Lecture 25 - Catabolic Pathways/Glycolysis
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
How is glucose pulled into the cell
By transporter
active transport
requires ATP
5 principles of metabolic pathways
series of separate reactions
each reaction is catalyzed by a specific enzyme
many metabolic pathways are similar in all organisms (conserved function)
in eukaryotes, metabolic pathways are compartmentalized in specific organelles
key enzymes can be inhibited or activates to alter the rate of the pathway (allosteric)
What is glycolysis
Oxidation of glucose
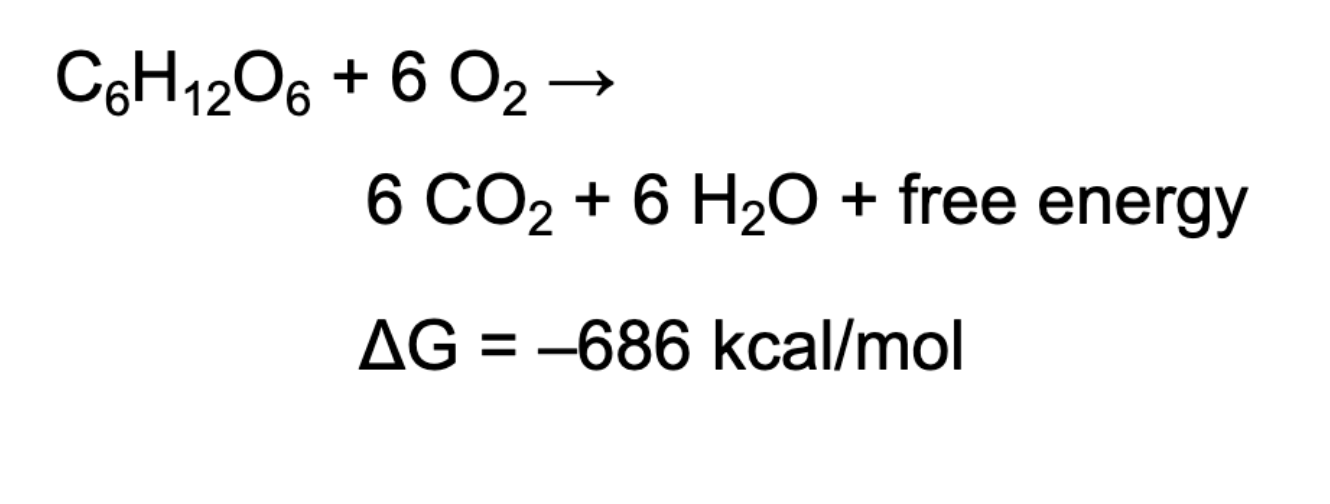
catabolic
very highly exergonic
free energy releases is harvested + used to drive anabolic processes (makes ATP)
What three processes are used to harvest energy from glucose
glycolysis - anaerobic
cellular respiration - aerobic (O2 available)
fermentation - anaerobic (No O2 available)
Glucose is partially oxidized by the end of ________
glycolysis
Which process is not favored to produce ATP
Fermentation, because net production of ATP is 2
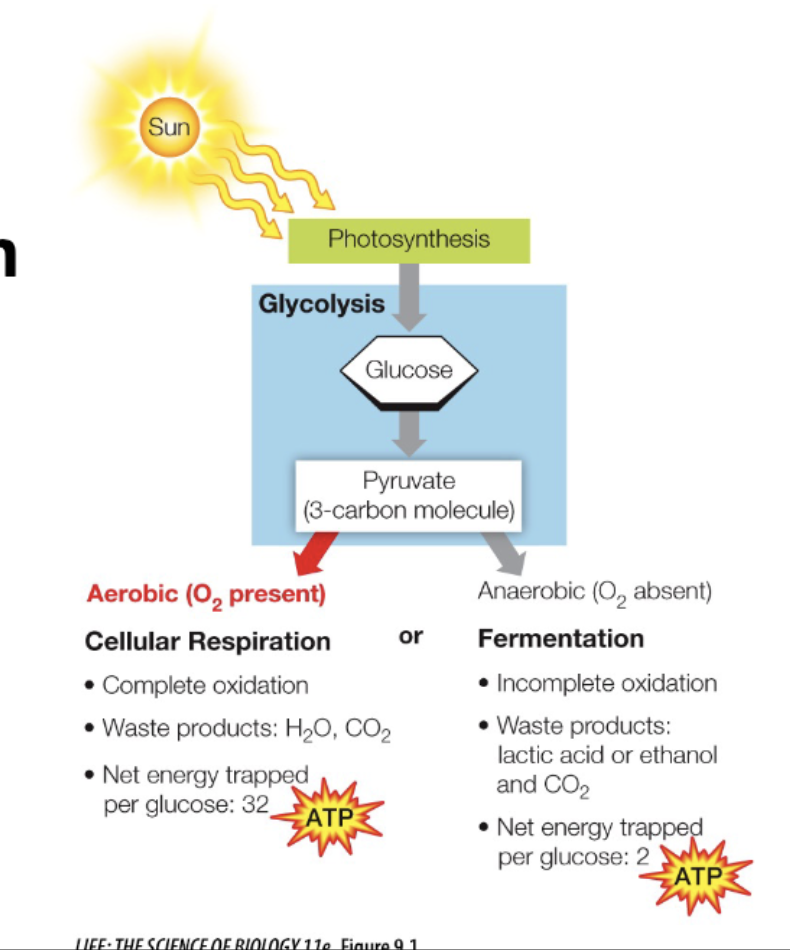
Redox reactions
transfer of electrons
OIL RIG
Oxidation is loss
Reduction is gain
Couple reactions, allows occur together
when something is oxidized in a reaction, the partner has to be reduced
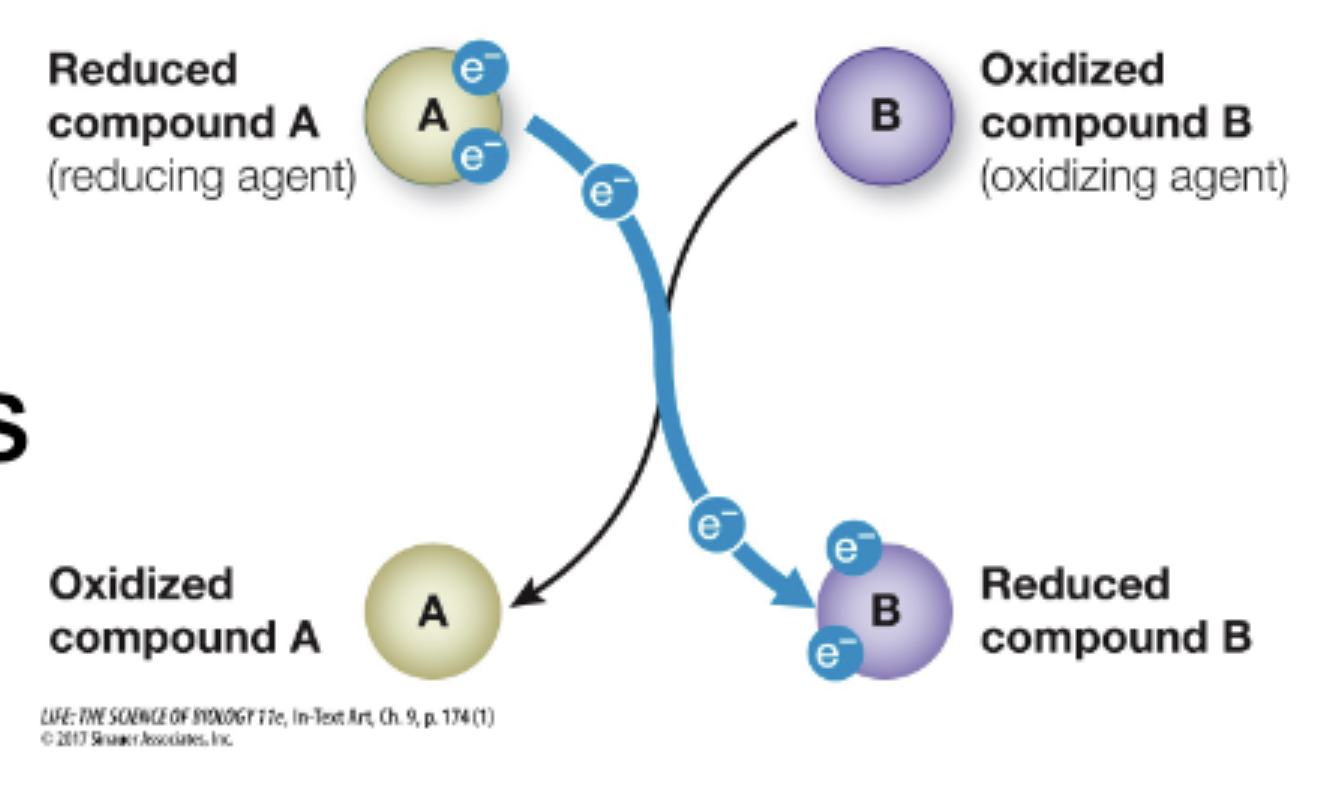
When a molecule loses H atoms it becomes oxidized
Move from long, weaker, nonpolar bonds to more stable, shorter, polar bonds
no energy left to extract
all hydrogens have been removed, electrons taken
Coenzme NAD+/NADH electron carrier
NAD+ is oxidized form
overall charge on nitrogen is positive
nicotinamide ring
H+ and 2e- are transferred
WhNADH is reduced form
loses overall positive charge
because 1e- neutralizes positive charge of nitrogen
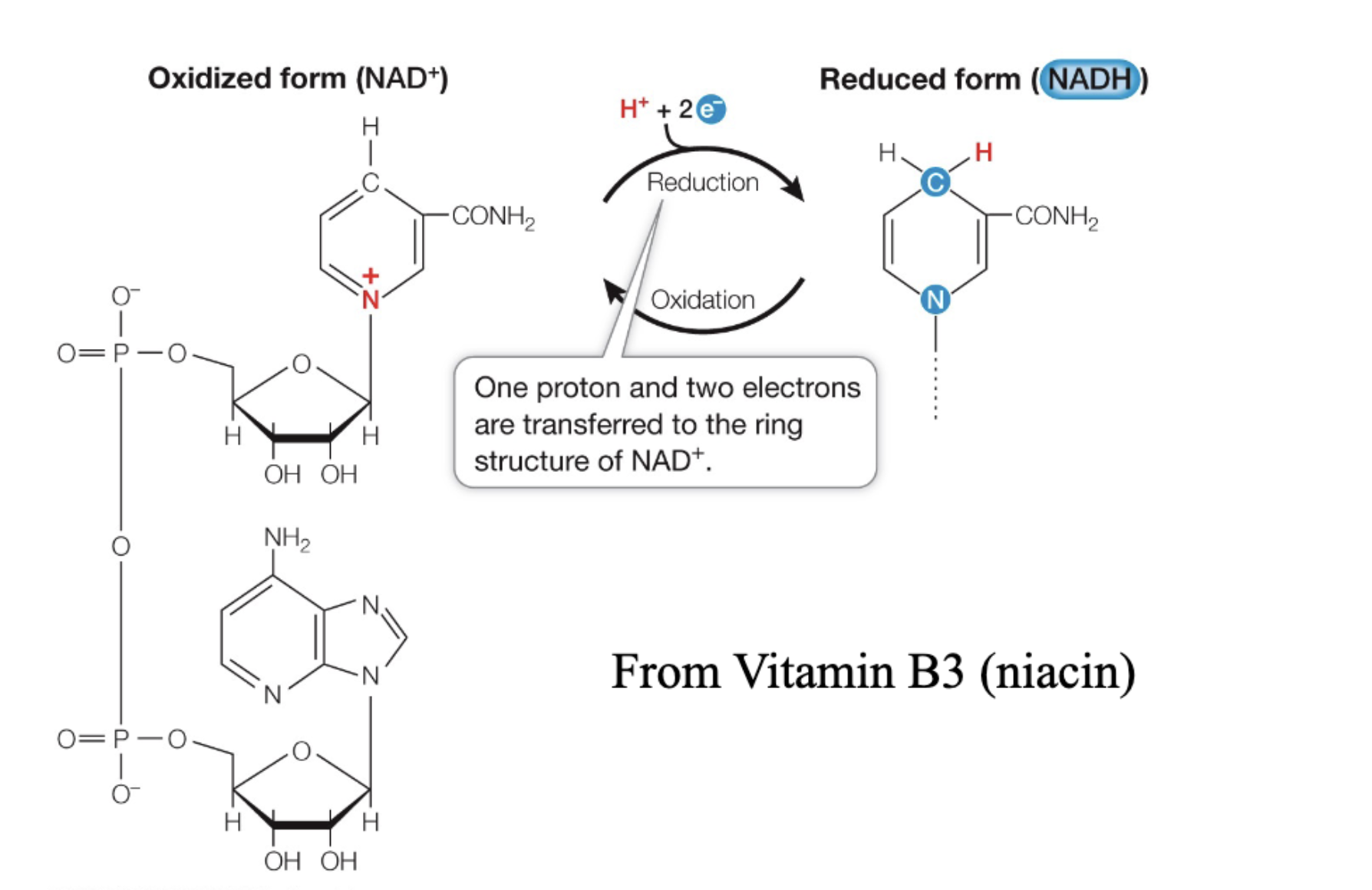
Where does NAD+ come from
Vitamin B3 (niacin)
mobile carrier
cofactor
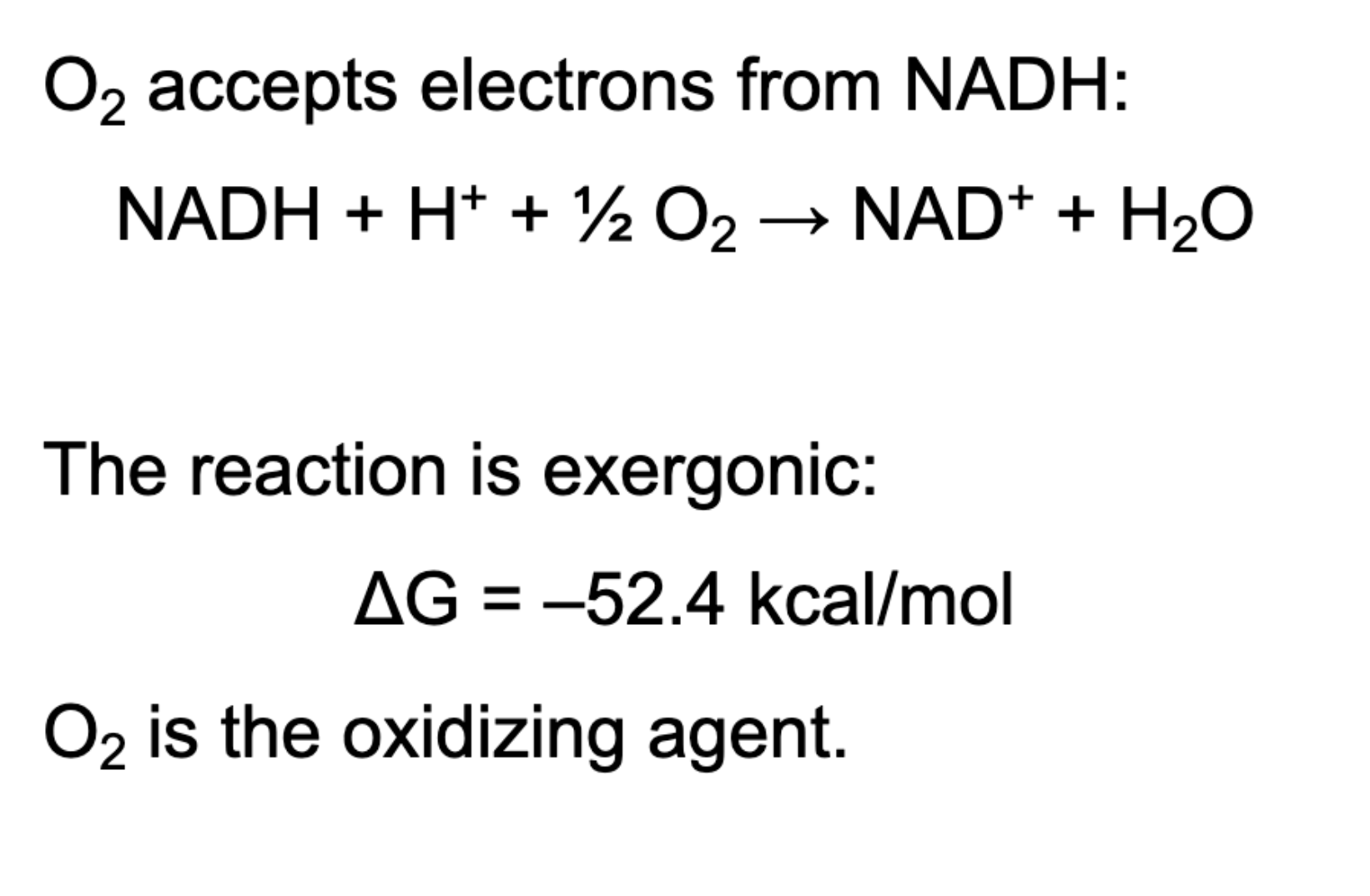
What does terminal electron acceptor O2 accept electrons from
NADH
NADH becomes oxidized to NAD+, it is recycled and available to take more electrons in glycolysis
Where does glycolysis occur
cytosol
Where does pyruvate oxidation occur
Mitochondria
Where does Citric Acid Cyle (CAC) occur
Mitochondria
Where does ETC/ATP synthesis occur
Mitochondria
Where does Fermentation occur
Cytosol
Where does complete oxidation of glucose occur
CAC
Glycolysis
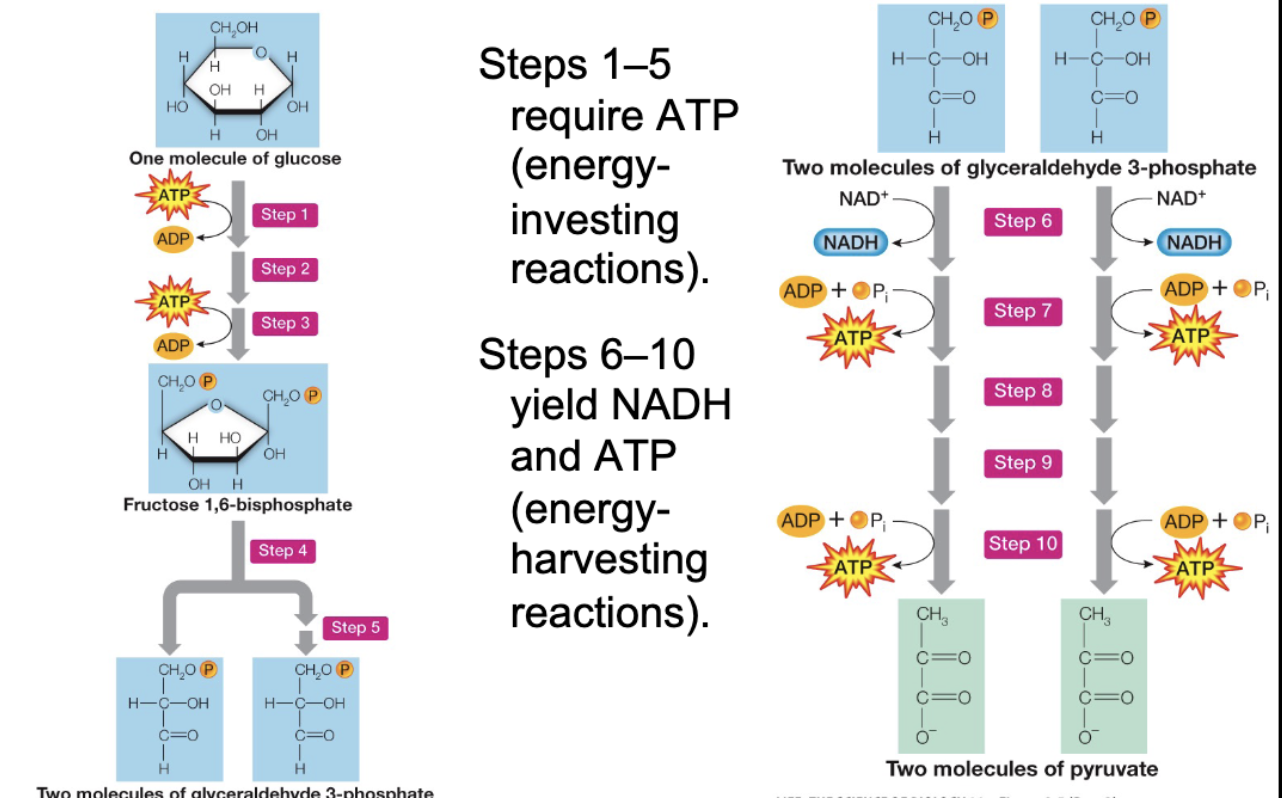
10 steps
steps 1-5 are energy investing
steps 6-10 are energy harvesting
occurs in cytosol
converts glucose into 2 molecule of pyruvate
produces 2 ATP and 2 NADH
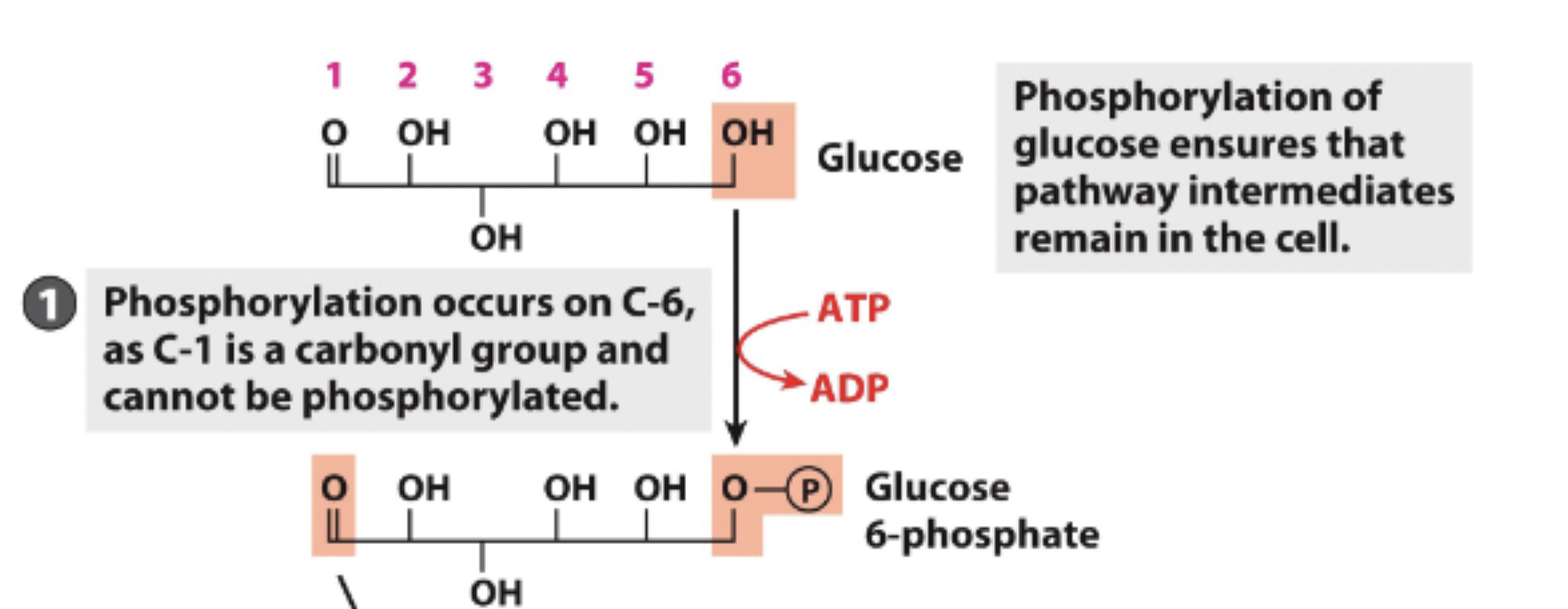
Glycolysis Step 1
Glucose is a 6 carbon sugar
Phosphorylation occurs on C-6
1 ATP invested
Cannot occur on C-1 because it is a carbonyl group and cannot be phosphorylated (due to double bond)
Forms Glucose 6-phosphate
Glycolysis Step 2
Now, the glucose-6 phosphate needs to be symmetrical on the carbon-1, but can’t due to carbonyl oxygen
So the doubled bonded O and OH switch positions
Forms Fructose 6-phosphate
ketose

Glycolysis Step 3
Now, carbon-1 can be phosphorylated
1 ATP invested
Forms Fructose 1-6 biphosphate

Glycolysis Step 4
Carbonyl group at C-2 (double bond) facilitates C-C bond cleavage
Forms 2 3-carbon products
Dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP)
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
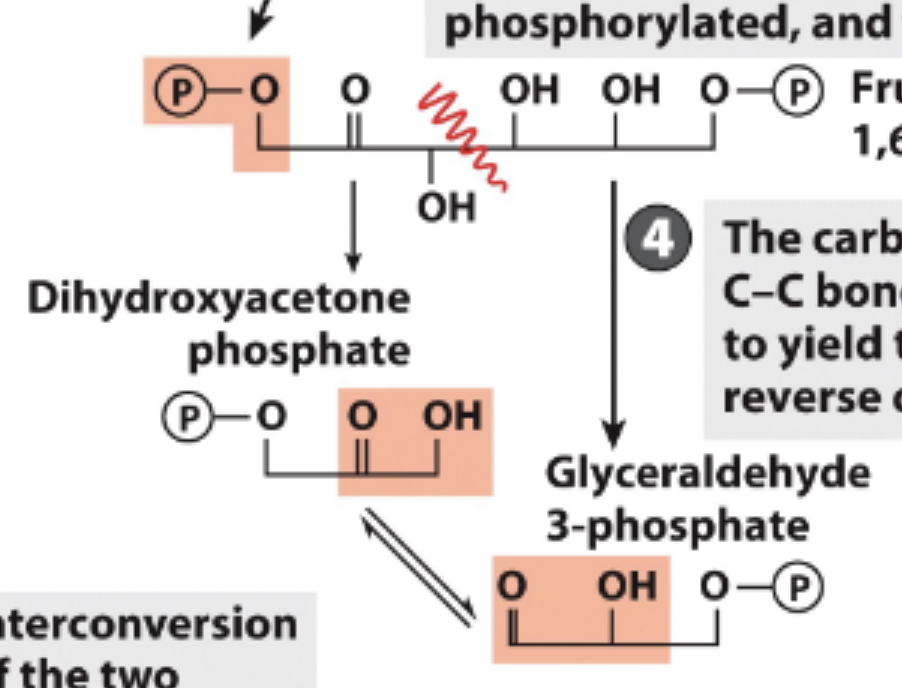
Glycolysis Step 5
Dihydroxyacetone phosphate is interconverted into glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
Now, there are 2, identical Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate products
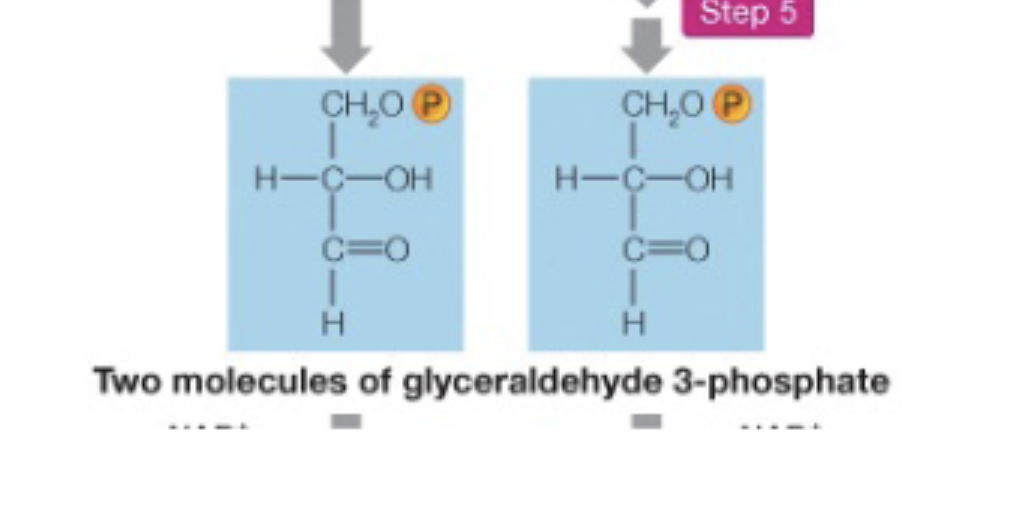
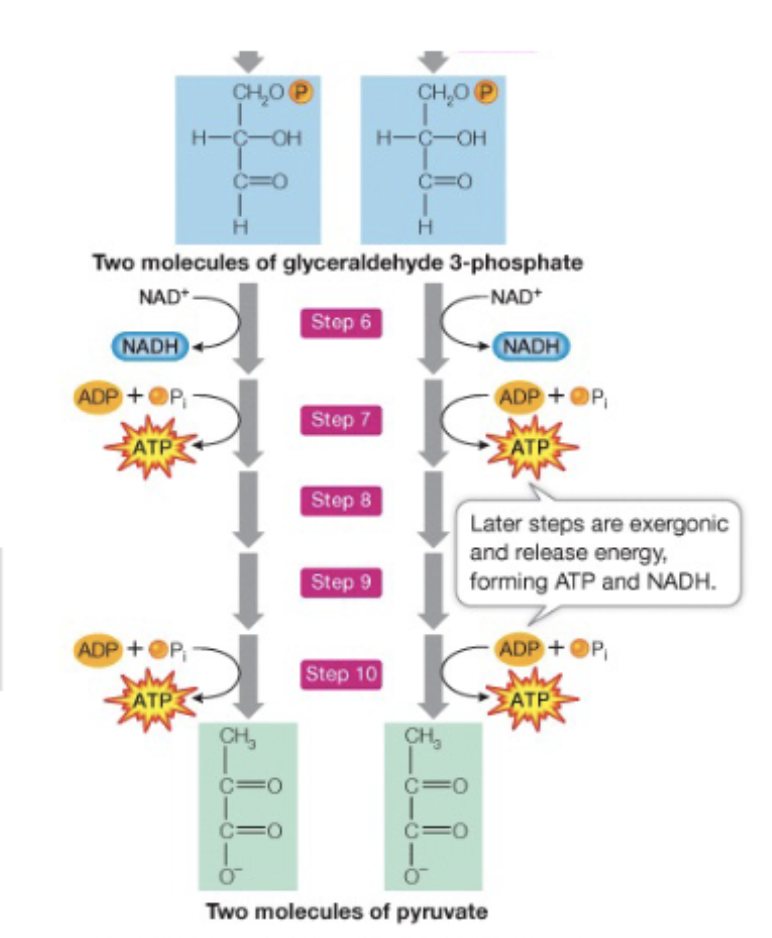
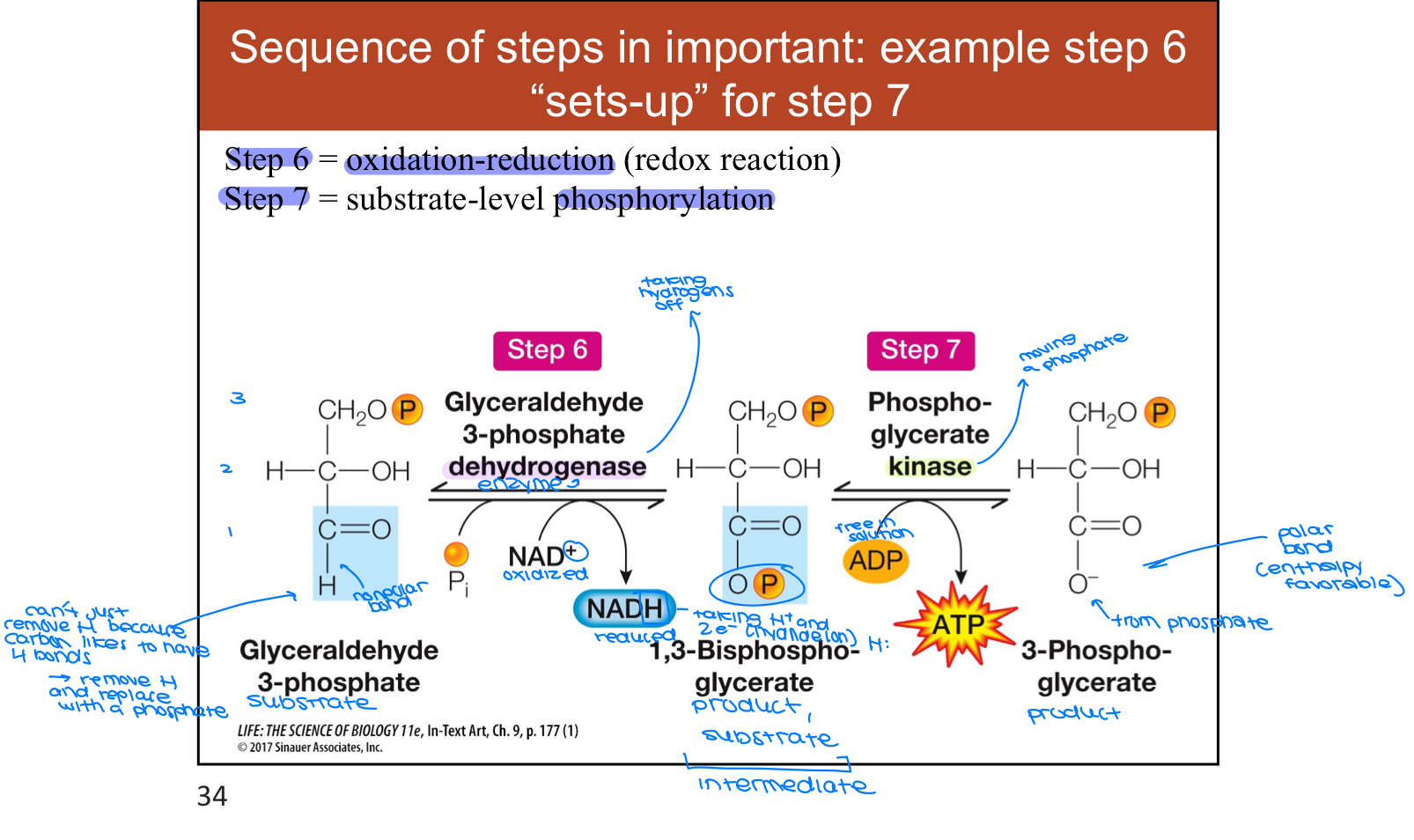
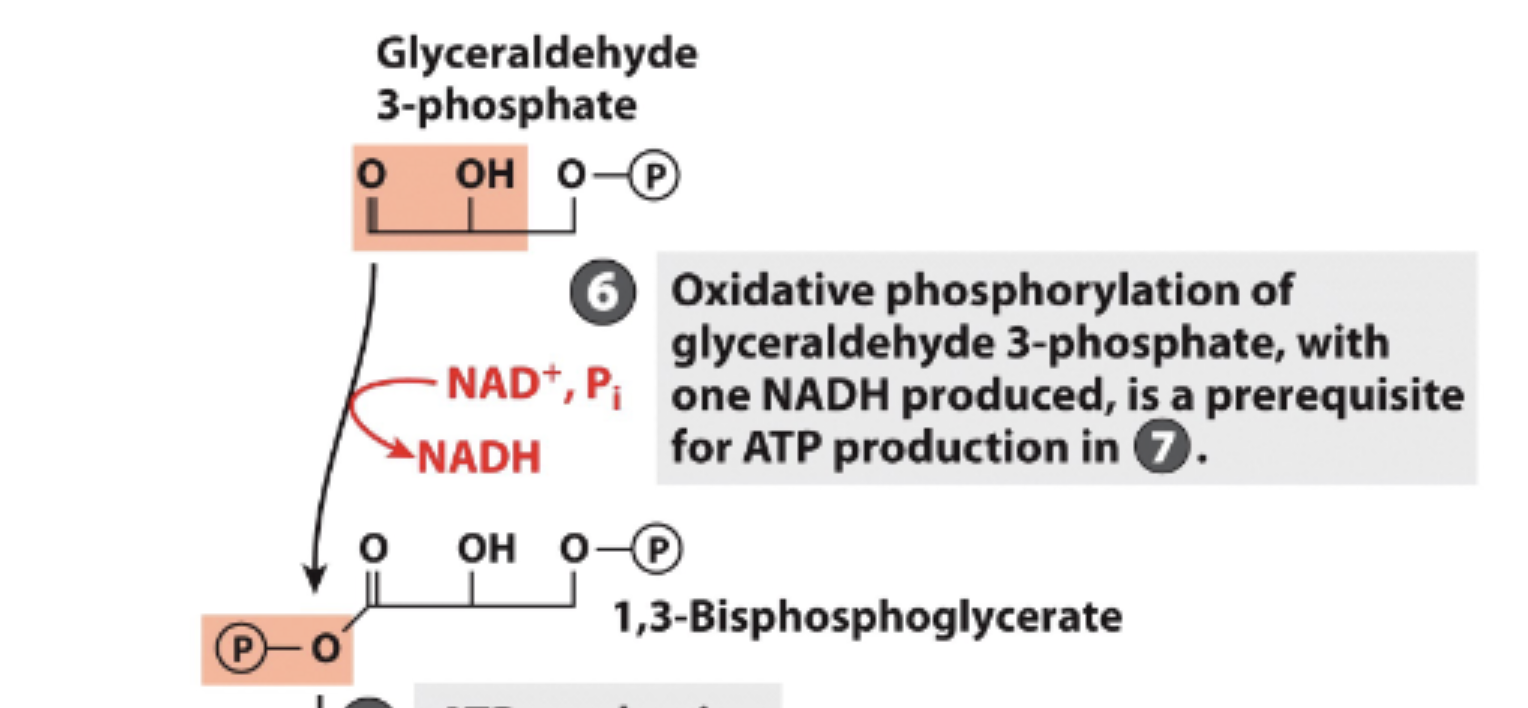
Glycolysis Step 6
oxidative phosphorylation of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate occurs
1 NADH produced —> reduced form, goes to ETC
Forms 1-3- biposphoglycerate
Glycolysis Step 7
ATP produced, 1 phosphate removed
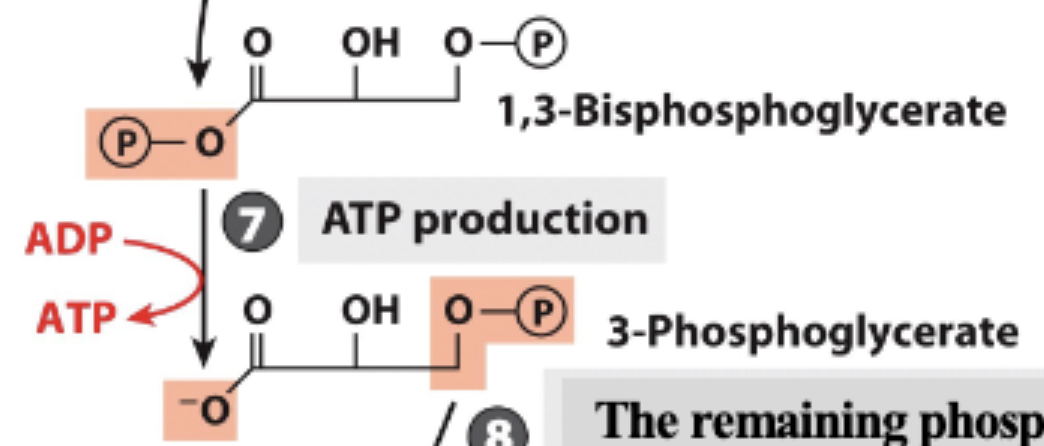
Glycolysis Step 8
Remaining phosphoryl group moved from C-3 to C-2
Forms 2-phosphoclycerate
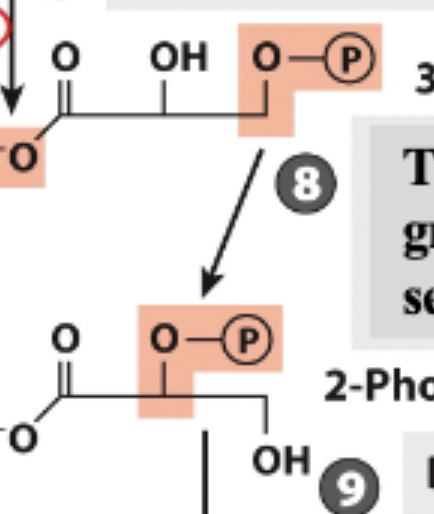
Glycolysis Step 9
Dehydration activates phosphoryl for transfer in step 10
Forms phosphoenolpyruvate
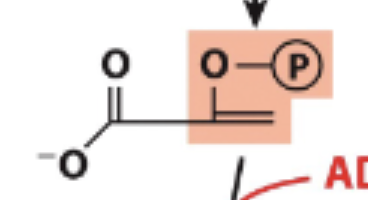
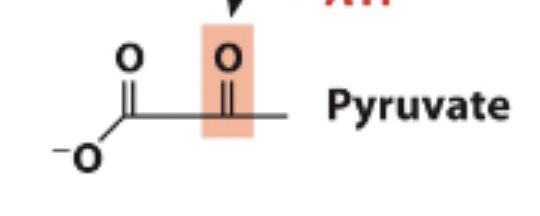
Glycolysis Step 10
Phosphate transferred to another ATP - 1 ATP produced
Final produce is Pyruvate
Steps 6-10 occurs 2x
So Net NADH and ATP production is 2 of each (1 during each round)