Lecture 2 - Nucleotides and Nucleic acids
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
What is a nucleic acid?
Essential macromolecules, like DNA and RNA, that carry and express genetic information, forming the blueprint for life by storing instructions to build proteins
What is RNA?
Polymeric molecule that is essential for most biological functions, either by performing the function itself or by forming a template for the production of proteins
What is B-form DNA?
The most common, right-handed, double helix, anti-parallel structure of DNA found in living cells.
Draw an ester bond.
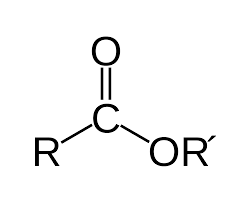
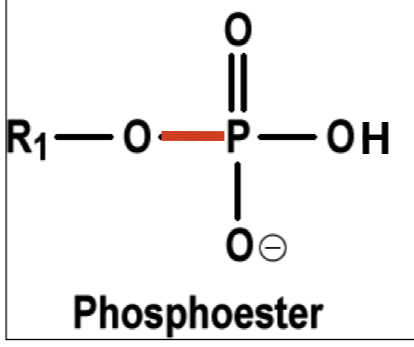
Draw a phosphoester bond.
Note: Only one oxygen is bonded to one carbon.
Draw a phosphodiester bond.
Note: There is two oxygens bonded to two carbons.
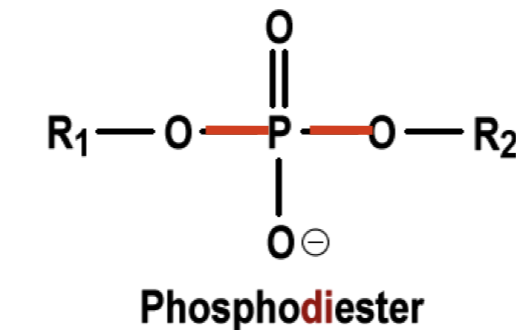
What is the purpose of phosphodiester bonds?
They connect sugars and phosphate groups, forming the continuous chain (backbone) of DNA and RNA, like links in a chain
Why are nucleic acids said to have a “sense of direction”?
Because the nucleic acid polymer has 5’ and 3’ ends that are structurally distinct.
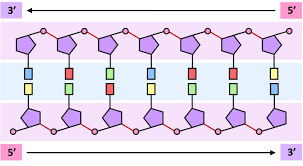
How do you identify the 5’ end of a nucleic acid base sequence?
By looking for the phosphate group attached to the fifth carbon (5') of the sugar molecule
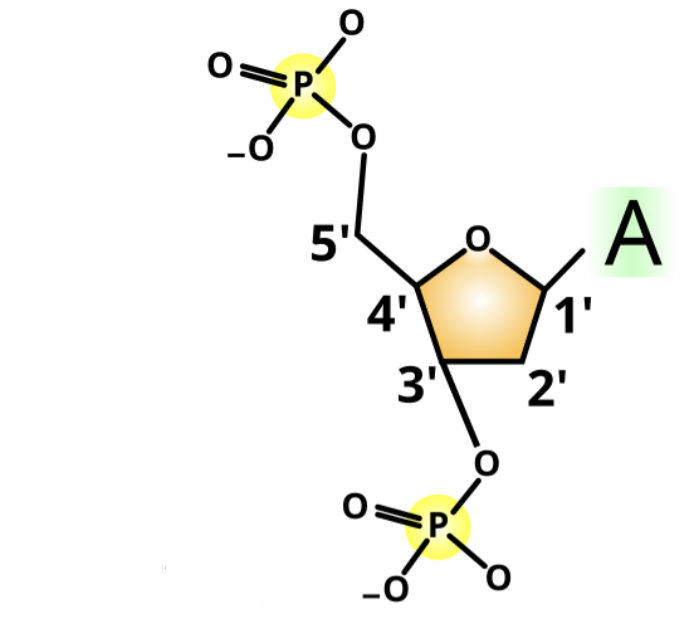
Identify the 5’ end.
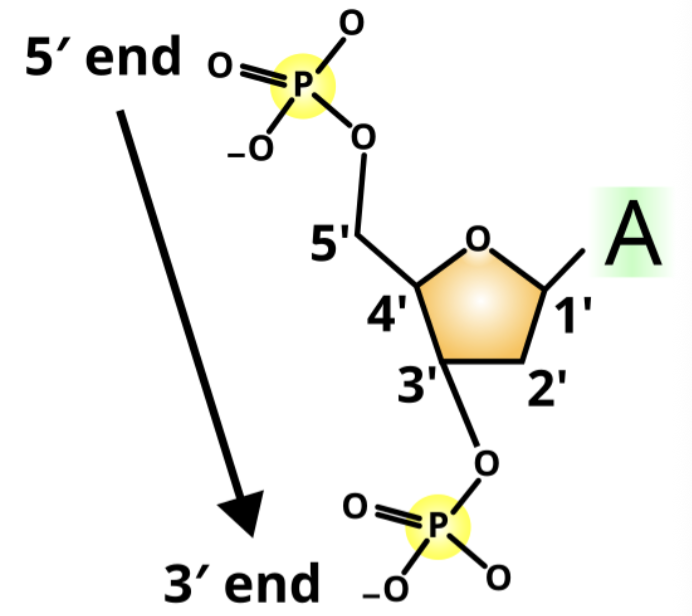
How do you identify the 3’ end of a nucleic acid base sequence?
3' end has a free hydroxyl group (OH) on the third carbon (3')
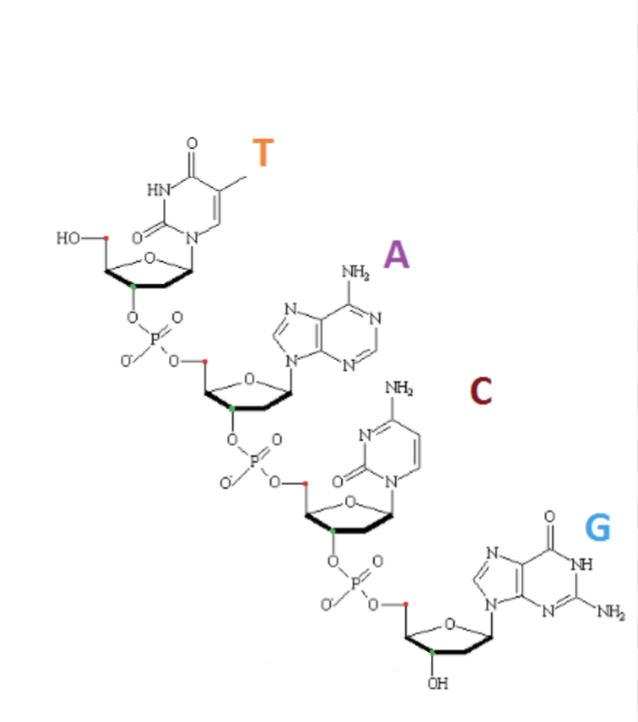
Identify the 3’ end.
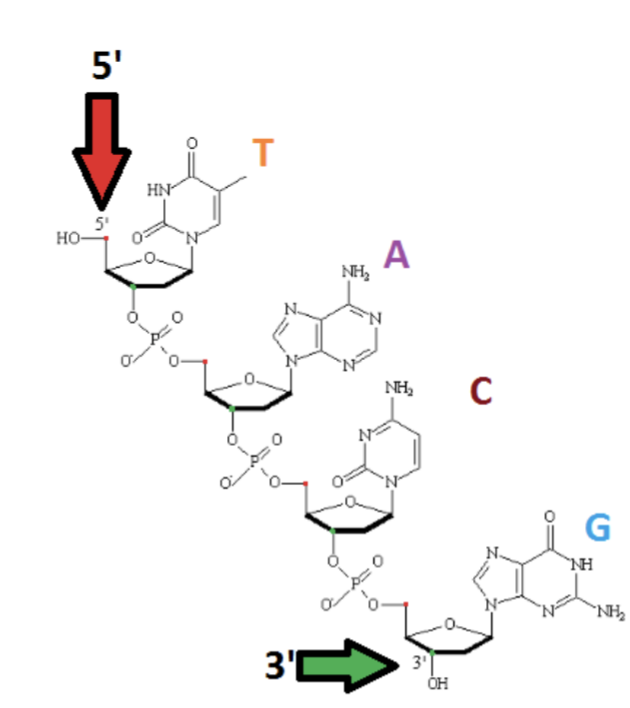
Describe the primary structure of DNA.
A chain of nucleotides, each containing a sugar (deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and one of four nitrogenous bases (Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, Cytosine)
Describe the difference in primary structure of DNA and RNA.
DNA uses deoxyribose sugar, while RNA uses ribose sugar.
DNA uses thymine, while RNA uses uracil.
What can primary structure be described as, in the sense of BIOCH 200 concepts.
The sequence of nucleotide residues stabilized by phosphodiester bonds.
Describe the process of alkaline hydrolysis.
In alkaline conditions, hydroxide ions promote cleavage of the phosphodiester bonds in the sugar-phosphate backbone of nucleic acids leading to strand breaks.
What is more stable: RNA or DNA?
DNA
Why is DNA more stable than RNA? (basic reasoning)
DNA is storing information and must stay stable, whereas RNA is just a messenger.
Why is RNA susceptible to alkaline hydrolysis whereas DNA is resistant?
DNA’s deoxyribose sugar lacks a reactive 2'-hydroxyl (OH) group, making it less prone to hydrolysis (and more stable).
What is the most essential force for primary nucleic acid structure?
Covalent bonding
What is “base stacking”?
Base stacking is the stabilizing interaction in DNA and RNA where adjacent flat bases lie parallel and stack on top of each other like coins.

What is the most essential force in secondary nucleic acid structure?
Base stacking interactions.
van der Waals (most important)
Hydrophobic forces
H-bonds (least important)
What groups in nucleic bases can form H-bonds?
Amino groups (–NH₂) as hydrogen-bond donors,
Ring nitrogens (=N–) as hydrogen-bond acceptors,
Carbonyl groups (C=O) as hydrogen-bond acceptors.
What groups in nucleic bases cannot form H-bonds?
C–H groups (hydrogen attached to carbon)
C=C and C–C bonds (hydrocarbon regions)
Positively charged nitrogens or nitrogens with no available lone pair (cannot accept H-bonds)