characterized by modest to severe delays in learning, development, and growth.
Edwards syndrome→A hereditary condition characterized by low birth weight and a few aberrant traits. It is brought on by having an extra copy of chromosome 18 in some or all of the body's cells.
Patau syndrome→A chromosomal condition in which the body's cells contain three copies of chromosome 13 rather than the typical two copies, leading to severe intellectual incapacity and numerous physical defects.
Turner syndrome→A genetic disorder of females characterized by a partially or completely missing X chromosome. Defects related to the syndrome include neurocognitive and cardiovascular system defects and possible delayed puberty.
antiphospholipid syndrome→An immune system disorder that increases a client's risk of developing clots.
A systematic evaluation of pregnancy can lead to an identified cause for intrauterine fetal demise approximately 75% of the time. The most common causes of IUFD are lack of adequate fetal growth (fetal growth restriction) and placental abnormalities. Fetal growth restriction may be a result of complications of pregnancy (such as preeclampsia), an infection, a birth defect, a maternal health condition, or maternal lifestyle. Anomalies of the placenta and umbilical cord-including placental abruption, placenta previa, a single umbilical artery, and abnormal cord insertion—are attributed to an increased incidence of IUFD. These can be detected via ultrasound during pregnancy and require additional monitoring by the provider. Diabetes is also associated with increased risk, especially for clients who have poor diabetic control. Clients who are obese have more than double the incidence of IUFD than clients who have a BMI within expected ranges for height and weight.
Clients who are Hispanic or Black have a higher incidence of intrauterine fetal demise than non-Hispanic White clients. While the precise cause for this disparity is unknown, there are many known contributing factors that can include an increased incidence of other risk factors that attribute to IUFD, including diabetes, hypertension, and placental abruption. Clients who are 35 years old or older, especially with their first pregnancy, are at increased risk for IUFD. The incidence of chromosomal abnormalities is increased in pregnancy in clients older than 35 and is often associated with IUFD. These chromosomal abnormalities include Down syndrome (trisomy 21), Edwards syndrome (trisomy 18), Patau syndrome (trisomy 13), and Turner syndrome. The use of tobacco, alcohol, and illicit drugs (such as opioids and methamphetamines) is a known risk factor of IUFD. Other factors that increase the risk of IUFD include gestational age beyond 40 weeks, late onset prenatal care, multiple gestation, and antiphospholipid syndrome.
Pregnancy History
A thorough review of the client's previous and current prenatal history should be done. Previous pregnancy information should include preterm births, infants who had fetal growth restriction, history of IUFD, hypertensive disorders, diabetes, blood transfusions, pulmonary embolism, and deep vein thrombosis. Review information about current pregnancy history, including any vaginal bleeding, trauma, infectious diseases, pregnancy weight gain, exposure to drugs or radiation, hypertensive disorders, diabetes, anemia, diagnosed fetal anomalies, or fetal growth restriction as well as when prenatal care started. Review laboratory results to ensure routine pregnancy labs have been done, and note the results. Ask about recent abdominal pain, pelvic pressure, and vaginal bleeding or discharge and also when the client last felt the baby move. Inquire about recent trauma.
Clinical Presentation
The client may present for routine prenatal care and have no report of any concerns regarding the pregnancy or may report decreased or no fetal movement.
Lab Testing and Diagnostic Studies
Fetal Heart Tones with Doppler
Routine prenatal Lab Studies
CBC, Hep B surface antigen screening, syphillis, HIV, rubella, anticoagulation, urine toxicology
Nursing Interventions
postpartum depression→Intense feelings that develop after birth that can include anxiety, sadness, irritability, loss of appetite, insomnia, and difficulty bonding with the baby.
Meet emotional needs Regarding options for aftercare of both infant & client

Treatment
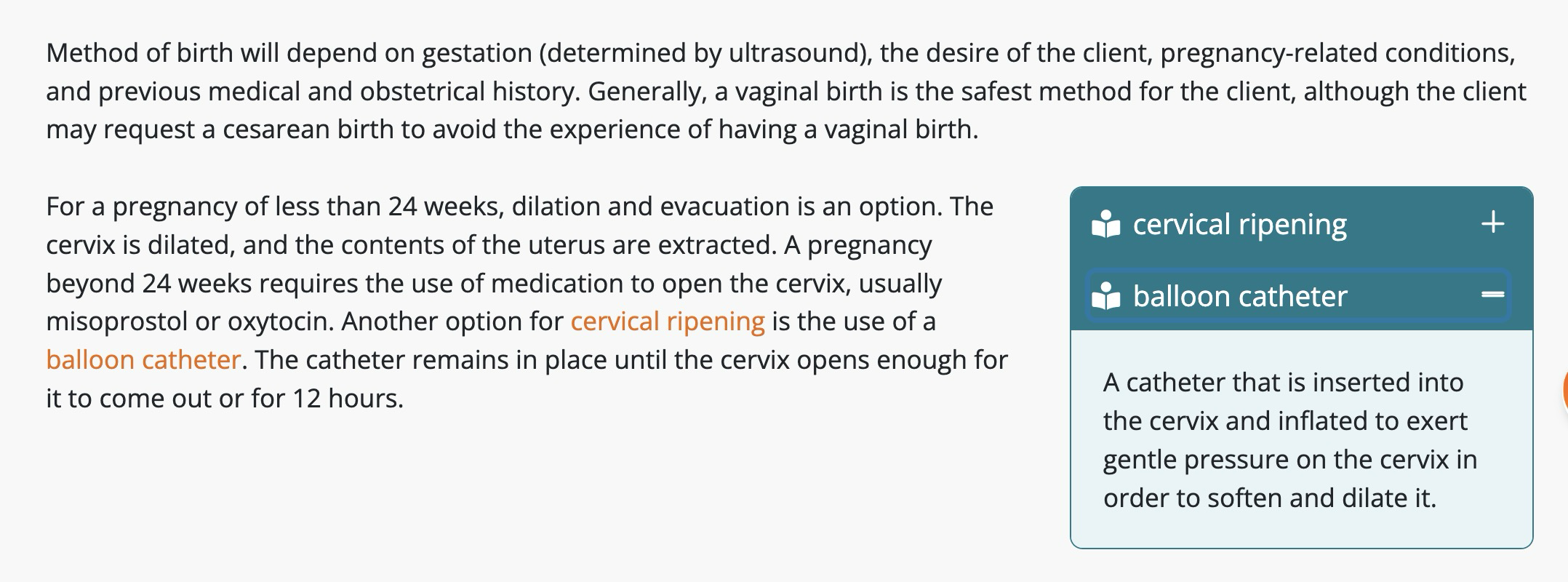
cervical ripening→Softening and opening of the cervix prior to the start of labor.
balloon catheter→A catheter that is inserted into the cervix and inflated to exert gentle pressure on the cervix in order to soften and dilate it.
Postpartum Care
Provide clients with information regarding breast care and steps to take to stop breast milk production.
Discuss the option of breast milk donation.
Offer the client a room on a unit away from the postpartum unit to avoid hearing infants crying. The family's support system should be assessed prior to discharge.
Postpartum follow-up phone calls should be made to check on the family and schedule appointments.
Topics to be discussed during postpartum visits may include birth control options, future pregnancies, and managing grief as well as screening for postpartum depression.