3.3- Waves
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
what is a node on a stationary wave
a point that doesn’t move from equilibrium position
what is an antinode on a stationary wave
a point that experiences maximum displacement from equilibrium position
how can stationary waves be created
two waves of the same frequency travelling in opposite directions
when will a wave diffract through a gap
when the gap is smaller than the wavelength
what does coherent sources mean
same frequency, constant phase relation
describe the interference pattern when white light is used
central white maximum, other maxima are spectrums with violet on the inside/ red on the outside
features of a single slit interference pattern
very intense central maximum that is twice as wide as the subsidiary maxima
how does a longer wavelength affect the fringe spacing
wider fringe spacing
how does a wider slit separation affect the fringe spacing
more compact fringe spacing
how does a further away screen affect the fringe spacing
wider fringe spacing
what colour of light refracts the most and why
red because it has the longest wavelength
applications of diffraction gratings
spectrometers to analyse composition of stars
spectrometers to analyse chemicals
x-ray crystallography
safety procedures when working with lasers
protective eyewear
don’t point at people’s eyes
usage clearly signposted outside the room
when is a ray totally internally reflected
when n₁>n₂ and θ>θc
a substance that has a higher refractive index is…
more optically dense and slows light down more
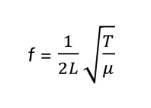
what are the meanings of the symbols in this equation
f= frequency
l= length of wire
T= tension in wire
µ= mass per unit length
what is the nth harmonic
when n half wavelengths take up the whole length of the wire
name the three parts of a fibre optics cable (and describe their optical densities if applicable)
optically dense core
less optically dense cladding
outer sheath
function of the core
allows total internal reflection to take place
function of the cladding
prevents signal degradation (light escaping the core), which causes information to be lost
prevents crossover of information to other fibres
function of the sheath
prevents damage to the cable
two ways a signal can be distorted
absorption and pulse broadening
consequences of pulse broadening
reduces amplitude- can lead to loss in information
different pulses could merge- leading to distorted final pulse
consequence of absorption
reduces amplitude, leading to loss of information
two causes (with brief description) of pulse broadening
material dispersion- when white light is used the different colours diffract differently so the pulse arrives over a longer period, as some rays take different paths
modal dispersion- when the light enters the core at different angles, so diffracts along different paths and the pulse arrives over a longer period
how to solve material dispersion
use monochromatic light
how to solve modal dispersion
use a very narrow core, so the range of “entry angles” is as small as possible
polarization means…
oscillations occur in only one of the directions perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation
what type of waves can be polarised
transverse
what happens when two polarising filters are at an angle to each other
maximum intensity at 0, 180, 360 ect, and no rays can pass at 90, 270 etc, inbetween it decreases like a cosine graph
what happens to light when it’s reflected off water
is partially plane polarised on the horizontal plane
how do polaroid sunglasses work
they vertically polarise light, so the horizontally polarised light from a surface (the glare) is reduced