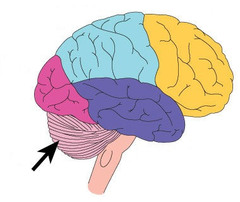
Senses and limbic system
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/105
Last updated 8:28 PM on 11/8/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
1
New cards
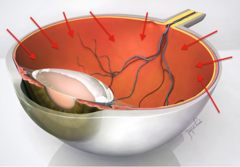
The internal cavity of the eye is filled with fluids called
humors
2
New cards
Lens separates internal cavity into (_______) and (_______) segments
anterior(aqueous) and posterior(vitreous)
3
New cards
function of sclera
White of the eye, protects the eye and anchors extrinsic muscles
4
New cards
Function of cornea
Transparent, central anterior portion, helps to focus light entering the eye
5
New cards
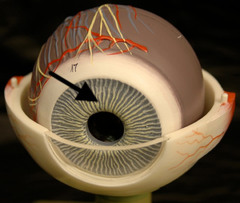
Iris
-colored part of eye that contains the pupil
-regulates the amount of light entering the eye
-regulates the amount of light entering the eye
6
New cards
pupil description
central opening of the iris
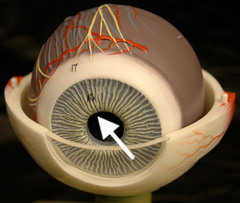
7
New cards
function of pupil
regulates the amount of light entering the eye along with the iris
8
New cards
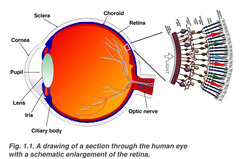
retina
light-sensitive tissue lining the back of the eyeball; contains photoreceptors (rods and cones)
9
New cards
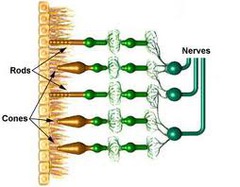
2 types of photoreceptors in the retina
rods and cones
10
New cards
Rods
dim light and peripheral vision receptors, found towards edges of the retina
11
New cards
Cones
bright light and detailed color, densest in the center of the retina (macula)
12
New cards
macula
-central section of the retina
- has high concentration of cones
- most detailed vision
- has high concentration of cones
- most detailed vision
13
New cards
Lens divides the eye into _____chambers, ________ and _______
2, anterior(aqueous) & posterior(vitreous)
14
New cards
aqueous humor
the clear fluid filling the space in the front of the eyeball between the lens and the cornea.
supplies oxygen and nutrients to lens and cornea
supplies oxygen and nutrients to lens and cornea
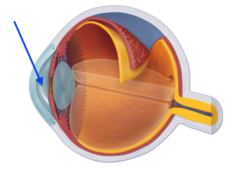
15
New cards
vitreous humor
soft, jelly-like material behind the lens in the vitreous chamber; helps maintain the shape of the eyeball
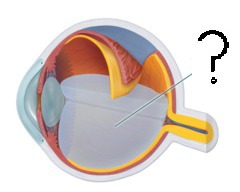
16
New cards
Lens
transparent, flexible, structure that allows precise focusing of light onto the retina
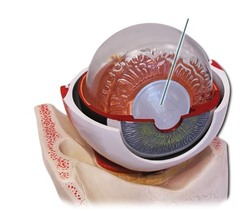
17
New cards
Vision pathway
cornea, pupil (through iris), lens, vitreous humor, retina (rods and cones), optic nerve, thalamus, visual cortex (occipital lobe)
18
New cards
Cornea and Lens are responsible for...
focusing images on the retina
19
New cards
Three disorders associated with the cornea or shape of the eye
Astigmatism
Myopia (nearsightedness)
Hyperopia (farsightedness)
Myopia (nearsightedness)
Hyperopia (farsightedness)
20
New cards
difference between myopia and hyperopia
myopia- focal point in front of retina (nearsighted)
hyperopia- focal point behind retina (farsighted)
hyperopia- focal point behind retina (farsighted)
21
New cards
3 sections of the ear
external, middle, internal
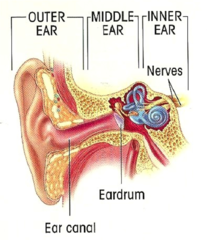
22
New cards
The inner ear functions in both
hearing and equilibrium
23
New cards
semicircular canals
three fluid-filled canals in the inner ear responsible for our sense of dynamic balance (rotational movement)

24
New cards
endolymph
fluid responsible for movement in cochlea and semicircular canals
25
New cards
Receptors in the semicircular canals respond to
Dynamic movements of the head (rotation)
26
New cards
Receptors in the vestibule respond to
Static equilibrium (head position in relation to gravity)
Which way is up / down
Which way is up / down
27
New cards
Hearing pathway external ear
Auricle, ear canal, tympanic membrane
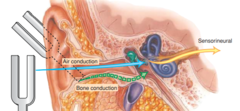
28
New cards
Hearing pathway middle ear
Tympanic membrane, ossicles (malleus, incus, stapes), oval window of the cochlea
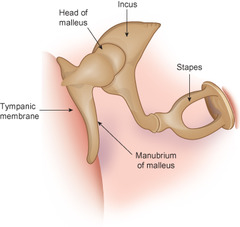
29
New cards
Hearing pathway inner ear
Oval window, cochlea (endolymph mores hair cells), vestibulocochlear nerve
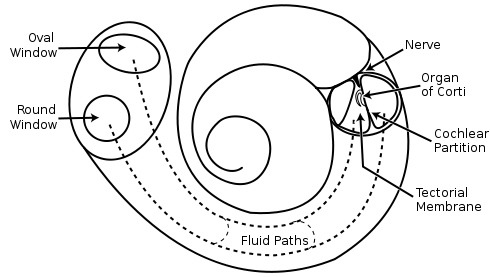
30
New cards
special senses include
taste, smell, sight, hearing, and equilibrium
31
New cards
myopia
nearsightedness
distant objects appear blurry
light is focused in front of the retina
abnormal curve of the cornea or the shape of the eye
distant objects appear blurry
light is focused in front of the retina
abnormal curve of the cornea or the shape of the eye
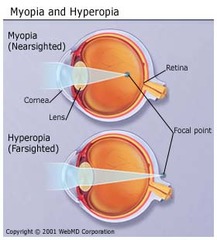
32
New cards
hyperopia
farsightedness
close objects appear blurry
light is focused behind the retina
abnormal curve of the cornea or the shape of the eye
close objects appear blurry
light is focused behind the retina
abnormal curve of the cornea or the shape of the eye
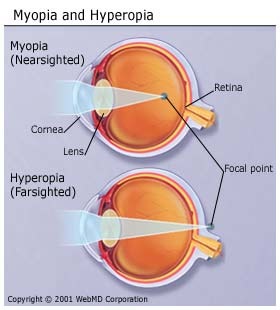
33
New cards
astigmatism
a condition in which the eye does not focus properly near or far
abnormal curve of the cornea or the shape of the eye
abnormal curve of the cornea or the shape of the eye
34
New cards
earwax glands
ceruminous glands
modified apocrine glands
modified apocrine glands
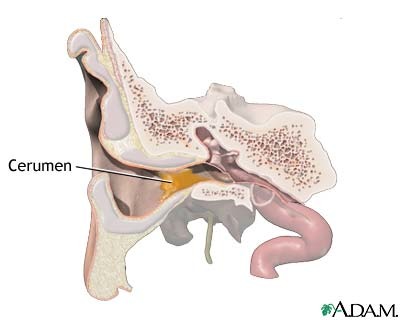
35
New cards
tympanic membrane
Eardrum.
vibrates in response to sound waves.
transfers vibrations between the external and middle ear.
vibrates in response to sound waves.
transfers vibrations between the external and middle ear.
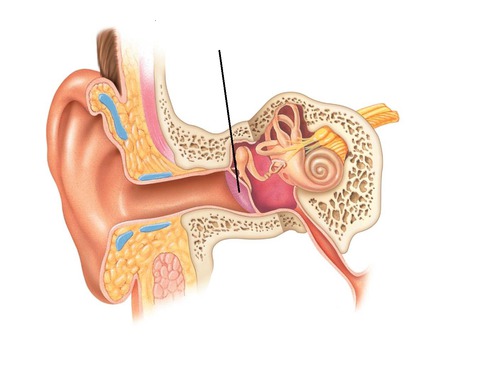
36
New cards
Middle ear cavity functions
Transmit vibrations from tympanic membrane to the fluids of the inner ear. Vibrations travel from the hammer to anvil to stirrup to the oval window
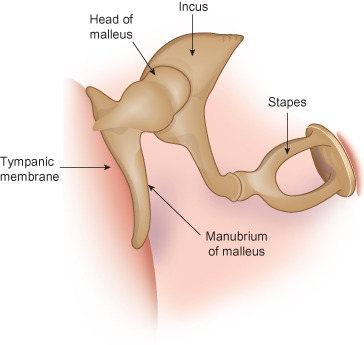
37
New cards
eustachian tube (auditory tube)
tube connecting the middle ear to the pharynx (throat)
equalizes pressure and drains fluid
equalizes pressure and drains fluid
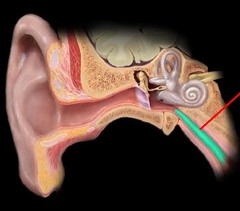
38
New cards
Ossicle bones
malleus (hammer), incus (anvil), stapes (stirrup)
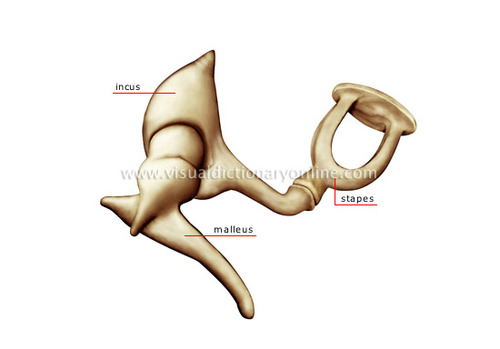
39
New cards
Chemorecptors
receptors for taste and smell
40
New cards
Olfactory receptors are located
roof of nasal cavity
41
New cards
gustatory cells are
taste receptors (inside taste buds) that respond to chemicals dissolved in saliva and have long hair that protrude through a taste pore.
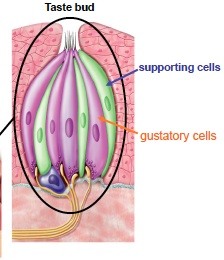
42
New cards
5 basic taste sensations
1. Sweet: sugars, alcohol, some amino acids, some lead salts
2. Sour: hydrogen ions in solution
3. Salty: metal ions
4. Bitter: alkaloids just as coffee and nicotine
5. Umami: amino acids glutamate and aspartate (beefy taste of meat)
2. Sour: hydrogen ions in solution
3. Salty: metal ions
4. Bitter: alkaloids just as coffee and nicotine
5. Umami: amino acids glutamate and aspartate (beefy taste of meat)
43
New cards
Cataracts
Vision disorder resulting from the loss of lens transparency
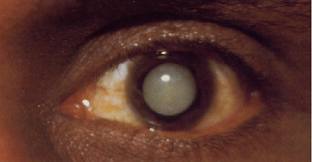
44
New cards
Somatic Senses
involve receptors from more than one place in the body general senses
45
New cards
mechanoreceptors
hearing, balance and touch
46
New cards
chemoreceptors
smell and taste
47
New cards
capsaicin stimulates
heat receptors
48
New cards
What is olfaction and where does it occur?
smelling
occurs in the upper chambers of the nasal passage
occurs in the upper chambers of the nasal passage
49
New cards
olfaction - sensory receptors respond to what?
chemical dissolved in the mucus of the nasal cavity
50
New cards
olfaction - when a receptor binds its specific odor molecule, where is a sensory impulse sent?
Olfactory bulb, olfactory tract, olfactory cortex and limbic system
51
New cards
What explains why smells trigger memories and emotions?
neural connections between the olfactory bulb and the limbic system
52
New cards
gustation
sense of taste
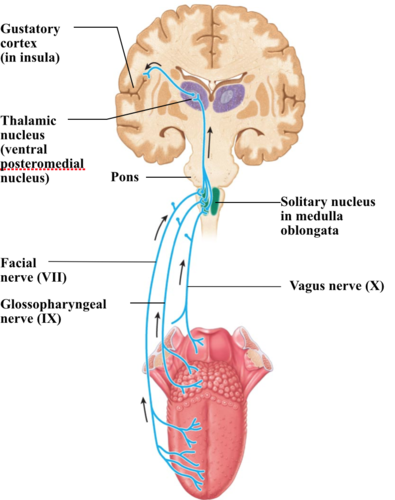
53
New cards
What five categories of taste can taste buds distinguish?
sweet
sour
salty
bitter
umami (savory)
sour
salty
bitter
umami (savory)
54
New cards
What are the three functional parts of the ear?
outer ear
middle ear
inner ear
middle ear
inner ear
55
New cards
outer ear
composed of the pinna and external auditory canal, both of which capture sound waves and funnel them into the middle ear
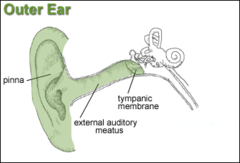
56
New cards
What happens in the inner ear?
the oval window bounces in response to movement of the stapes, creating fluid waves in the cochlea
57
New cards
dynamic equilibrium (rotational equilibrium)
semicircular canals detect acceleration or deceleration of your head in three directions
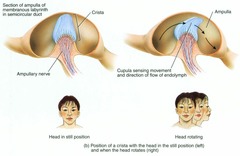
58
New cards
static equilibrium (gravitational equilibrium)
physical response to gravity that tells us which direction is down
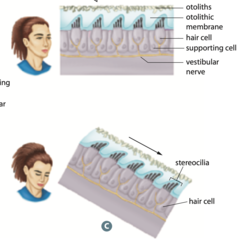
59
New cards
structure that detects static equilibrium
vestibule
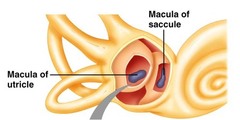
60
New cards
sclera
white of the eye
provides shape and protects inner parts
provides shape and protects inner parts
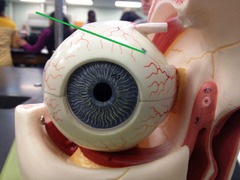
61
New cards
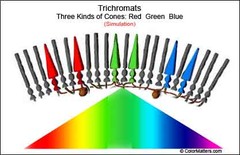
There are three types of cones, each sensitive to a different wavelength of light. What are the colors of light of these wavelengths?
red
green
blue
green
blue
62
New cards
When light enters the eye, what does the iris do?
muscles in the iris adjust the size of the pupil to let in more or less light
63
New cards
Olfaction
The sense of smell
64
New cards
Cerebral Cortex
Outer layer of the cerebrum where information is processed
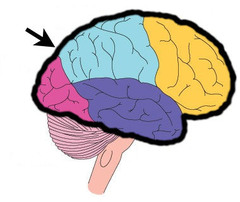
65
New cards
Auricle picture
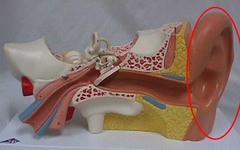
66
New cards
Tympanic Membrane picture
(vibrates)
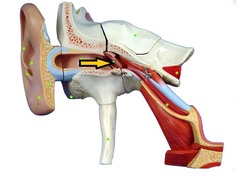
67
New cards
Malleus picture
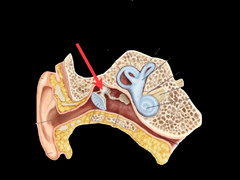
68
New cards
Incus picture
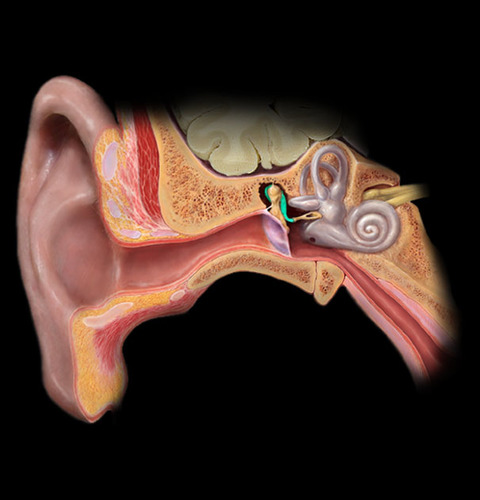
69
New cards
Stapes picture
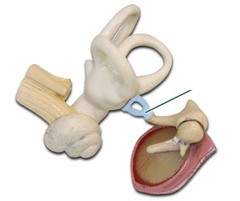
70
New cards
Vestibule picture
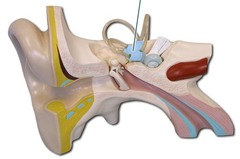
71
New cards
Cochlea picture
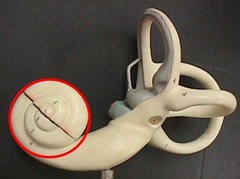
72
New cards
Eustachian tube (auditory tube) picture
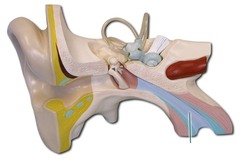
73
New cards
Vestibulocochlear Nerve picture
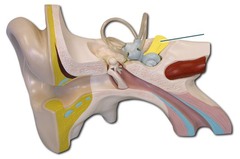
74
New cards
hair cells in cochlea
vibration of the endolymph causes them to bend and detect sound
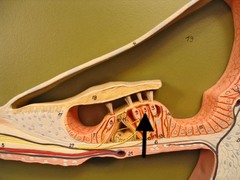
75
New cards
Optic Nerve picture
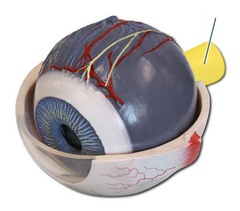
76
New cards
Aqueous Humor picture
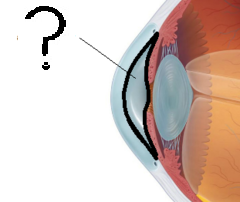
77
New cards
Vitreous Humor picture
(M)
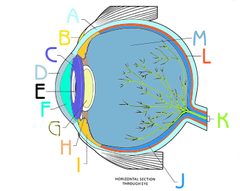
78
New cards
Pupil picture
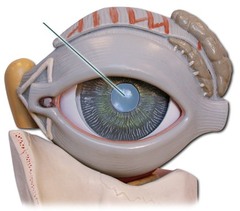
79
New cards
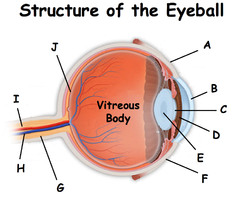
Lens picture
(E)
80
New cards
Iris picture
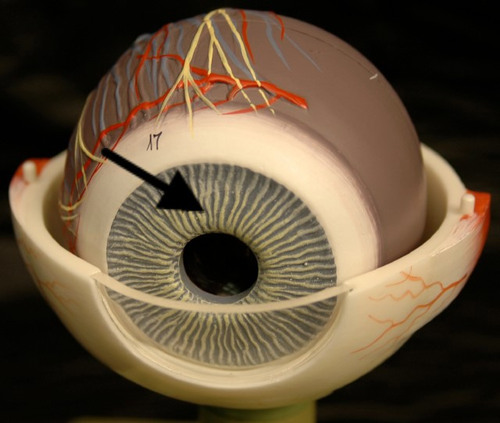
81
New cards
Cornea picture
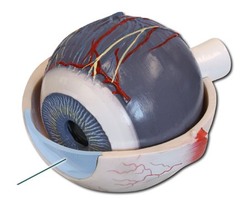
82
New cards
limbic system physiology
responsible for memory and emotion
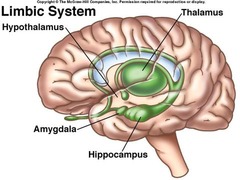
83
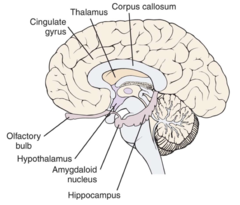
New cards
Limbic system structures
hippocampus, hypothalamus, amygdala, thalamus
84
New cards
Hippocampus
responsible for processing memory (E)
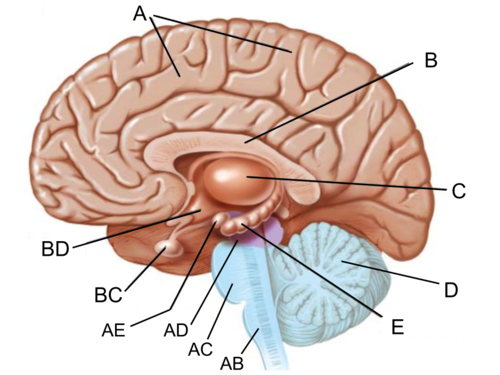
85
New cards
hippocampus picture
(E)
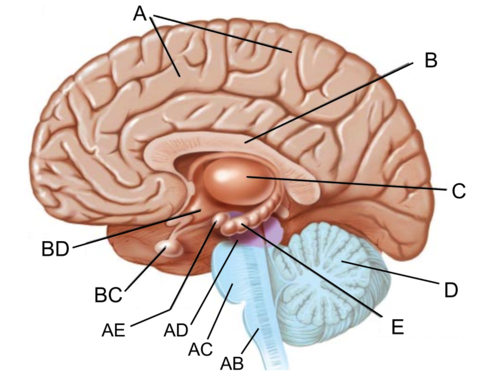
86
New cards
amygdala
responsible for fear responses and emotions (anxiety, fear, anger) (AE)
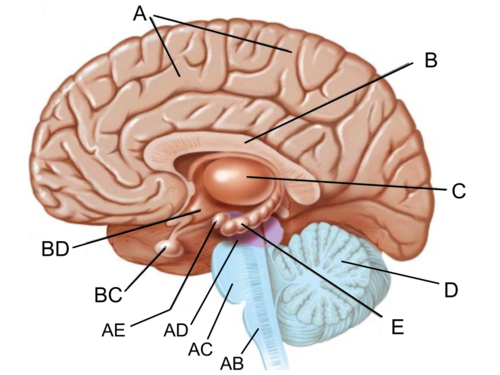
87
New cards
hypothalamus picture
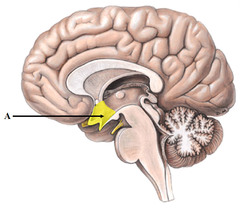
88
New cards
hypothalamus
responsible for maintaining homeostasis
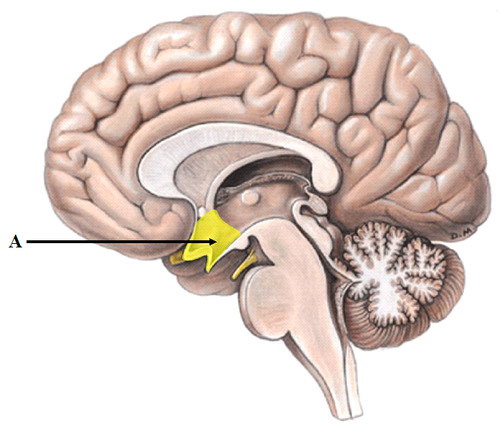
89
New cards
amygdala picture
(AE)
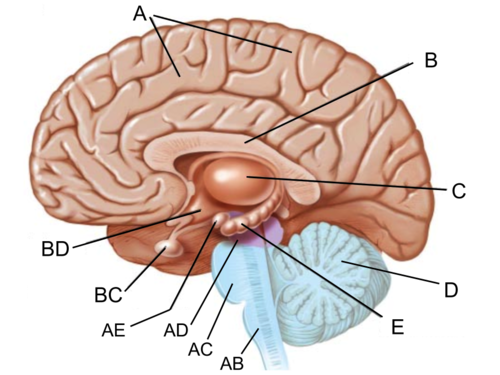
90
New cards
thalamus
the brain's sensory switchboard, located on top of the brainstem; relays information between lower brain areas and the cerebral cortex
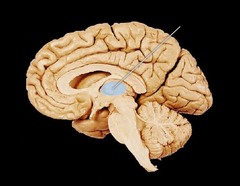
91
New cards
thalamus picture
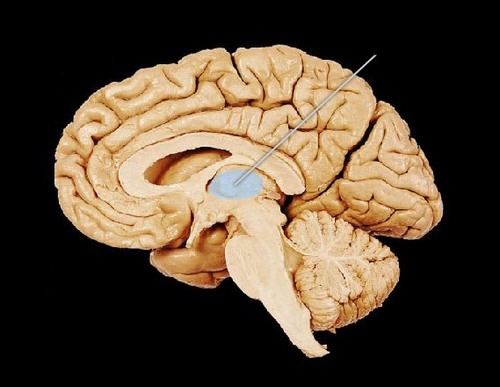
92
New cards
Conjunctivitis
inflammation or infection of the conjunctiva; pink eye
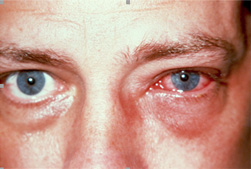
93
New cards
jaundice
yellowing of the skin and the whites of the eyes
can be a sign of problems with liver
can be a sign of problems with liver
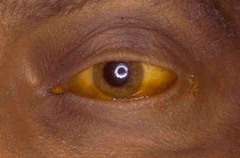
94
New cards
glaucoma
increased pressure due to aqueous humor not draining
can damage retina/ optic nerve
can damage retina/ optic nerve
95
New cards
colorblindness
lack of or dysfunction of cones
inability to see colors
genetic disorder more common in males
inability to see colors
genetic disorder more common in males
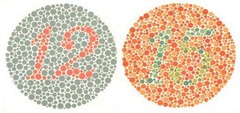
96
New cards
olfactory cortex
frontal and temporal lobes (smell)
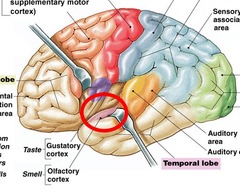
97
New cards
gustatory cortex
parietal lobe (taste)
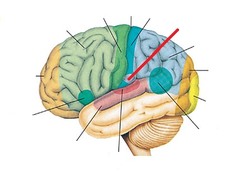
98
New cards
auditory cortex
temporal lobe (sound)
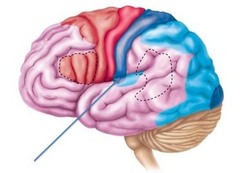
99
New cards
visual cortex
occipital lobe
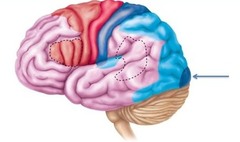
100
New cards
Cerebellum
the "little brain" at the rear of the brainstem
controls equilibrium and coordinated movement
controls equilibrium and coordinated movement