Carbon
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Organic Carbon
carbon from or in organisms
Inorganic Carbon
CO2 (carbonic acid), carbonate (HCO3-), and bicarbonate (CO32-)
Photosynthesis
CO2 + H2O (sunlight + chlorophyll) → C6H12O6 + O2
inorganic C → organic C
Respiration
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP
are freshwaters or oceans more important in the global C cycle (while recognizing that there is extreme uncertainty)?
freshwaters
sources of organic C in lakes
Input from streams (allochthonous)
Production by phytoplankton (autochthonous)
sources of inorganic C in lakes
Atmosphere (CO2) diffusion
Respiration by consumers
Organic C processes in lakes
Respiration of organic C
Inorganic C processes in lakes
Primary production
Organic C sinks in lakes
Sedimentation and burial
Export (transport) to downstream
Inorganic C sinks in lakes
Photosynthesis (taking up CO2)
Export (transport) to downstream
Atmosphere (release of CO2)
Phytoplankton Production >> Respiration
net sink (ex: Duck Pond)
Phytoplankton Production << Respiration
net source (ex: Pandapas)
are most freshwater sources or sinks?
sources (emit CO2 to atmosphere)
Methane (CH4)
25-34x more potent of a greenhouse gas than CO2
How is methane produced?
via respiration under anoxic conditions:
Anoxic sediments
Anoxic bottom waters
Two main methane release processes to atmosphere:
Diffusion
Ebullition (bubbles)
Methane accumulates in anoxic hypolimnion during summer stratified period and is released to atmosphere during ____ ____________
fall turnover
Where are lakes that are substantial sources of methane to the atmosphere?
In the Arctic
do freshwaters or oceans bury more C?
freshwaters
do freshwaters or terrestrial ecosystems emit more greenhouse gases?
freshwaters
From ice cores, we can see our current high CO2 levels are ___________
extraordinary
Carbon dioxide (CO2) — inorganic carbon
very soluble and reacts with water to form carbonic acid
Dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC)
= sum of carbon dioxide (carbonic acid) + bicarbonate + carbonate
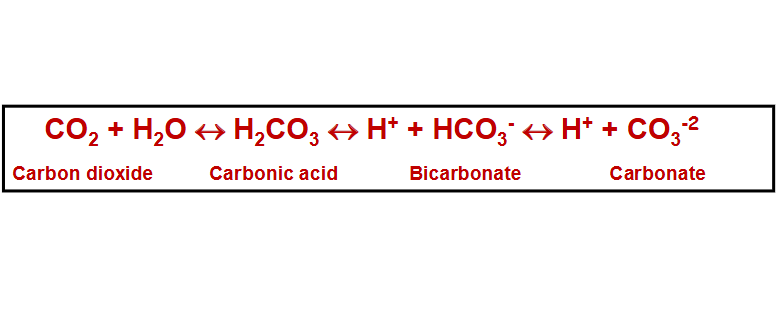
carbonate equilibrium is formed by…
chemical conversions between carbon dioxide, carbonic acid, and bicarbonate
bicarbonate equilibrium is coupled to ___
pH
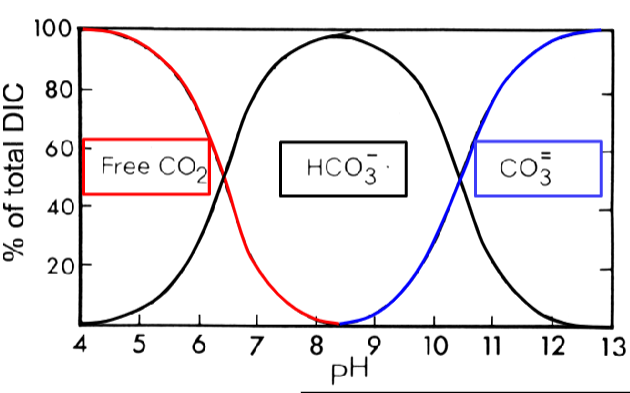
as the proportion of _____________ ions change, the pH will respond
inorganic C
Weathering of carbonate rocks (e.g., limestone)
The presence of carbonate and bicarbonate buffers the solution against pH change
Limestone buffers acid rain by increasing water’s ___________ (acid buffering capacity)
alkalinity
If carbonate or bicarbonate are not present, pH can…
change rapidly
Very high photosynthesis can…
deplete CO2 and cause CaCO3 to precipitate (encrust marl on aquatic plants/algae)
marl
calcareous deposits
lake whiting
water suddenly becomes chalky white due to the precipitation of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) particles
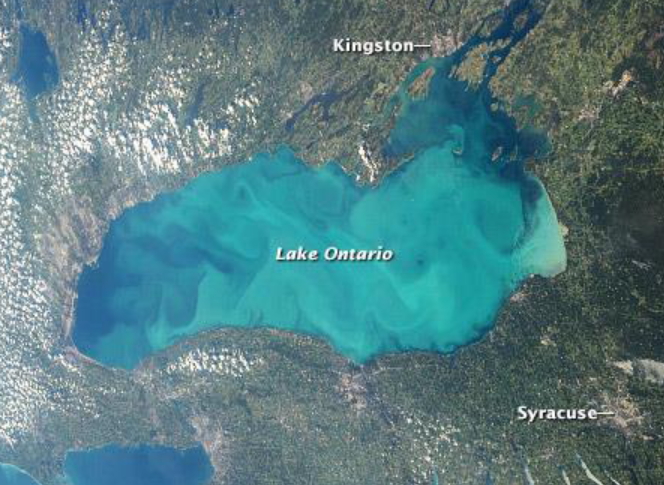
what is required for lake whiting to happen?
BOTH high background levels of calcium carbonate + rapid drawdown of CO2
Why is Lake Superior’s pH going up?
Warming temp increases algae (chlorophyll), it takes up more CO2, and pH increases because there’s not enough calcium carbonate to buffer pH change. Using up CO2 leaves just HCO3 and CO3 in solution, causing higher pH
The C cycle in freshwaters is expected to change with _________ change
climate
If alkalinity is high…
algal blooms can cause marl deposits
If there is low alkalinity…
algal blooms can increase pH
C reacts with water to make carbonic acid:
CO2 + H2O <-> H2CO3
Carbonic acid dissociates:
H2CO3 <-> H+ + HCO3-
Bicarbonate dissociates:
HCO3- <-> H+ + HCO3-2