Emphysema and gas exchange
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
last updated: May 27th, 2024
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
external respiration
exchange of O2 and CO2 between air & blood (in lungs)
alveoli surrounded by tiny blood vessels (capillaries); both have walls that are only single celled layer thick to allow diffusion of gases
how does external respiration work?
O2 in inhaled air is greater than O2 in blood capillaries in the lungs
CO2 in the inhaled air is less than CO2 in blood of capillaries
gases exchanged due to differences in concentration
external respiration: O2 [__] from alveoli to capillaries, CO2 [__] from [__] to alveoli
diffuses; capillary
internal repsiration
exchange of O2 & CO2 between blood and the cells of surrounding tissue
how does internal respiration work
as O2 passes body cells, O2 diffuses from capillaries to tissue, CO2 diffuses from tissue to capillaries
causes of emphysema
smoking (80% of cases)
dust
air pollution
chemical fumes
genetic reasons (alpha 1-antitrypsin def)
describe the air sacs affected with COPD compared to healthy air sacs
thick and narrow bronchioles with with excess mucus
destruction of alveolar walls
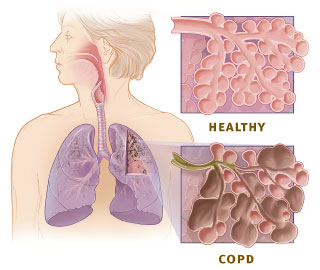
emphysema
Smoking cause the inner walls in the air sacks to lose it elasticity to stretch → eventually becomes weak and breaks
lung tissue becomes less elastic, air gets trapped inside alveoli
dmged alveoli doesn’t work properly, leaving no room for fresh air to enter as old air gets trapped, impairing gas exchange
effects of emphysema
reduces amt of O2 that reaches blood stream
O2 deficiency leads to heart failures (less O2 to make energy)
as air gets trapped in alveoli, lungs become hyperinflated → causes shortness of breath
overinflation of lungs is from trapped air (unable to deflate fully, combo of non-stretchy alveoli & narrowed airways)
symptoms: shortness of breath, wheezing, chest tightness/pain, cough (won’t leave)
why is thin alveolar membrane important for effective gas exchange?
so that diffusion can actually happen and happen quickly due to thinness; thinner the membrane, faster the diffusion
why is moist surface in alveoli lining essential?
allow gases to dissolve so they can diffuse quickly and pass across gas exchange surface
why is O2 important to take in and CO2 important to eliminate?
cells need O2 to make ATP for energy (to stay alive), and this thus affects tissues and organs as well.
CO2 is a waste product and needs to be expelled or blood will become acidic and it also takes up carrying capacity (so less O2 intake)
main cause of emphysema and how it harms gas exchange in the respiratory system
smoking -
inner walls of alveoli weaken and rupture, reducing the surface area and thus also gas exchange
thick and narrow bronchioles makes it harder to breathe, excess mucus makes it harder to clear lungs and perform gas exchange
why is gas exchange important for blood circulation?
red blood cells can carry O2 around the body and to tissues needing O2
CO2 can be diffused and removed from bloodstream to air sacs to be exhaled
important so that the blood can carry O2 to organs to function
effects of emphysema on other systems
can affect the nervous system from low levels of O2, neurological disorders like dementia
muscle strength decreased from less O2 for cellular respiratoin