lecture 4 - lipids and membranes
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
1
New cards
what are the roles of lipids?
* simple triacylglycerides are a major form of chemical energy storage
* phospholipids form membranes
* lipids can anchor to membranes
* lipids serve as signaling molecules
* phospholipids form membranes
* lipids can anchor to membranes
* lipids serve as signaling molecules
2
New cards
What are some features of the biological membrane?
* hydrophobic tail and hydrophilic head
* spontaneously form
* asymmetric
* contain cholesterol and protein
* spontaneously form
* asymmetric
* contain cholesterol and protein
3
New cards
What is a saturated fatty acid?
fatty acid with NO double bonds
4
New cards
What is an unsaturated fatty acid?
fatty acid with at least ONE double bond
5
New cards
What is the typical structure of fats/oils?
a glycerol backbone, ester bonds, and fatty acid tails
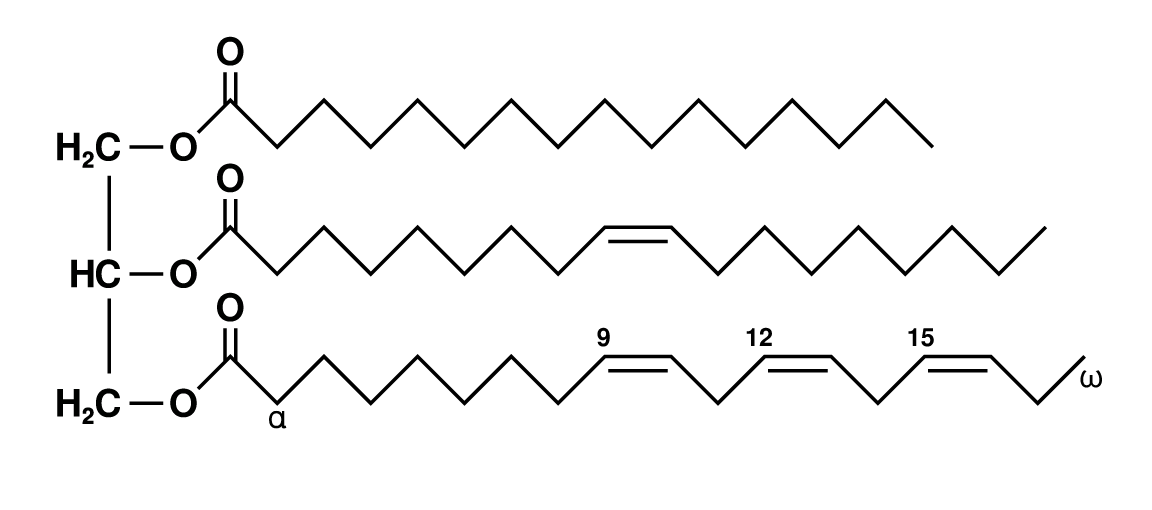
6
New cards
What kinds of membrane lipids are there?
* phospholipids
* glycolipids
* cholesterol
* glycolipids
* cholesterol
7
New cards
What is a phospholipid? What does its structure look like?
A phospholipid is one of the most abundant membrane lipids
8
New cards
What is a phosphoglyceride (type of phospholipid)?
Phosphoglycerides are composed of a glycerol backbone with two fatty acid tails, plus a phosphate and alcohol
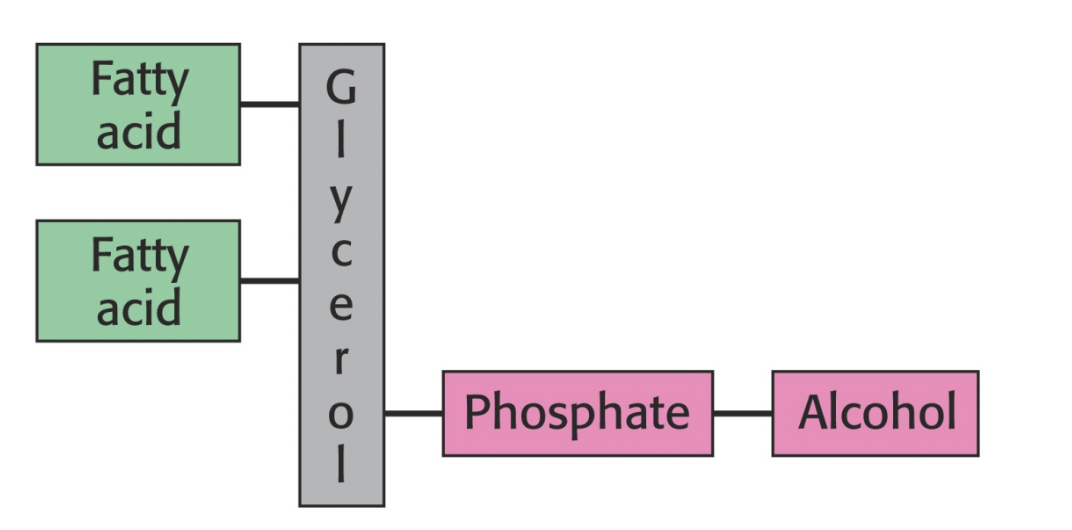
9
New cards
What is a sphingomyelin (type of phospholipid)?
\
A sphingomyelin is structurally the same as a phosphoglyceride, except the glycerol backbone is replaced as the amino alcohol sphingosine
A sphingomyelin is structurally the same as a phosphoglyceride, except the glycerol backbone is replaced as the amino alcohol sphingosine
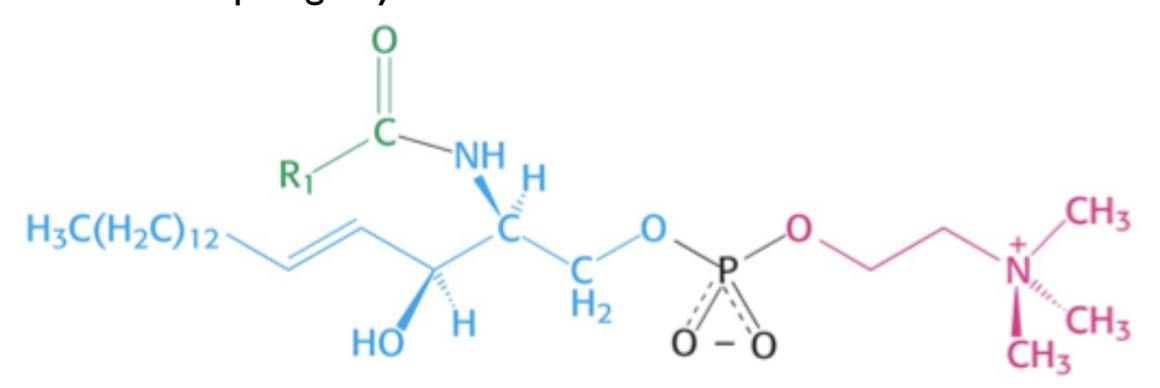
10
New cards
What are glycolipids?
Glycolipids are a type of membrane lipid that are structurally similar to sphingomyelin, but the hydroxyl group is ether linked to one or more sugars instead of phosphocholine.
\
The simplest glycolipid is a cerebroside.
\
The simplest glycolipid is a cerebroside.
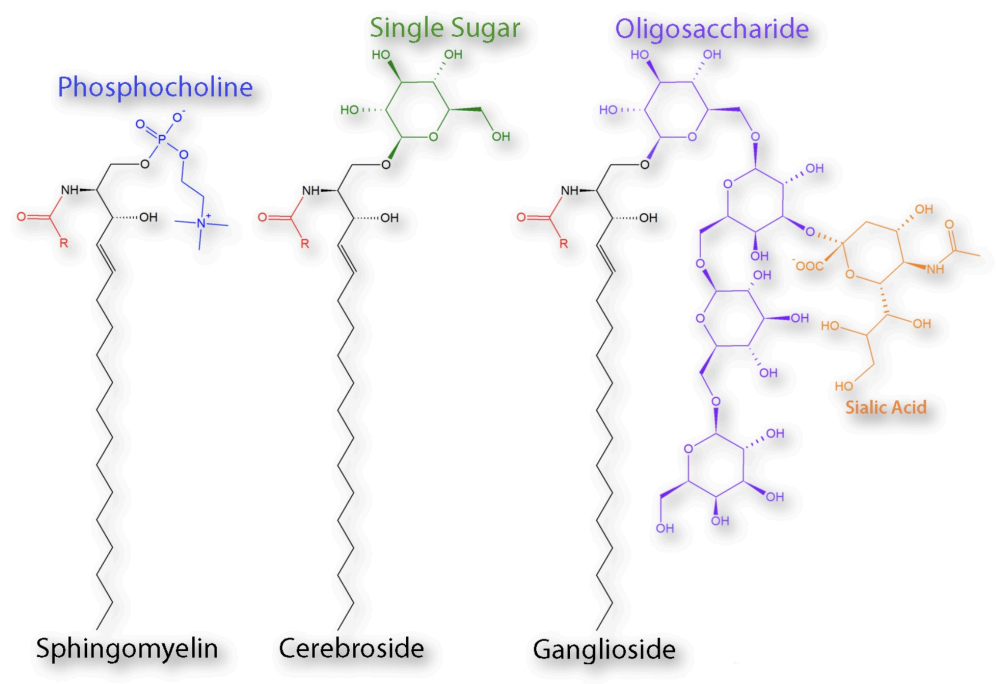
11
New cards
What is a cerebroside (type of glycolipid)?
A cerebroside is the simplest glycolipid, only containing a monosaccharide ether-linked to the hydroxyl group
12
New cards
What is a ganglioside (type of glycolipid)?
A ganglioside is a more complex cerebroside, where they contain branched sugars instead of one monosaccharide
13
New cards
Where are the sugar residues from glycolipids located on the membranes?
Extracellular side
14
New cards
What is cholesterol?
Cholesterol is a membrane lipid that is amphipathic (water loving and hating). Cholesterol is able to prevent extreme membrane fluctuations in hot and cold temperatures due to the large size of the molecule.

15
New cards
What does amphipathic mean?
part hydrophilic and part hydrophobic
16
New cards
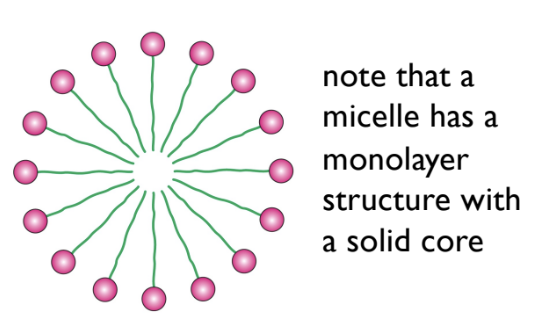
What are micelles?
Micelles are molecular aggregates with both hydrophilic and hydrophobic components. Typically shown in circular form. Micelles are useful for the transport of lipids and fat soluble vitamins
17
New cards
How does spontaneous membrane layer formations occur?
Hydrophobic interactions via van der waals attraction of the hydrophobic tails
\
Hydrophilic interactions via electrostatic and hydrogen bonding of the hydrophilic heads
\
Hydrophilic interactions via electrostatic and hydrogen bonding of the hydrophilic heads
18
New cards
What is the difference between a micelle and a liposome?
A liposome has a double layer (bilayer) of lipids that forms an aqueous inner bubble
\
A micelle has a monolayer of lipids, with outer hydrophilic heads and a hydrophobic inner bubble
\
A micelle has a monolayer of lipids, with outer hydrophilic heads and a hydrophobic inner bubble
19
New cards
What are some uses for liposomes?
They can be used for DNA and drug delivery
20
New cards
Are lipid bilayers permeable to ions?
no, ions and polar molecules cannot cross without the help of protein complexes
21
New cards
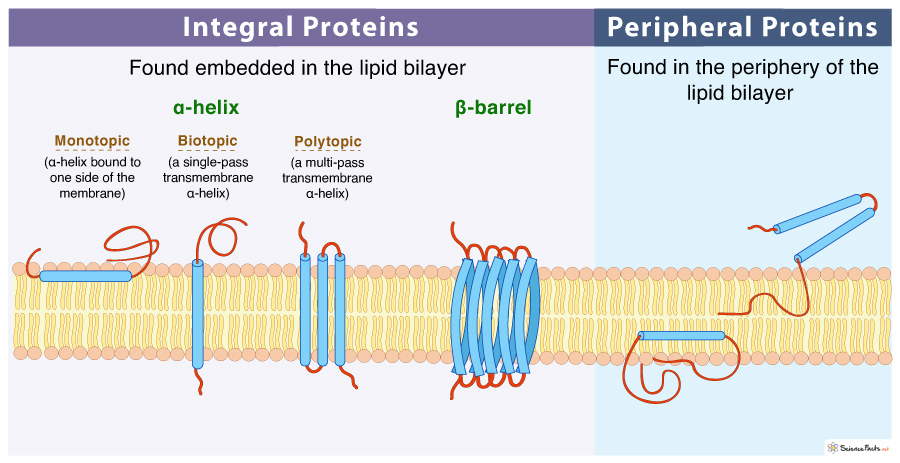
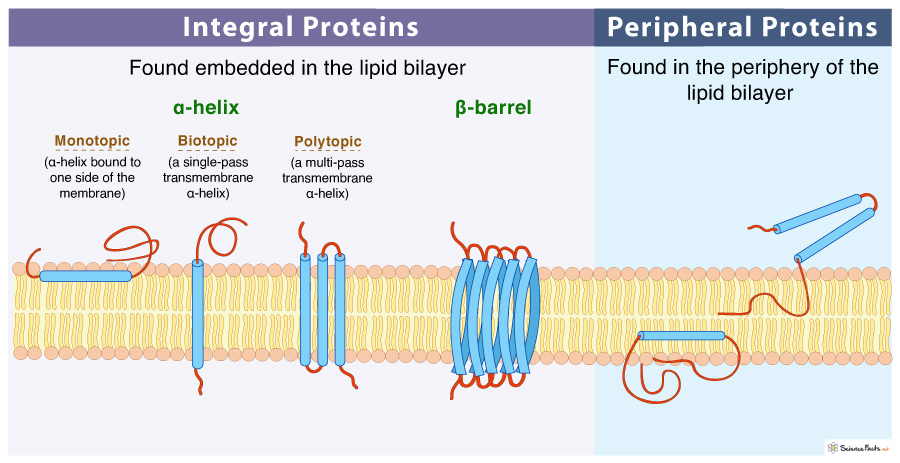
What is a peripheral protein?
Peripheral proteins are found in the periphery of the bilayer, or sometimes partially embedded into the bilayer
\
Can be extracted through mild conditions.
\
Can be extracted through mild conditions.
22
New cards
What are integral proteins?
Integral proteins are found embedded into the lipid bilayer, they span the entire membrane.
\
They can be extracted by detergents.
\
They can be extracted by detergents.
23
New cards
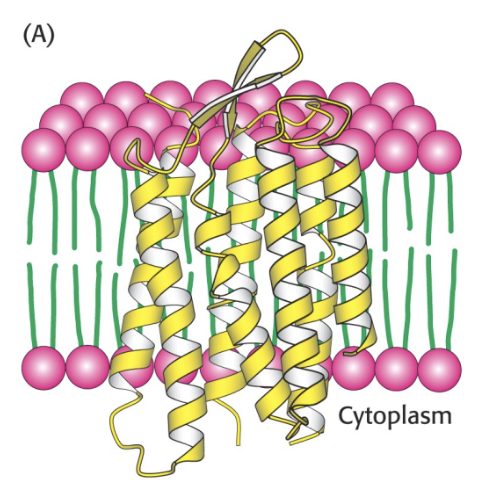
what is an alpha helical membrane spanning region?
It is a helix of hydrophobic amino acids that act as a transmembrane domain
24
New cards
How can transmembrane proteins be predicted within a hydropathy plot?
THe hydropathy plot contains a threshold that defines hydrophilic from hydrophobic. If a peak goes above the threshold, then that peak counts as one transmembrane domain.
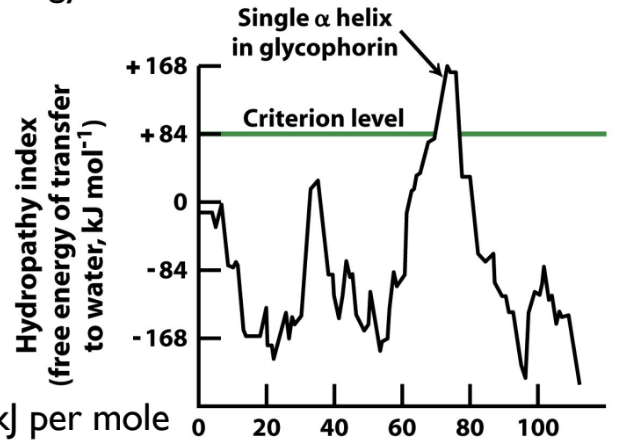
25
New cards
What is a beta barrel?
A beta barrel is a bunch of beta sheets linked together to form ion channels
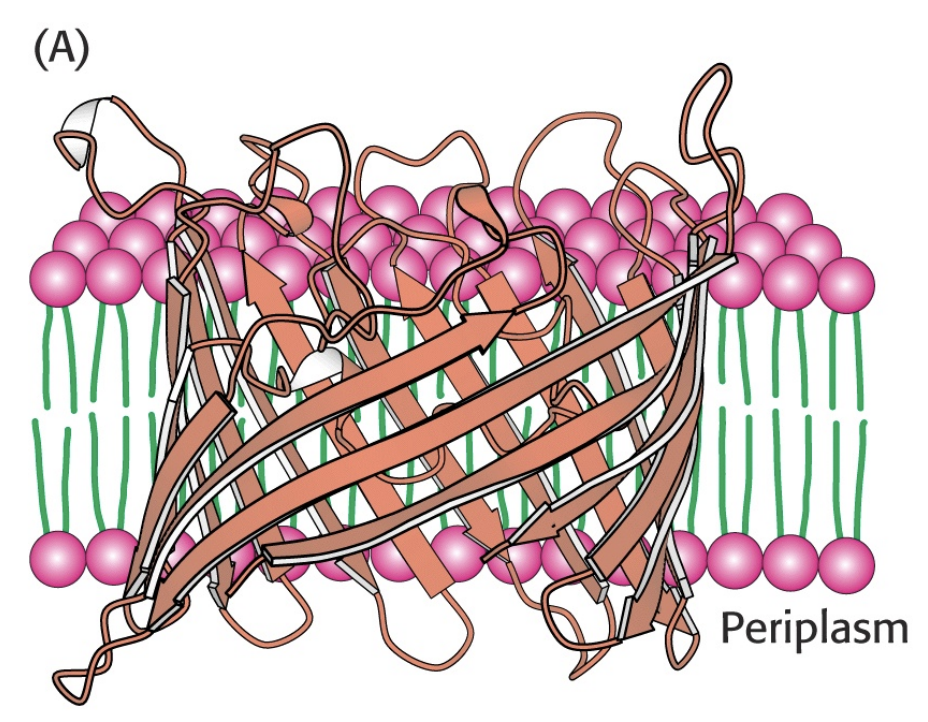
26
New cards
How can the membrane repair itself?
Using flippases, floppases, and scramblases
27
New cards
How does the membrane change in fluidity if the temperature increases?
The membrane will become more fluid
28
New cards
How does the membrane fluidity change if the temperature decreases?
The membrane becomes more packed and ordered
29
New cards
If a lipid has double bonds (unsaturated), what phase would the lipids be in?
liquid
30
New cards
If a lipid has no double bonds (saturated), what phase would the lipids be in?
solid