CSCI 2100 Final Exam
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
What is the Shannon-Weaver Model?
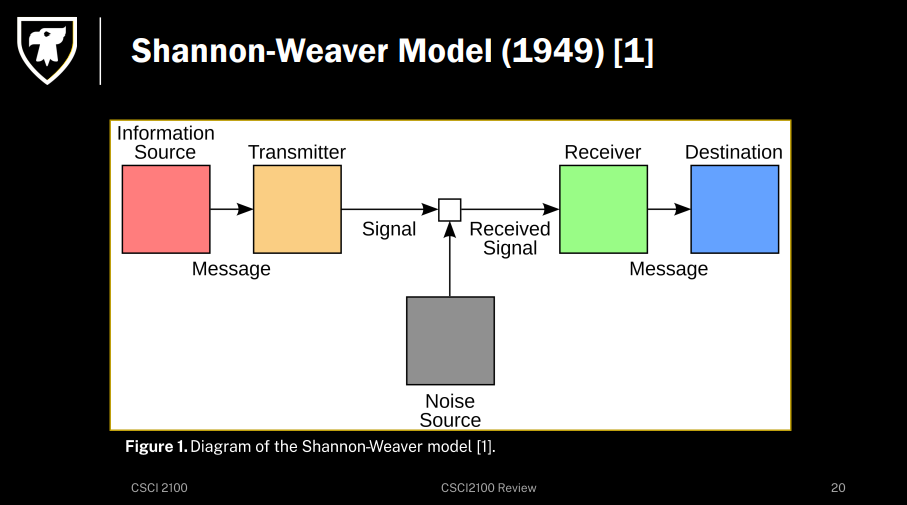
What is a Sender, Receiver and Noise?
Sender: Speaker/writer
Receiver: Audience
Noise: Anything interfering with the message successfully moving from sender to receiver
What are the 7 Cs of Communication
For effective Business Communication
Concise (it must not contain unnecessary information)
Complete (it must contain all relevant information)
Courteous (it must be polite and professional)
Considerate (it must meet the needs of your audience)
Clear (it must be understandable by your audience)
Correct (it must be free of errors)
Concrete (it must be specific and contain valuable details)
What is the Document Development Life Cycle (DDLC)?
Stage 1. Analysis and planning (who/what/why)
Stage 2. Design (how does this need to be presented?)
Stage 3. Content Development (what info do we need to present? what does our audience need?)
Stage 4. Proofreading and Editing (does it accomplish its goals? any errors?)
Stage 5. Publishing (share your communications)
Stage 6. Maintenance* (when will it be reviewed?)
What are some networking tips?
Preregister
Volunteer
Bring a friend
Know your goal
Arrive early
Look at the nametags
Scan the room
Be open
Line up for food
Focus on others
Resume Writing
1-2 pages, well-spaced easy to read
clear sections/layout
titles, organization names and dates
reverse chronological order
consistent formatting
bullet points with action verbs
clear results
What is an Applicant Tracking System (ATS)?
automatic application processing, reduces applications
offer/rejection processes → auto-rejection tools
strips formatting
Why automation?
hundreds of applicants
dozens of positions
limited time
bypass the ATS with referrals provided by current employees
Cover Letter Writing
1 page
correctly addressed
clearly stated role and company
use of examples
connects experience to job requirements
formal letter format
correct information and contact
What are the different Interview Question Types?
about you:
first question, break the ice, meet candidate, build trust
behavioural:
expects a clear examples, most common, based on experience
“tell us about a time when you worked in a team” (STAR/PAR method)
hypothetical:
often linked to real challenge, shows your thought process
“a team member is not completing their work on time. how would you deal with that?”
technical:
knowledge/skill based, chance to show your comprehension
“please explain how computer allocates memory”
brainteasers/tricks/problem solving:
rare, generally poor practice
“how many basketballs would fit in this room?”
How are interviews run?
Structured:
prepared questions, clear processes, managed interactions
documentation required, often a rubric/marking scheme
pros:
more objectivity/less bias
clear connection between jobs and questions
legally defensible
cons:
limited conversation, relies on preparation, limited recruiter discretion
Unstructured:
general conversation, limited pre-planned questions, evaluated holistically, ranked by overall perception
pros:
more opportunity to meet the candidate
less formal, candidate may be more comfortable
may highlight unexpected skills
cons:
bias
inconsistency/lack of connection to the role
legal risk
What works well when virtual interviewing?
clear, audible, strong internet, no background noise
landscape orientation
eye-level
some gestures are ok
Explain Google’s team effectiveness research
Impact (least important)
Meaning
Structure and clarity
Dependability
Psychological safety (most important)
Explain Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
Self-Actualization
Esteem
Social
Safety
Physiological
Explain McCelland Acquired-Needs Theory
Achievement
Affiliation
Power
Explain Tuckman stages of group development
Forming > Storming > Norming > Performing > Adjourning
Explain Thomas-Kilmann Conflict Mode
Competing
Avoiding
Compromising
Accommodating
Collaborating
Explain challenges with conflict
Isolating
Hijacking
Hitchhiking
Explain how to evaluate sources
who wrote this?
why did they write this?
what do they have to gain?
are they presenting facts or opionions?
Factual, verifiable information is better than opinions
What doesn’t need to be cited?
your own experiences
your own ideas
your own images
“common knowledge” ie information that the average educated reader would accept as reliable without having to look up
if you’re unsure, cite
How to use IEEE Format
This sentence is an idea from Paper A [1].
“This quote comes from Paper A” [1, p. 23].
Reference list:
in numerical order
first reference = first citation in document
clear indentation between number and reference
must be the correct reference type
URLs:
remove tracking links, provide the full URL

Explain how to summarize
Writing the main ideas in your own words
must be cited
must accurately represent the source
What is a fact? What is Ad-speak?
Fact:
A piece of information presented as having objective reality.
VERIFIABLE
Ad-speak:
The sort of language used in advertisements, typified by bold claims and optimistic encouragement.
“This product is unbelievable good”
vagueness, partial information, hyperbole, emotion
What are the types of misleading information?
Misinformation:
false information that is not intended to cause harm
Disinformation:
false information that is intended to manipulate, cause damage, or guide people, organisations, and countries in the wrong direction
Malinformation:
information that stems from the truth but is often exaggerated in a way that misleads and causes potential harmm.
What is lateral reading?
Lateral reading is the act of evaluating the credibility of a source by comparing it with other sources. SIFT is a way to do lateral reading.
What is the SIFT method?
The SIFT method is a four-step strategy for evaluating the credibility of online information and sources.
Stop
what did the article make you feel?
does it make sense?
who is the author?
Investigate
who is the publisher?
who is the author?
what are their interests?
Find better coverage
is this reported elsewhere?
is it listed on fact checking sites?
are there better sources?
Trace claims, quotes and media
was it taken out of context?
is it accurate to the original?
has it been reframed?
What is the debunking approach?
Exposing and correcting misinformation by presenting factual evidence and clear explanations.

Explain Ethical AI Use/Concerns with AI
Concerns with AI
environmental cost
bias in training data
missing context
unknown data use
leaking company data
harmful outputs
liabilities regulatory risks
What is Technical English? Jargon?
Goal of “Technical English”
writing that is simple and universally understood
ensures message is received correctly and efficiently by the audience
Jargon:
the technical terminology or characteristic idiom of a special activity or group
aka, important within a group and meaningless outside of a group
use short, simple words
remove unneccesary words
What is active voice? Passive voice?
Active voice:
Subject → verb → object
I kicked the ball
Susan rebooted the server
Passive voice:
acceptable if you don’t care about the subject
Object → verb → subject
The server was rebooted by Susan
Formal vs Informal report
HaliHali Halibut report was informal.
Formal reports have:
letter of transmittal
title page
summary
table of contents
list of tables/figures
introduction
discussion
conclusions
reccomendations
glossary
references
appendices
What are the different types or reports?
Documentation:
creating a permanent record
often required for compliance
justify future actions
Progress:
creating a permanent record
present facts and status
identifies future work
Reccomendation:
creating a permanent record
present facts about options
justify a future decision
Explain Report Structure (A3)
General formatting:
single space text, non-heading font size between 10-12pt
consistent font, no paragraph indentation
left aligned, consistency
Executive Summary
summarizes the rest of the report
the last section written
no new information provided
Context (A2)
what was happening that caused the report to be written?
who is this report for? what are you comparing? how will they be compared ** (the three criteria: ease of use, security, integration)
Details (A2)
research
Comparison Table
Conclusion
comparison of the products against the criteria
should be objective
Reccomendations
your informed suggestion of the best product
can contain opinions
Headings/Lists/Illustrations
Headings
clear, logical, identifiable
seperate content
Lists
we use lists to clarify and emphasize information
must always start with a lead-in.
Ex:
The following products will be reviewed: ← lead-in
Product A
Product B
Product C
Numbered lists → only when order is important
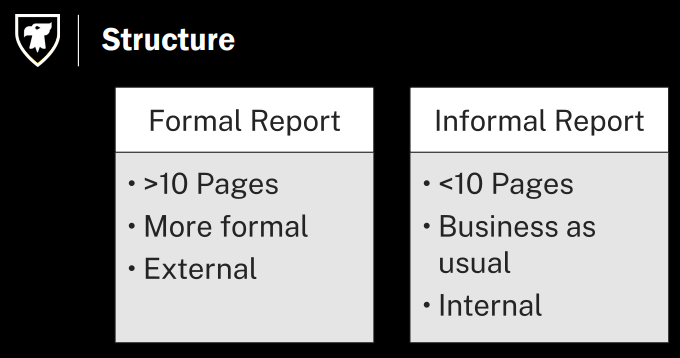
Illustrations
Tables
rows & columns
usually contains numbers
captions go on top of tables
Table 1. Number of students and chairs per tutorial in CSCI2100 Winter 2023
Figures
any visual element except tables
captions go below figures
refer to the illustration by number (e.g. see Figure 9)
use bold for figure/table numbers
What are instructions?
Introduction
what is the context? who should follow these? what is required?
Step-by-Step Instructions
step-by-step, action focused, chronological
use the reader to complete a task
Conclusion Troubleshooting
if readers could make a common mistake, add troubleshooting
E.g. is the connection light is yellow, unplug and reattach the ethernet cable
Notes = helpful hints
Caution = prevent damage or instructions failing
Warnings = harm to the user
Danger = likely harm or death
What is CODS?
Basic principles of simplification
C - Comparison (X is similar to Y)
O - Outcome (what do i need you to understand)
D - Demonstration (show me!)
S - Stepping Stones (use what they already know)
How to have a professional tone
Professional tone
be polite and clear
ensure you are asking not demanding
address people appropriately
if in doubt → be more formal
Professional does not mean wordy
clear simple sentences, short concise paragraphs, only relevant information
what are the CRAP principles? What makes good/bad slides?
C - Contrast (helps it stand out)
R - Repetition (consistency)
A - Alignment (quicker to read)
P - Proximity (clear relationship, keep like things next to eachother)
Slides should:
enhance your presentation
provide visual highlights
guide your audience
if using text make it big (32pt +)
acknowledge sources
Slides should not:
distract the audience
be full of text
cover everything
How might communicators cause harm?
Poor communication can cause real-world harm.
Unethical behaviour hurts everyone
reduced trust in you/your company/in the profession
Understand your limitations
be transparent, know what you don’t know, do further research
What are the Ethics in Technical Communication?
Don’t mislead
don’t cause your reader to believe something false (lying, misrepresentation, plagiarism)
Don’t manipulate
don’t peruade people to do something that is against their needs (provide alternatives, focus on your audience)
Don’t stereotype
watch for biases, watch for gender assumptions (singular they, etc)
More info about the HaliHali Halibut report
What did your audience need?
simple, non-technical information
focused on their criteria
comparison of options
professional and formal tone
report:
simple, short sentences/paragraphs
active voice
clear layout/headings
easy to skim
presentation:
cohesive and consistent
free of errors
trustworthy presentation, builds trust
does the information match the visual? check facts before communicating.