Botany- 2b: Roots and Mangroves
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
roots functions
- absorption and conduction
- anchorage
- storage
- secretion
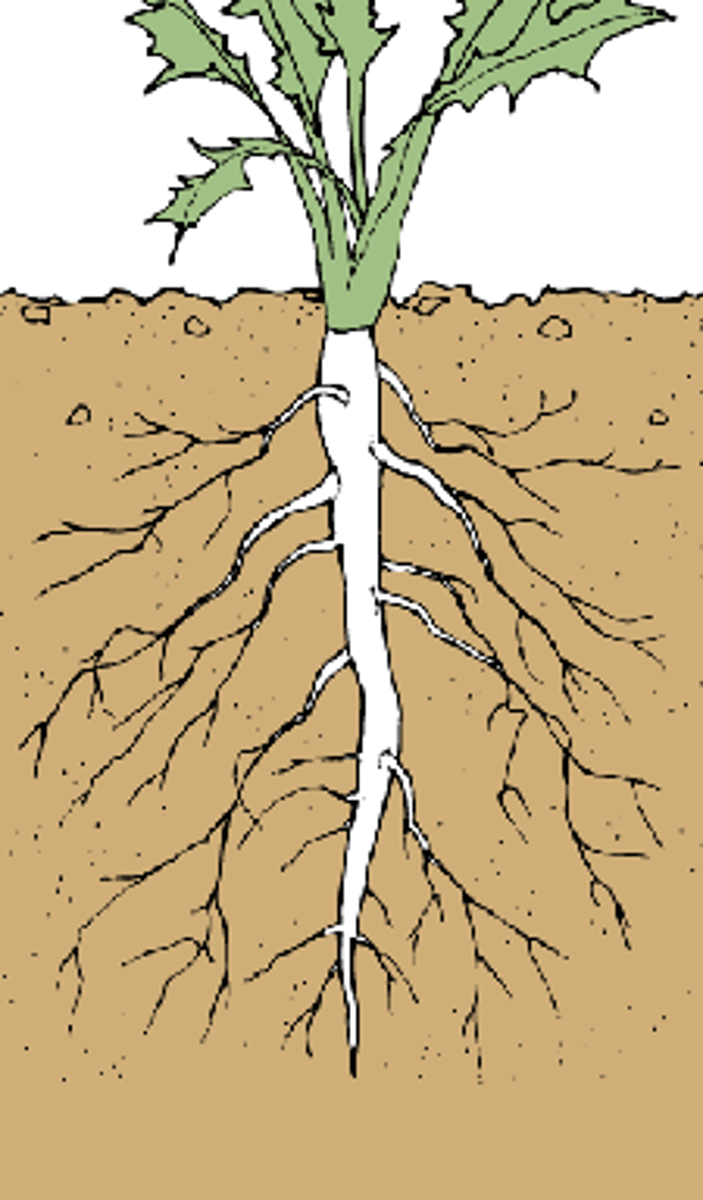
tap roots
has one central primary root (thick, deep root) usually with few lateral roots
- ex: carrots
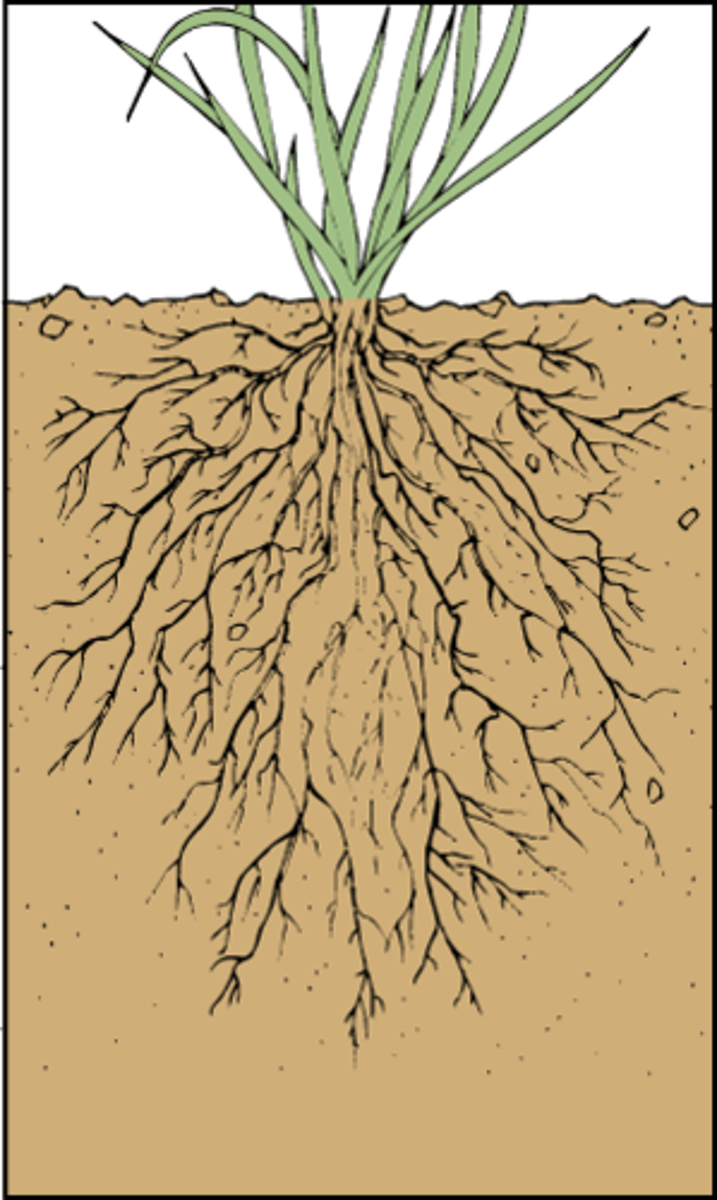
fibrous roots
part of a root system in which roots branch to such an extent that no single root grows larger than the rest
feeder roots
upper portion of root system (roots at or near the soil surface) that do the majority of absorption of minerals
external anatomy of roots
- spread greater than the shoot
- larger surface area than shoot
- balance of root and shoot
- lack nodes
dicot roots
tap roots
monocot roots
fibrous roots
mucilage sheath
coats root tips growing in the soil (#5 in pic)
- originates in peripheral cells of the rootcap
(polysaccharide)
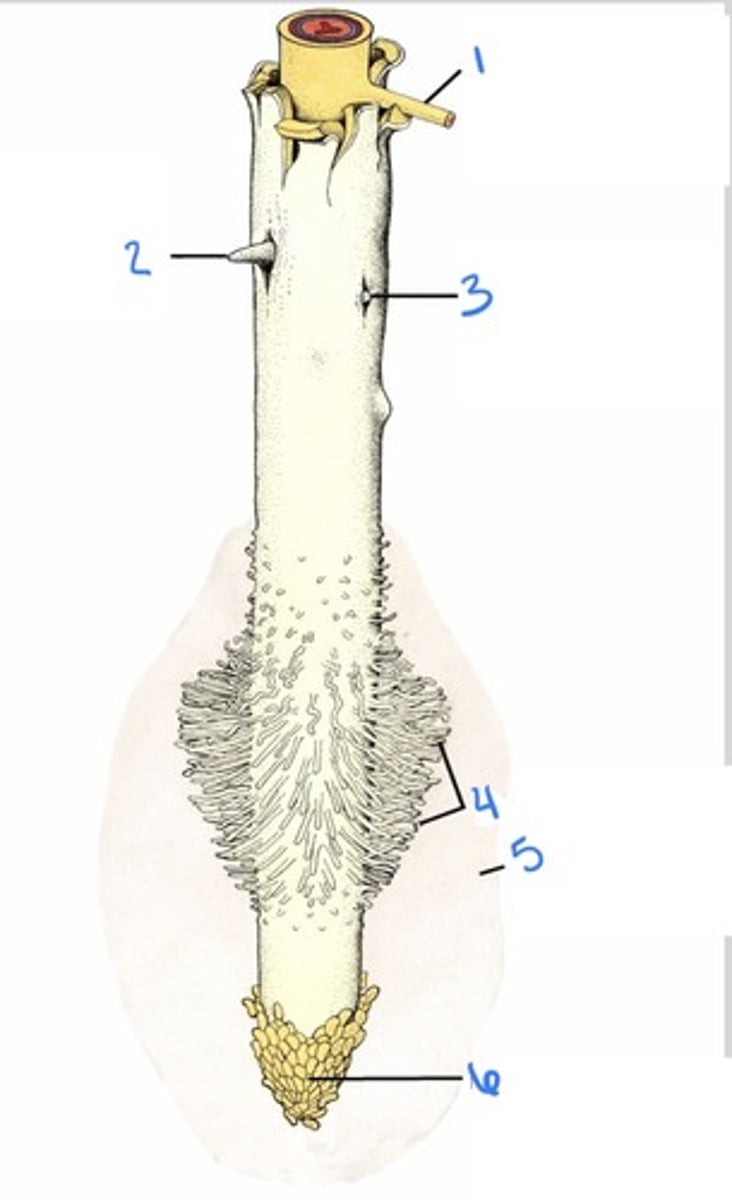
root cap
tough covering of the root tip that protects the meristem
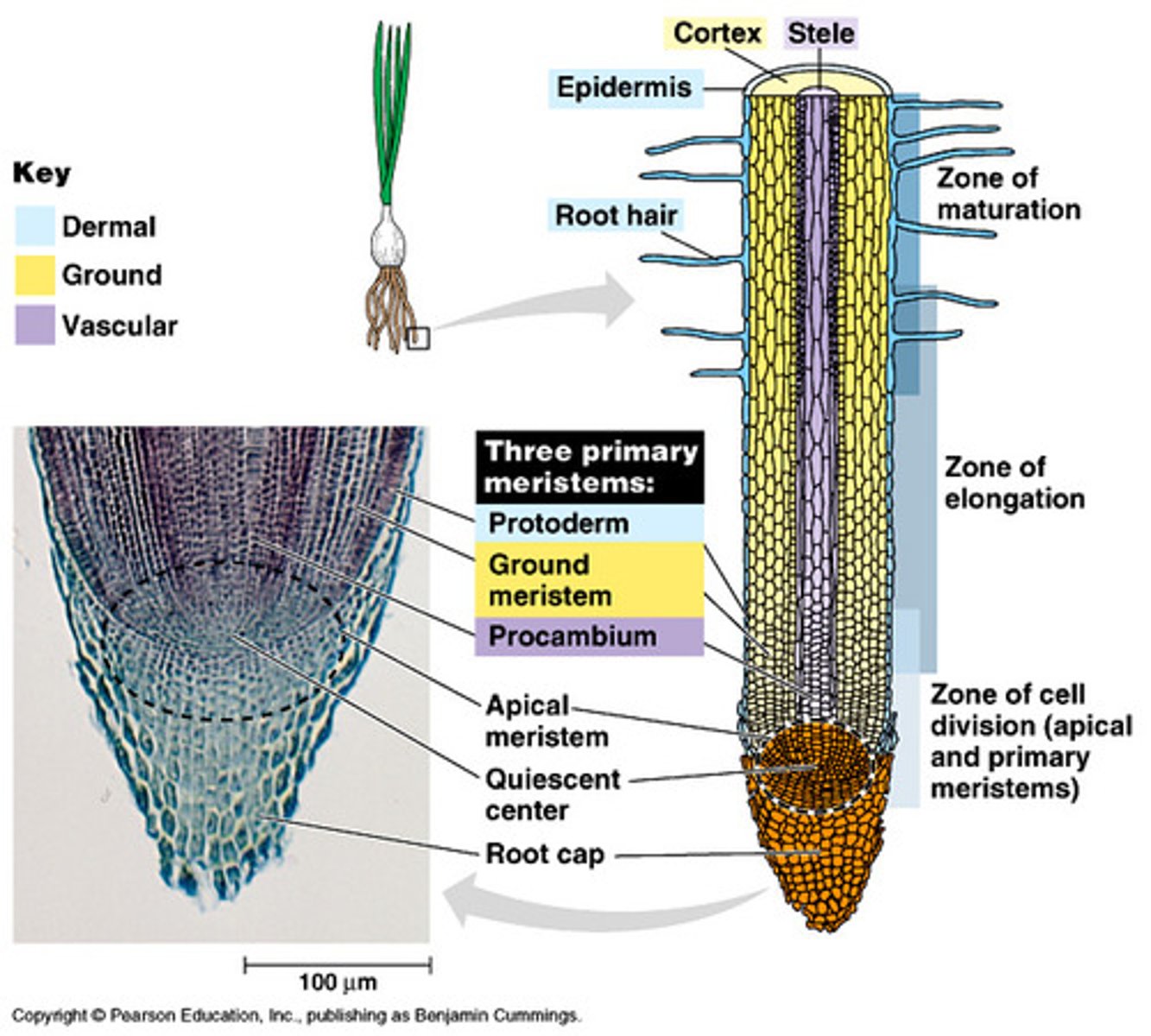
protoderm
The outermost primary meristem, which gives rise to the epidermis of roots and shoots
ground meristem
gives rise to the ground tissue system
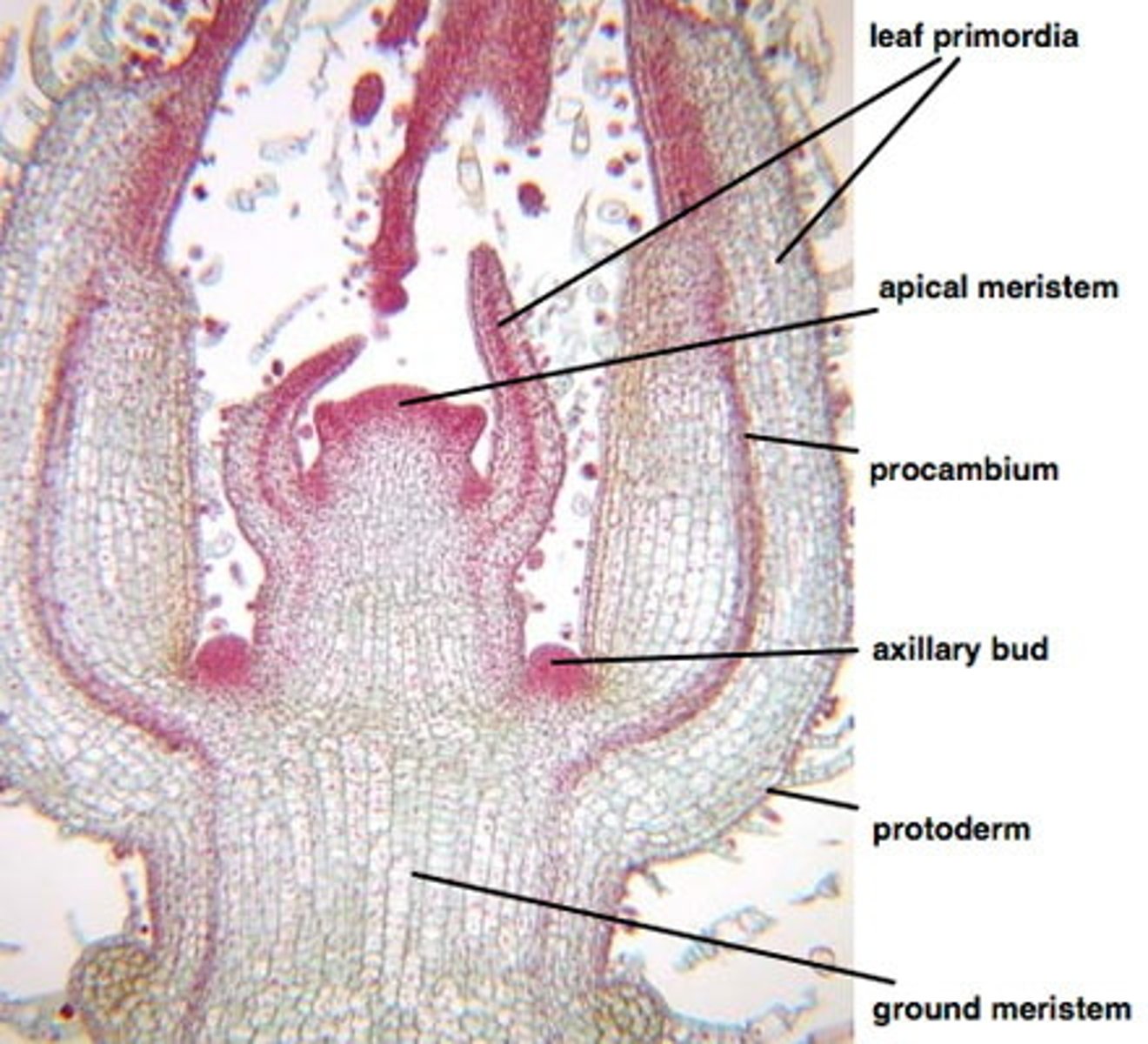
apical meristem
group of undifferentiated cells that divide to produce increased length of stems and roots
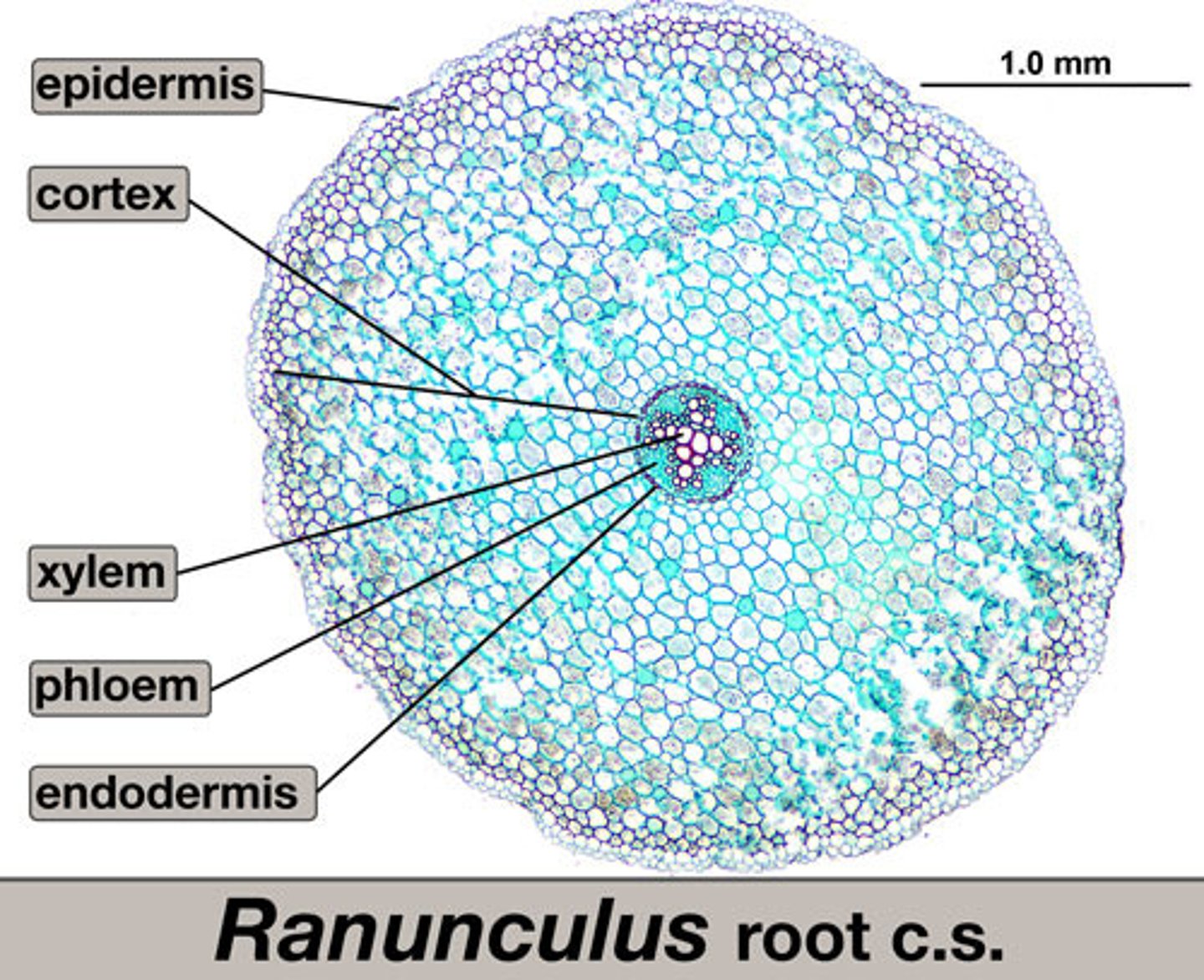
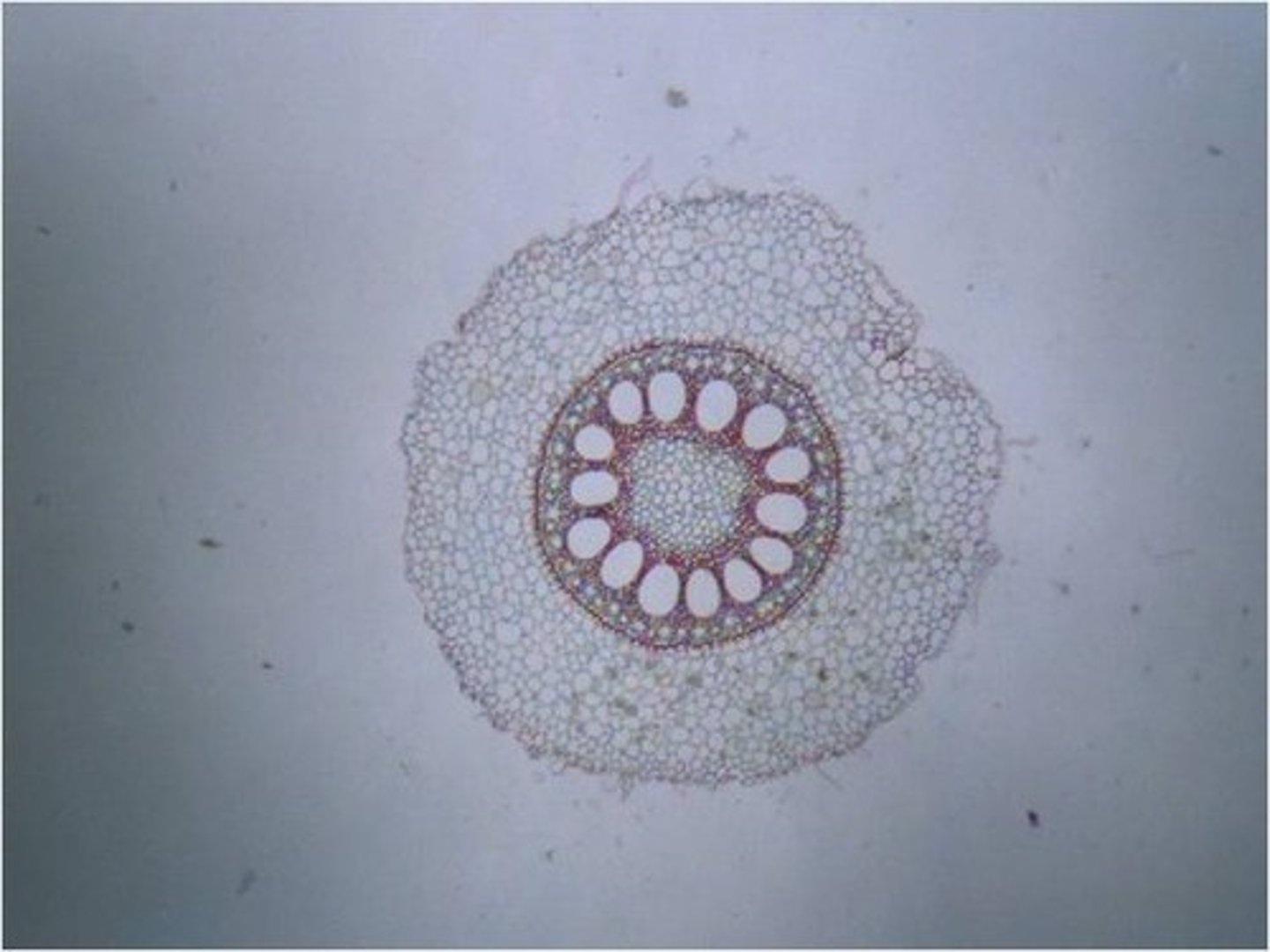
monocot root
pith inside vascular cylinder
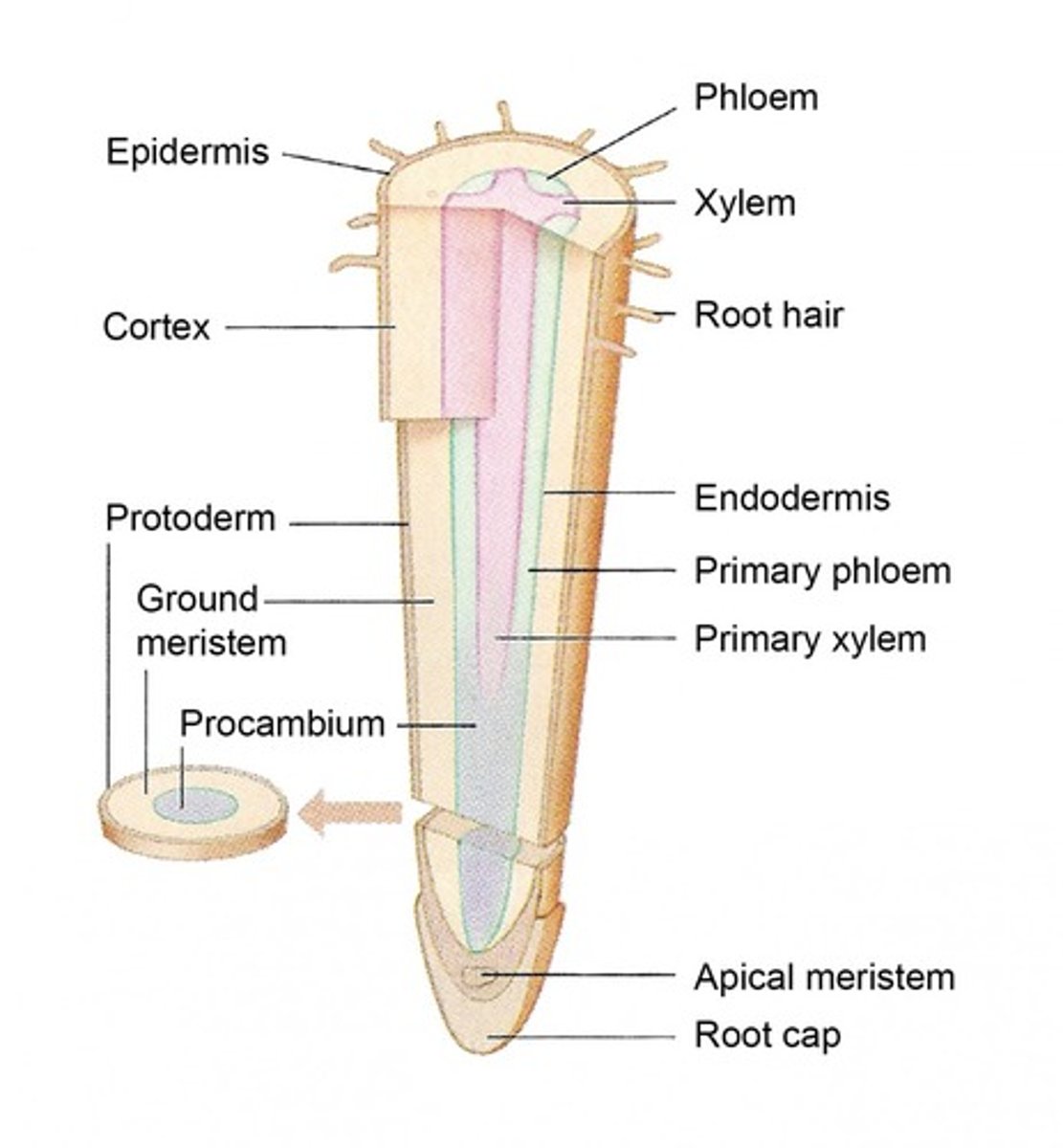
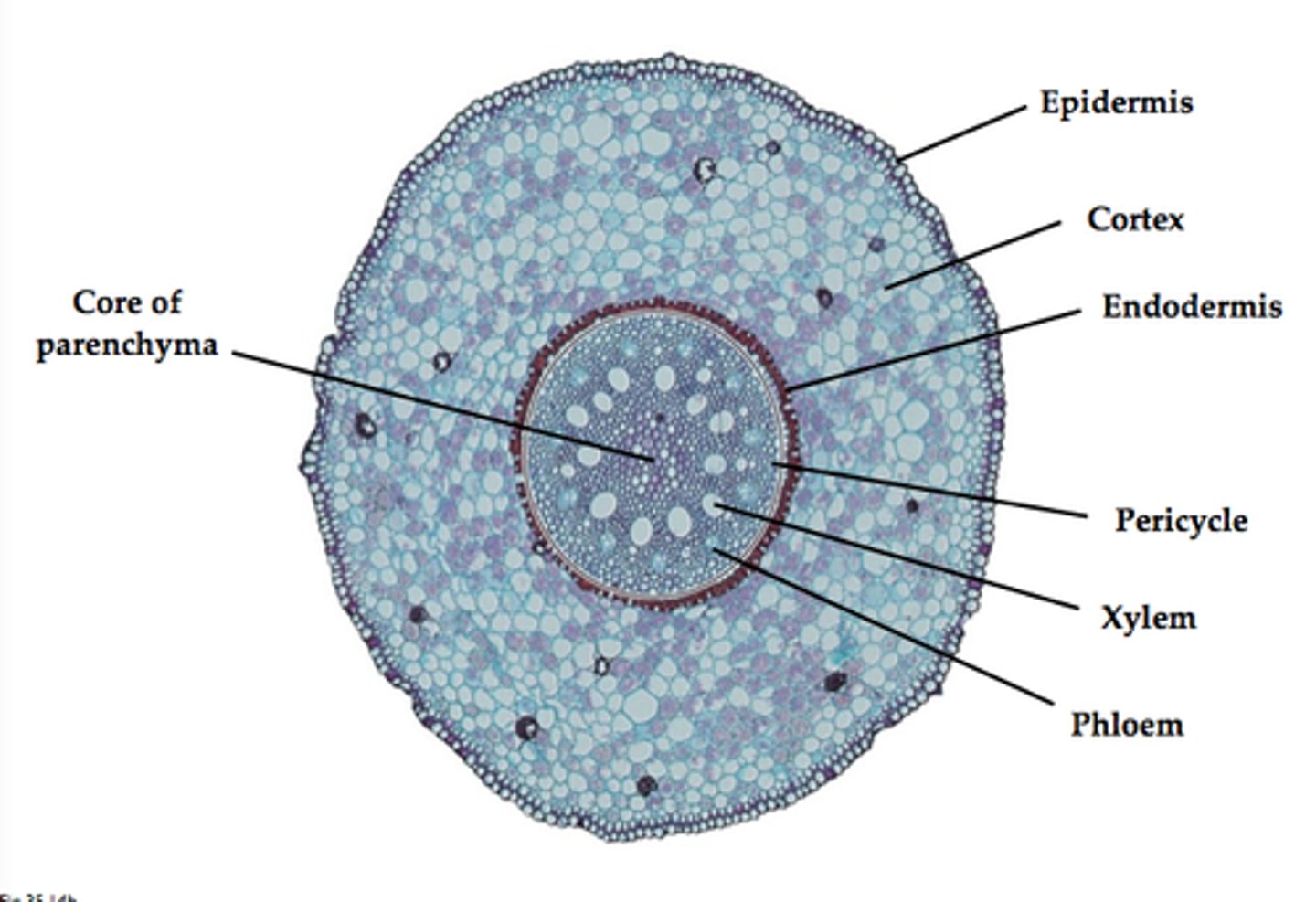
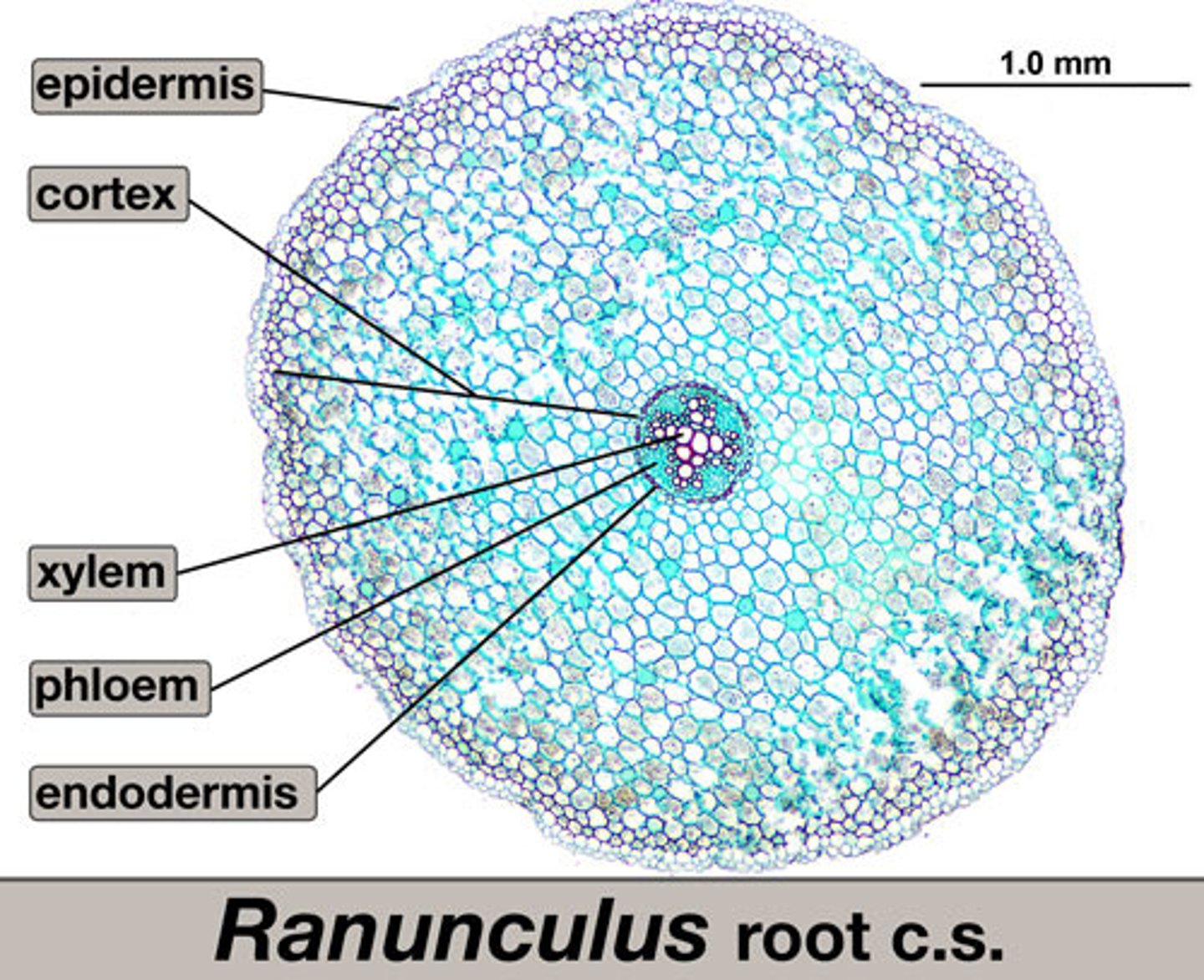
vascular cylinder
central region of a root that includes the vascular tissue-xylem and phloem
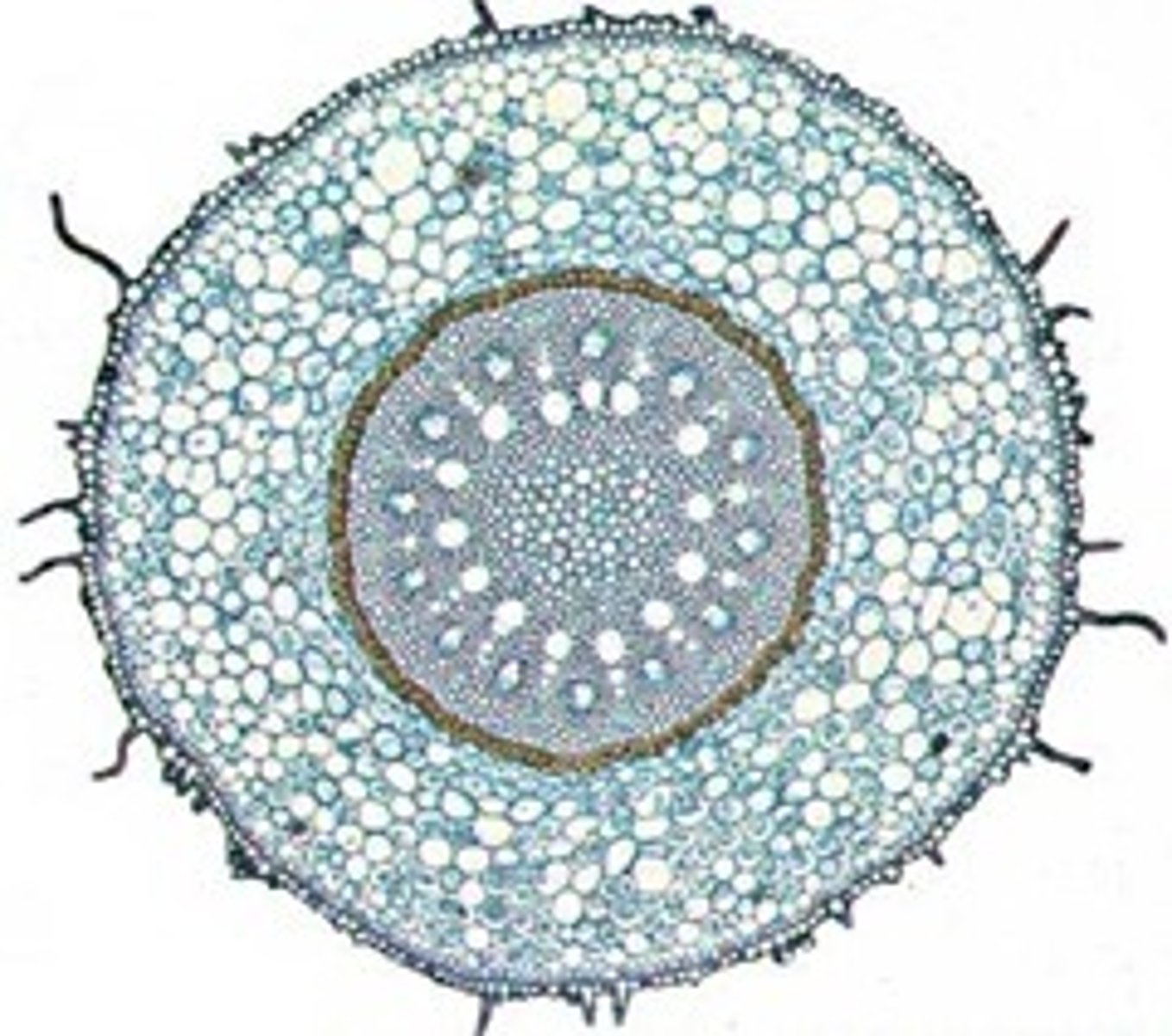
vascular cylinder with no pith
in eudicot roots
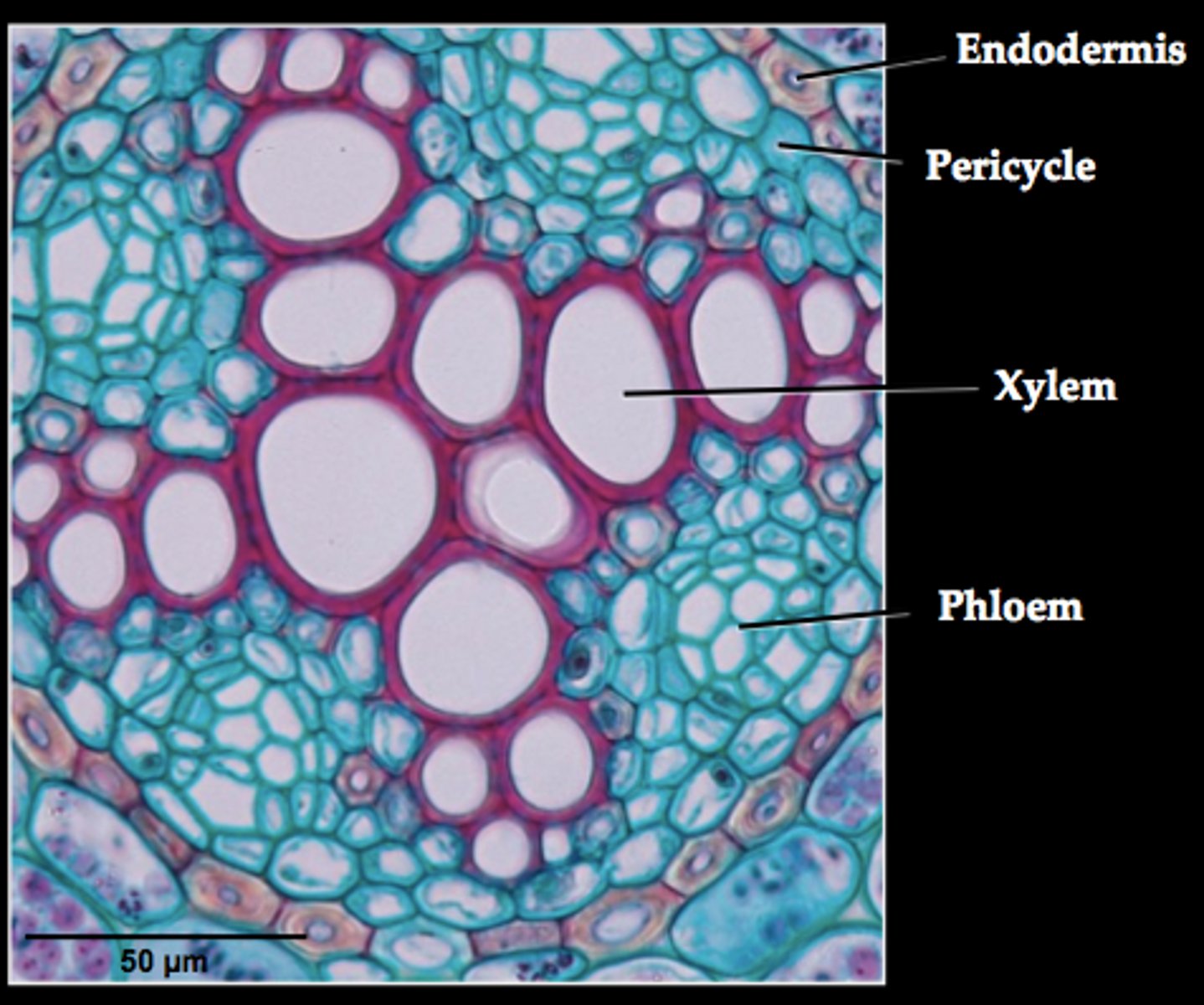
eudicot root
phloem between arms of xylem
- no pith inside vascular cylinder
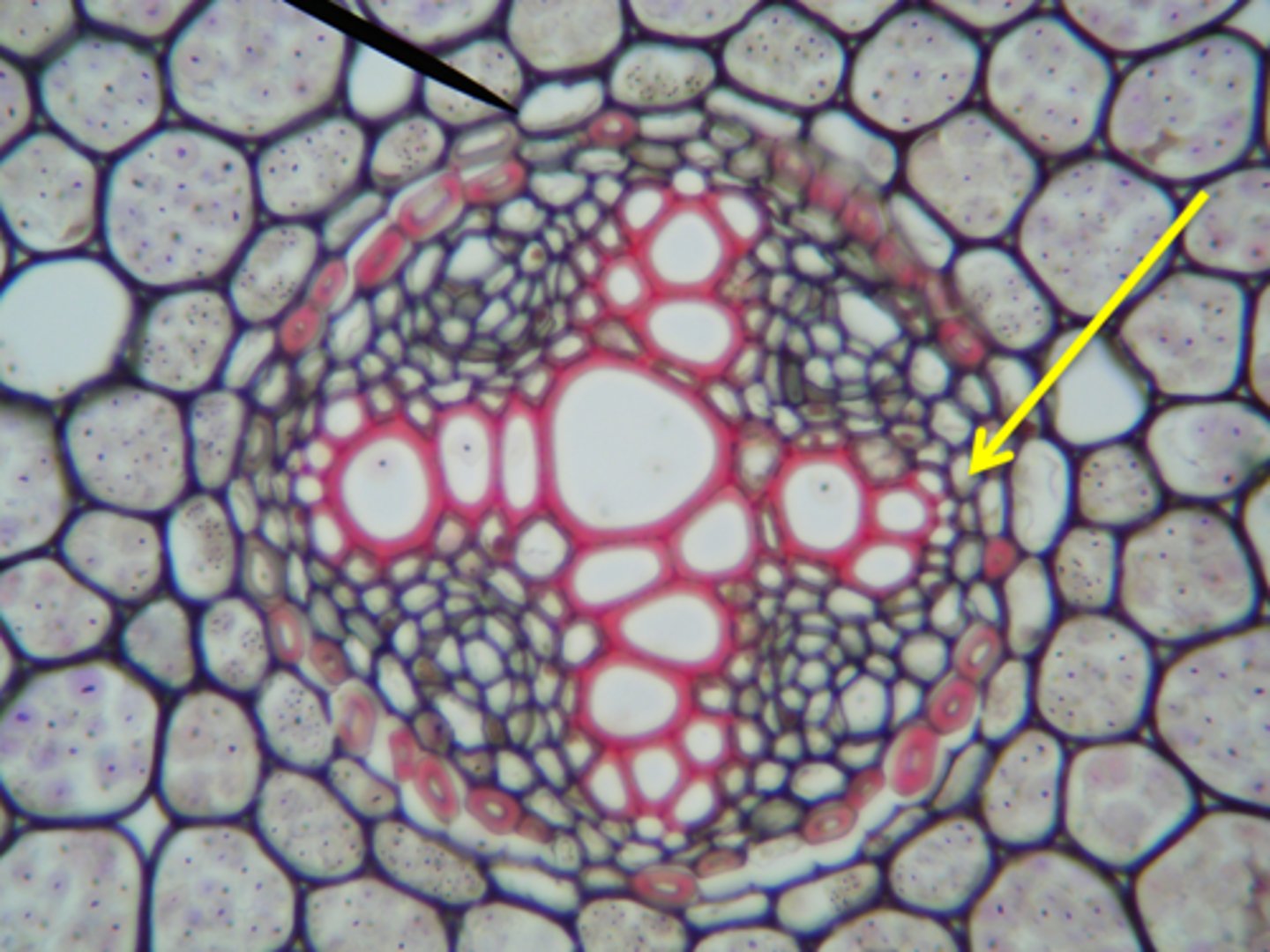
pericycle
a thin layer of plant tissue between the endodermis and the phloem
- outermost layer in the vascular cylinder, from which lateral roots arise.
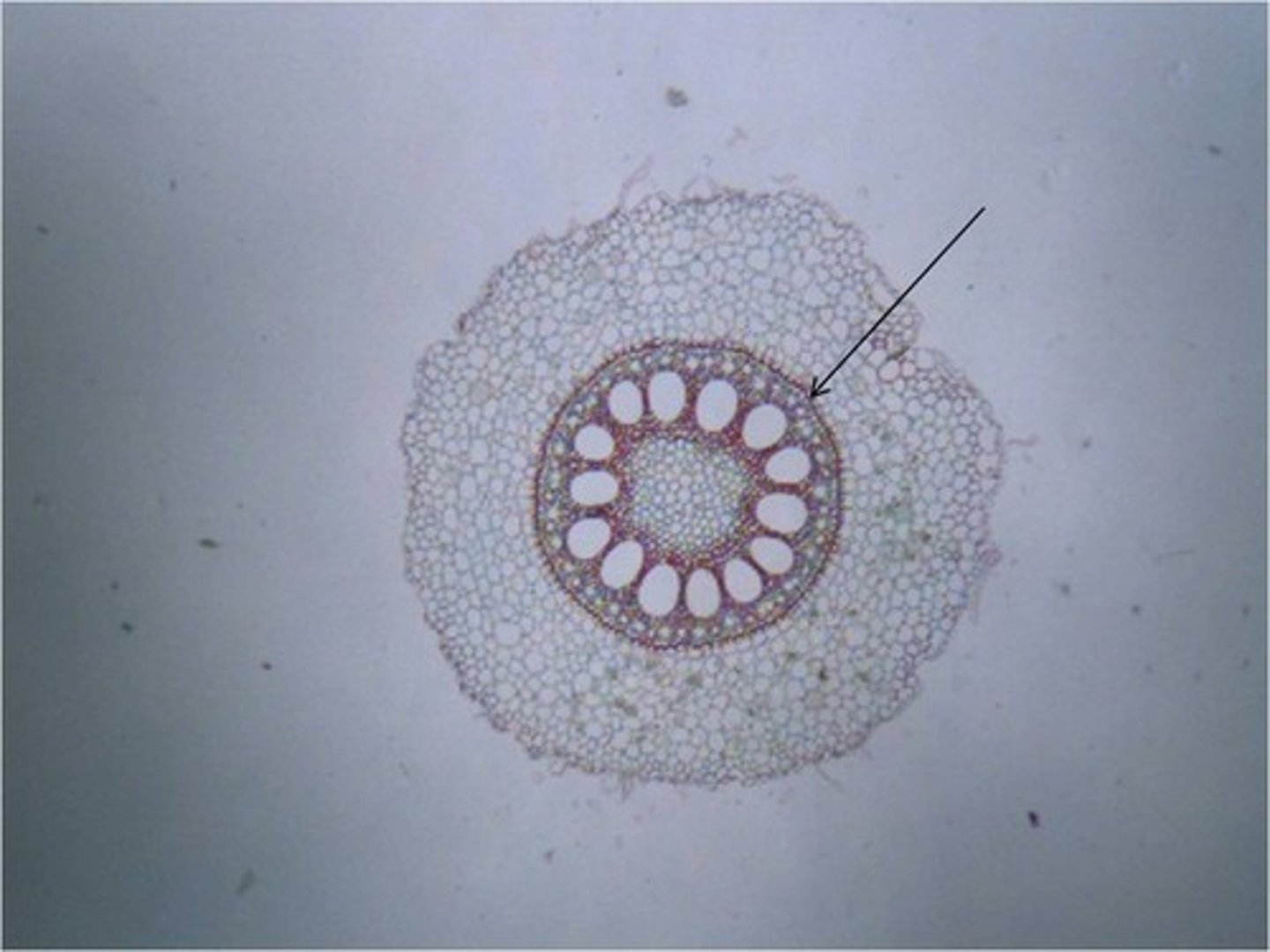
endodermis
The innermost layer of the cortex in plant roots; a cylinder one cell thick that forms the boundary between the cortex and the vascular cylinder.
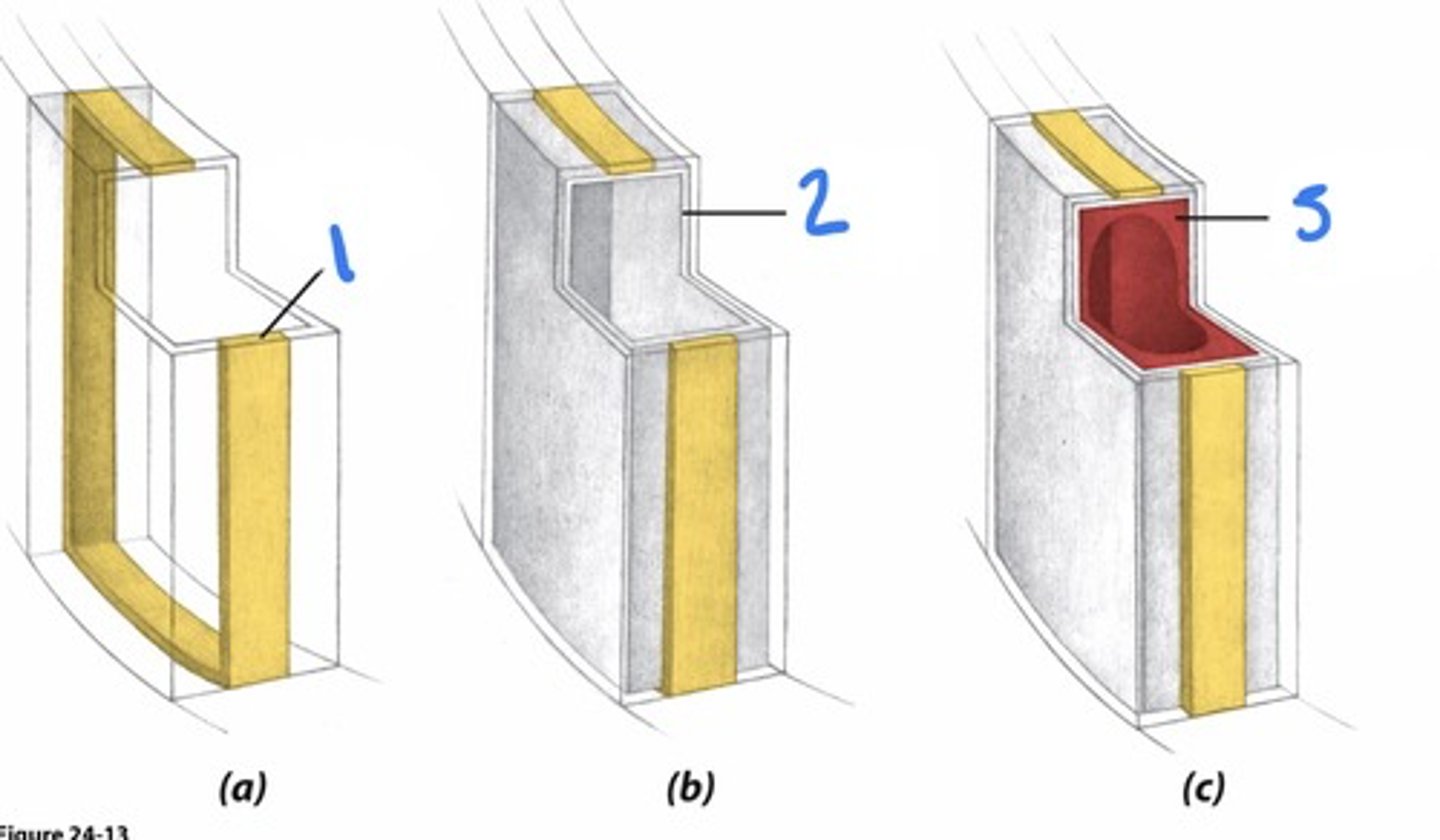
endodermis developments
1. casparian strip (suberin)
2. suberin lamella
3. layer of cellulose
secondary growth internal anatomy
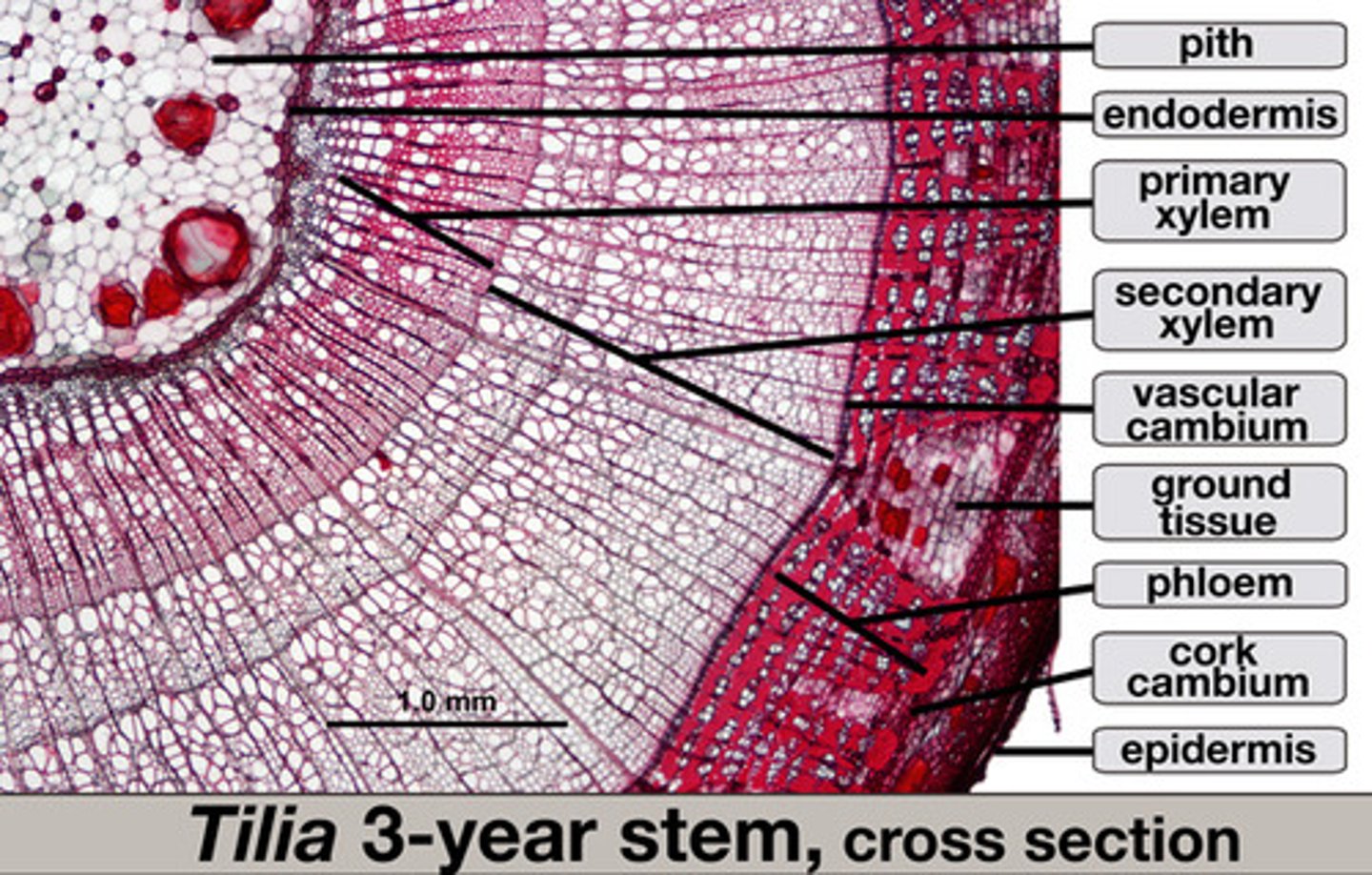
root modifications
sweet potato
aerial roots
root nodules
mycorrhiza
adventitious roots
- prop roots
- stilt
- pneumatophores
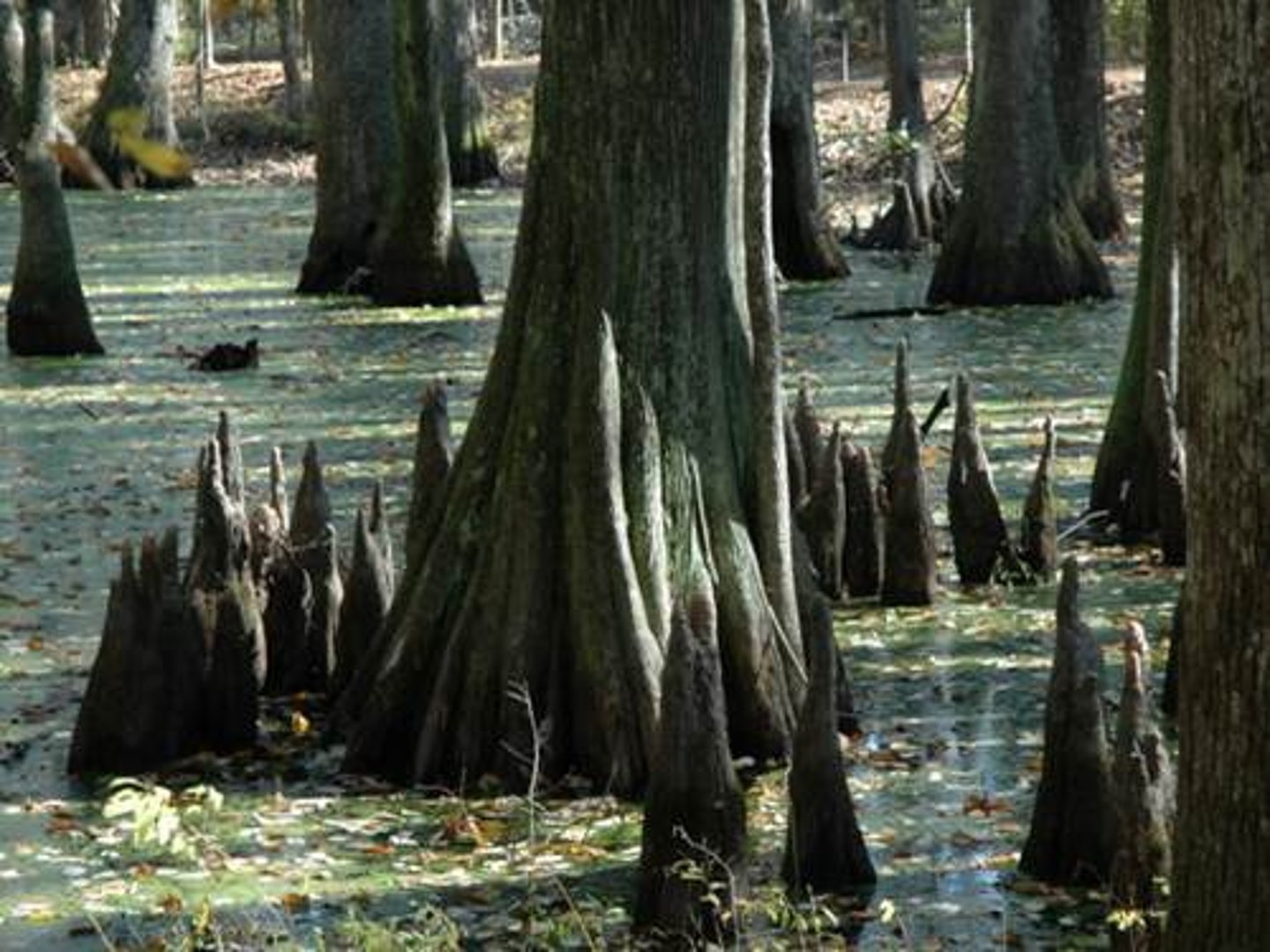
cypress knees
help keep the trees from falling over in the soft, wet soil of the swamp and helps them "breath" (O2)
- native to wetlands

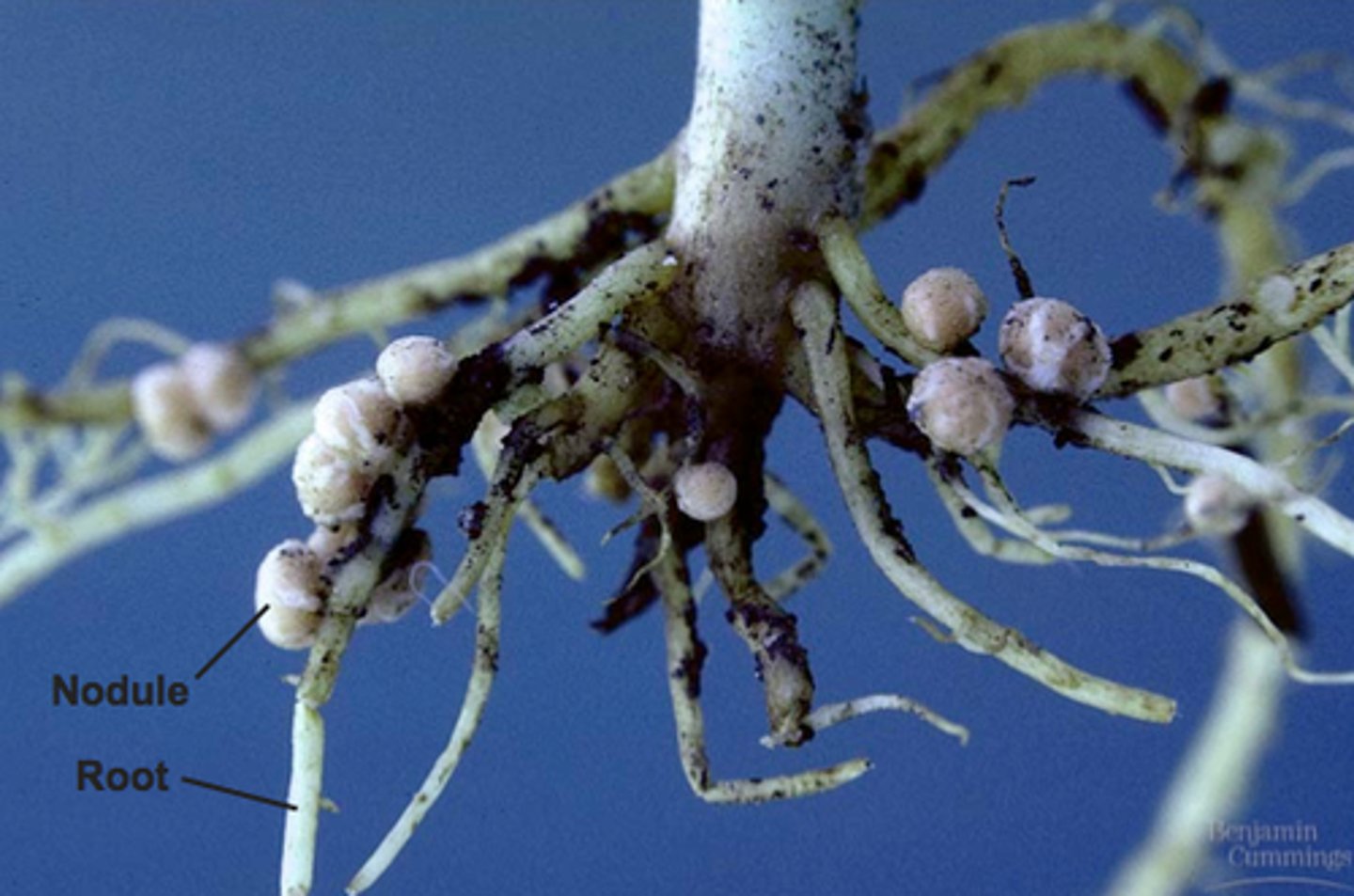
root nodules
Swellings of some plant roots that contain nitrogen-fixing bacteria
- most famous in legumes

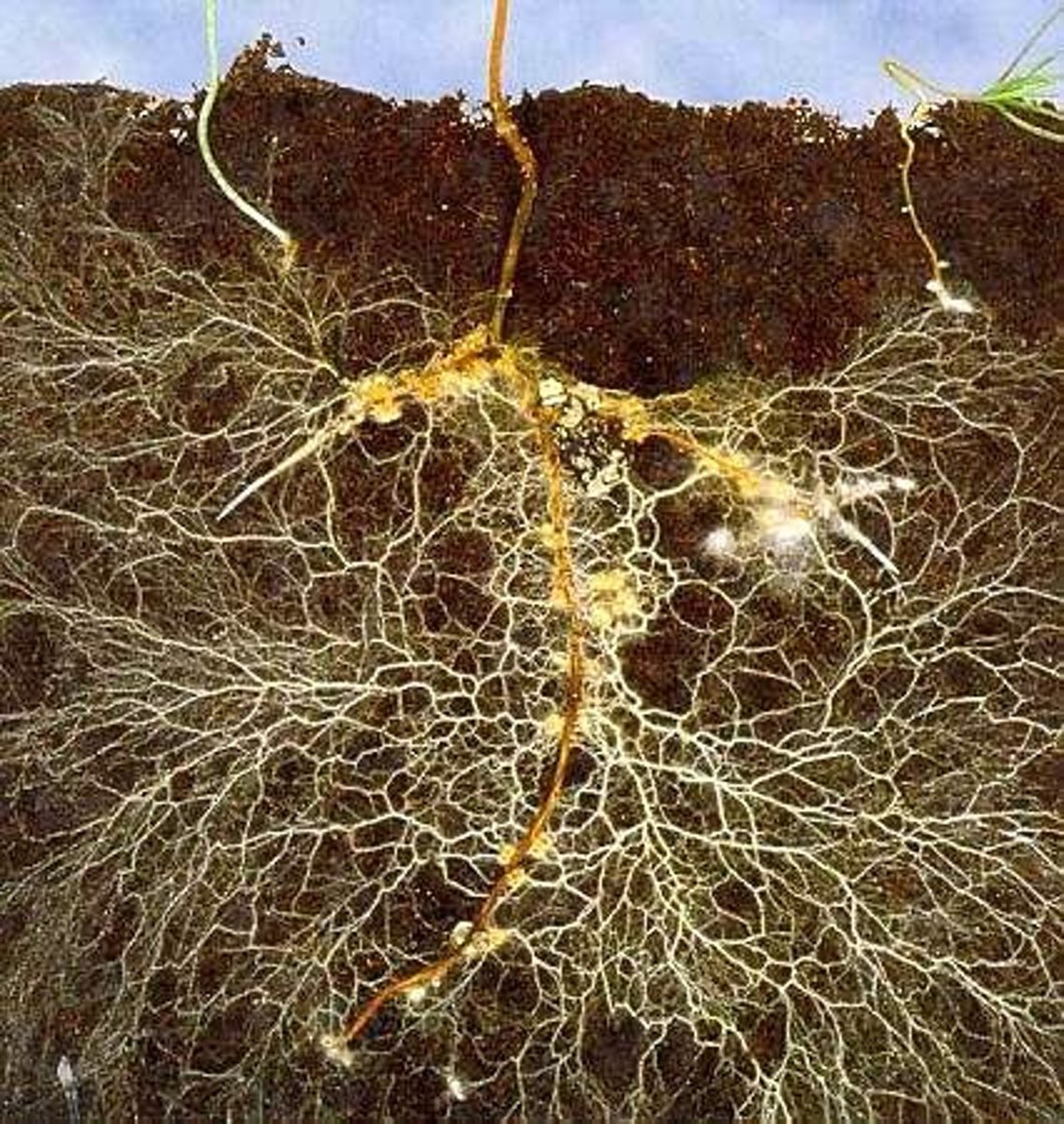
mycorrhizae
A mutualistic association of plant roots and fungus

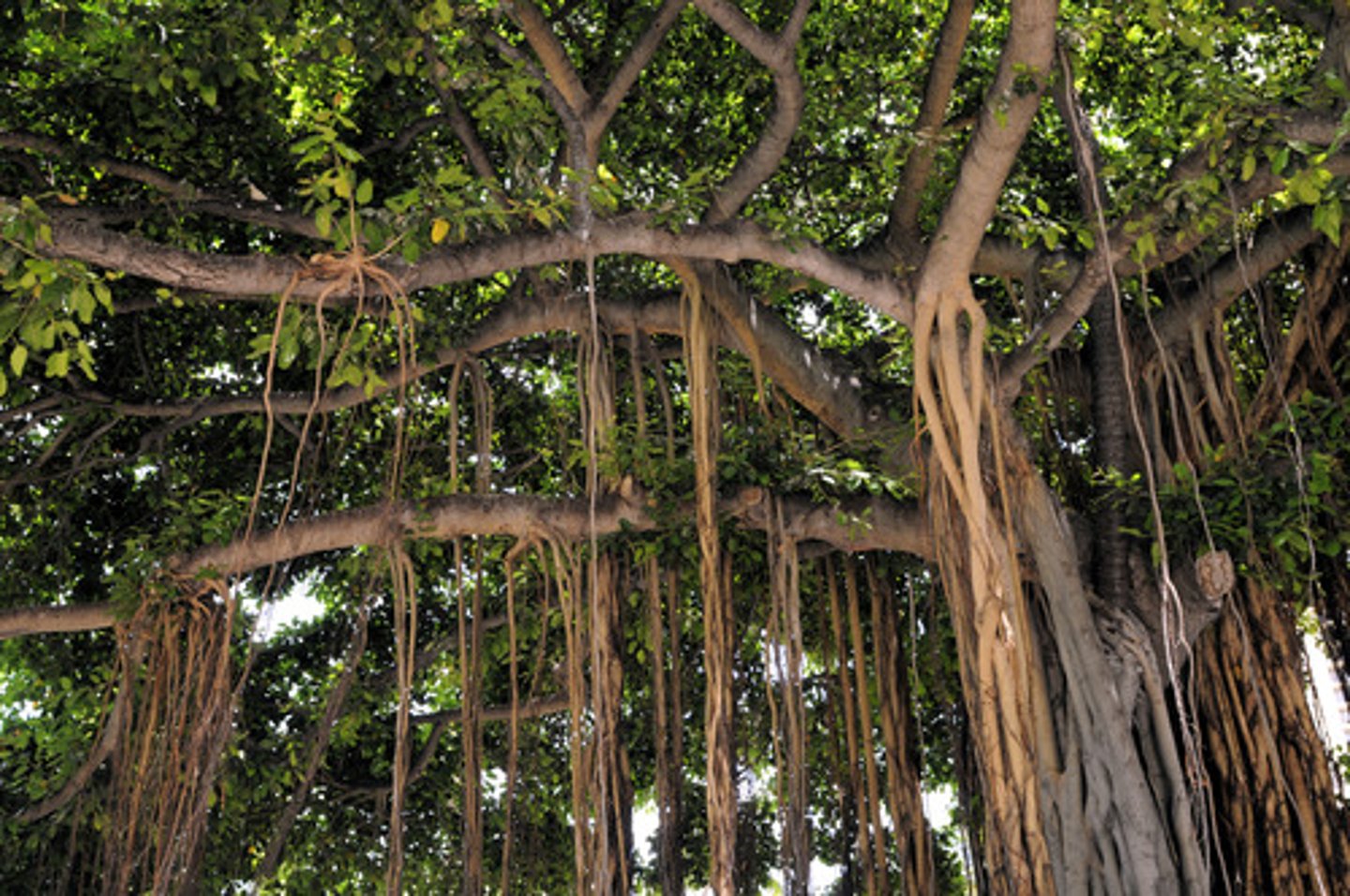
aerial roots
roots produced above ground and are photosynthetic
- ex: orchids

adventitious roots
roots that grow in unusual places, such as on the stem of the plant
- aerial roots
- prop roots
- stilt
prop roots
roots that grow partially in the air and partially in the ground; arise from node on stem
- stilt
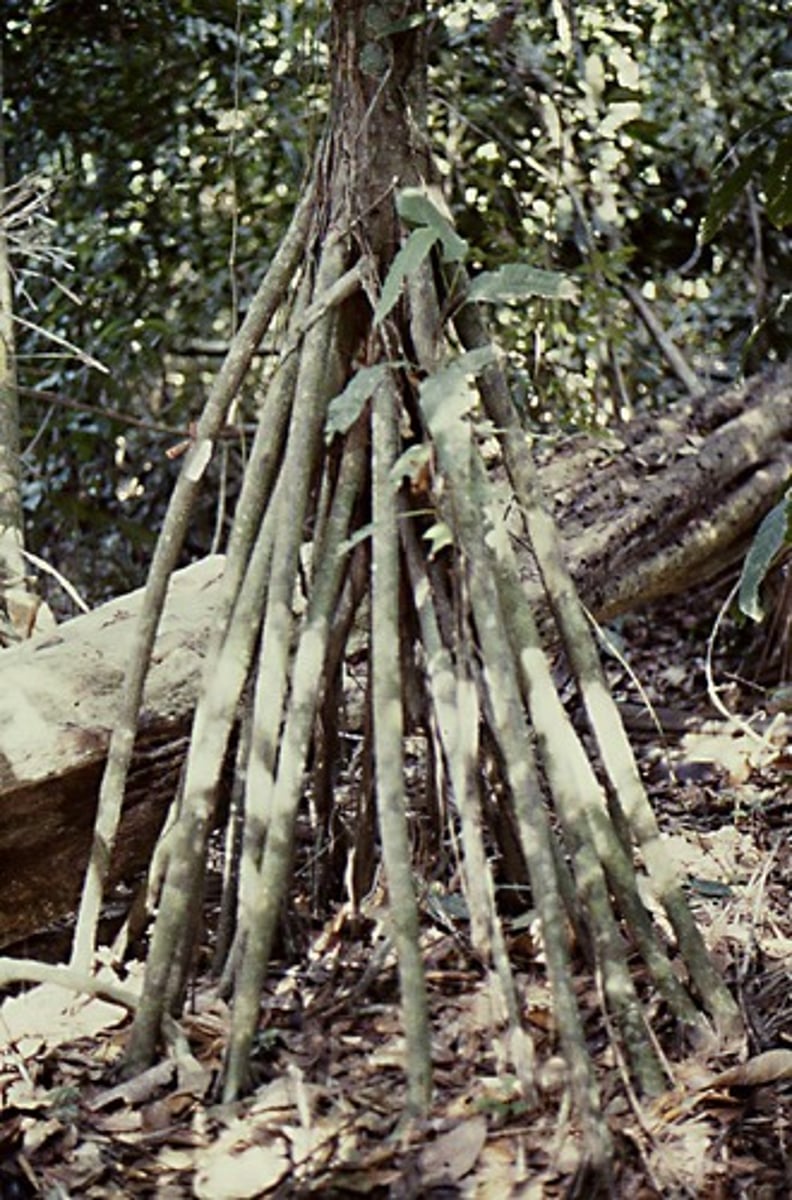

stilt roots
roots grown from branches
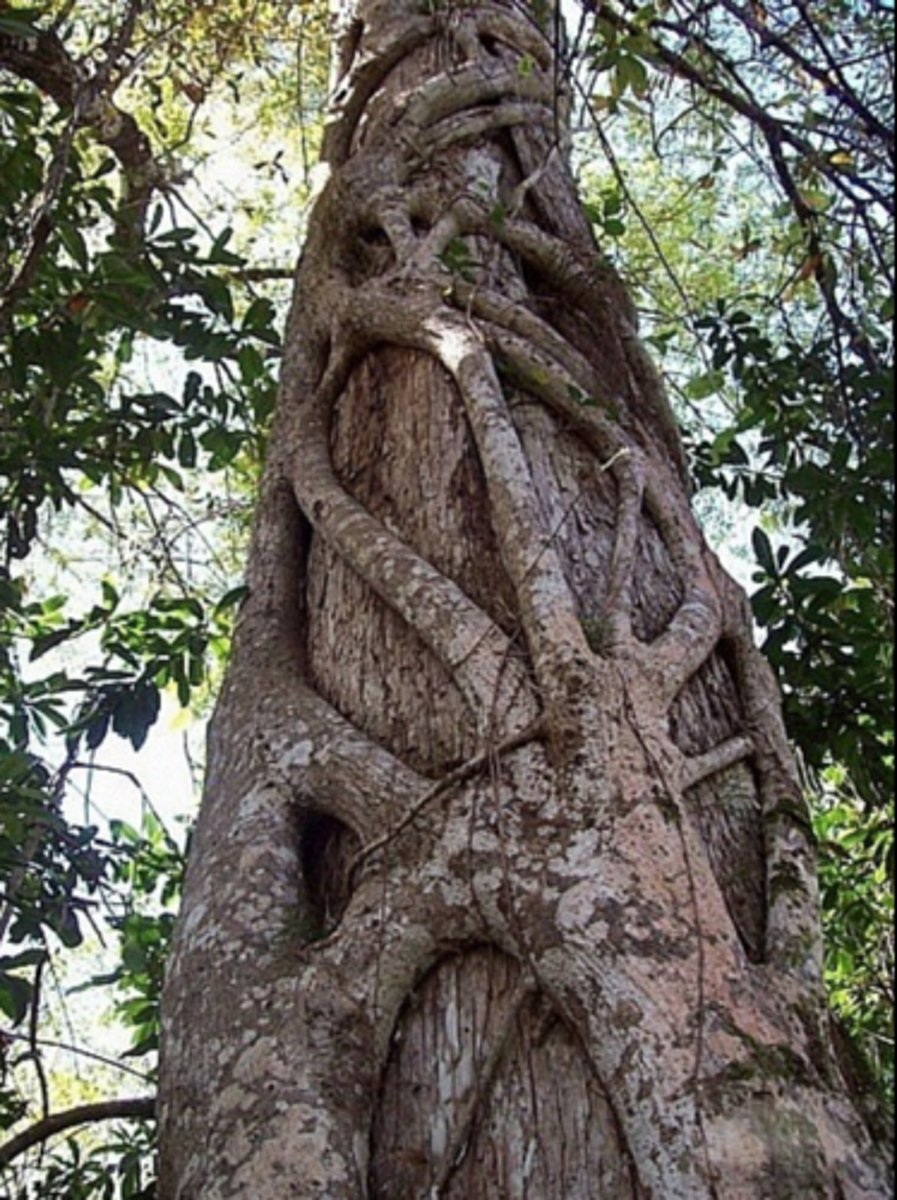
strangler fig
climbs and "chokes" tree

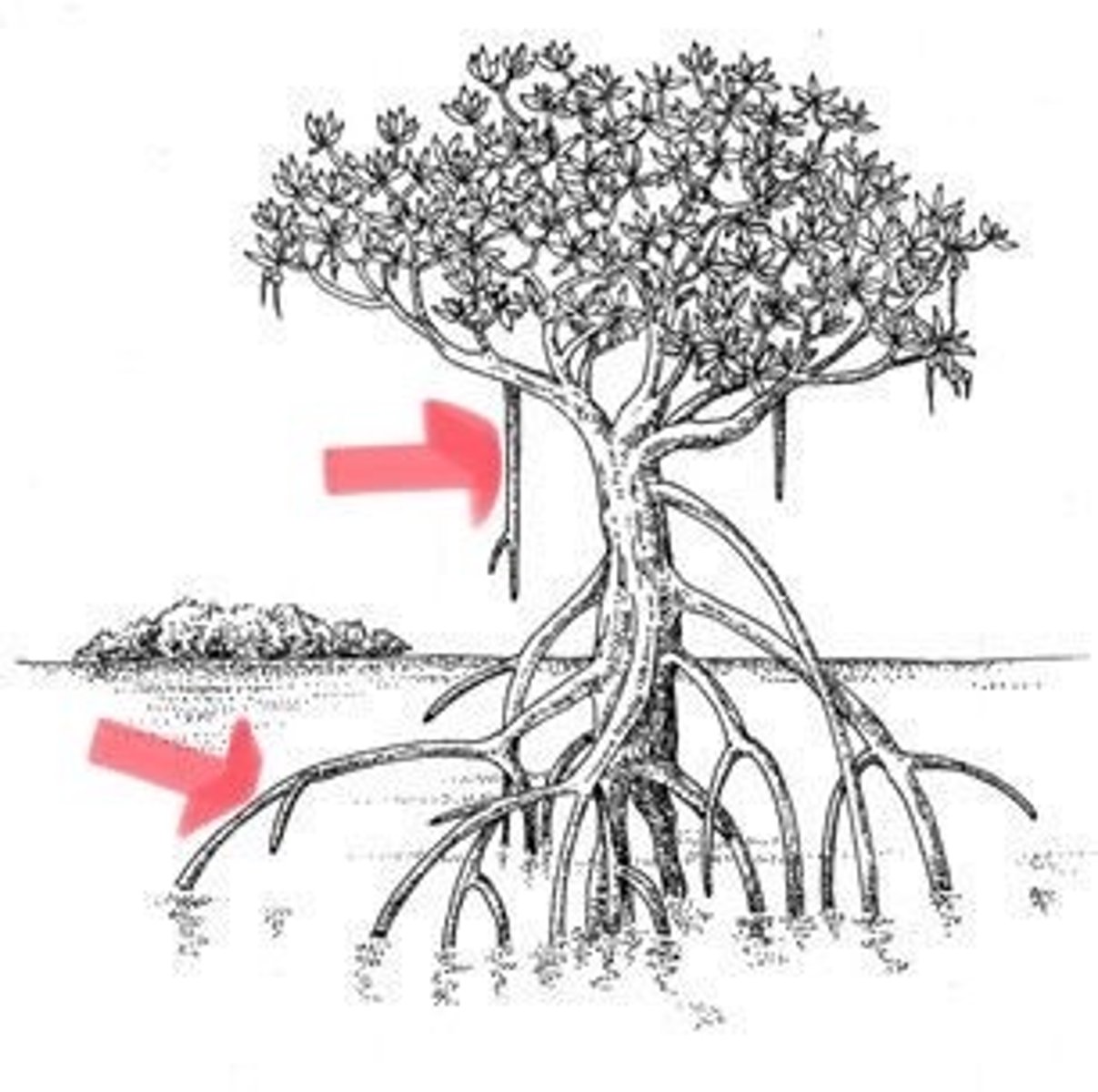
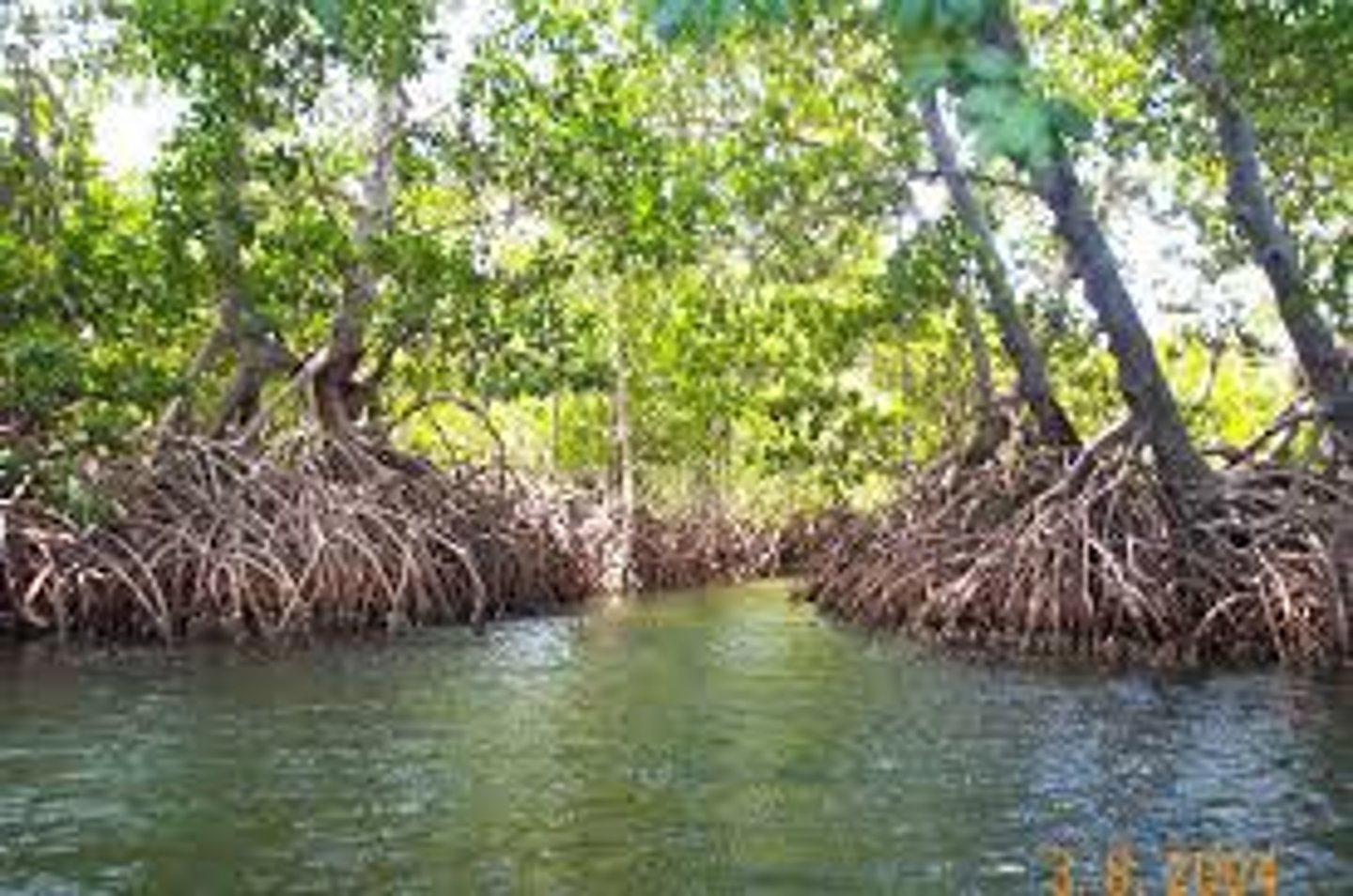
Rhizophora mangle
red mangrove
- stilt (prop) roots
- "land building" (traps sediment)
- self-fertilizing (large root grows from seedling)
- sensitive to the cold

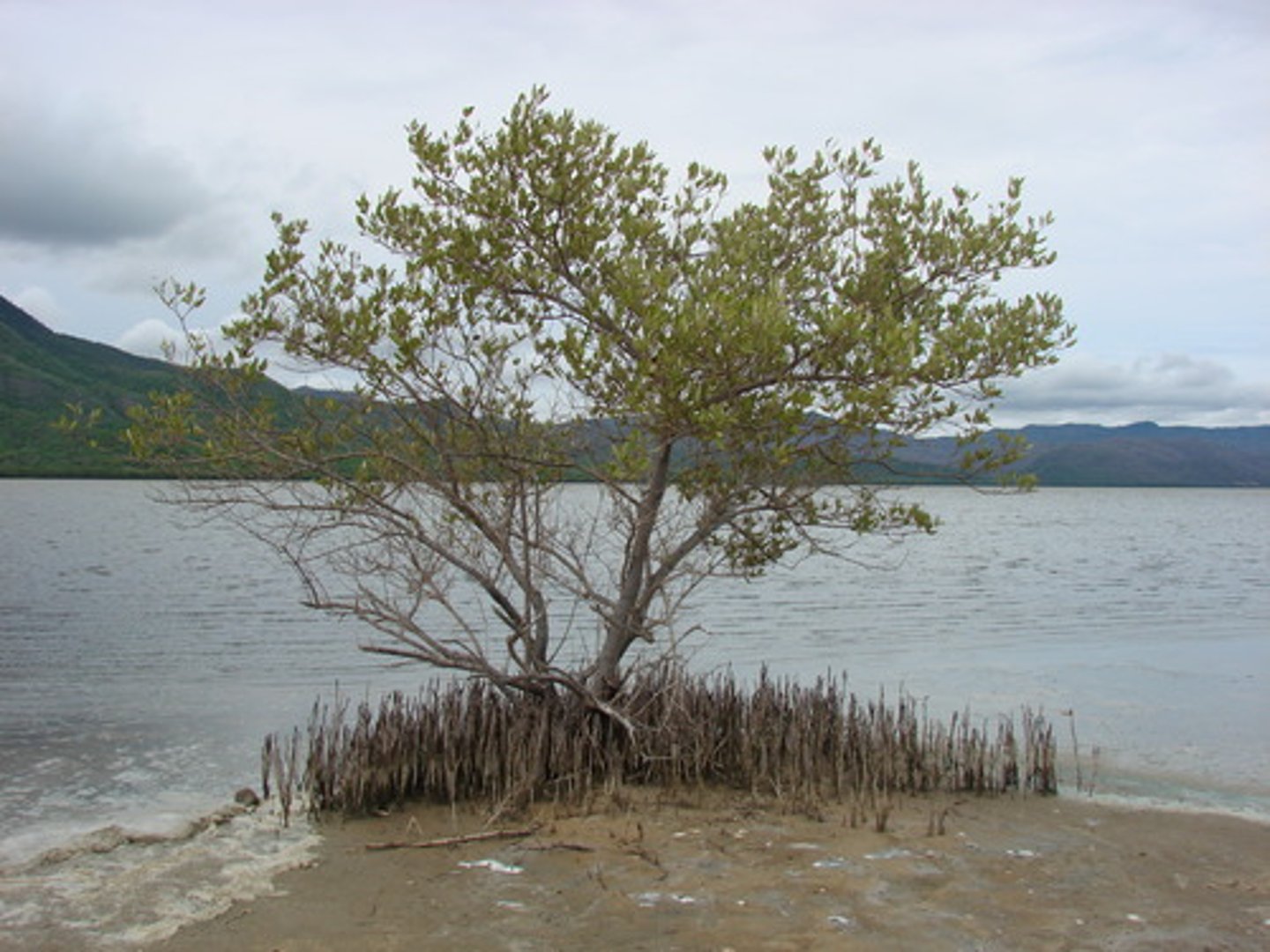
Avicennia germinans
black mangrove
- pneumatophores (photosynthesis and "land building")
- dark trunk
- salty leaves, lighter underside
- more tolerant to cold weather

mangrove community
(in order of open water ----> dry land)
Red Mangrove (Rhizophora mangle) - stilt (prop) roots
Black Mangrove (Avicennia germinans) - pneumatophores ("dead man's fingers")
White Mangrove (Laguncularia racemasa) - glands on leaves
Buttonwood (Conocarpus erectus) -
mangrove food pyramid
Mangrove leaf Detritus --> Decomposers (bacteria and fungi) --> other detritus feeders (commercial & recreational species like fish and crab) --> higher trophic levels (commercial & recreational species like pelicans and blue heron)
benefits of mangroves
- trap sediments and nutrients (buffer for offshore reefs and intercoastal)
- protection against sedimentation and eutrophication of offshore reefs
- protection against storm damage