Inventory management
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Stock
Stock is any item stored by a business for use in production or sales. Stock can be raw materials and components or finished goods.
Inventory management
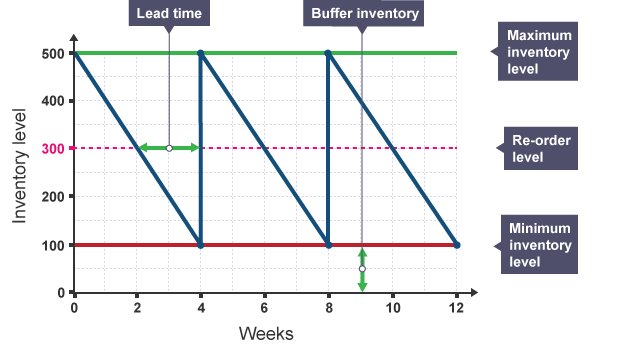
Maximum inventory level: The largest amount of items to be stored on site.
Minimum inventory level: The lowest amount of items to be stored on site.
Re-order quantity: The amount of stock ordered to restore inventory levels to their maximum point.
Lead time: Is the amount of time taken between ordering stock and the stock being delivered.
There is always a buffer inventory of 100 items held in case deliveries are held up or there is an unexpected large order.
Just in time (JIT)
JIT inventory control system occurs when a business holds no stock and instead relies upon deliveries of raw materials and components to arrive exactly when they are needed.
Advantages
No money is tied up in inventory meaning it can be used elsewhere in the business.
Less storage space/warehousing is required which will reduce costs.
Reduced wastage as less risk of stock going out of date or out of fashion.
Disadvantages
Delay in receiving orders from suppliers will lead to production having to stop.
Lose out on economies of scale as fewer bulk orders will be required.
Stock being delivered frequently increases administration and delivery costs.
Centralised storage
This is when a company chooses one central location to store all the stock for the organisation. The stock will be distributed to departments as required from the central warehouse.
Advantages
Supplers are delivering to one location which reduces delivery costs.
Economies of scale are gained due to bulk ordering.
Specialised staff can be employed to manage inventory which will reduce theft and improve efficiency.
Disadvantages
High costs incurred due to specialist equipment and large storage facilities.
May incur increased delivery times and delays in receiving stock to departments.
Increased wage costs as specialist staff are required to manage4 the storage and distribution of stock.
De-Centralised storage
This is when each department within the organisation is responsible for ordering and storing their own stock.
Advantages
Inventory is accessible so no delay in receiving required goods.
Small amounts of stock being held prevents wastage.
Departments are more responsive to local needs and changes in the market.
Disadvantages
Increased delivery costs due to low amounts of inventory being delivered to multiple locations.
Security may not be as effective leading to increased theft.
No specialist staff dealing with stock may lad to disorganisation and delays.
Logistical management of inventory
This is the process of dealing with the whole order from start to finish.