5.2 Age of Revolutions
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
AP World History: Modern; Unit 5.1; Age of Revolutions (1750-1900)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

18 Terms
Napoleonic Wars (1803-1815)
campaign to build a European French empire; SIGNIFICANCE: caused disruption of European politics, spread democratic ideals, created a reactionary push for political conservatism, and sparked nationalism
Year of Revolutions (1848)
widespread dissatisfaction with conservative monarchs prompted demands for democratic processes, freedom of the press, and economic and social changes for the industrial working class; SIGNIFICANCE: unsuccessful, but led to a surge in nationalism.
ancien régime
French political and social system from the Late Middle Ages until the French Revolution (1789); SIGNIFICANCE: extraordinarily conservative.
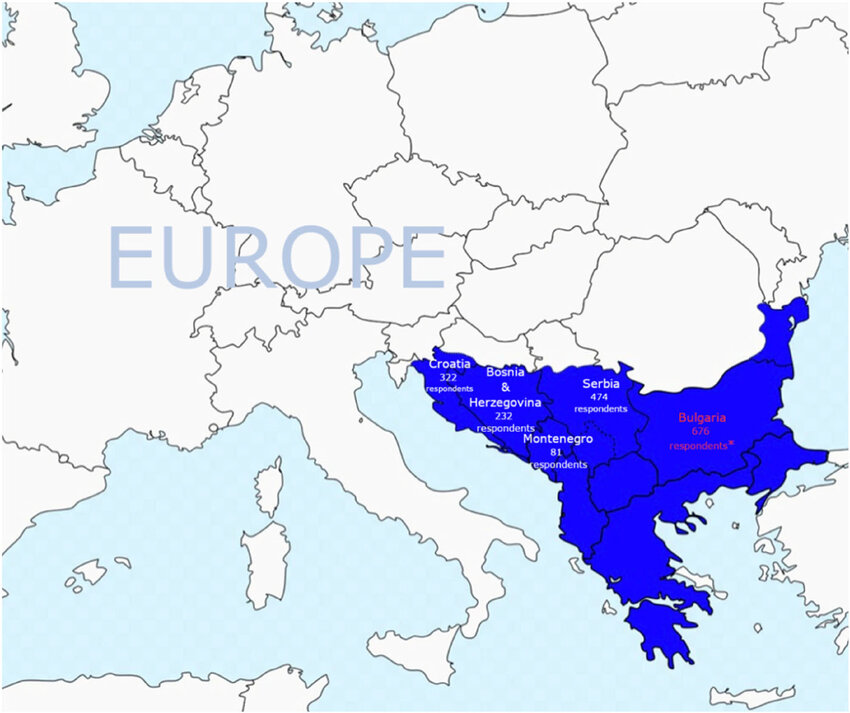
Balkan region
mountainous region of SE Europe conquered by the Ottoman Empire; SIGNIFICANCE: poverty of region leads to origin of devshirme and the rise of nationalism among its diverse ethnic groups.
caudillos
Mexican landowners with political and military strength; SIGNIFICANCE: creates instability as they fight for political influence, often leading to civil wars and shifting power dynamics.
Congress of Vienna
meeting after Napoleonic Wars to promote and balance the power of conservative governments; SIGNIFICANCE: suppresses the development of nationalism among multi-national empires.
constitutionalism
legal, personal rights under a government; SIGNIFICANCE: places limits on power of a ruler and ensures the rule of law.
enlightened despot
absolute monarch who uses enlightenment philosophy to consolidate authority; SIGNIFICANCE: creates illusion of liberalism and reforms while maintaining strict control over the state.
Estates General
parliamentary body of France with advisory power only; SIGNIFICANCE: unequal representation favoring upper Estates led to the French Revolution.
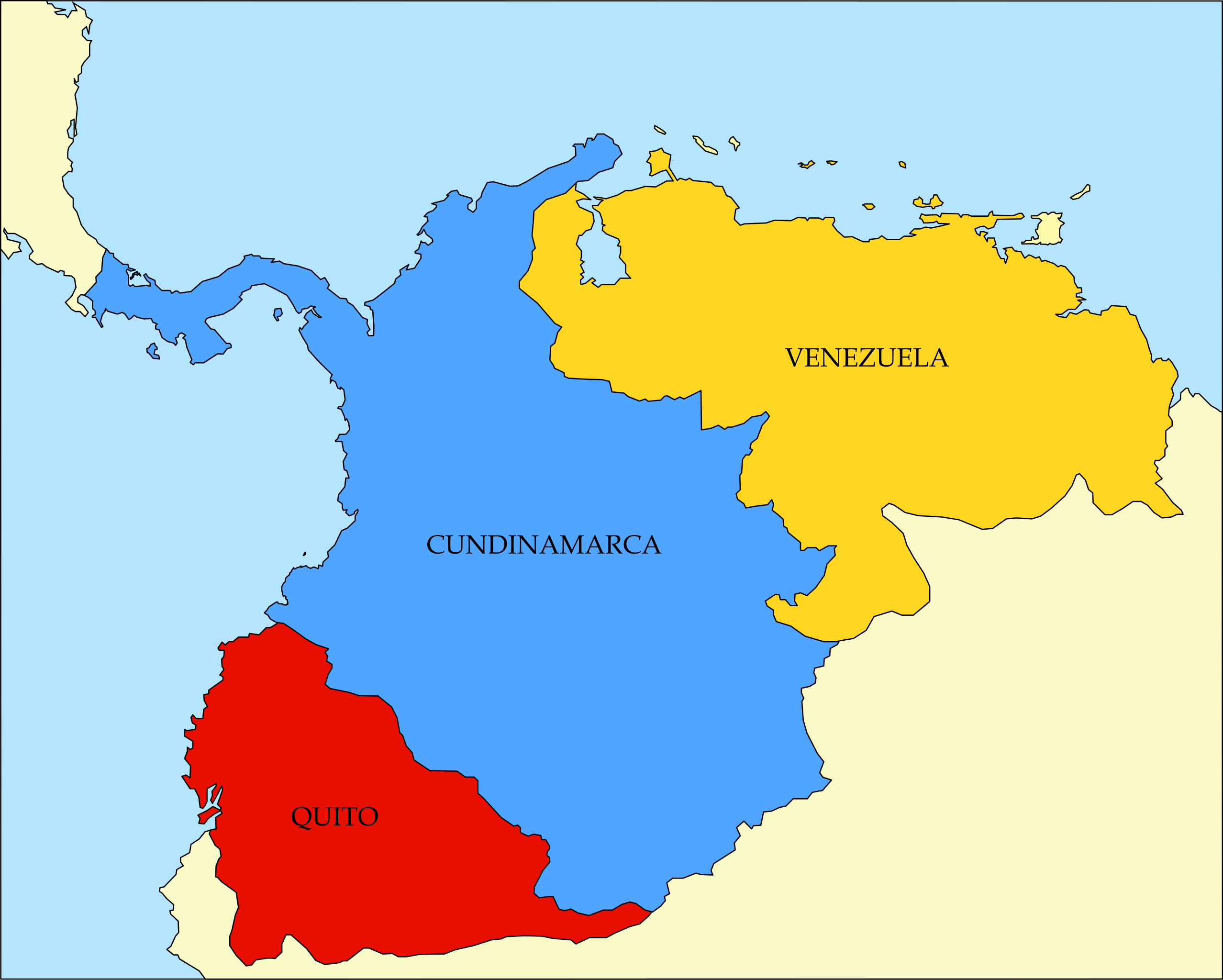
Gran Colombia
a united Venezuela, Columbia, and Ecuador much like the United States; SIGNIFICANCE: fails due to political and economic inexperience of freed Spanish colonies.
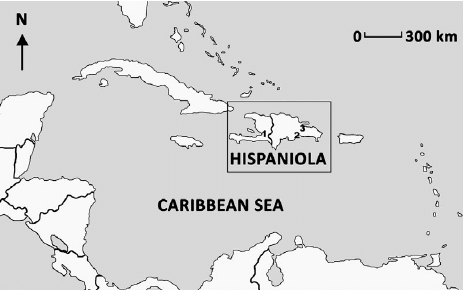
Hispaniola
Caribbean island of French Saint Domingue (modern Haiti) and Spanish Santo Domingo (modern Dominican Republic); SIGNIFICANCE: origin of Haitian Revolution.
maroon
(repeated term from Unit 4) escaped enslaved person living in secret wilderness community; SIGNIFICANCE: often formed independent settlements, resisting colonial authorities.
Napoleonic Code
post-Revolutionary civil code of France; SIGNIFICANCE: meritocratic but also very patriarchal.
nation-state
a sovereign country whose citizens or subjects are relatively homogeneous (the same) in factors such as language or descent; SIGNIFICANCE: diversity within empires often leads to the desire for self-determination.
realpolitik
political ideology that promotes practical politics without moral ideologies; SIGNIFICANCE: becomes the basis for modern politics and emphasizes the importance of power and national interest over ethics.
Reign of Terror
period of French Revolution characterized by repression of all anti-revolutionary thought or protest, punished by guillotine; SIGNIFICANCE: used as tool to preserve radical change and eliminate perceived enemies of the revolution.
self-determination
self rule; SIGNIFICANCE: US self-determination through the American Revolution inspires similar desires among other colonies and multi-ethnic empires.
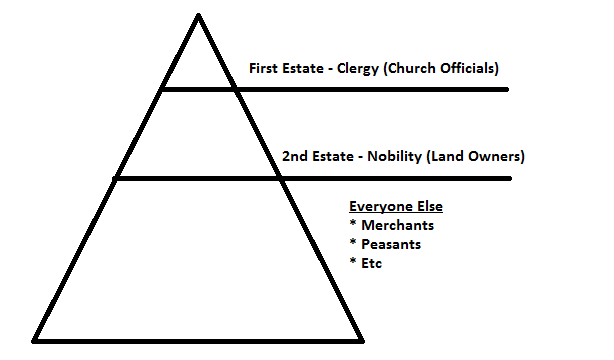
Three Estates
three main classes of France; SIGNIFICANCE: 3rd estate larger than 1st and 2nd states combined and played a crucial role in the French Revolution by demanding more representation and rights.