chem1046 exam 2
1/115
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
116 Terms
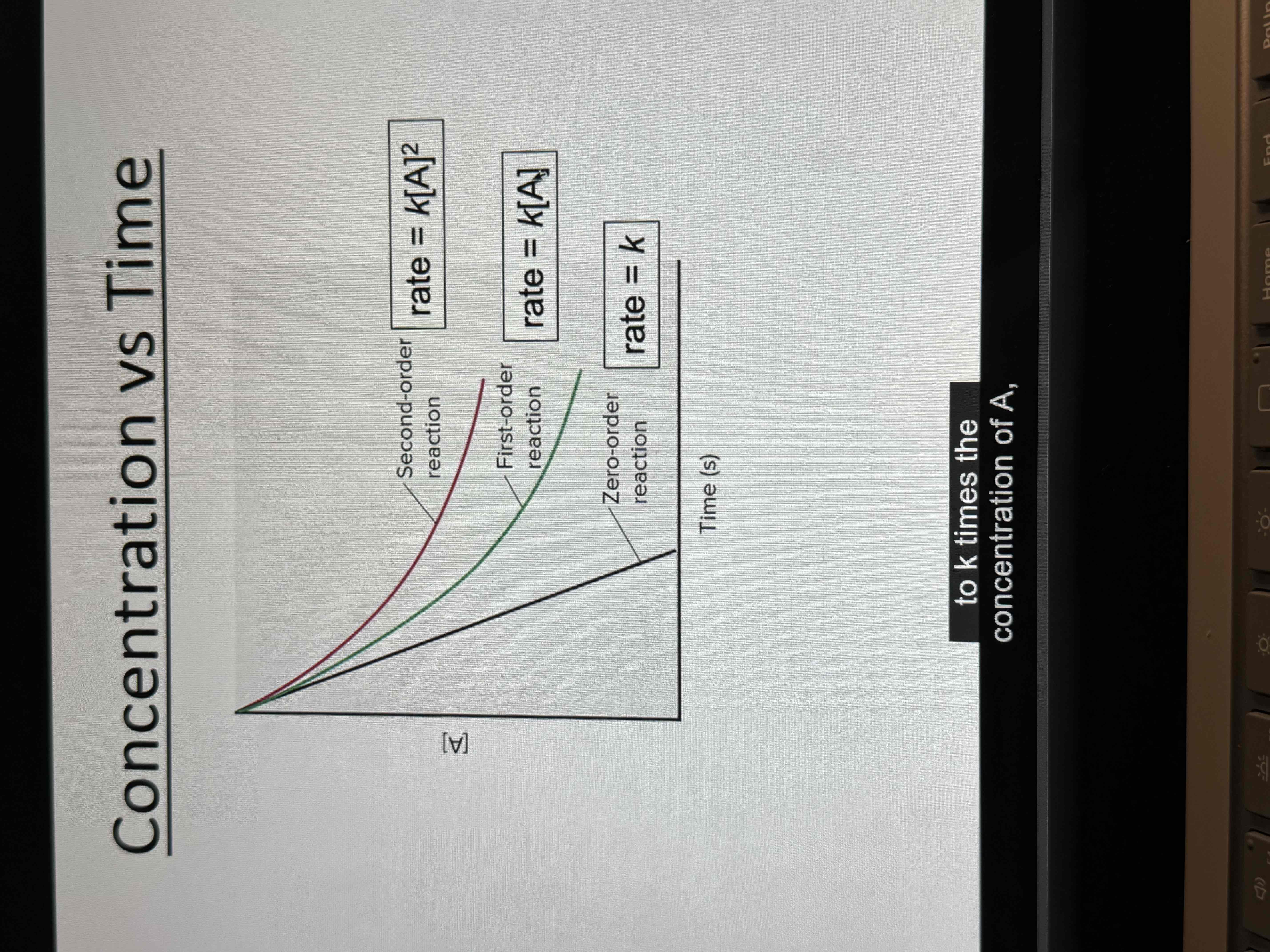
0 order rate law
rate =k
zero order unit
M s^-1 or M/s
1ST Order rate law
rate= k[A]
1st order unit
s^-1 or 1/s
2nd order rate law
rate = k [A]^2
rate = k [A][B]
2nd order k units
M-1 s-1 or 1/Ms
3rd order rate law
rate = k [A]^3
rate = k [A]^2[B]
rate = k [A][B][C]
3rd order k units
M-2 s-1 or 1/M²s
How to find units
X=-(m+n-1)
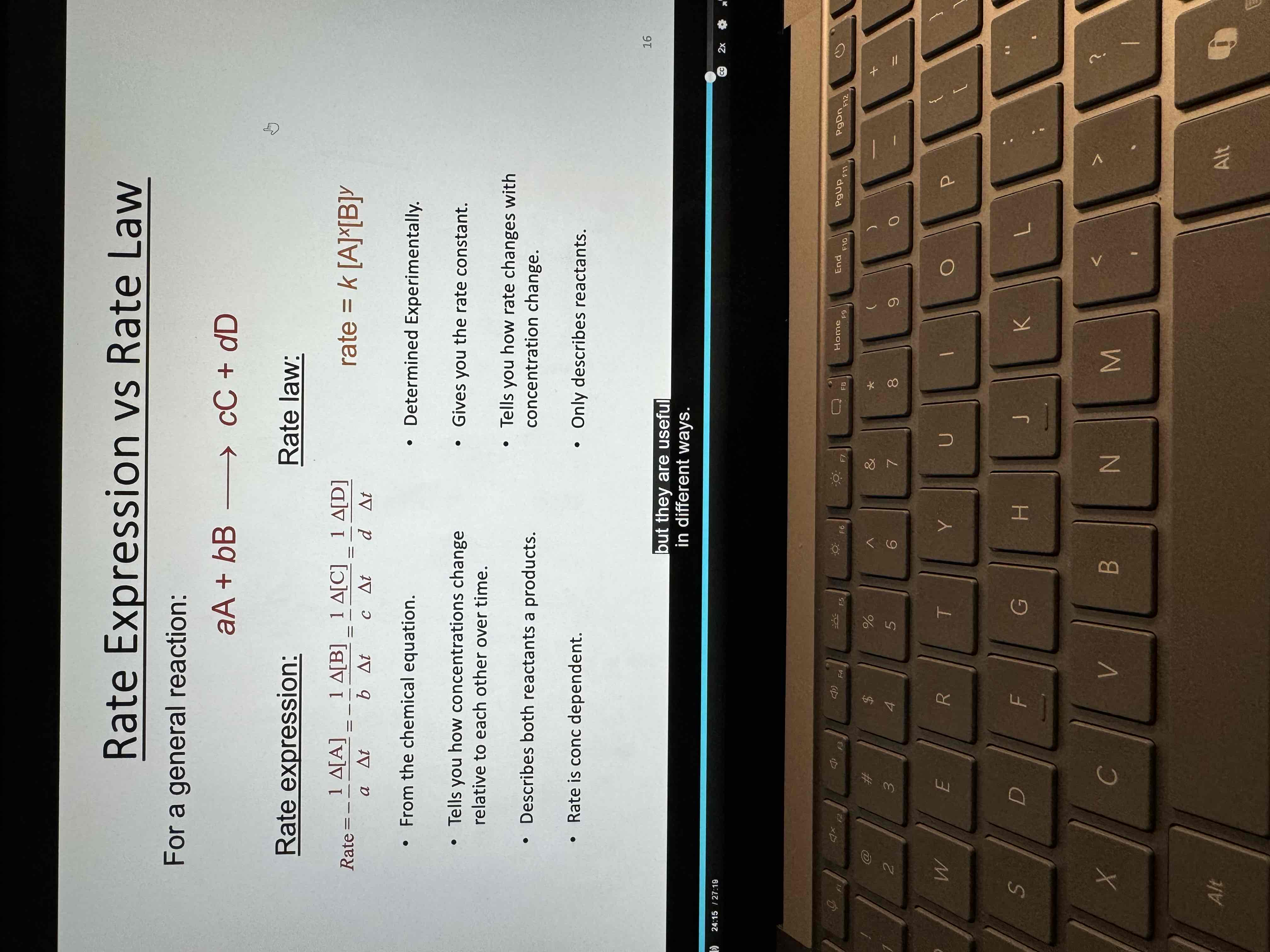
Rate law
rate=k[A]^x[B]^y
expresses the relationship of the rate of a reaction to the rate
constant and the concentrations of the reactants raised to some powers
The rate law is defined in terms of reactant concentrations (not products).
x and y are the order of the reaction.
The power coefficients x and y are not the same as the stoichiometric coefficients a and b.
For rate laws (x and y) are determined experimentally.
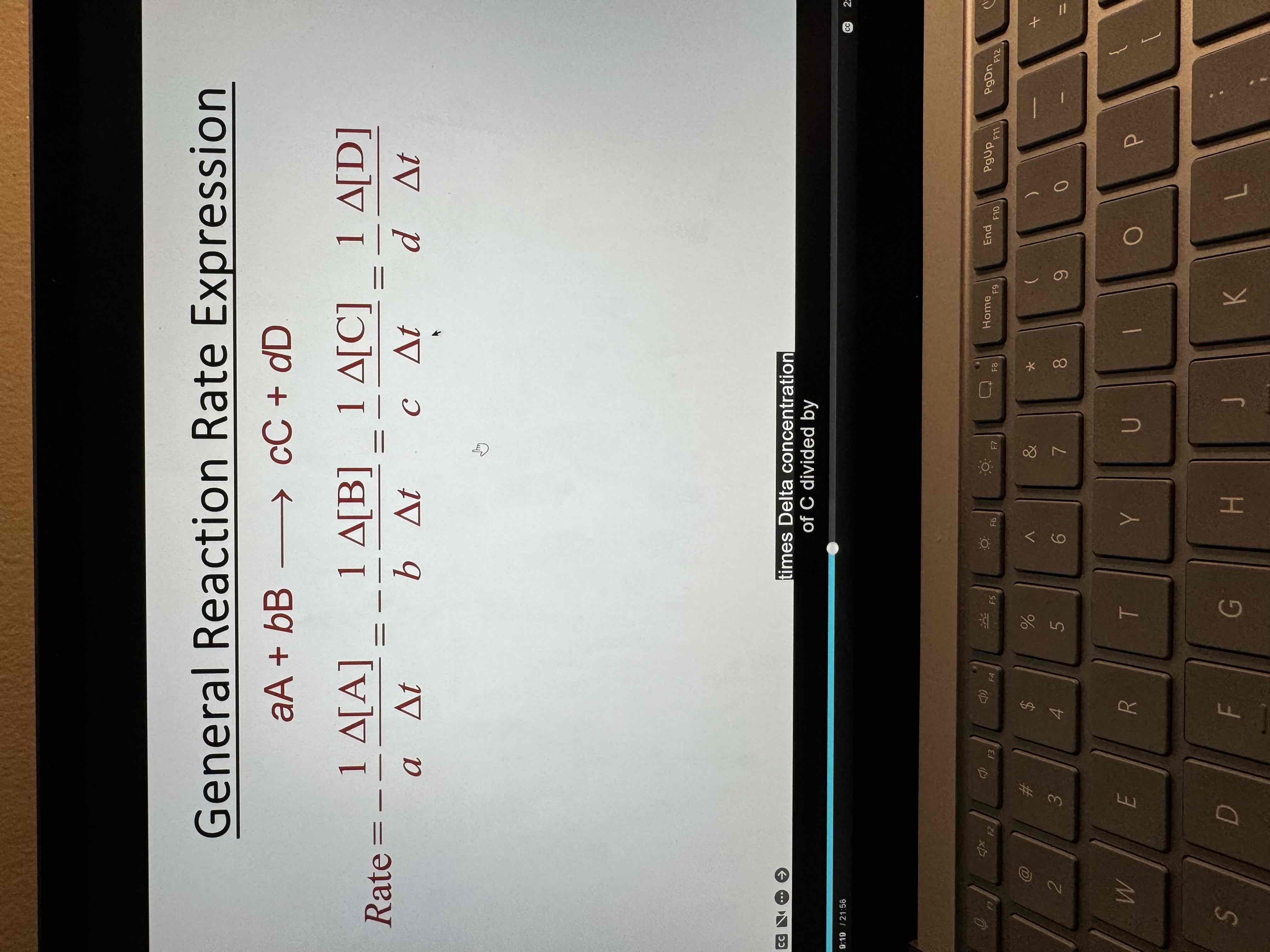
Rate expression
From a chemical equation
Tells you how concentrations change
Rate depends on concentration
Rate law
Determined experimentally
How rate changes relative to concentration change
Reaction
How fast
Chemical kinetics
Understanding the rates of chemical reactions
Reaction rates
The change in amount of stuff (reactant or product) per time interval
Reaction rate units
M/s

rate equation

all rates are __
Positive
Look
Yay
Initial rate
The rate calculated at the start of the reaction
Instantaneous rate
The rate calculated at any specified moment during the reaction
factors affecting reaction rates
Nature of the reacting species
State of reactants (powder vs solid)
Temp (faster at higher temps)
Catalyst
Concentration of reactants (reg oxygen normal or liquid oxygen explosion)
Rate constant
Constant of the proportionality between the reaction rate and the Concentration of reactant
Rate law
Expresses the relationship of the rate of a reaction to the rate constant, and the concentrations of reactants raised to some powers
reaction order
Specify the relationship between the concentrations of reactants, A and B and the reaction rate
reaction rate F2 + 2ClO2 → 2FClO2
Rate = k[F2][ClO]^1
MUST BE DETERMINED Experimentally
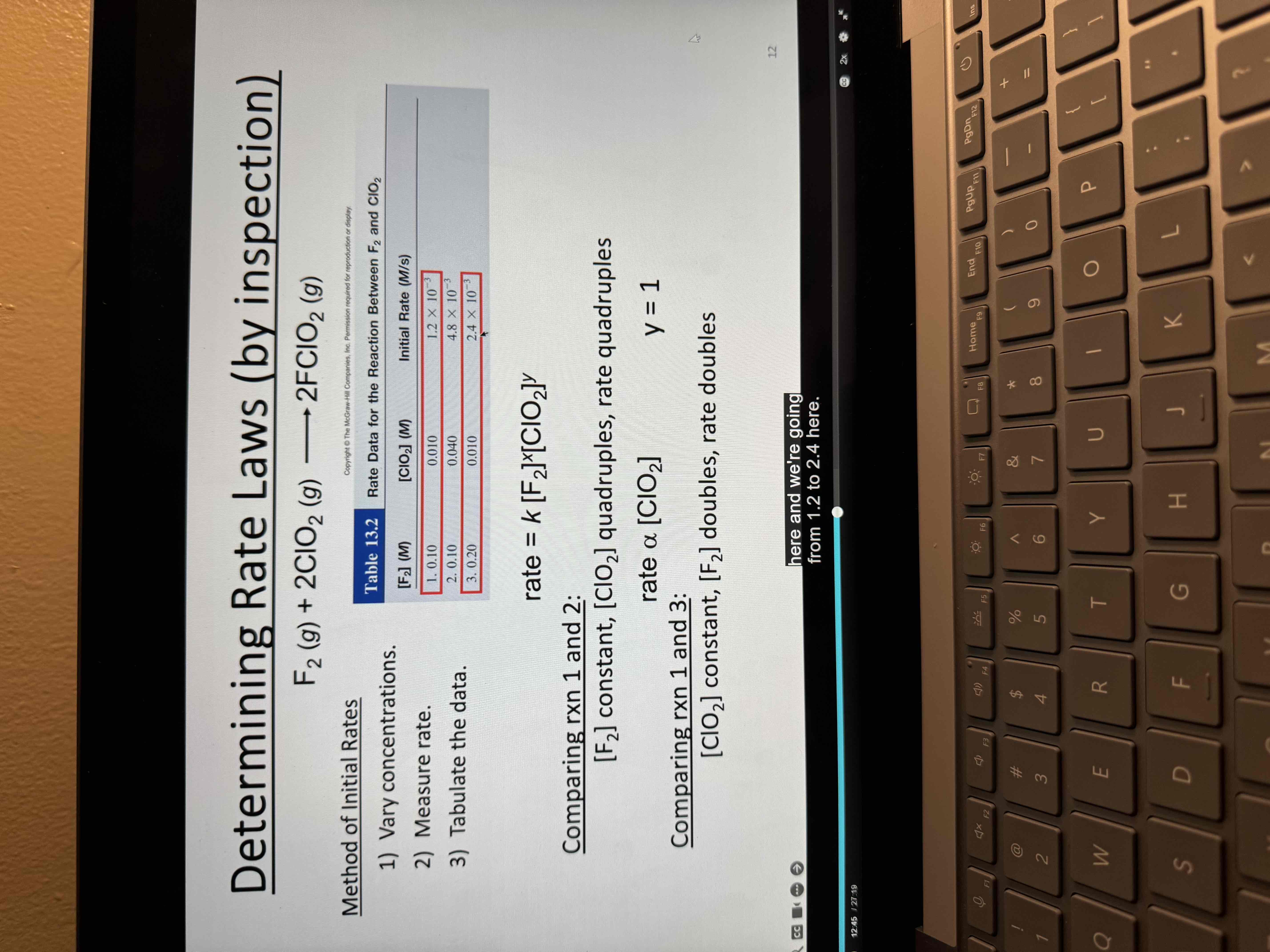
Determine rate laws by inspection
Calculating rate constant
Find rate then plug in 1 experiment and do algebra
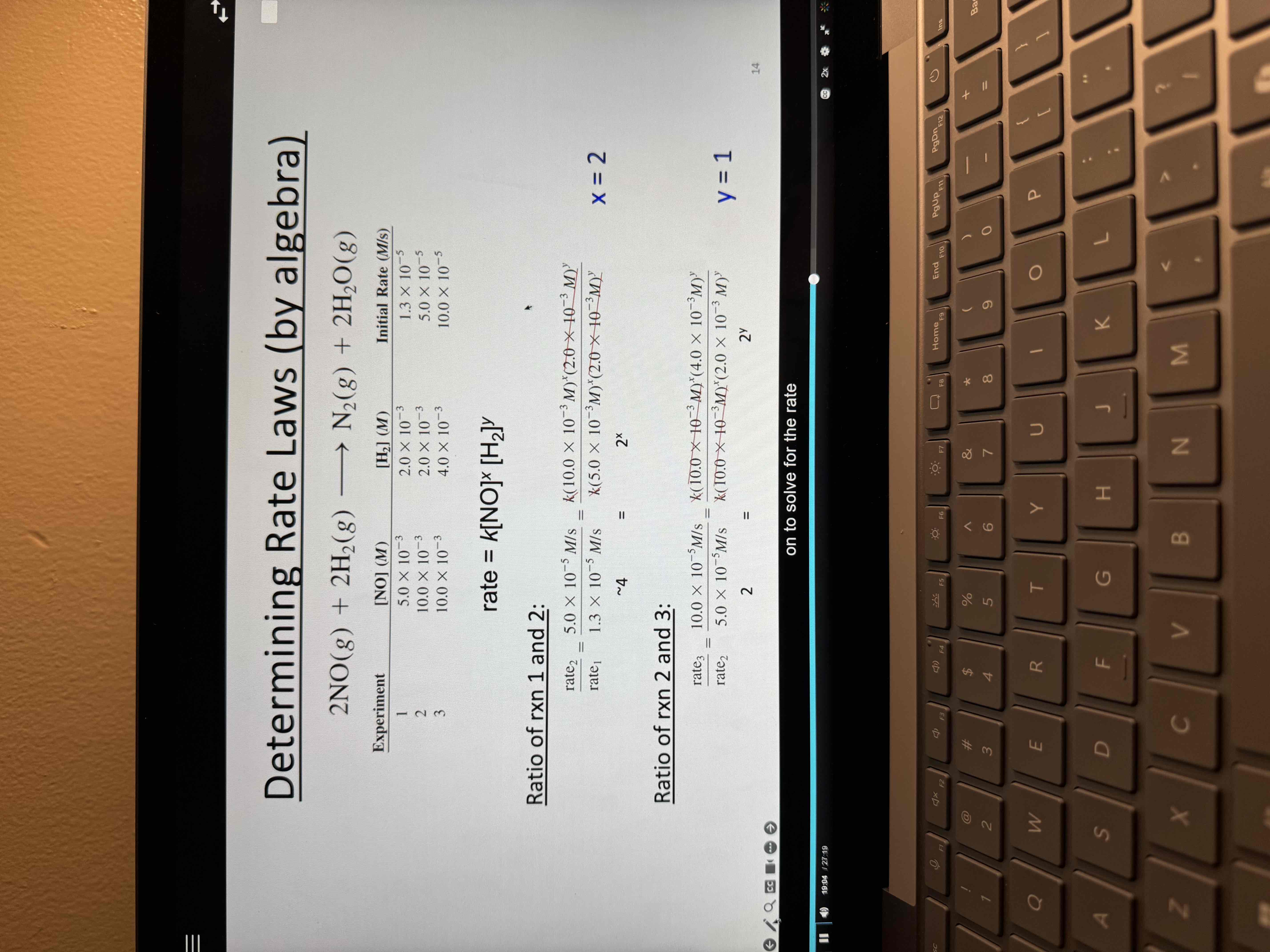
Not by inspection
Reaction order
Reaction is xth order in A
Reaction is yth order in B
Reaction is (x+y) order overall
Reaction orders
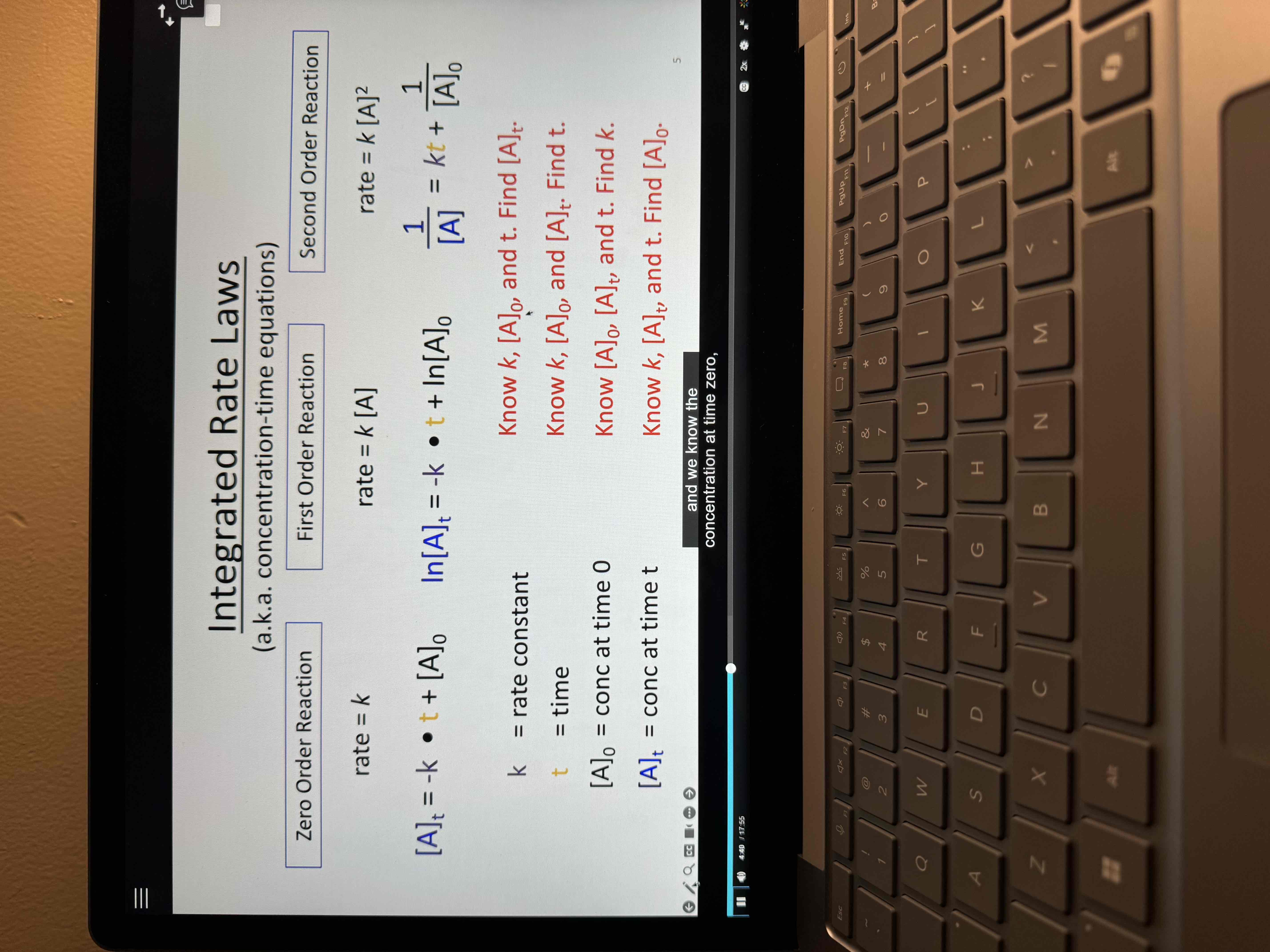
Integrated rate laws (concentration time equations)
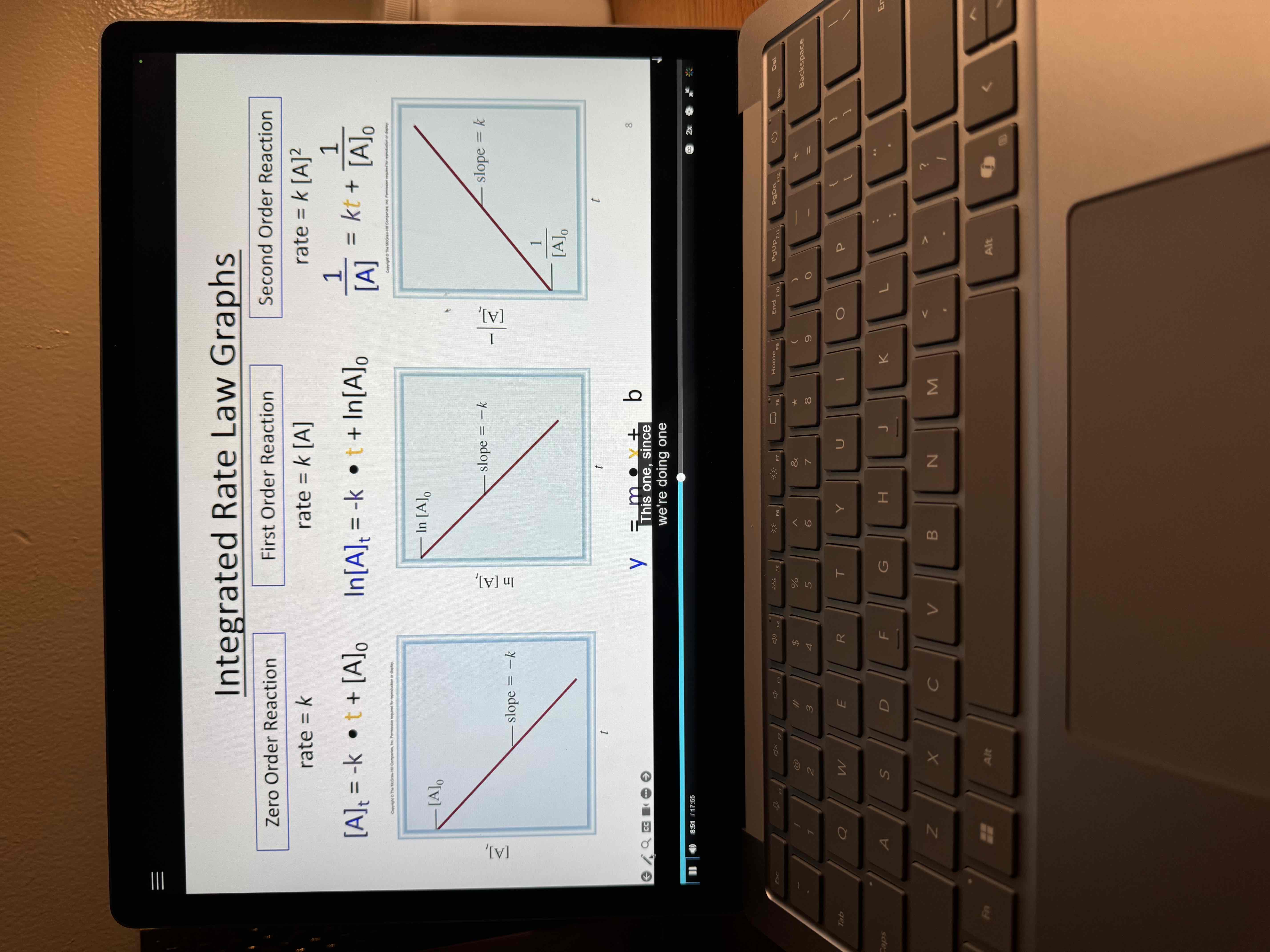
Graphs of integrated rate laws
Experimental kinetics
Set up reaction
Measure concentration change over time
Graph the result in different ways
Find the graph that generates a straight line
Determine order rate law and k
Half lives
Amount of time required for an amount of substance to be reduced by 50%
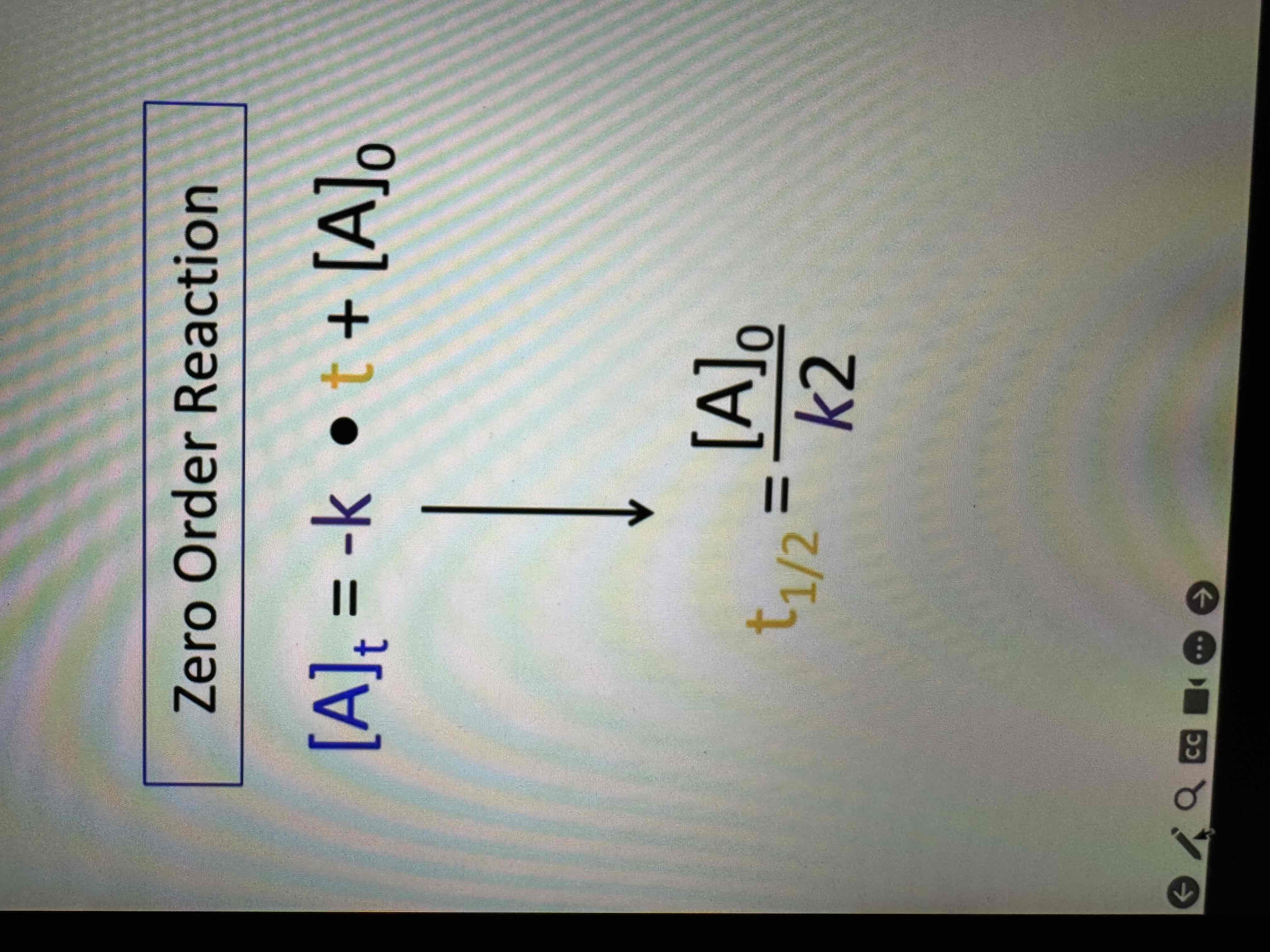
half life equation 0th order

1st order half life
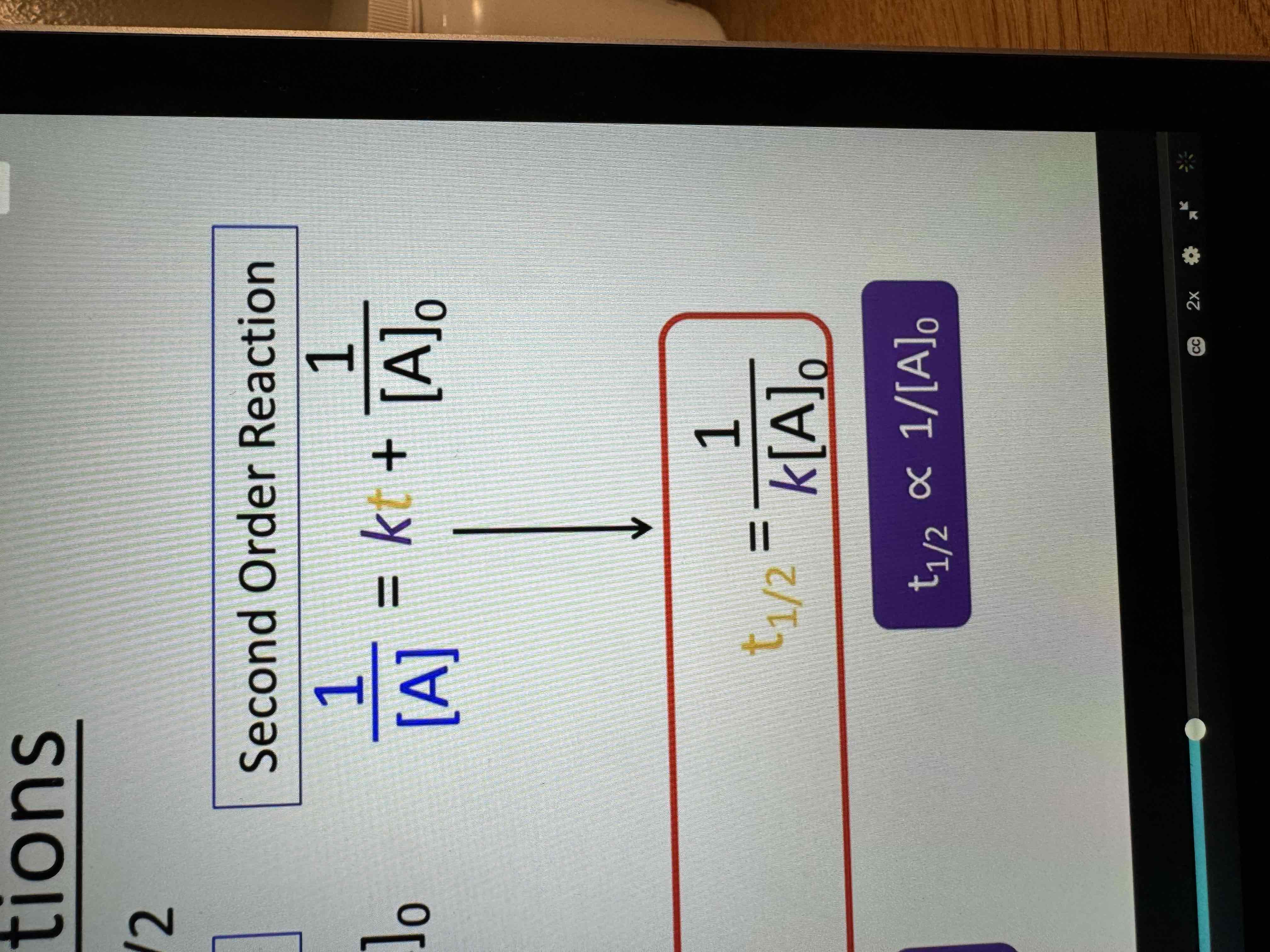
2nd order half life equation
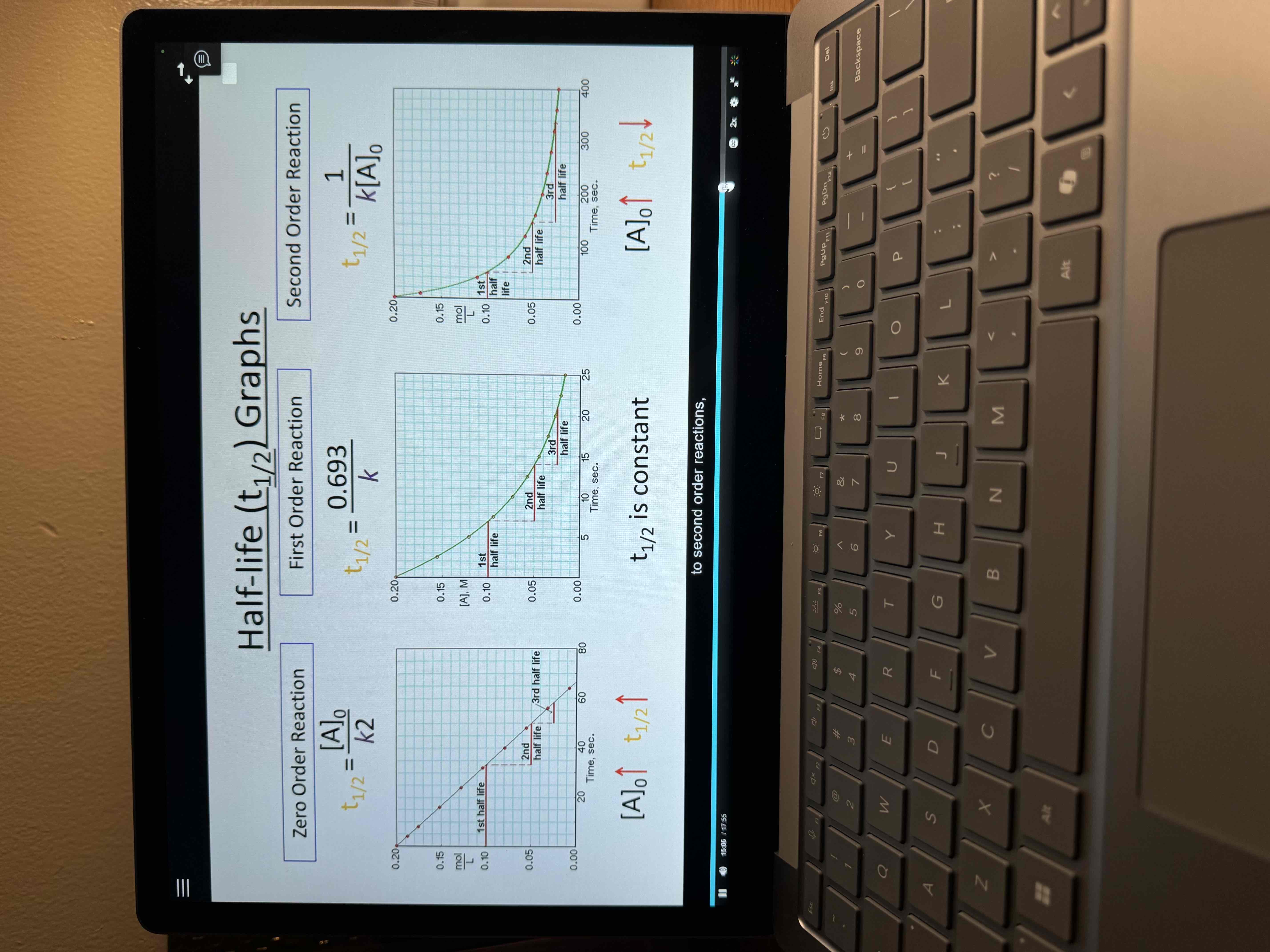
Half life graphs
Collision theory
Molecules must collide
Have enough energy to make and break bonds
Have the correct orientation to react
Rate = #collisions / time
Lower temp
Slower molecules
Less collisions
Lower rate
Higher temp
Faster molecules
More collisions
Increased rate
Concentration collision theory
Rate doubles with concentration doubling
Kinetic energy < bond energy
Bounces
no reaction
Kinetic energy > bond energy
Collide bond breaks
Form two new molecules
Reaction occurs
Activation energy
Minimum energy that must be overcome for the reaction to occur
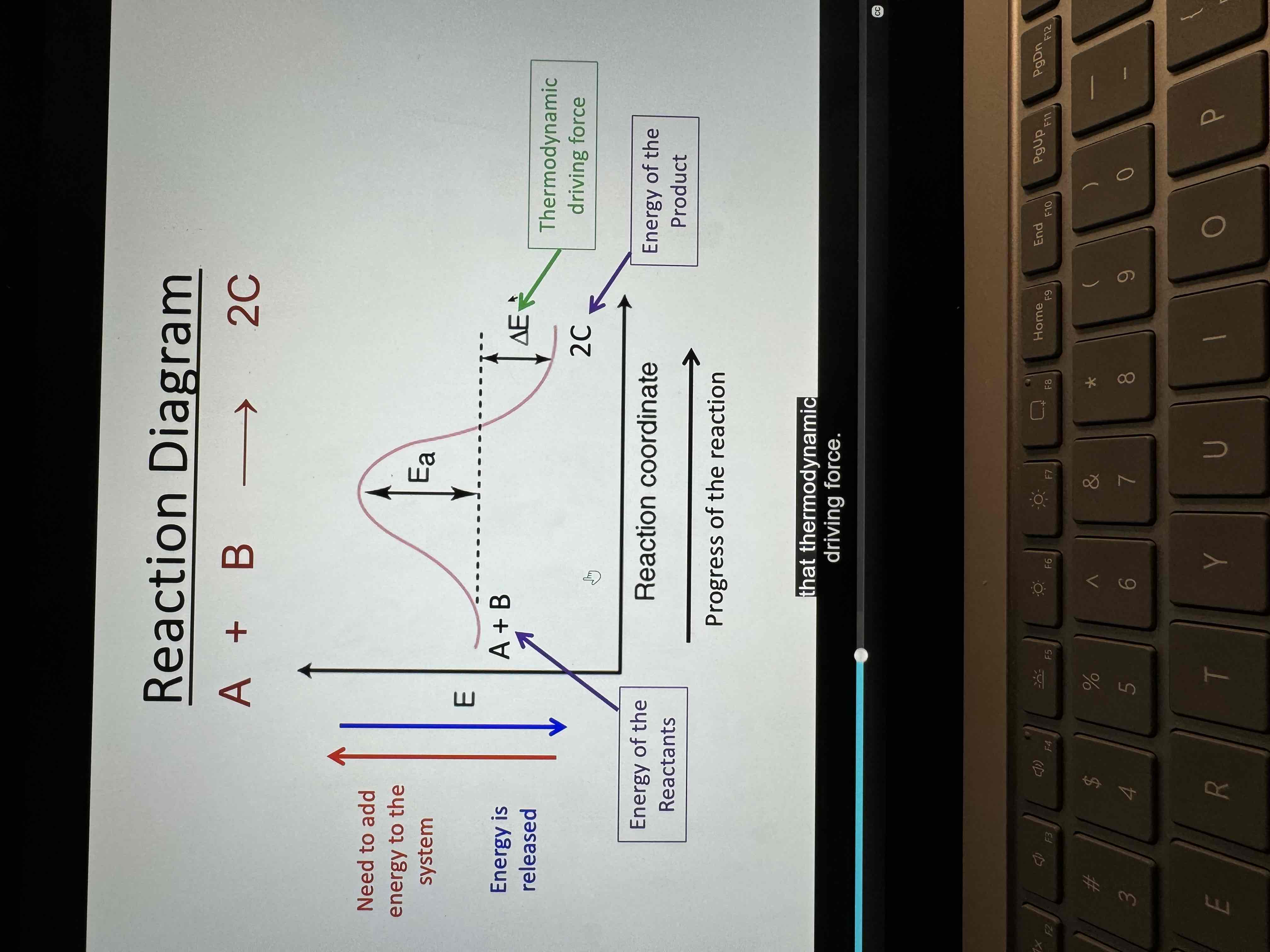
Reaction diagram
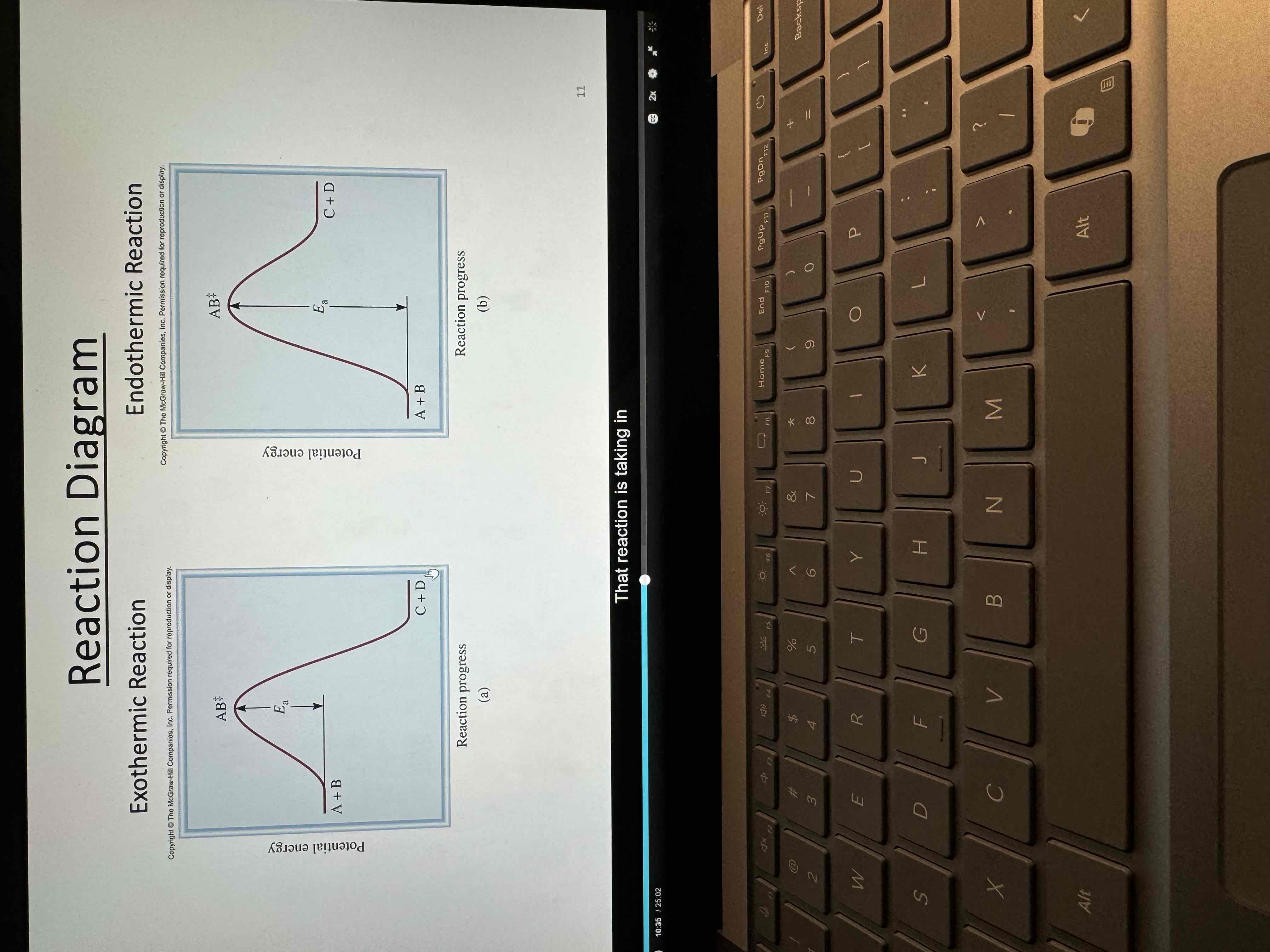
Exo vs Endo graphs
Reaction rate
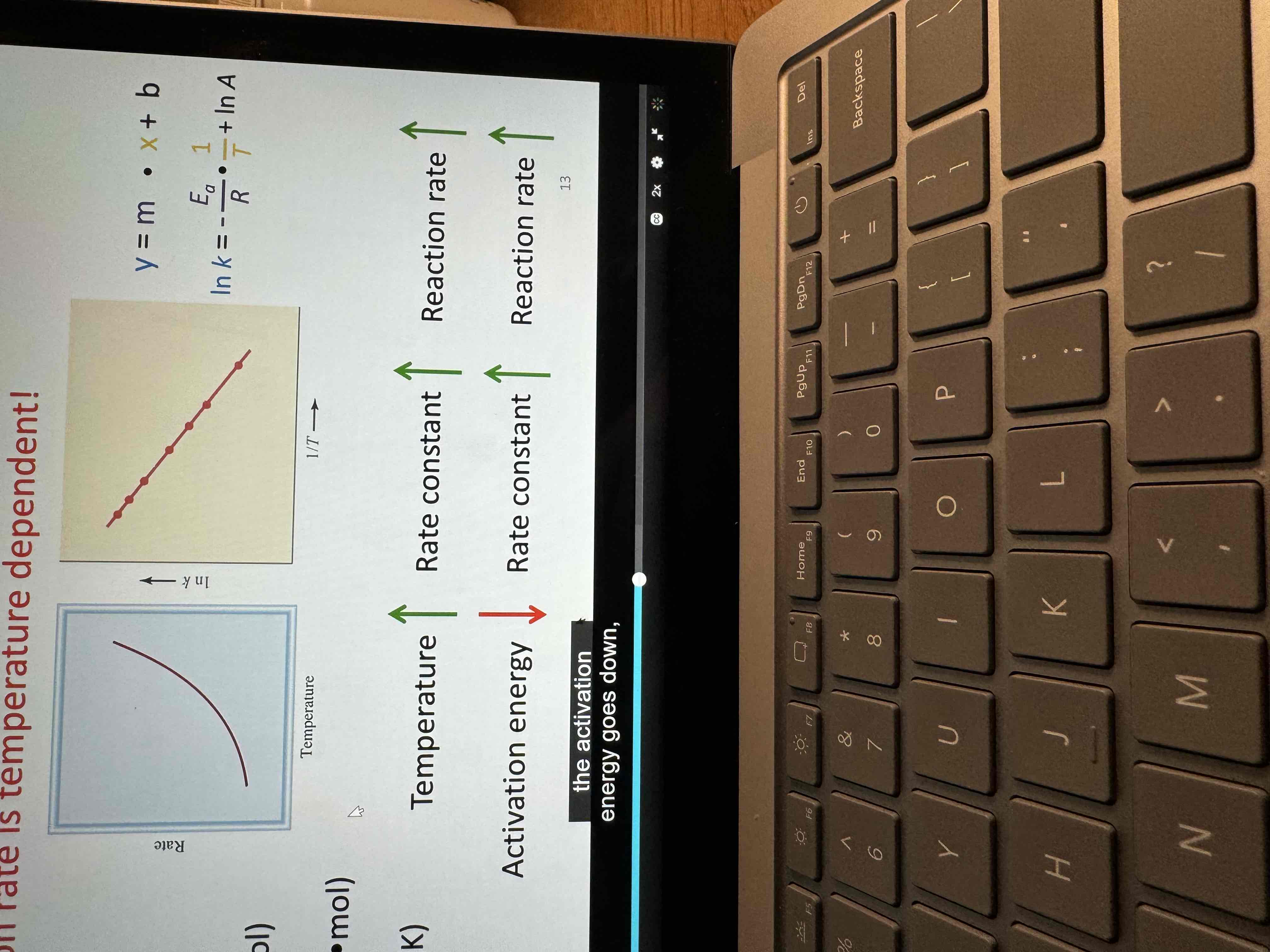
Depends on kinetic energy and temperature
Reaction rate is temperature dependent
Arrhenius equation
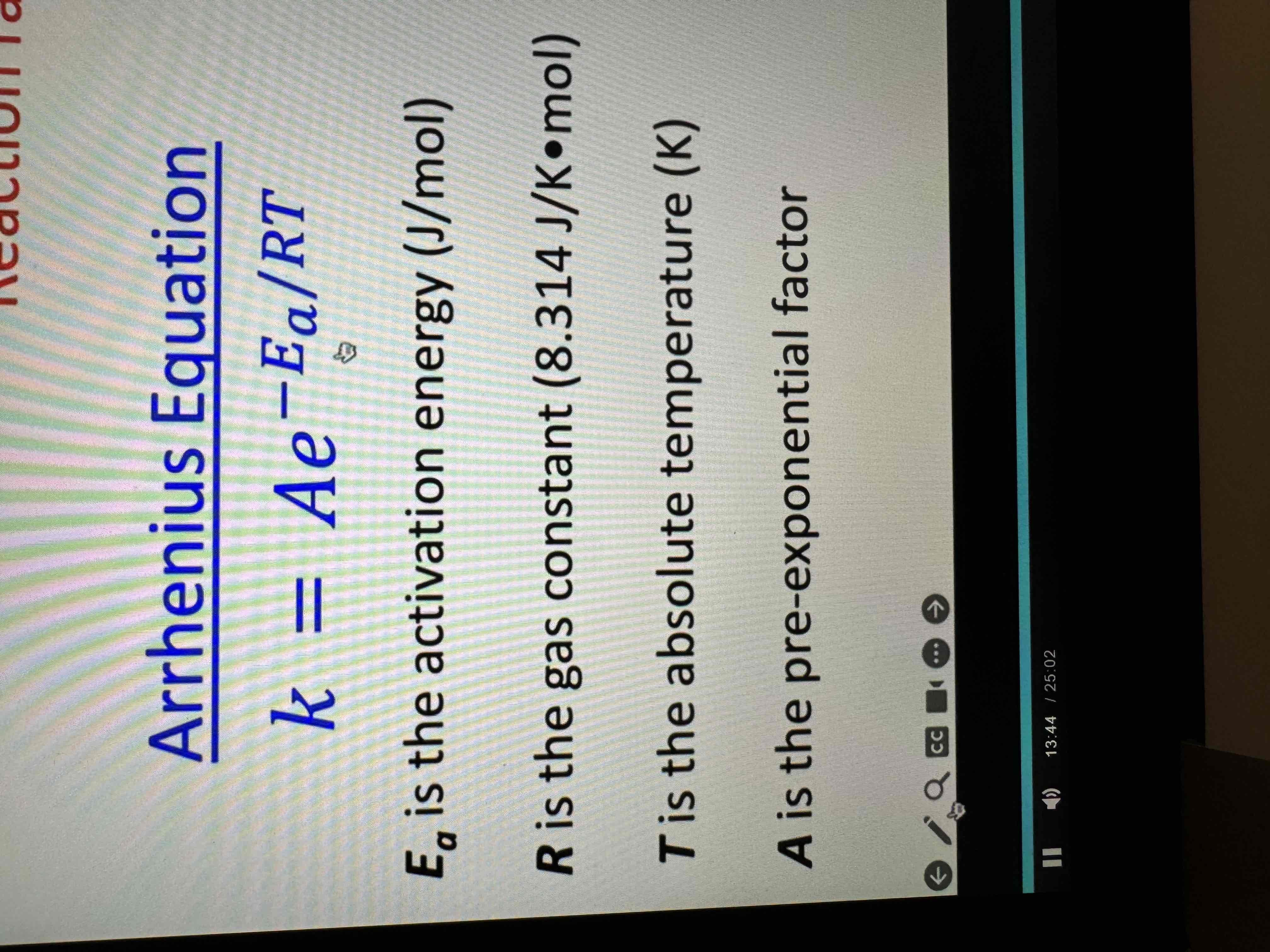
Know
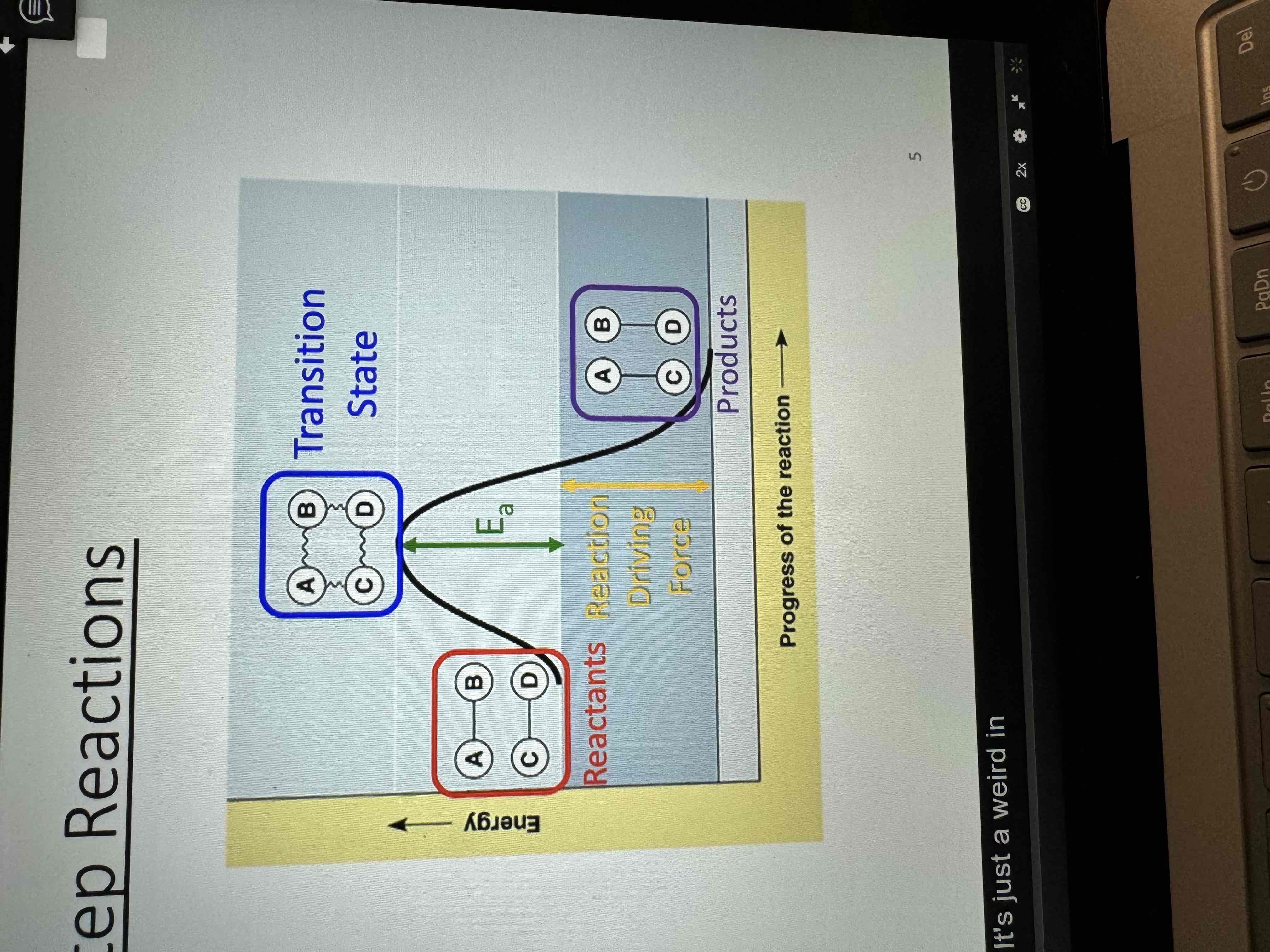
Transition state
Short-lived, high energy configuration of atoms at an energy maximum in a reaction energy diagram
Neither reactant nor product but a transition species with partial bonds
Cannot be isolated
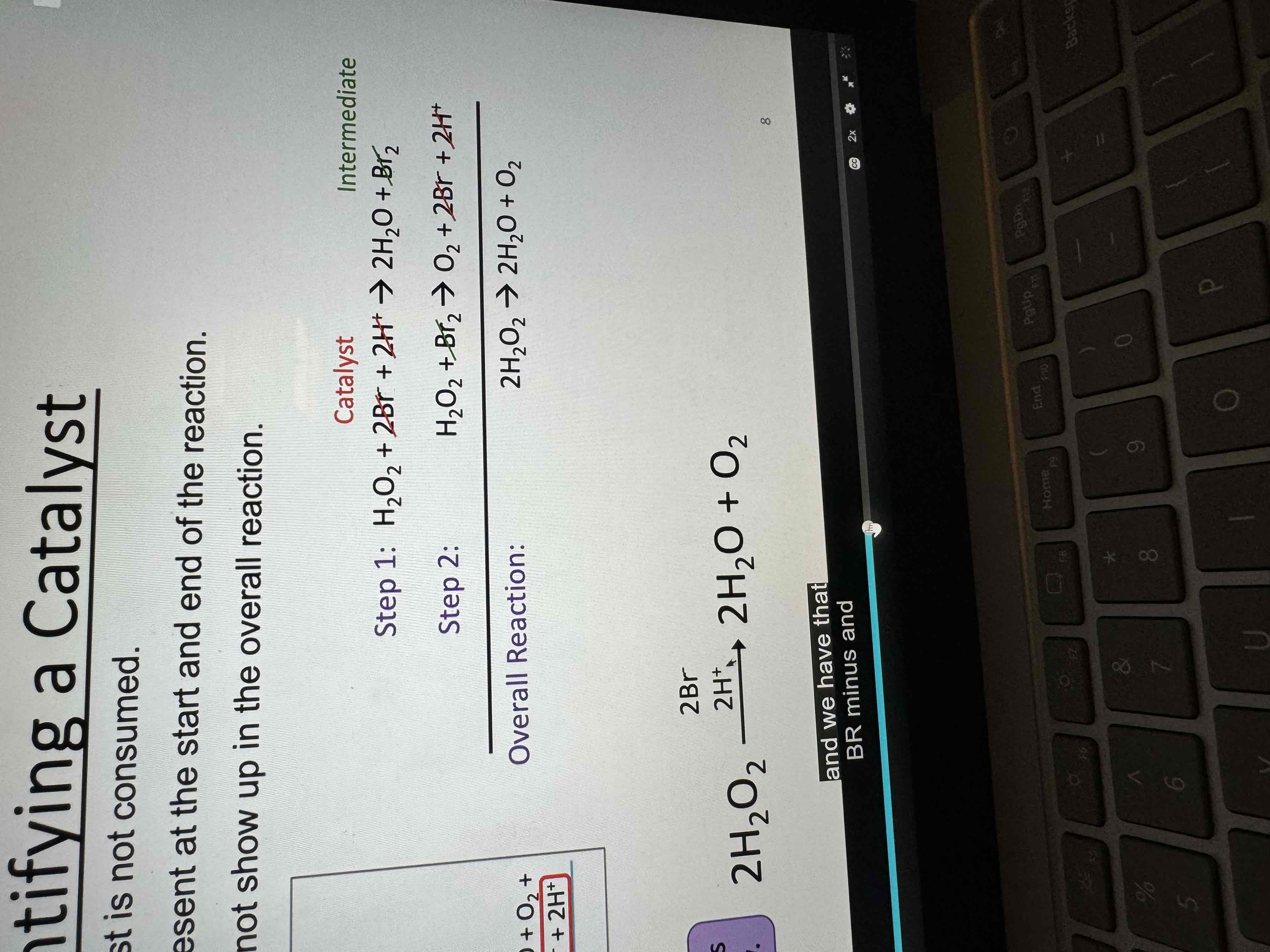
Intermediate
A species that is produced in one step and consumed in a subsequent step
Appears in the steps, but does not appear in the overall reaction
Product for one step reactant for the next
Can sometimes be isolated
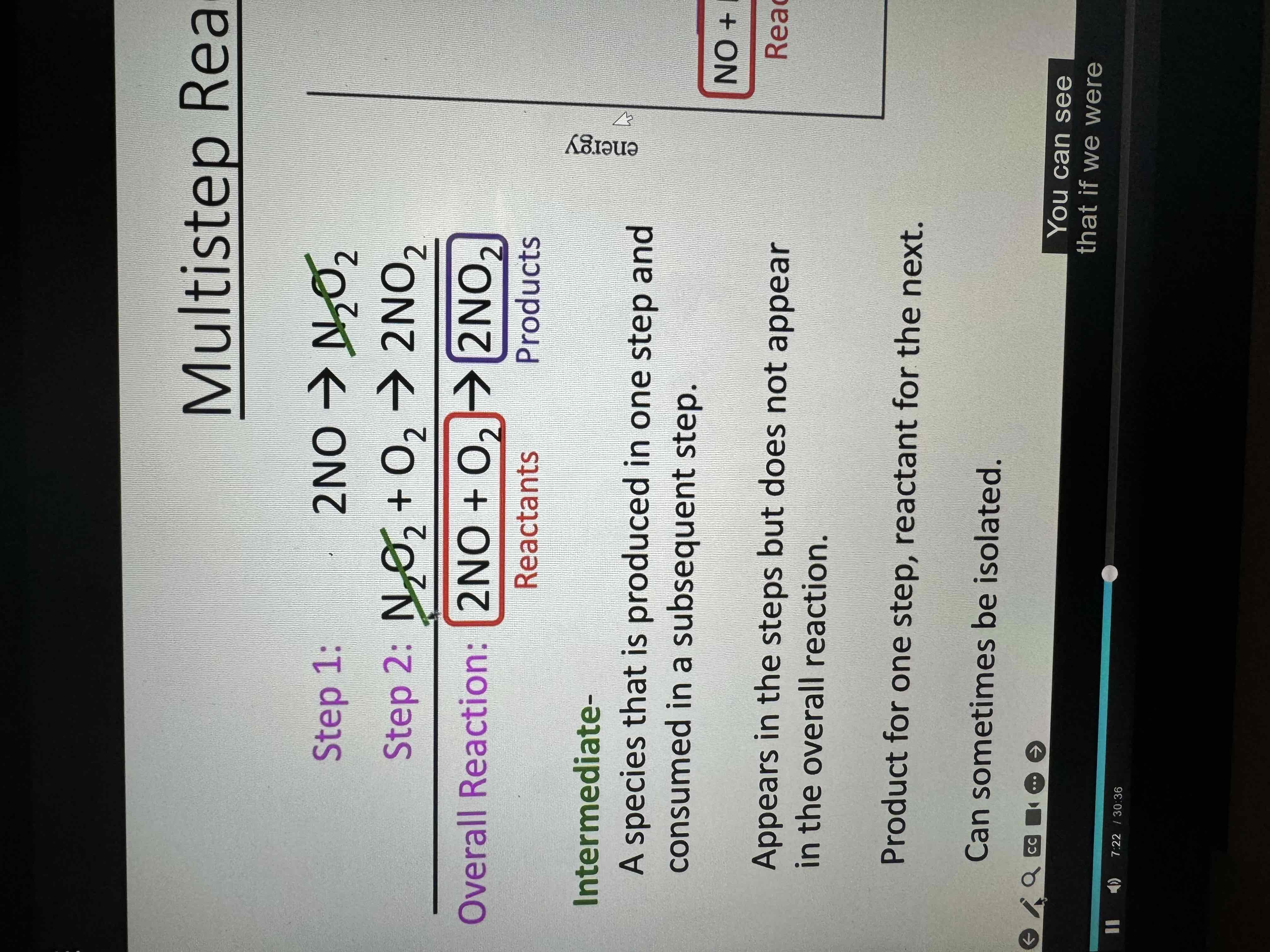
Each hill on a reaction diagram
Is each step
Elementary step / reaction
Explicit Representations of the change taking place
Reaction occurs as depicted with intermediates
Only one hill on the diagram
Molecularity
Number of molecules that come together in an elementary step
Reactants only add coefficients
Some of the stoichiometric Coefficient of the reactants
Only one hill on the reaction coordinate diagram
Rate law for elementary step
Per each elementary step
Elementary steps
Coefficients can be used for Rate coefficients !!! ONLY ELEMENTARY
Overall rate law for elementary steps
Determined experimentally by the slowest step!!
Rate limiting step (rate determining step)
The slowest step of a multi step reaction
The rate limiting step is the one with the highest activation energy
Dictates the overall rate and rate law for a multi step reaction
As Ea increases , k and rate decrease
For Arrhenius equation
Overall rate law (of a multistep reaction) can only contain
Reactants not intermediates
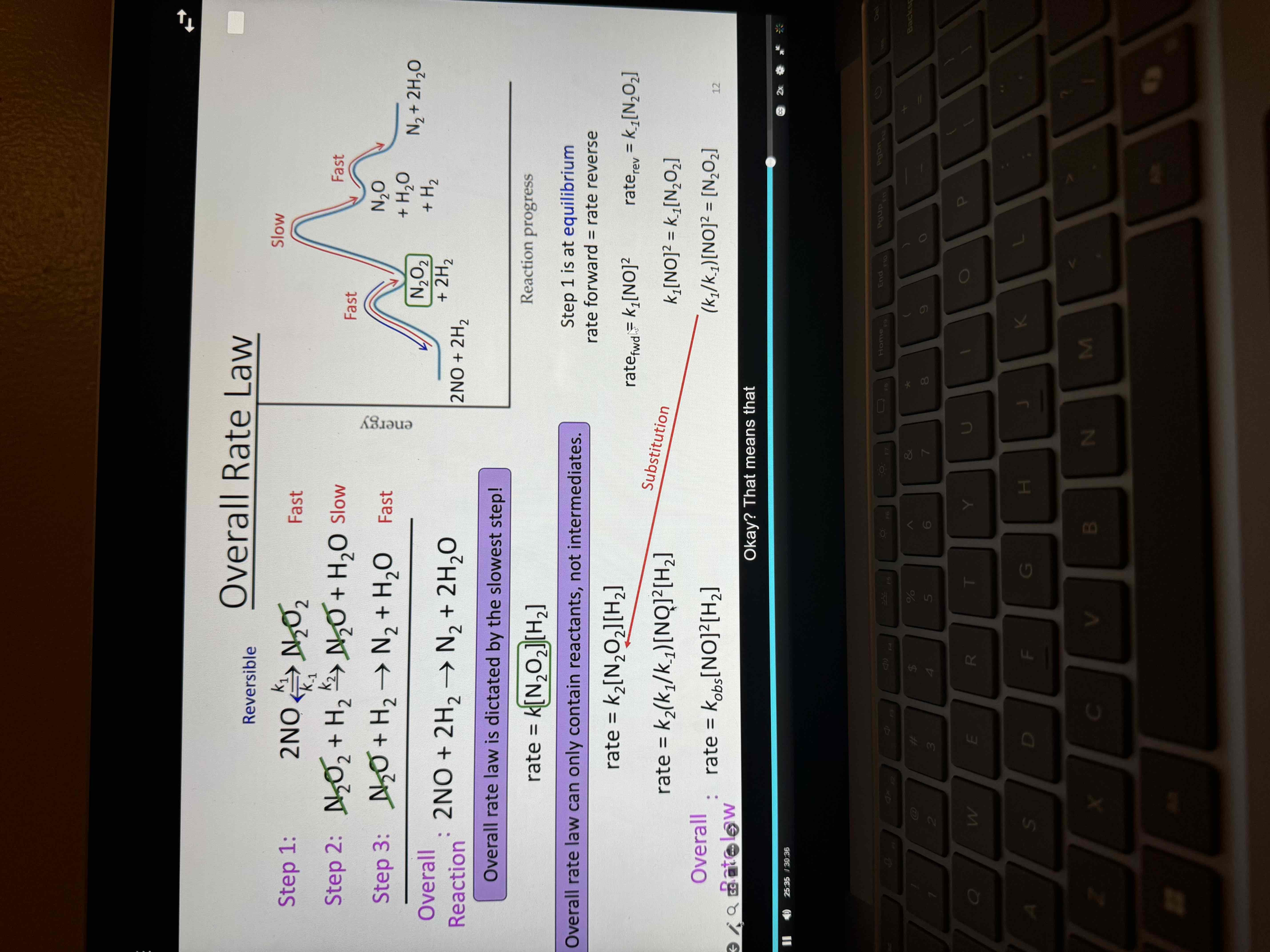
If intermediate is in an elementary rate determining (slow) step you must
find which step is At equilibrium, find the forward and reverse rates
then set them equal to each other
Replace what you get for the intermediate into the final rate law
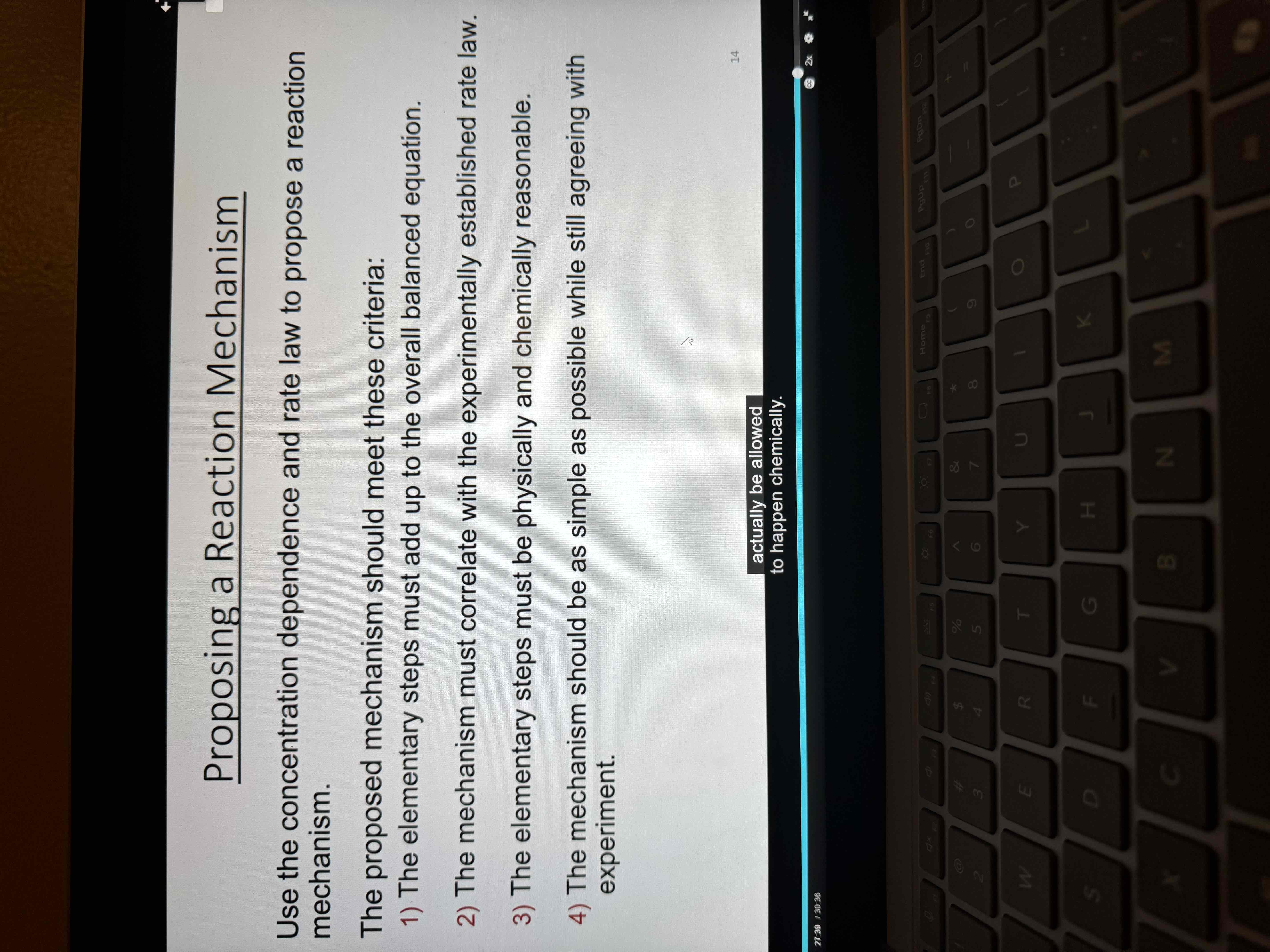
Proposing a reaction mechanism
Catalyst
A substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed
Catalysts
Takes part in the reaction
Lowers the Ea by changing the mechanism of the reaction
Is not consumed
Speeds up both the forward and reverse reactions
Does not increase the yield of product but gets the products more quickly
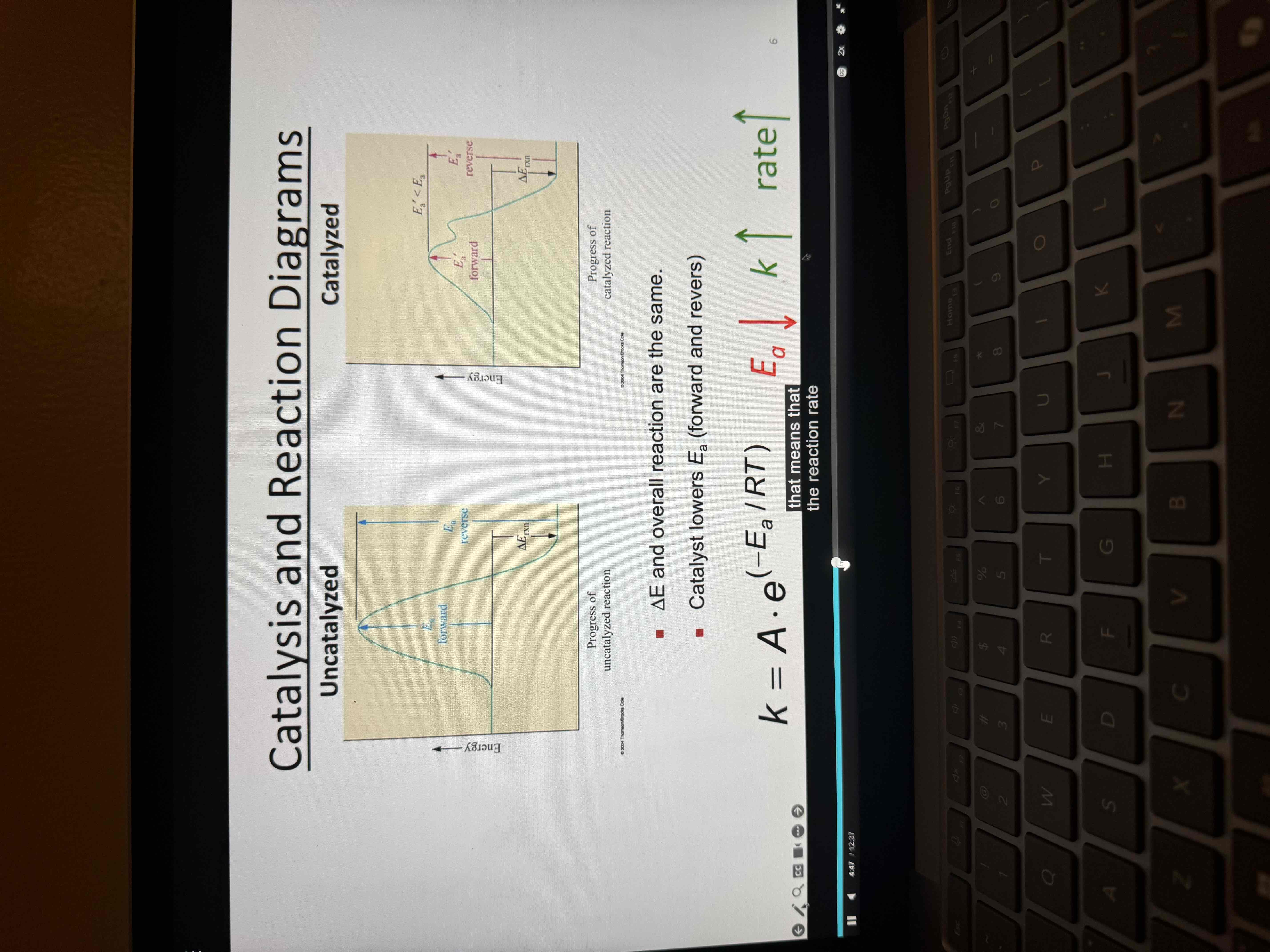
Catalyzed vs un catalyzed
How does a catalyst lower the activation energy
It changes the mechanism of the reaction
Identify a catalyst
Not actually being consumed
Not in overall reaction
Homo vs hetero catalysts
Homo - same phase as reactants
Hetero- different phase than reactants
Bio catalysts
Enzymes- biological molecules (proteins) The act as homogeneous catalyst in the Aqueous solution of cells
Ex : lock and key catalysts
Only one shape fits in active site of enzyme
Chemical equilibrium
A reversible process where the reaction rates in both directions are equal so that the system gives the appearance of having a static composition
Reaction must be
Reversible
The system must be closed
The rate of forward and reverse reactions are equal
A chemical change is occurring, but Concentrations of the reactants and products remain constant
equilibrium does not mean
The concentrations of reactants and products are equal
The molecules are unchanging
Example of equilibrium graph
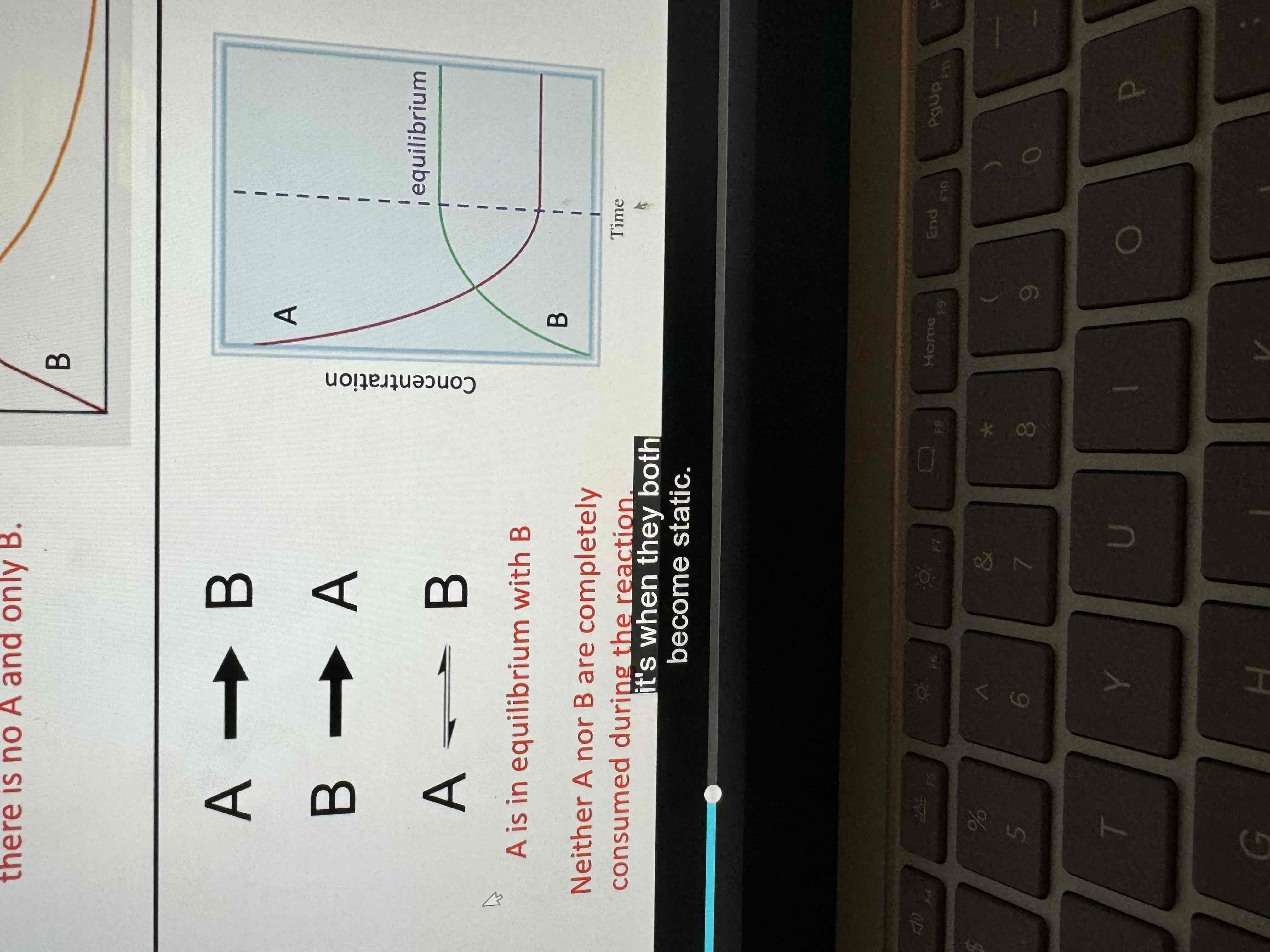
Equilibrium graphs
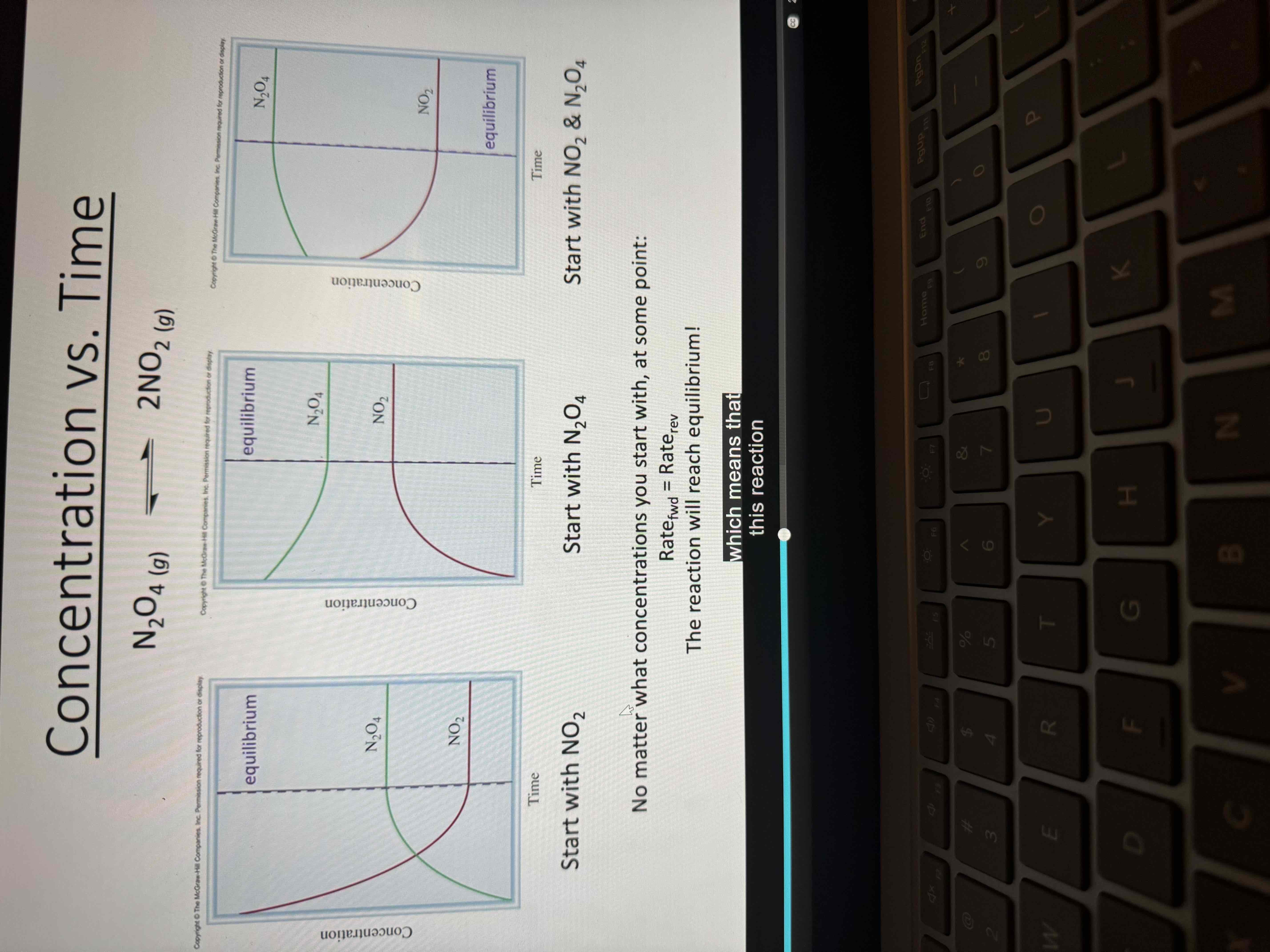
Why a system won’t see equilibrium
Not enough reactant/product
Not enough time
Not a closed system
Remember about chemical equilibrium
Equilibrium does not mean that concentrations are all equal
It does mean that the rate of Forward and reverse reactions are equal
Every equilibrium has an equilibrium constant
Equilibrium rate
Rate A→ B = Rate B → A

Equilibrium constant formula
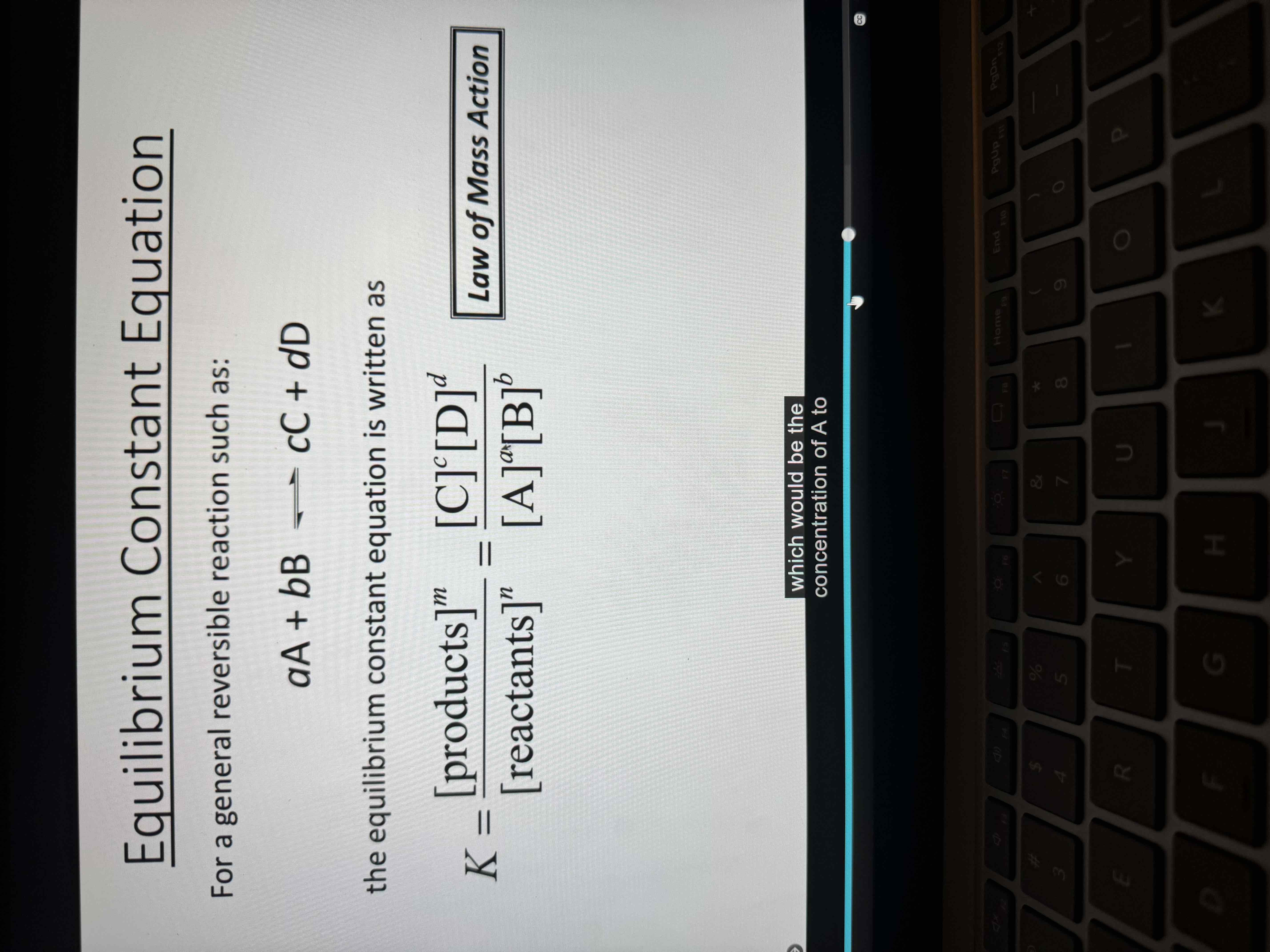
Equilibrium constant has ___ units
No
If kfwd > Krev
Mostly products
Kfwd<krev
Reactant formation favored
Homo equilibrium
All reacting species are in the same phase
Hetero equilibrium
Reacting species in different phases
Concentration of pure liquids and solids are ____ included in the expression for the equilibrium constant
never
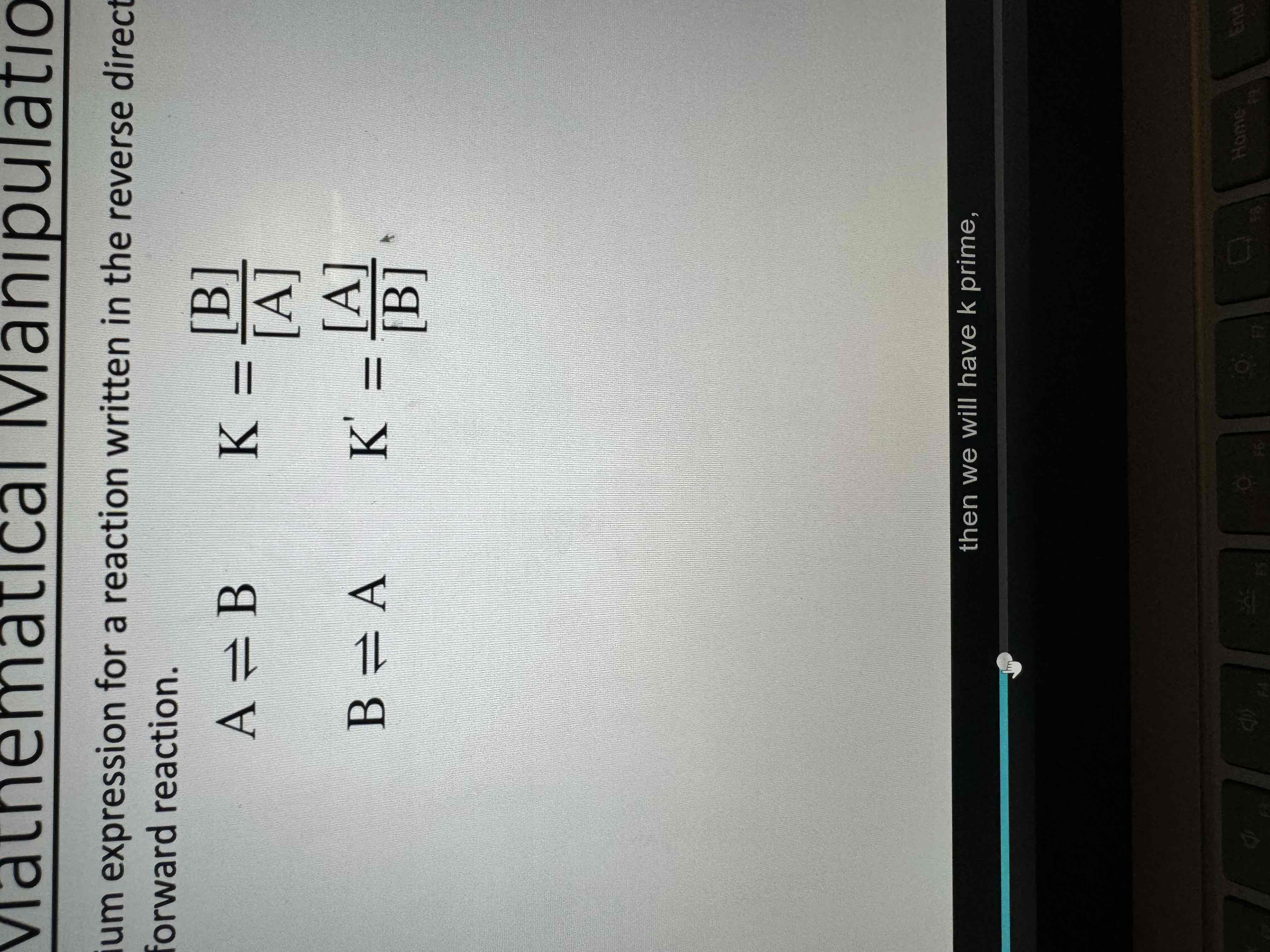
The equilibrium expression for a reaction written in the reverse direction is the
Reciprocal of the one for the Forward reaction
If the coefficients in a balanced equation are multiplied by a factor of x, the equilibrium expression is raised to the xth power

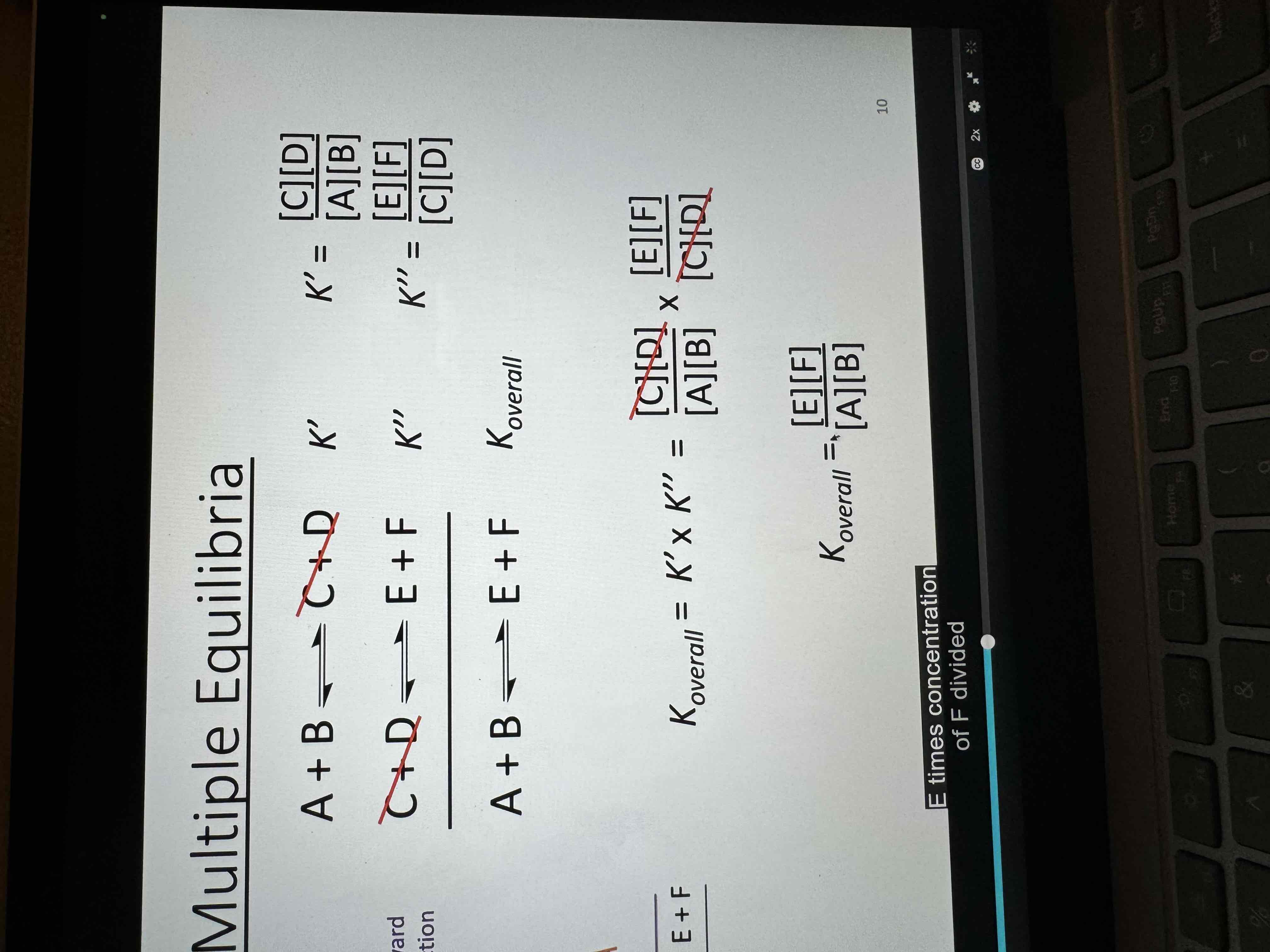
If two or more reactions are added to give another the equilibrium constant for the overall reaction is
the product of the equilibrium constants of the equations added
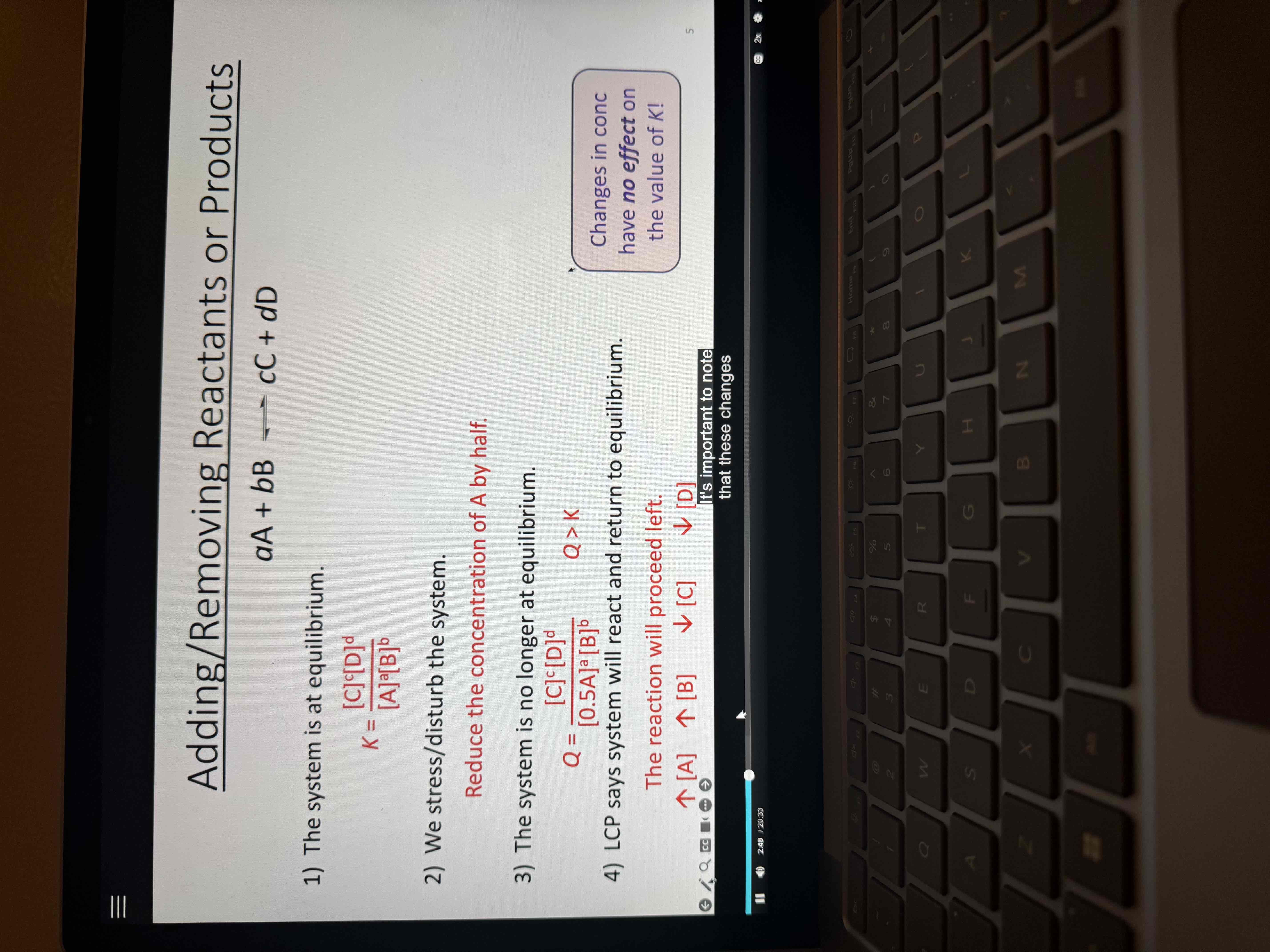
Reaction quotient (Q)
Measures the relative amounts of products and reactants present during a reaction at a particular point in time
Reaction quotient
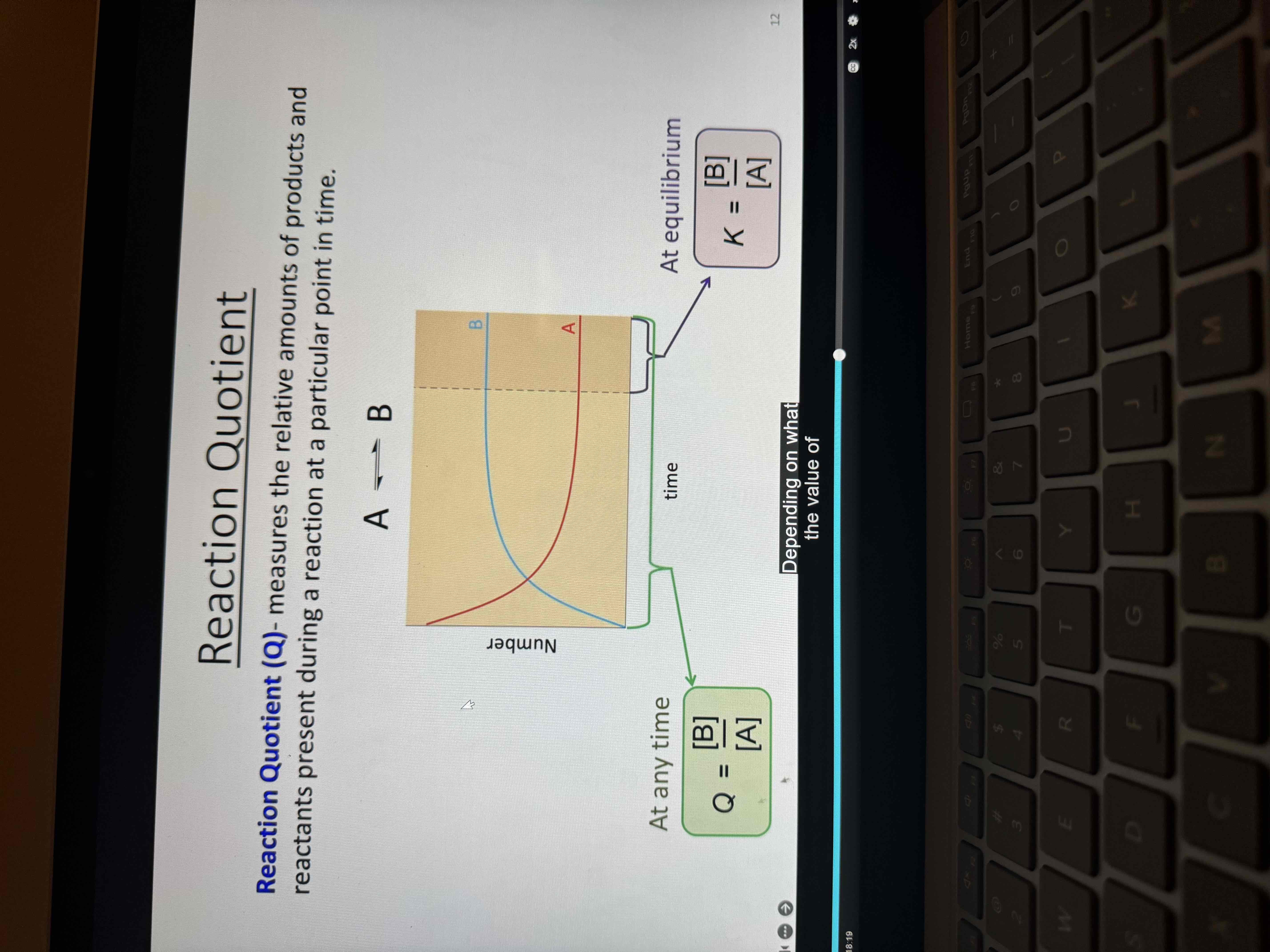
K is constant at a given temperature Q..
Changes depending on the reaction progression
Q vs K
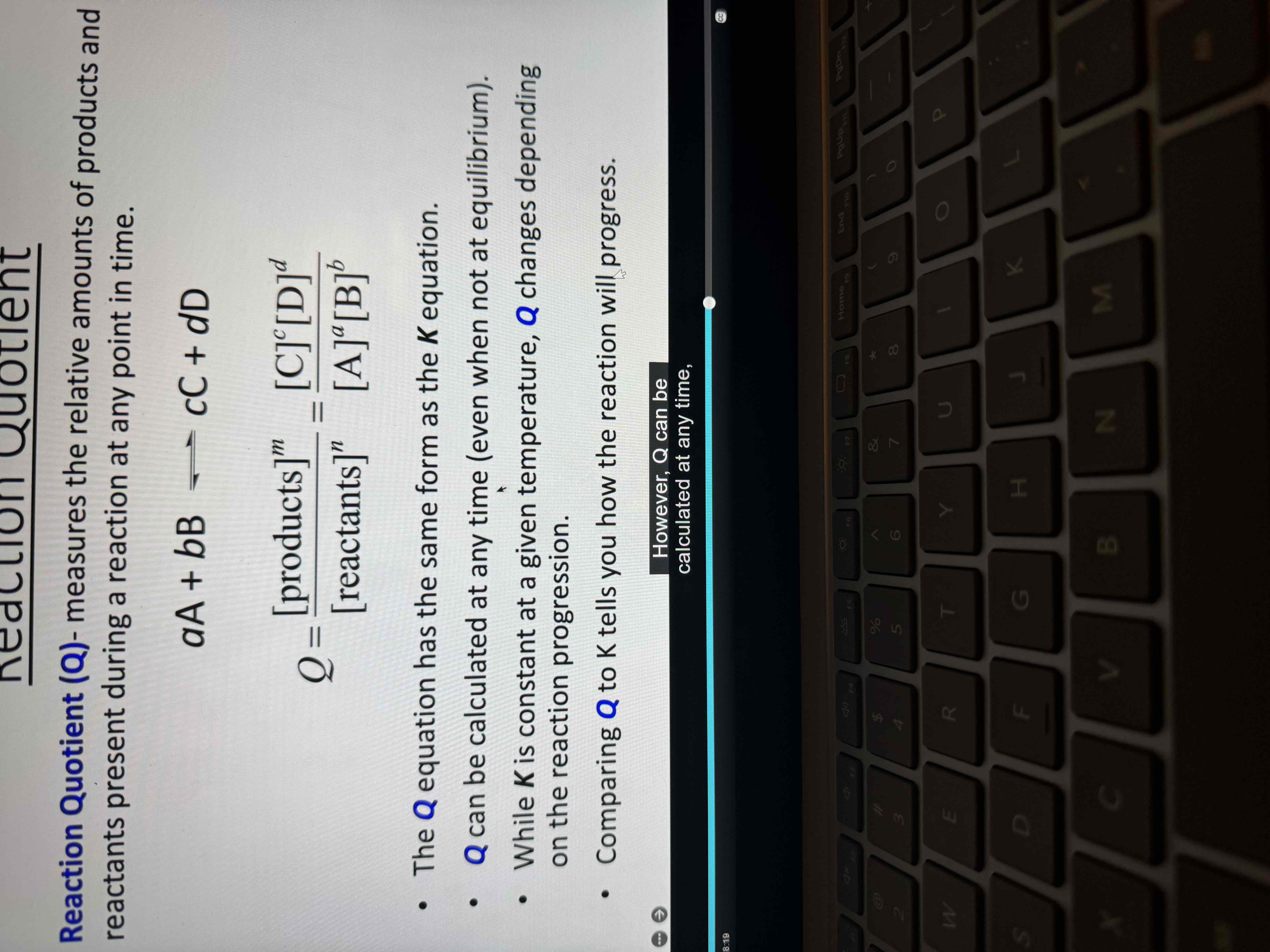

Q VS K
Q= K
Equilibrium
Q<K
Too many reactants Not enough products
Reaction proceeds to the right
Generate more Products Consume reactants
Q> K
Too many products, not enough reactants
The reaction proceeds to the left
Will generate more reactants, consume products
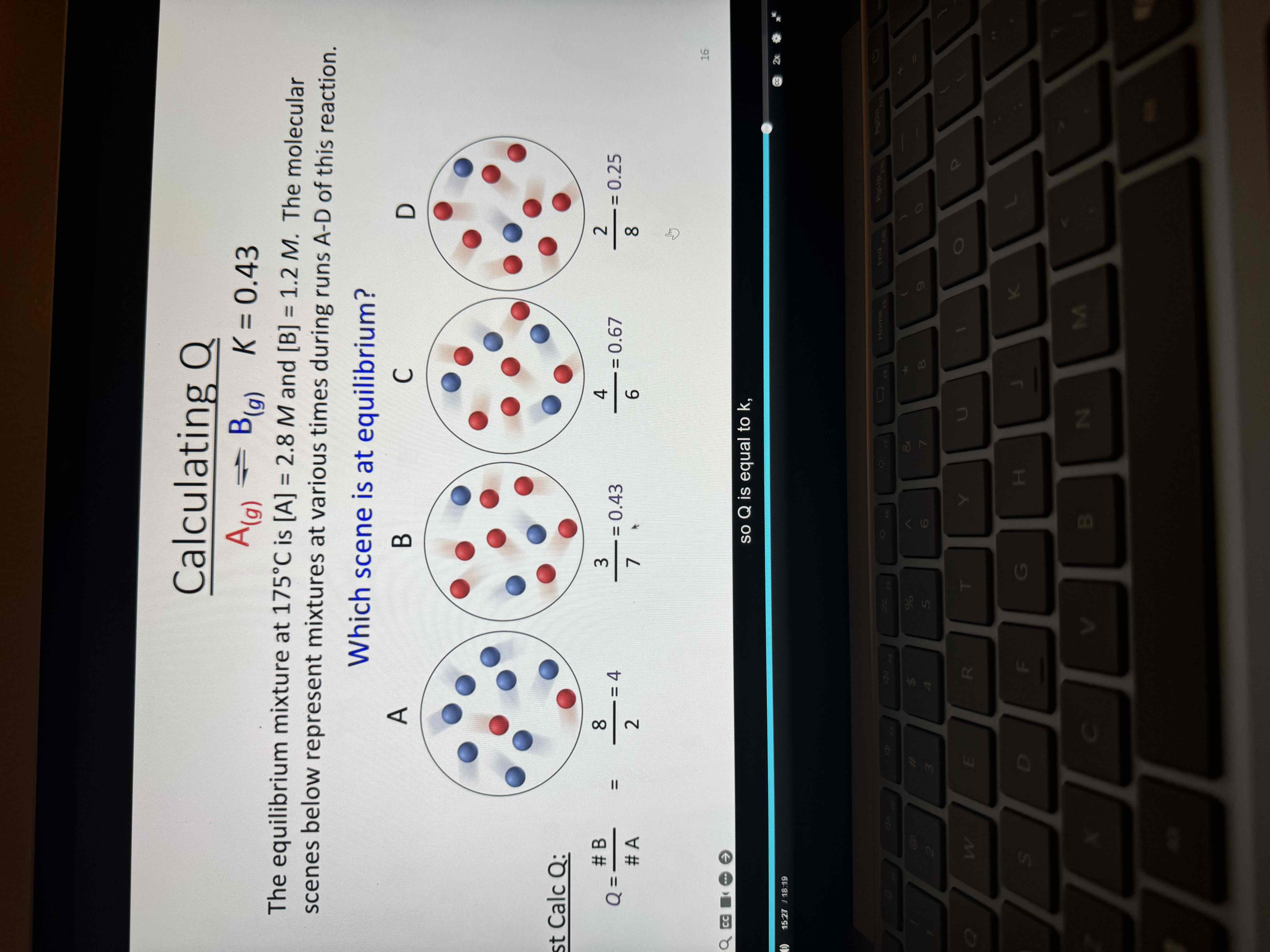
Solving for Q
First find K
K = B/ A
1.2/2.8 = .43
Find Q
Count b and a to do so
Find which one matches K
Answer is B
Le chateliers principle
When I chemical system at equilibrium is disturbed, it returns to equilibrium by undergoing net reaction that reduces the effect of the disturbance
Le chateliers principle In action.