Spinal and Pediatric Orthoses
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
Flexible Spinal Orthosis - components
mostly cloth and bendable materials
Main purpose of Flexible Spinal Orthosis
for sensory feedback
True/False: Flexible Spinal Orthosis does not restrict movement at all
True

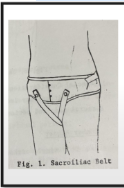
Identify the Orthosis
sacroiliac belt
Sacroiliac belt - placement
under, at the level of sacrum; does not reach the level of the iliac crest
Sacroiliac belt - Feature
Pre-fabricated belt, 5.1 cm to 10.2 cm wide
Encircles the pelvis b/w the iliac crests and trochanters
Sacroiliac belt - Special Consideration
Used in post-partum and posttraumatic sacroiliac separations.
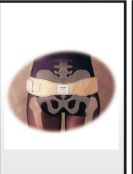
Features of this Orthosis
Traditional type; belt placed under perineum for further support which pushes the pelvis upward.
Disadvantage: uncomfortable in the groin area dt friction
Advantage: lifts the entire perineum up which lessens the pain
Features of this Orthosis
Pushes the pelvis, particularly the SI joint together to avoid separation
Acts as a support to approximate the SI joint together

Features of this Orthosis
For postpartum and pregnant women specially during the latter part of the trimester
Lifts the belly up to prevent conditions such as low back strain
Sacroiliac Corset - Features
A cloth garment with the superior border located at the iliac crest both anterior and posterior sides.
Inferior border is located at the pubic symphysis and gluteal bulge, respectively.
Entire pelvis including the gluteus maximus is lifted up.
It has strings which allows additional pressure
Sacroiliac Corset - Function
Assist in elevating intraabdominal pressure
Postpartum
Post-traumatic stabilization of pelvic joints (SI and pubic symphysis)
Sacroiliac Corset - Special Considerations
Posterior rigid to lessen movement of the pelvis, posterior sacral pad to prevent irritation on the sacrum, and perineal straps
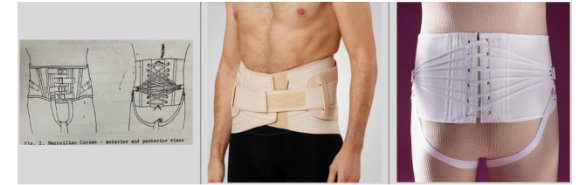
Identify this orthosis
Sacroiliac Corset
Lumbar Binder - Feature
Wrapped around the lumbar region and held in place by Velcro closure.
Lumbar Binder - Function
Trunk support through increasing intra-abdominal pressure and provides sensory feedback for proper posture.
Lumbar binder is usually for patients who suffers from ___________
mild cases of lumbar strain
Most common flexible orthosis
Lumbosacral corset
Lumbosacral Corset - Features
Encompasses the torso and hips
Anterior Sup border: xiphoid process; Posterior Sup border: inferior angle of the scapulae
Lumbosacral Corset - Function
Unloads pain on the pelvis and lumbar spine
Decrease loading on the vertebrae and discs on minimal cases
Sensory feedback to restrict motion.
May limit FEL but not rotation (rotation of the spine happens on the thoracic level)
Thoracolumbar Corset - Feature
Encompasses torso and hips
Anterior sup border: same LS; will be painful especially for females if to be extended until the bosom/chest and might compromise breathing
Posterior sup border: level of the scapular spines
Thoracolumbar Corset - Function
Trunk Stabilization
Dec loading on vertebrae and discs
May restrict motion: FELR
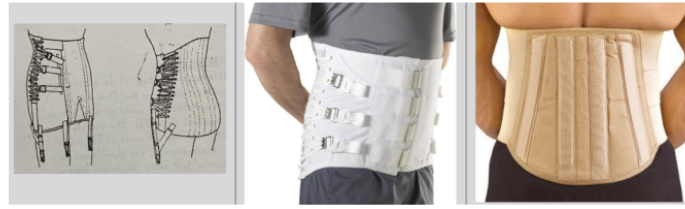
Identify this orthosis
Lumbosacral corset

Identify this orthosis
Thoracolumbar Corset
Rigid Spinal Orthosis - Effecting in elevating _______ pressure
intraabdominal pressure
Issues in lower spine may tend to be affected by
gravity; adds to pain
Rigid spinal orthosis - Can lessen pain for about __ folds as compared to flexible spinal orthosis
5 fold
True/False: Rigid spinal orthosis may modify skeletal alignment
True; but not entirely corrected - need a lot of treatment not just orthosis
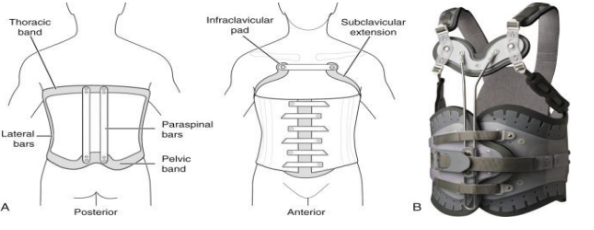
Identify Parts
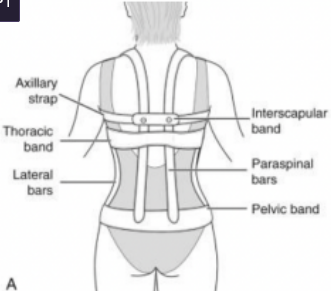
Identify parts

Rigid Spinal Orthosis Components - Pelvic Band
level of greater trochanters, above the inferior edge of the sacrum below the PSIS
Rigid component made of metal or aluminum
Rigid Spinal Orthosis Components - Thoracic Band
Sup border: T9-T10 (below the inf angle) 2.5 cm
Rigid Spinal Orthosis Components - Anterior Extensions of Thoracic band with subclavicular band
curving around pec. Major, ends just below the clavicle and lat to deltopectoral groove; 5.1 cm in diameter
Rigid component for those exceeding the lumbar spine
Rigid Spinal Orthosis Components - Lumbosacral and Thoracolumbosacral posterior uprights
Sup border: Scapular spine/
Inf angle / Inf border: inferior edge of the pelvic band
Placed along the paraspinal muscles and must avoid bony prominence
Rigid Spinal Orthosis Components - Lateral uprights
ends at the edge of the thoracic and pelvic bands
Restricts lateral movements
Rigid Spinal Orthosis Components - Oblique lateral uprights
obliquely placed on both thoracic and pelvic bands
Restricts rotational movements
Rigid Spinal Orthosis Components - Interscapular band
crosses the distal 3rd of the scapulae
When orthosis extends beyond the lumbar spine
Holds posterior uprights together and limits friction during scapular movements
Rigid Spinal Orthosis Components - Full-front abdominal support
Placed on the abdomen
Restricts flexion when tight
L-S FE Control is AKA
Chairback orthosis
Chairback orthosis limits:
Slightly limits lateral flexion and rotation since it doesn’t have lateral uprights; only has posterior upright and abdominal support
LS FEL Control is AKA
Knight brace
Chairback vs Knight brace
knight brace has lateral uprights
Knight brace limits what movements?
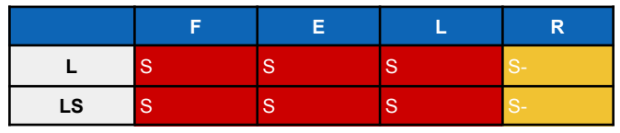
LS EL Control is AKA
William
William limits?
Limits extension and lateral motion but encourages flexion; reduces lumbar lordosis
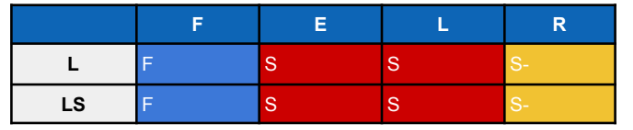

Identify this Orthosis
Chairback Orthosis

Identify this Orthosis
Knight Brace

Identify this Orthosis
Wiliiam
TLSO FE control is AKA
Taylor
Taylor limits what movements?
Limits the trunk extension, primarily in the mid-to-lower
thoracic and upper lumbar areas with a compensatory
increase in motion at the upper thoracic, lower lumbar, and
lumbosacral junction
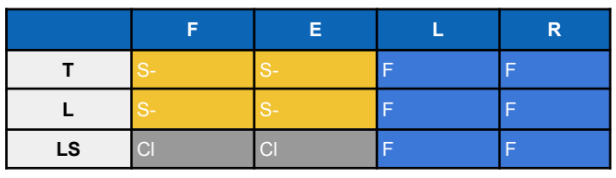
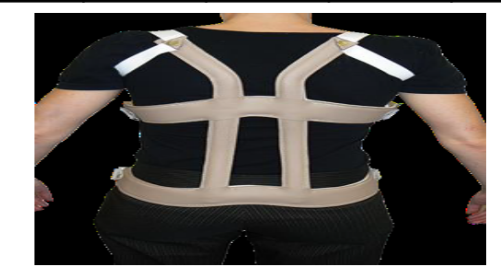
Identify this Orthosis
Taylor

Identify this orthosis
Knight-Taylor
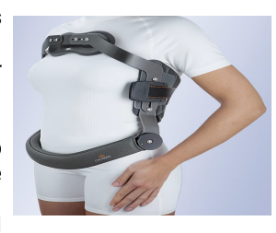
Identify this Orthosis
Cowhorn
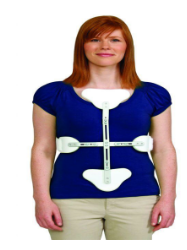
Identify this Orthosis
anterior hyperextension/Jewett brace
Identify this orthosis
cash-cruciform anterior spinal hyperextension
TLSO FEL Control is AKA
Knight-Taylor
Knight-Taylor limits what movements?
Addition of lateral uprights in an attempt to limit lateral trunk motion
Lumbosacral segment - may increase flex/ext depending on how the orthosis is made
TLSO FLR is AKA
Cowhorn
Cowhorn limit what movements?
Will not limit ext on thoracic area d/t thoracic band stopping below the scapular spine; it has to go higher if you want to limit thoracic extension
Ext in LS greatly limited d/t thoracic and pelvic band
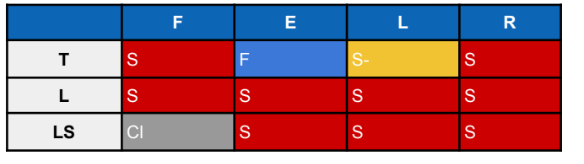
TLSO F Control is AKA
Anterior hyperextension / Jewett brace
True/False: Jewett only limits extension
False; Flexion
Jewett brace tends to _____ spine
hyperextend spine to avoid kyphosis; promote extension posture
Cash-Cruciform Anterior Spinal Hyperextension vs Jewett
Jewett will provide much of the restriction however, there are some forms of inconvenience.
Cash will provide restrictions on the flexion movement and is more comfortable for the patient but is recommended for pts who has a much more stable spine (orthopedic specialists will tell PT)
Identify this Orthosis
Plastic Body Jacket

TLSO Plastic Body Jacket limits what movements?
maximum immobilization
TLSO Plastic Body Jacket is for?
Recommended for pts c severe destabilization of the spine or severe immovability of spine (pts who underwent motor vehicular accidents, spinal fractures)
Cervical Orthosis - Usually used for soft-tissue injury or arthritic changes
FE Control
Cervical FE Control - Basic Collar
Provides sensorium
Not totally restricts movement
Cervical FE Control - Rigid Collar
Has some forms of restriction of movement
Pressure ulcer formation is a potential complication of rigid collar use
Fragile or insensate skin is particularly vulnerable to ulceration.
Common areas susceptible to damage are the occipital protuberance, mental protuberance of the mandible (chin), clavicles, and ears
Shearing forces can arise due to facial hair and skin sliding over the collar surface, or from positional changes
Philadelphia Collar has a _____ component compared to a basic collar
Chin component
Philadelphia Collar - Hole in the collar
pts who underwent neck surgery
less irritation
Philadelphia Collar - purpose
for short-term use
For pre-hospital emergency stabilization
does not provide significant mechanical immobilization in unstable cervical spine and may be ineffective in preventing displacement
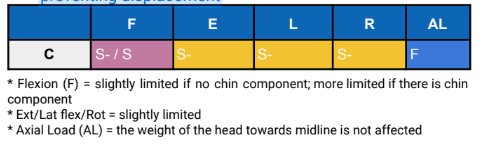
Cervical - FER Control is AKA
SOMI - Sterno Occipital Mandibular Immobilizer
Cervical FER Control Features
Presence of uprights
Good restriction for cervical flexion
Since this device lacks posterior thoracic support it cannot limit extension
The longer it is, the more it will provide axial load and approximate the chin.
The mandibular support can be removed/lowered for eating, etc
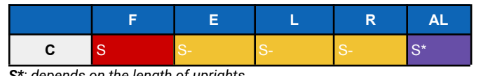
Uses of cervical FER Control
May be an appropriate option for bedridden patients since
it lacks posterior thoracic coverage
Because the SOMI limits flexion it may be used in cases of atlantoaxial instability with an intact dens, such as in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and in C2 neural arch fractures
FER Control - No Mandibular Support
Used primarily for eating but not definitive for treatment
Indicated for pts who does not have concerns with axial loading
Not for pts with severe neck injuries
Cervical - FELR Control is AKA
Post Appliance / Four Poster
Four Poster - Features
Restricts all four movements, with flexion & extension being more limited than lateral flexion & rotation
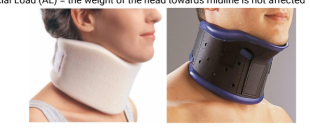
Identify this Orthosis
Basic Collar
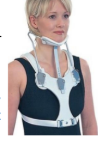
Identify this Orthosis
Cervical FER Control / SOMI
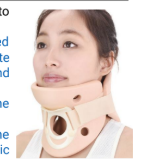
Identify this Orthosis
Philadelphia Collar
Custom Molded - Cuirass Orthosis - Features
Restricts all neck motions including some thoracic motions
Extends up to level of chest
Indicated for severe cervical injuries
Custom Molded - Minerva Orthosis - Features
Restricts all neck motions including some thoracic motions
Indicated for much more severe cervical injuries concerning mobility e.g. high cervical cord injuries
Extends up to mid-level of thoracic area up to cervical area c forehead support
Permanent use
aka CTO (Cervical thoracic Orthosis)
Custom Molded-Halo Orthosis - Features
Restricts all neck motions including some thoracic motions
Indicated for acute injuries but not permanent use (only to accommodate healing) before changing to more permanent orthosis such as Minerva.
aka CTO (Cervical thoracic Orthosis)
Halo Orthosis has been used postoperatively as an adjunct to?
to internal fixation for upper cervical and mid-cervical fractures and dislocations and as the primary method for conservative fracture stabilization
Advantages of Halo Orthosis
Provides immediate cervical spinal stability in
patients sustaining an acute fracture or subluxation
○ Nonsurgical alternative for patients refusing operative
care or for whom surgical intervention is
contraindicated
○ Permits early mobilization without risk of
compromising spinal alignment
Precautions for the halo vest:
limit the patient’s shoulder abduction to 90 degrees and avoid shoulder shrugging.
In general, ample space should exist between the shoulders and the shoulder vest straps to prevent excessive distraction forces on the cervical spine.
When this space is reduced, the shoulders press against the straps and changes in forces are created.
Care must be taken not to lift, turn, or move the patient by pulling on the plastic vest, the rods, or the superstructure. External forces applied to these areas could affect the spinal alignment and loosen pins.
True/False: Halo Orthosis are not compatible for X-ray
False
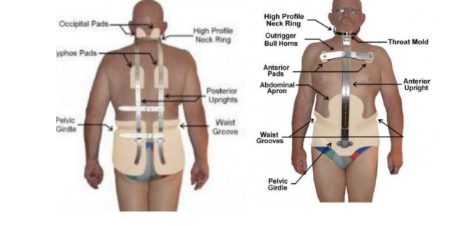
Scoliosis - TLS is AKA
Boston
Boston Orthosis is used for?
Used for mid-thoracic or lower scoliosis curves of 40° or less
As high as T6
Common TLSO for S type or double curve
Open side area is for concave side;covered contralateral side for convex
Also used to treat spondylolisthesis and conditions of
severe trunk weakness (muscular dystrophy)
Scoliosis - CTLS is AKA
Milwaukee Orthosis
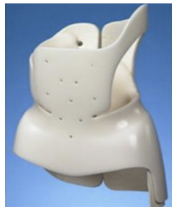
Milwaukee is used for?
Maybe used for all kyphotic and scoliotic curves of 40 deg or less
Used for scoliosis management that provides control of
flexion, extension, and lateral bending of the cervical,
thoracic, and lumbar spine.
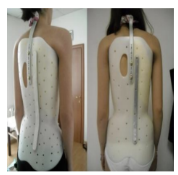
Wilmington Orthosis
Presence of posterior uprights
T10-T12
The TLSO low-profile scoliosis orthoses provide dynamic action using three principles (end-point control, transverse loading, and curve correction) to prevent curve progression and to stabilize the spine.
Pediatric Orthosis - Standing Frame
Consists of broad base, posterior non articulated uprights extending from a flat base to a mid torso chest band, a posterior thoracolumbar band
Training upright position and only permits standing with knees straight
For children and adults

Pediatric Orthosis - Swivel Walker
Similar to standing frame
Base has two distal plates that rock slightly to enable swiveling gait
A swivel walker is a modification of the parapodium that translates trunk rotation into forward movement of a dual footplate mechanism

Pediatric Orthosis - Parapodium
Differs from the standing frame by virtue of joints that permit the wearer to bend the knee to sit
Children with myelodysplasia
Articulated
For children only (school use)
