Chap. 1 What is Economics?
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ECON
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What is economics?
The study of how humans make decisions in the face of scarcity.
What is scarcity?
When human wants for goods, services, and resources exceed what is available.
What is specialization?
Focusing on a particular small job or task so workers concentrate on parts of the production process where they have an advantage.
What is comparative advantage?
When someone can produce a good or perform a task at a lower opportunity cost than others; people differ in skills and are relatively better at some jobs.
What is a core competency?
A business’s main strength or focus — often when a business concentrates on one or a few products.
What are economies of scale?
For many goods, as production increases, the average cost of producing each unit declines.
What is microeconomics?
The study of actions of individual agents in the economy, such as households, workers, and businesses.
What is macroeconomics?
The study of the economy as a whole — issues like total production (growth), unemployment, inflation, government deficits, and trade (exports and imports).
What is monetary policy?
Policies that affect bank lending, interest rates, and financial capital markets.
What is fiscal policy?
Government decisions about spending and taxes.
What is an economic model?
A simplified representation of reality used to explain or predict economic behavior.
What is a theory?
A simplified representation of how two or more variables interact.
Who was John Maynard Keynes?
A British economist (1883–1946) who argued economics is also a way of thinking about choices and the role of aggregate demand.
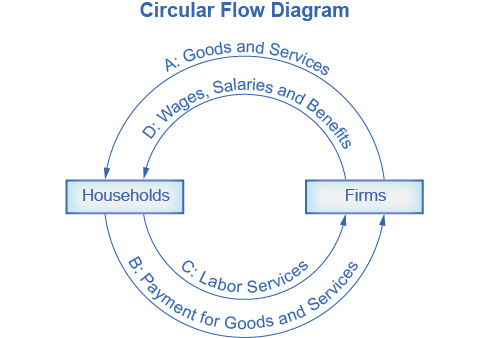
What does the circular flow diagram show?
It pictures the economy as households and firms interacting in the goods and services market and the labor market, with flows of goods/services, labor, and payments between them.
What is the goods and services market?
The market in which firms sell goods and services and households buy them.
What is the labor market?
The market in which households supply (sell) labor and firms demand (buy) labor.
What is a traditional economy?
The oldest economic system, where customs and traditions shape economic activity; used in some parts of the world.
What is a command economy?
An economy where production and resource-allocation decisions are made by a central authority or ruling class.
What is a market economy?
An economy in which decision-making is decentralized and guided by prices, supply, and demand.
What is private enterprise?
When private individuals or groups own and operate the means of production (resources and businesses).
What are underground economies (black markets)?
Markets where buyers and sellers transact without government approval or regulation.