Final week 12 proprioception
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
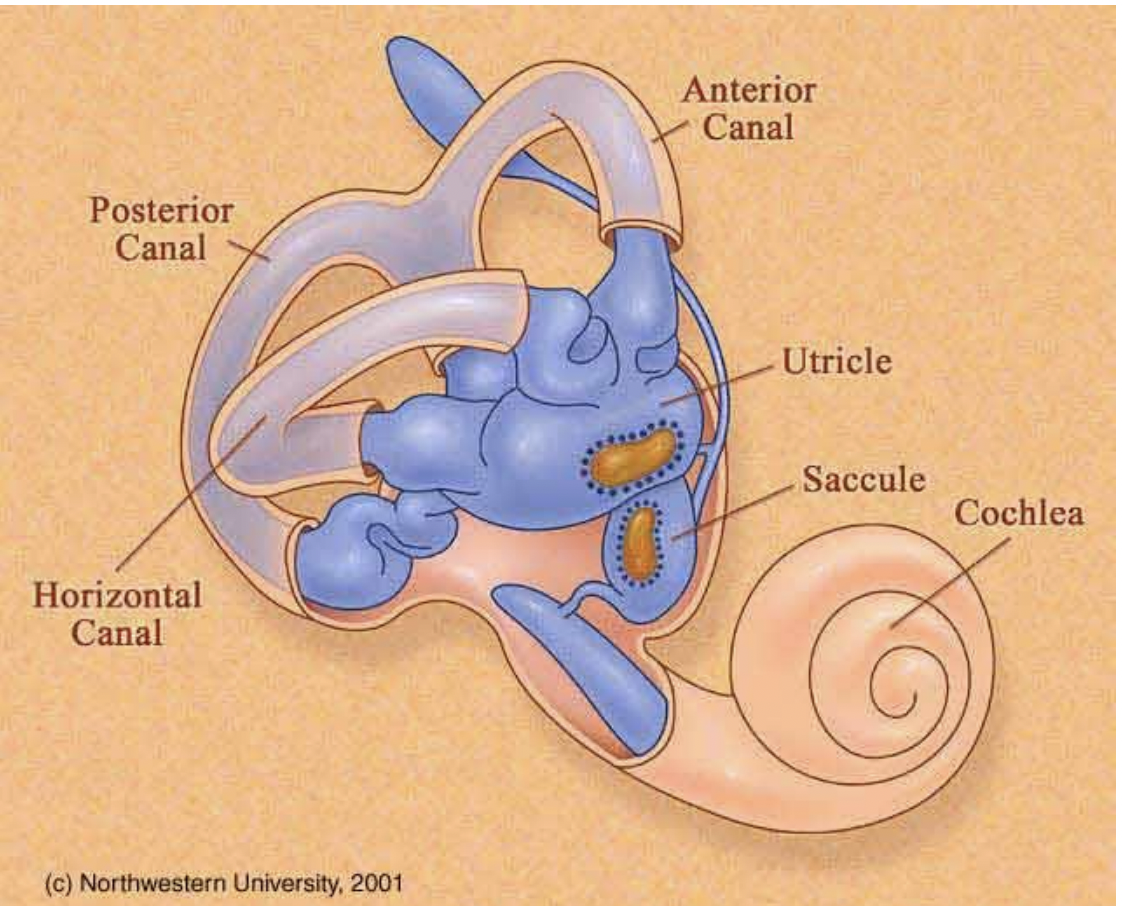
what is the Vestibular system made up of?
Made up of 5 organs: 3 semicircular canals and 2 otolith organs
what is this area?
vestibular system
what does the Vestibular system do?
Allows for the sense of spatial orientation by detecting:
Tilt
Angular motion
Linear motion
what reflect counterrotates our eyes to compensate for head movement?
Vestibulo-ocular reflex
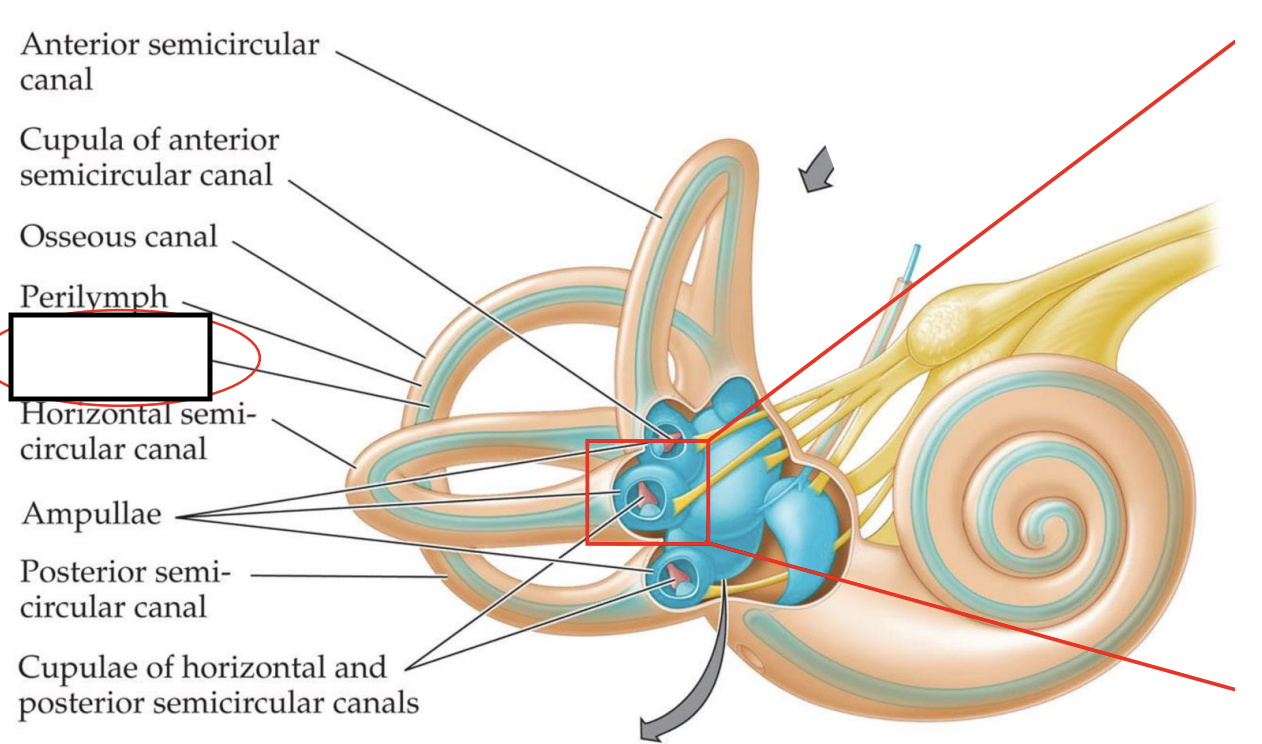
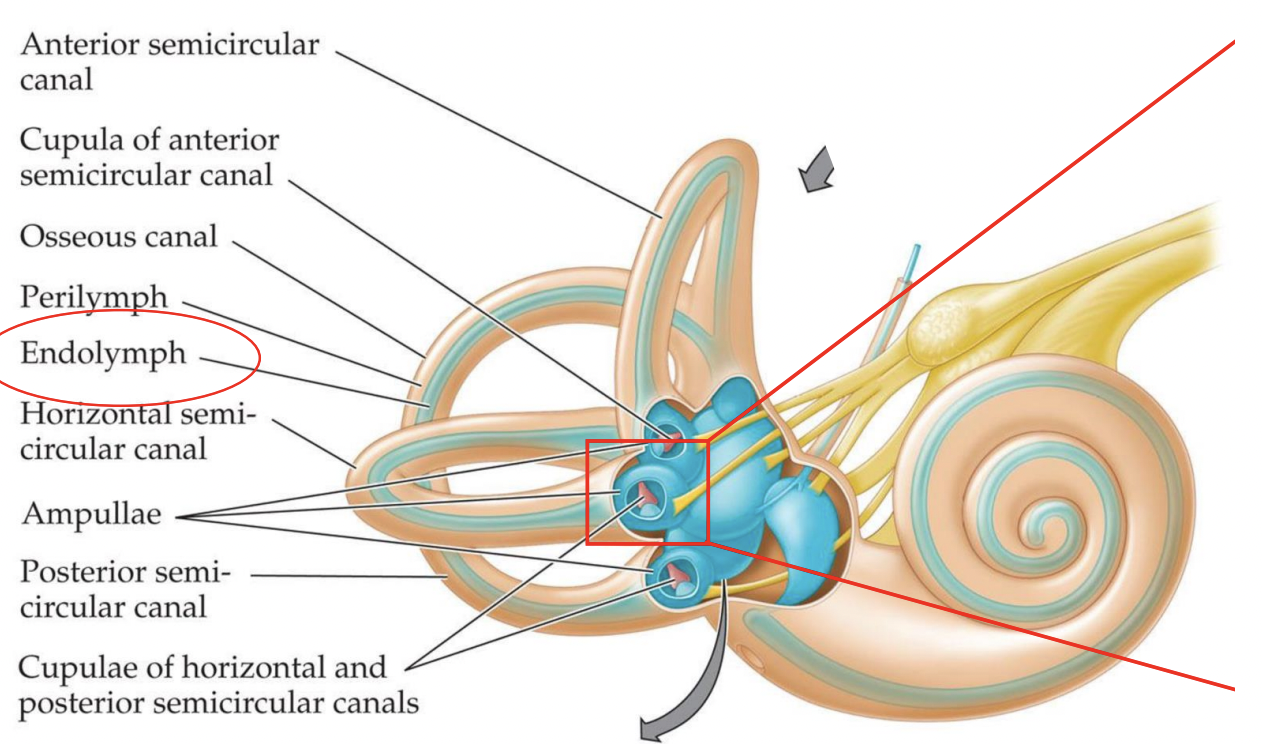
what is this inside the canals that is enriched in K+ ions?
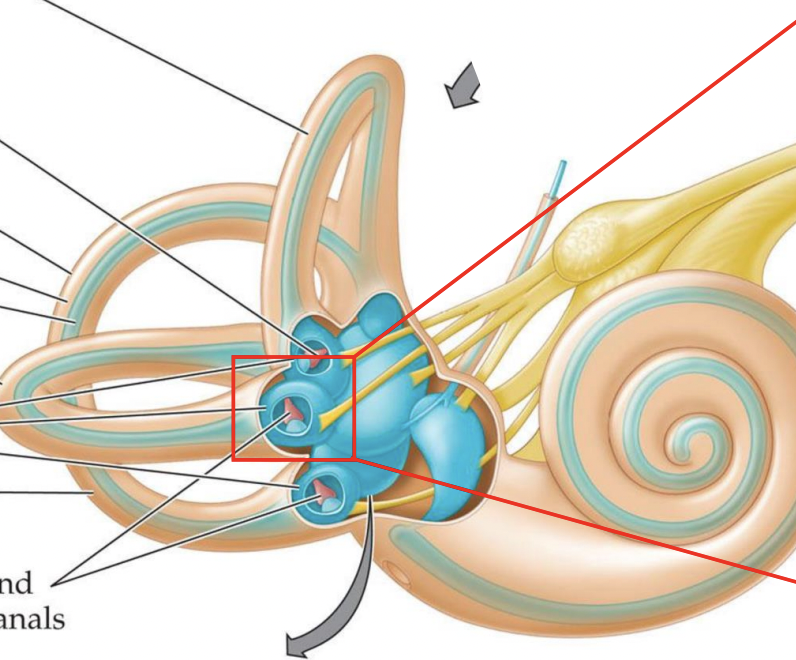
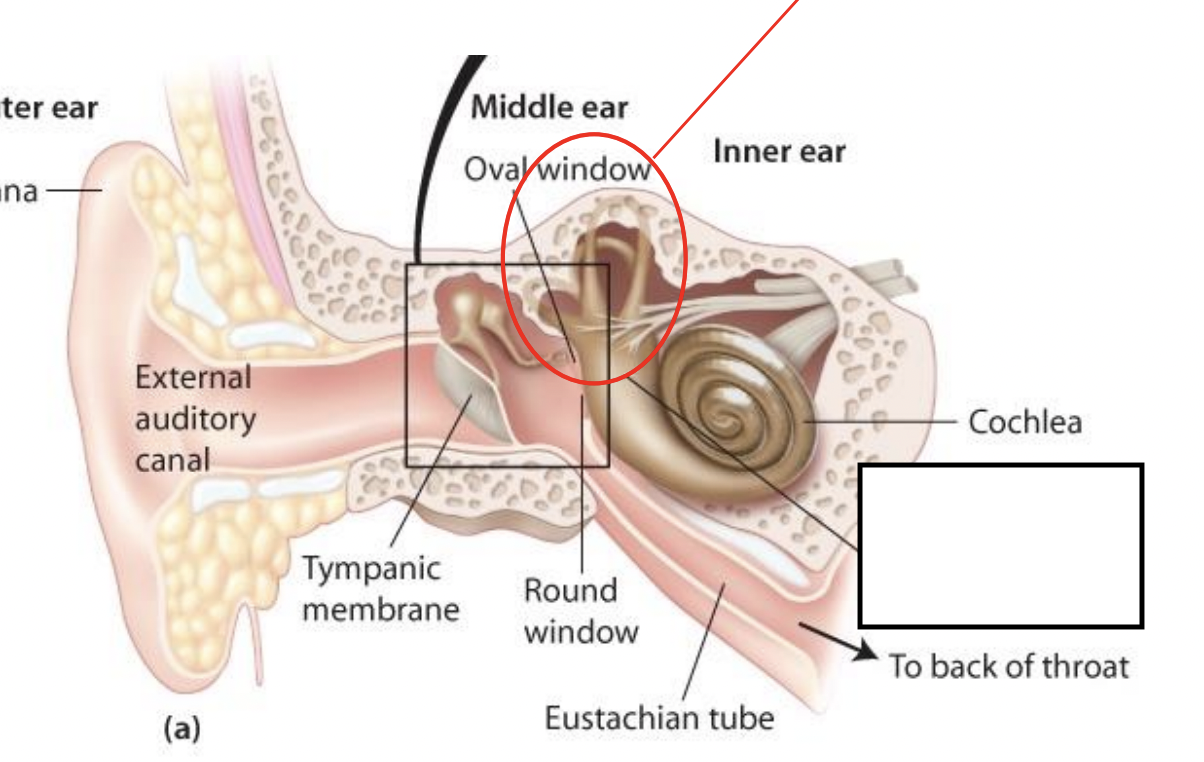
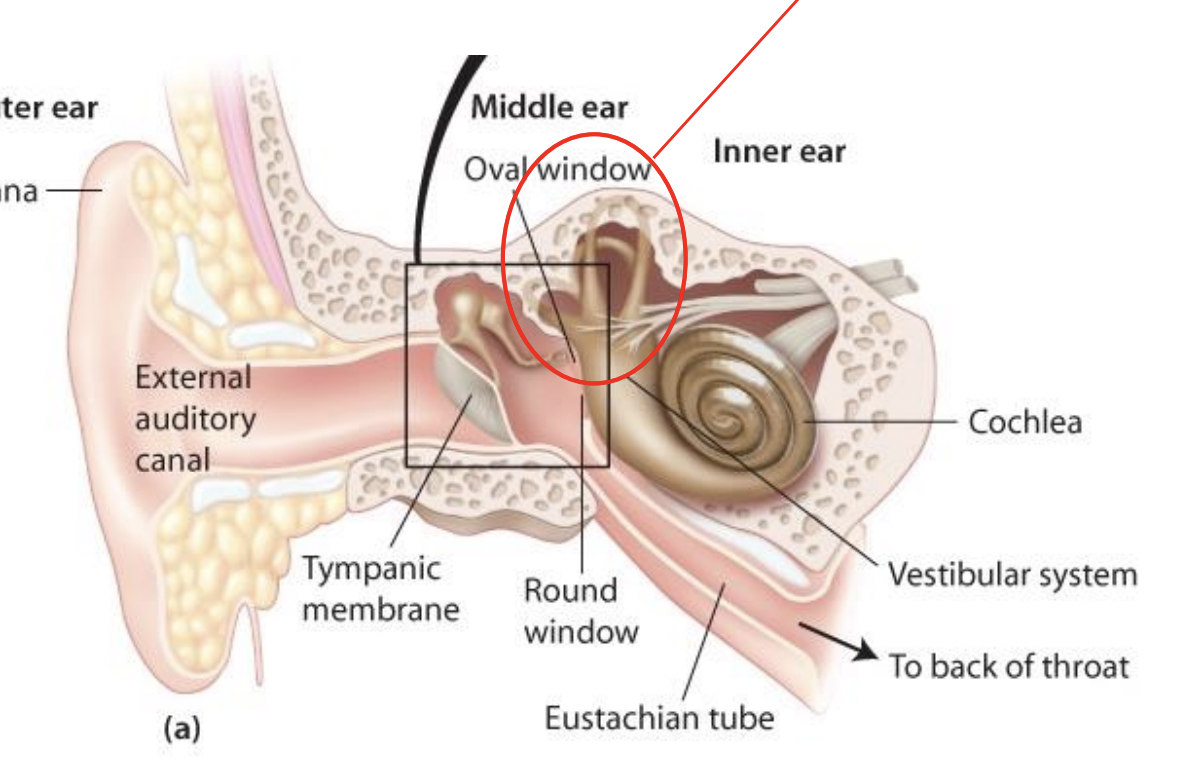
what’s in the box
The ampula
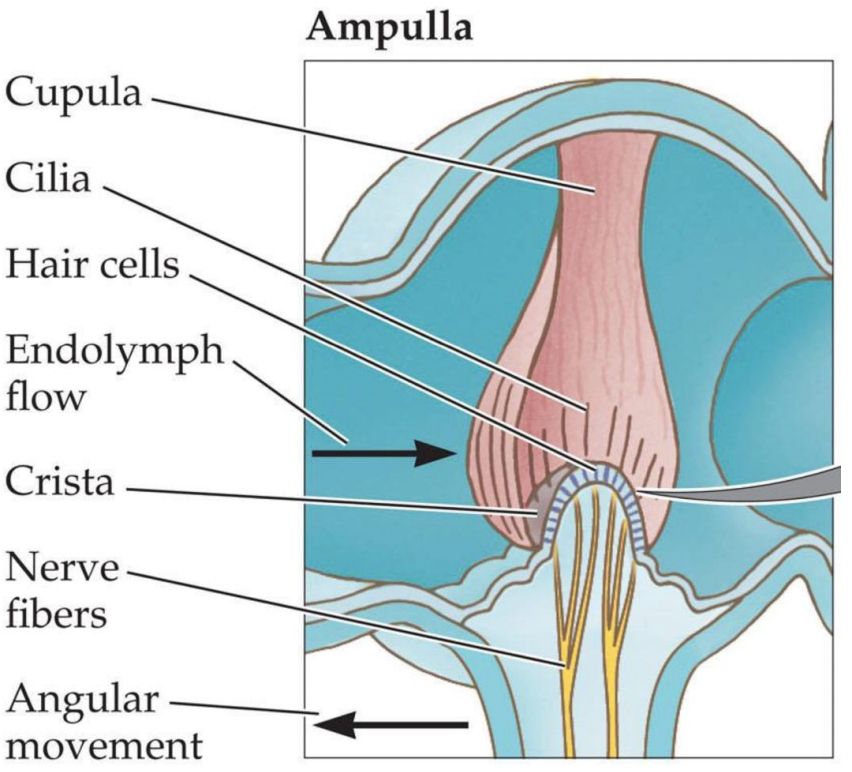
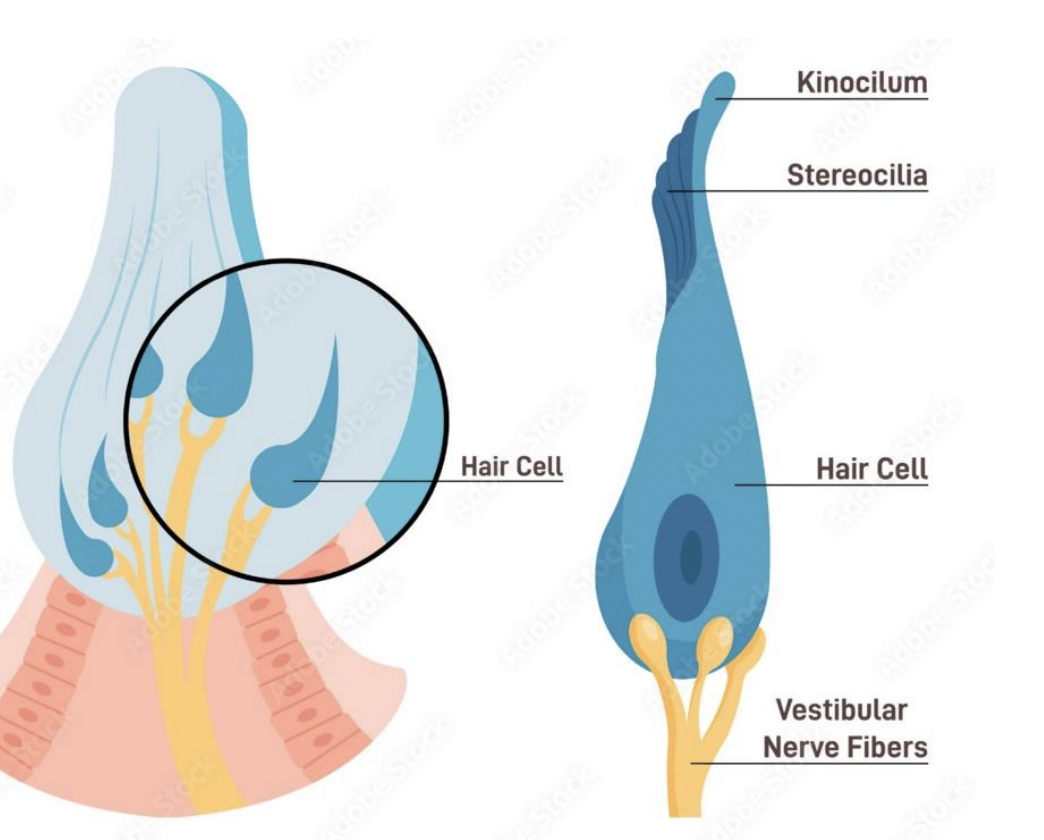
what are these in the Vestibular system
Vestibular mechanoreceptros!
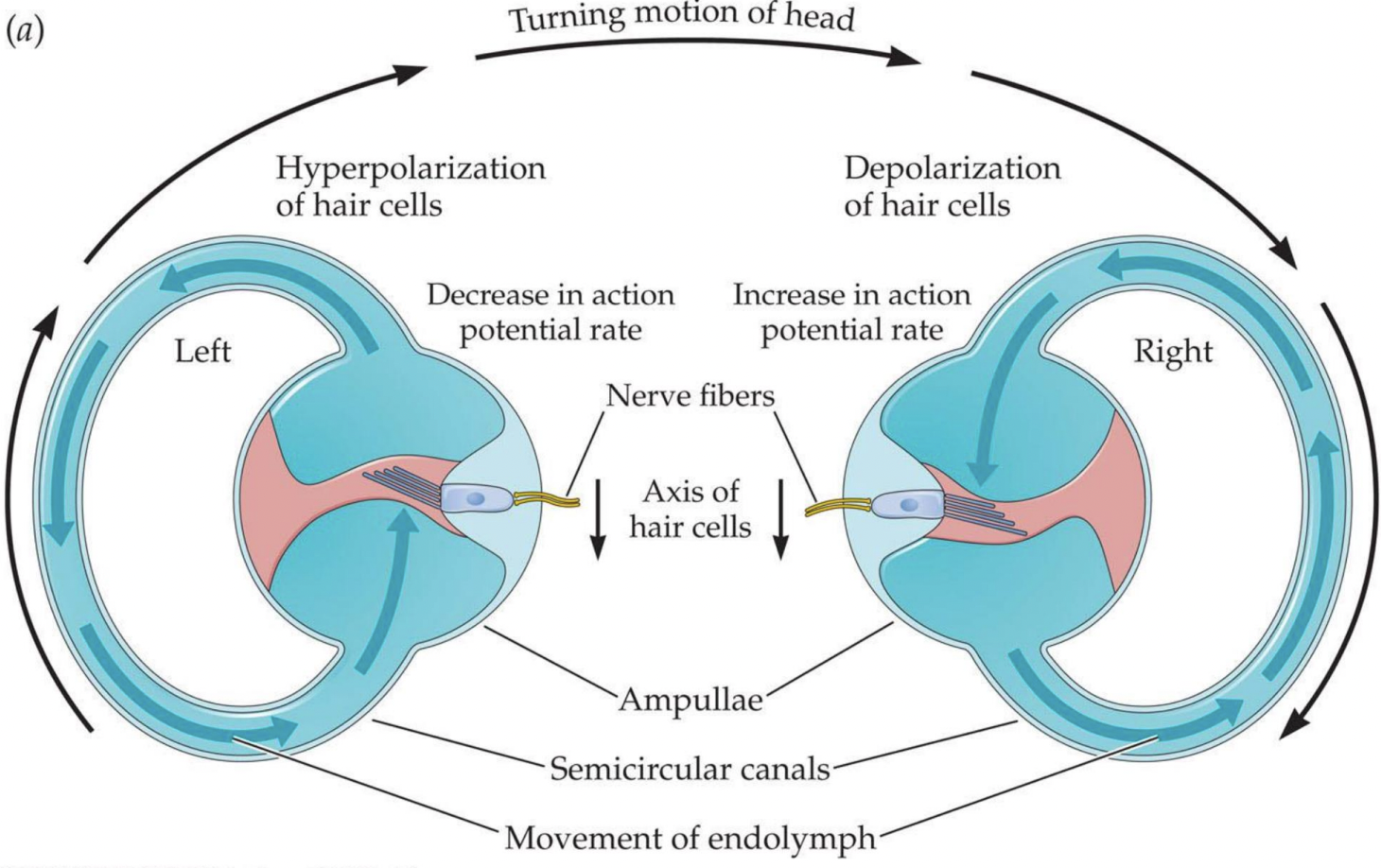
Hair cells in opposite ears respond to movement in what kind of fashion?
complementary fashion. try to understand diagram.
what do Otolith organs allow for?
sensation of linear acceleration, tilt, and gravity
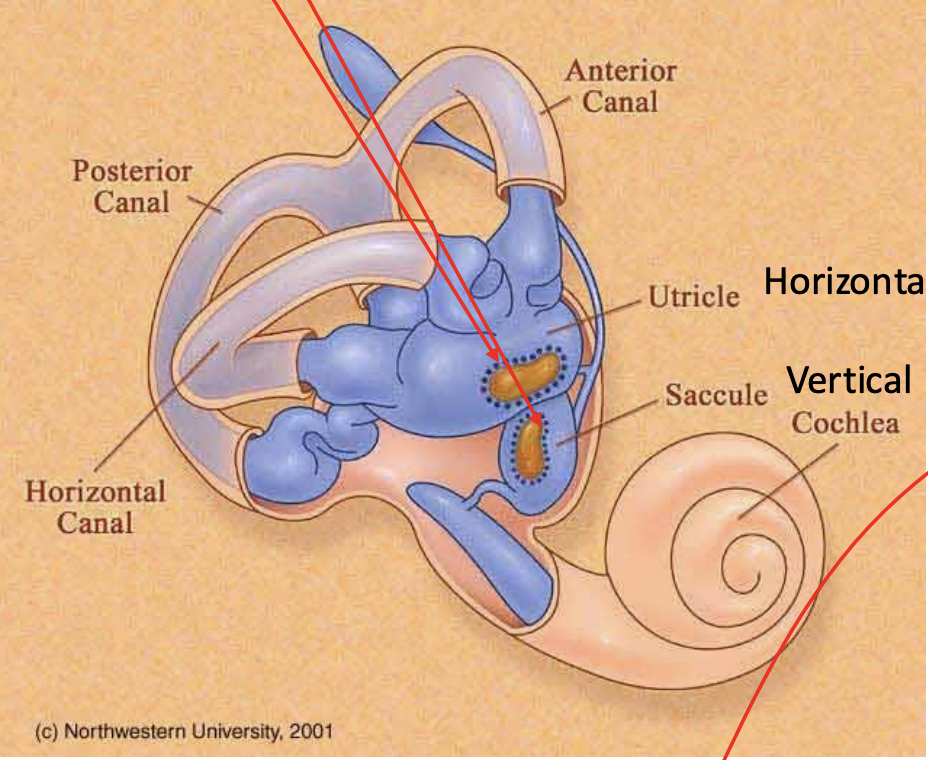
what are the arrows pointing to?
the otolith organs.
Detection of mostly planar, shearing forces occurs where/
macula
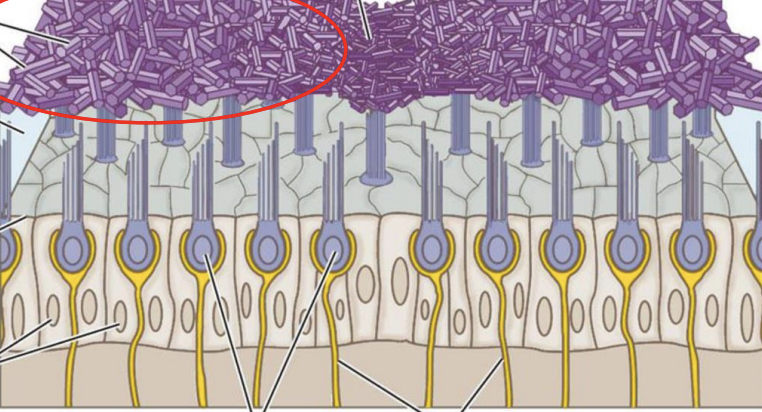
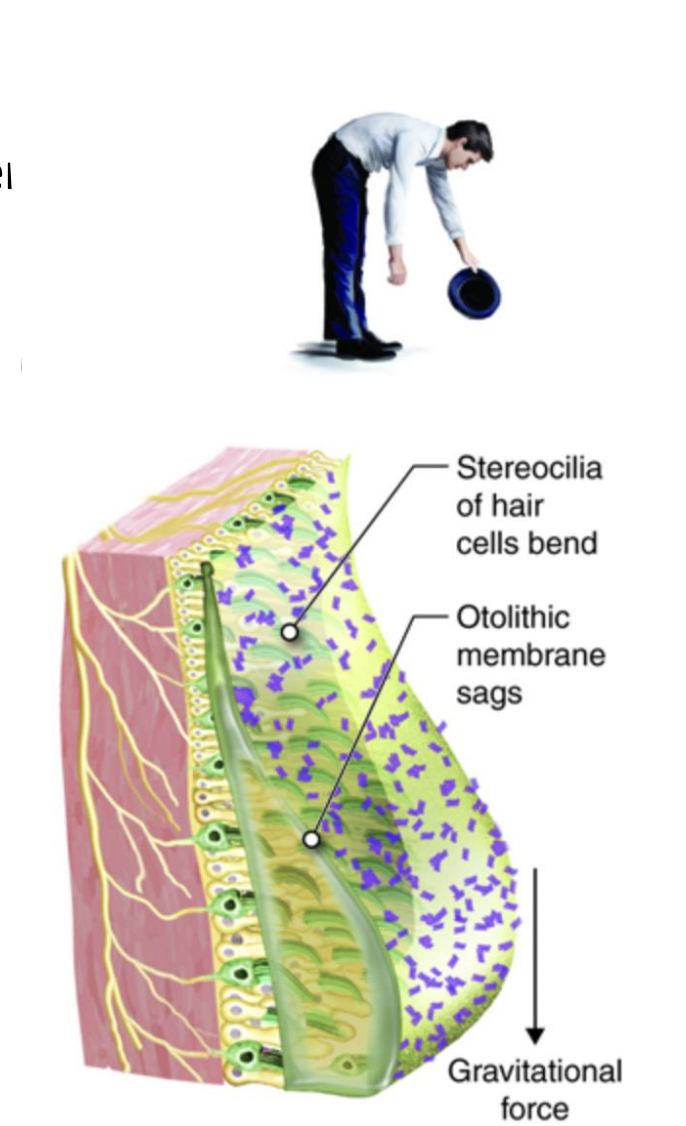
what are these on the otolith membrane and what do they do?
Calcium carbonate crystals – added weight to aid the otolithic membrane shift with static tilt… gravity!
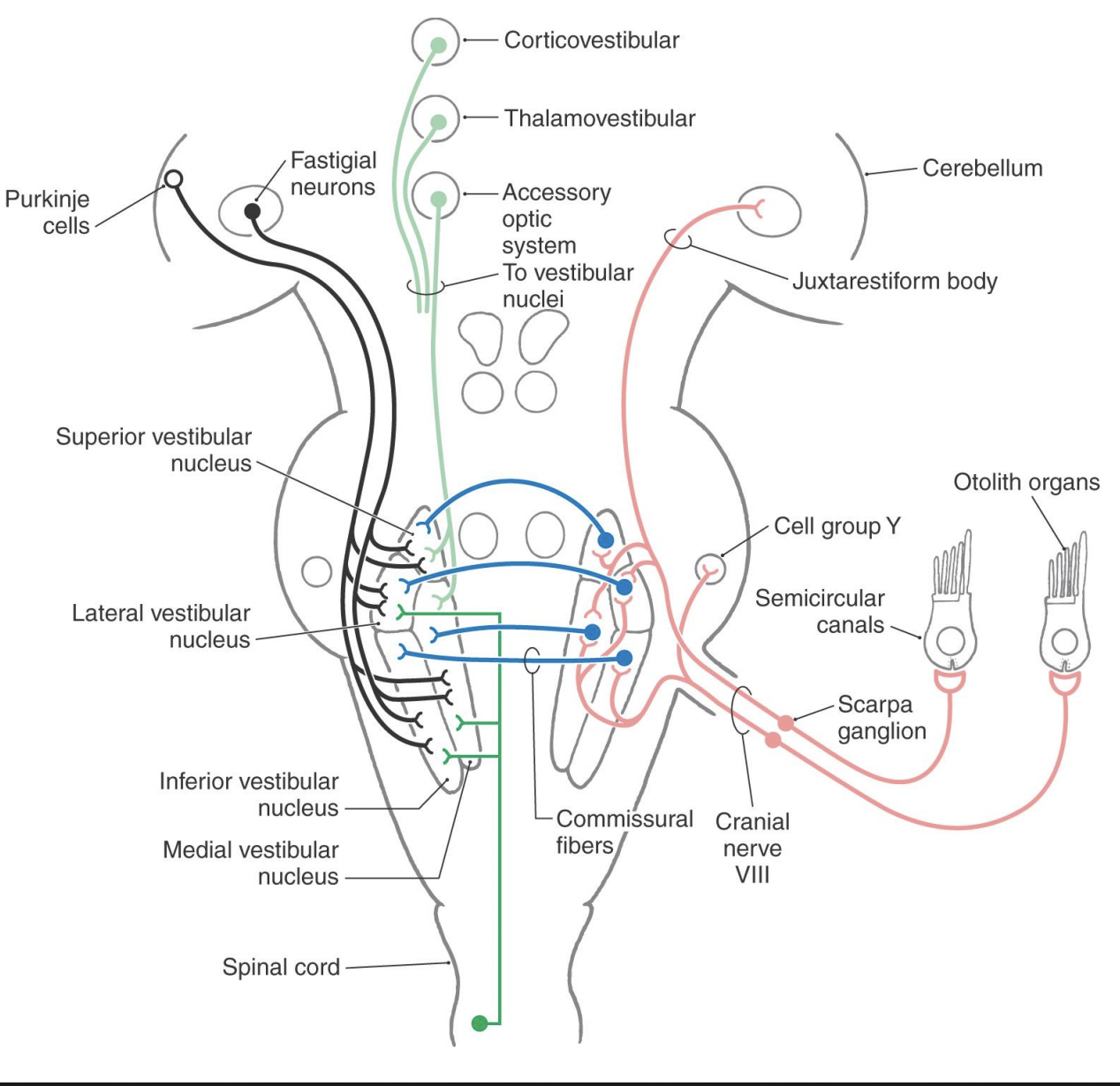
Ascending pathways project to multiple brain regions associated with various behaviors relying on vestibular information. what are some?
Vestibular system disease example
Ménière’s Disease: Build up of endolymph fluid in inner ear – affects vestibular AND auditory systems!
Symptoms include:
vertigo, tinnitus, loss or muffled hearing, loss of low frequency hearing, pressure, loss of balance
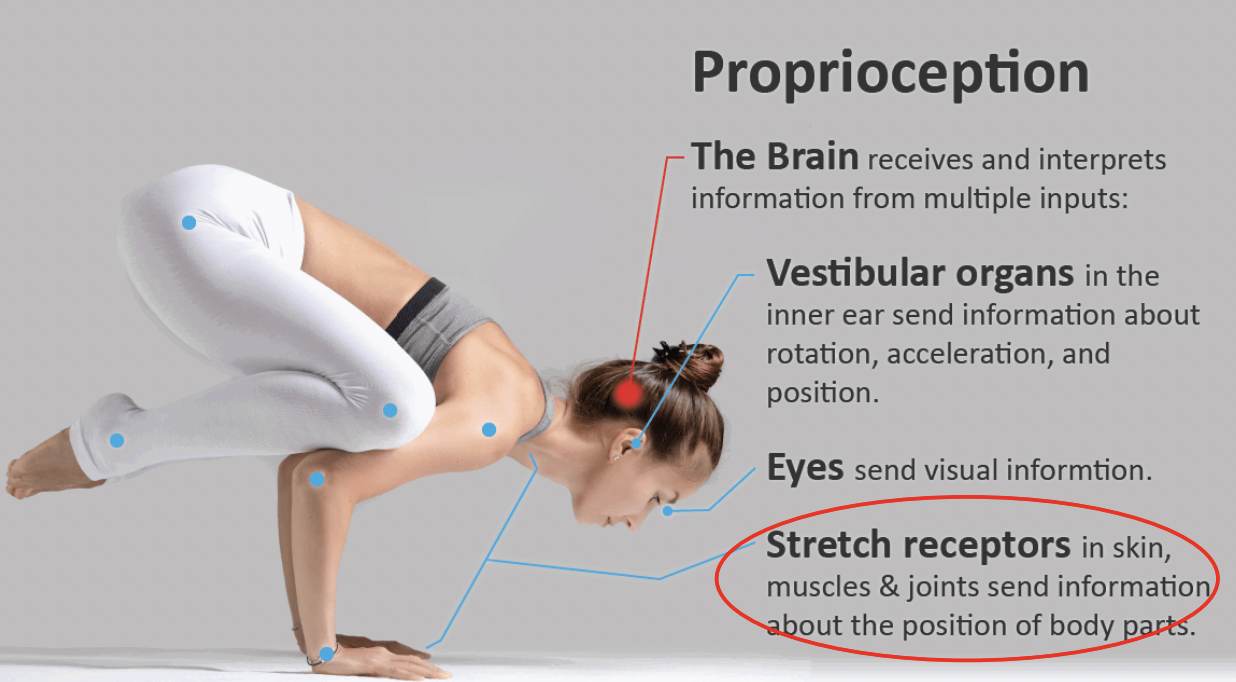
what is Musculoskeletal positioning?
Proprioceptive mechanism allowing for detection of body’s position and movement in space. (Sense of tension or force and of the effort exerted by acting muscles)
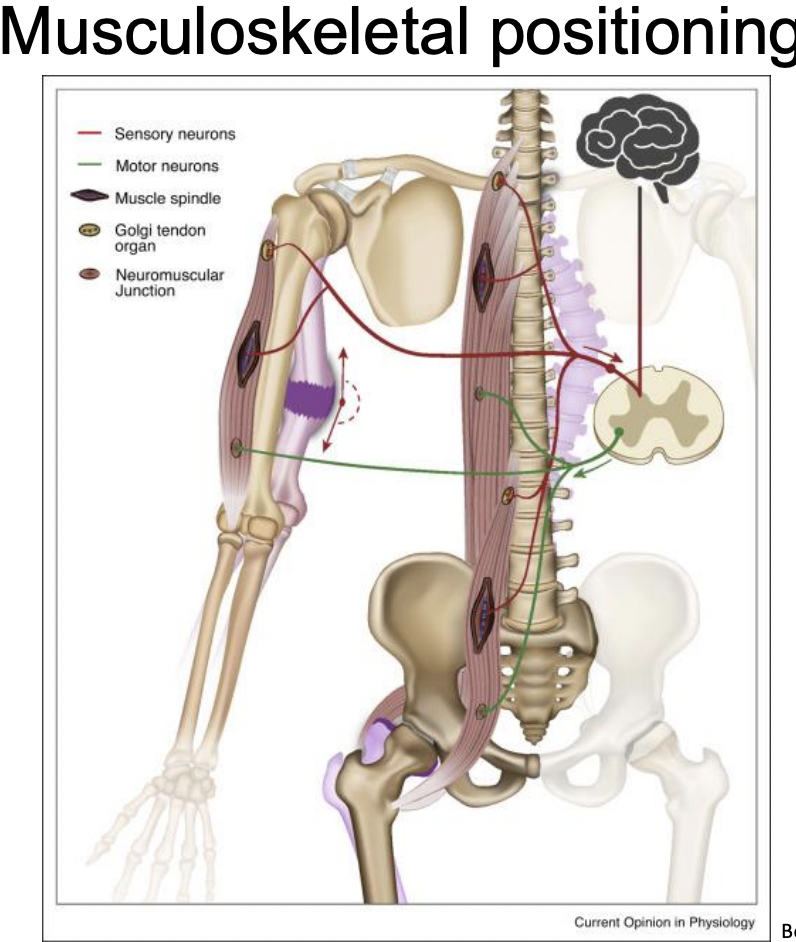
Maintaining balance requires what stimuli?
proprioceptive, vestibular, and visual stimuli!
How does the Nervous System (NS) know how much, or if a muscle is contracted or relaxed?
Stretch receptors
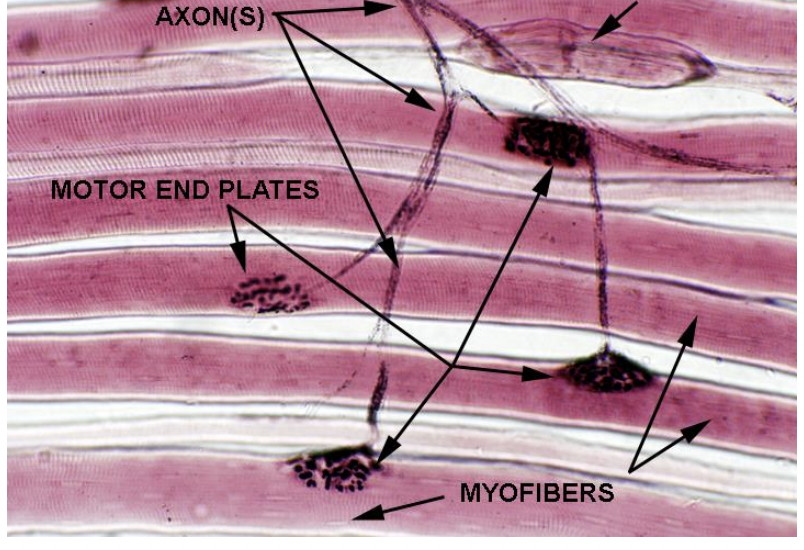
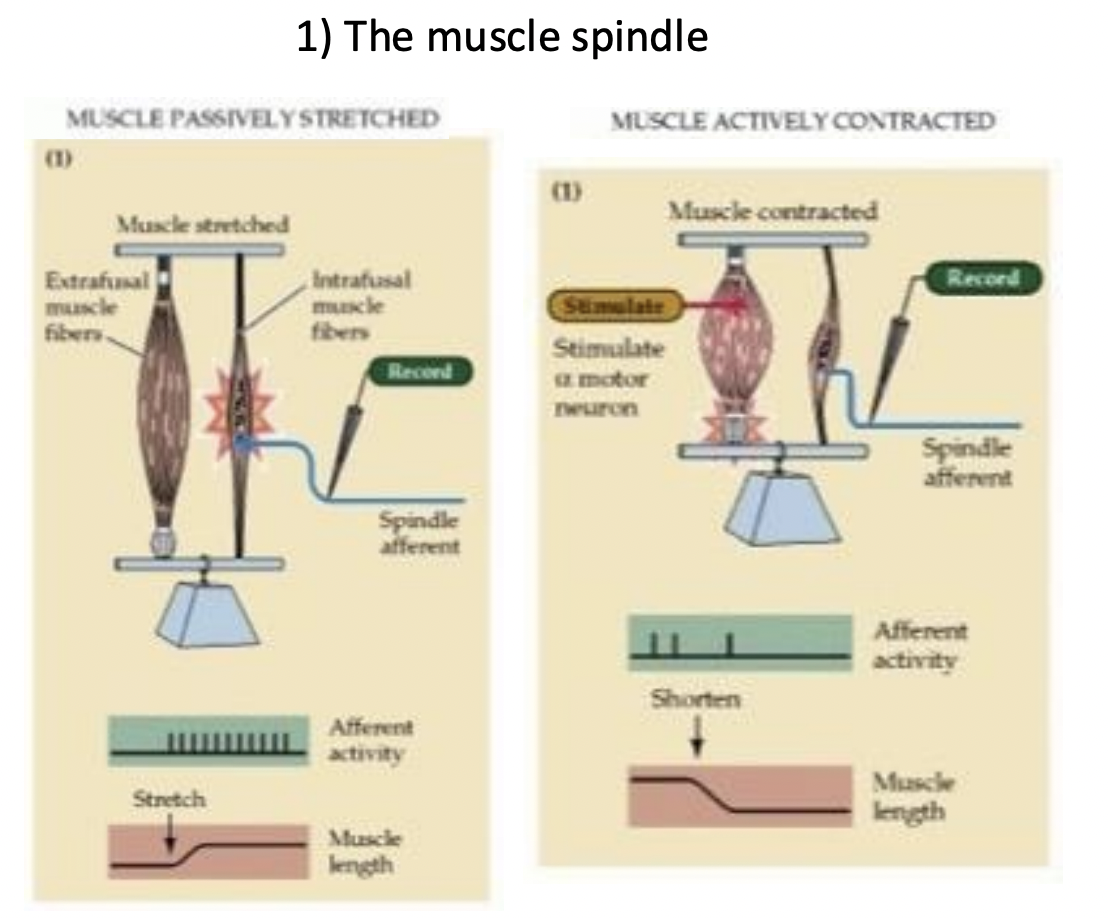
what is this? its used for Musculoskeletal positioning
muscle spindle
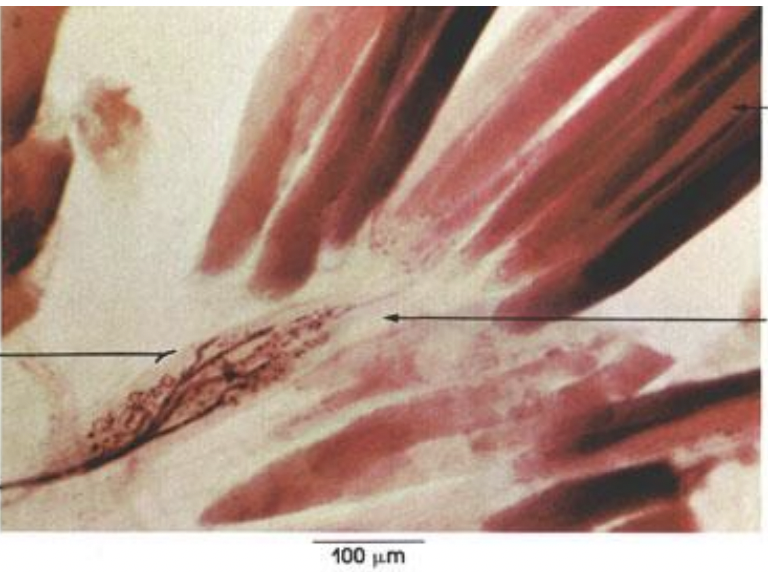
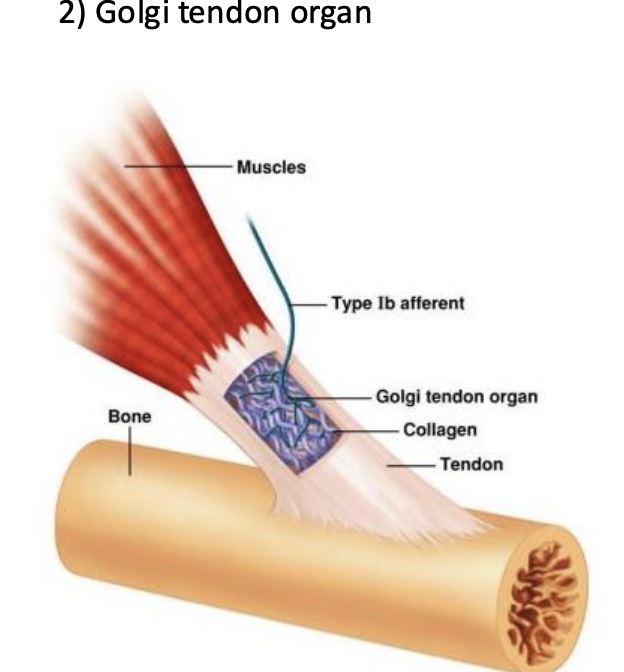
identify this. It is used for Musculoskeletal positioning.
Golgi tendon organ.GTO
what are GTO’s good at detecting?
GTOs are primarily sensitive to muscle tension rather than changes in muscle length
What do muscle spindles primarily detect?
changes in muscle length
what is the muscle spindle wrapped in?
The primary sensory organ.
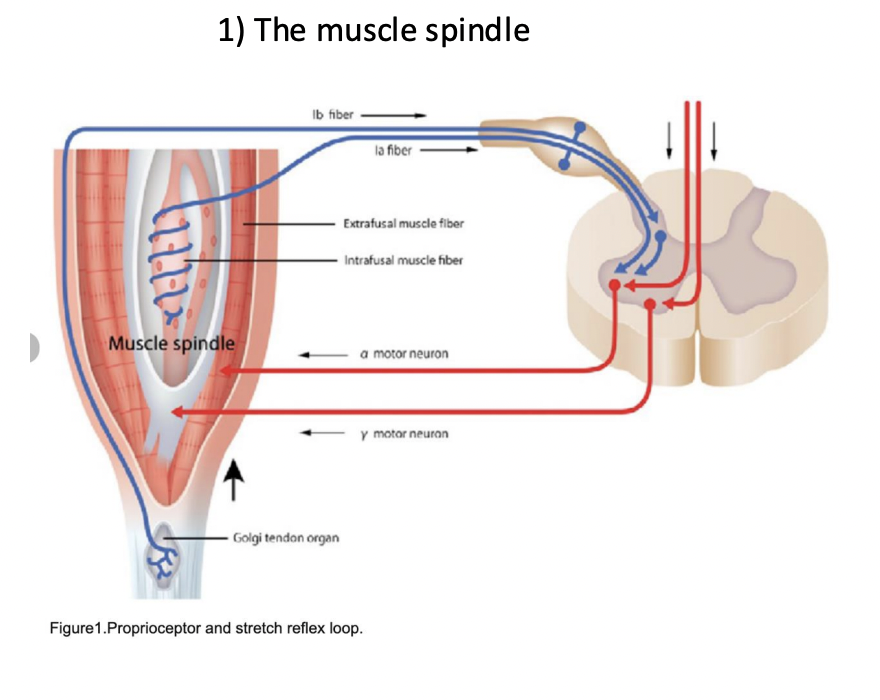
what do the muscle spindle and golgi tendon organ do?
tell your nervous system where your skeleton is
where does the GTO live and what does it detect?
lives in the connective tiisue between muscle and bone. and detects contractions.
when and why does the muscle spindle lose action potential?
When muscle contracts because it gets too lose?
what does the GTO measure exactly?
How squished the muscle gets, firing accordingly.
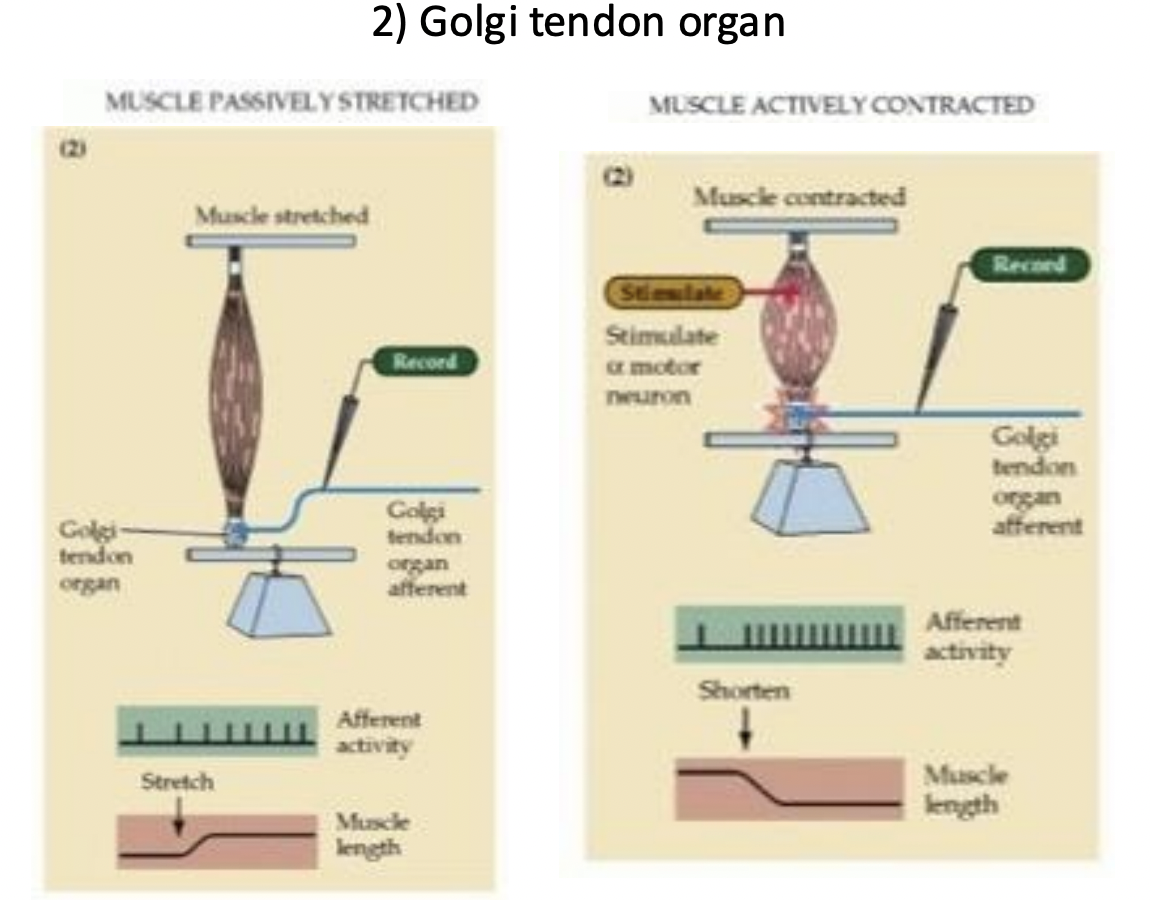
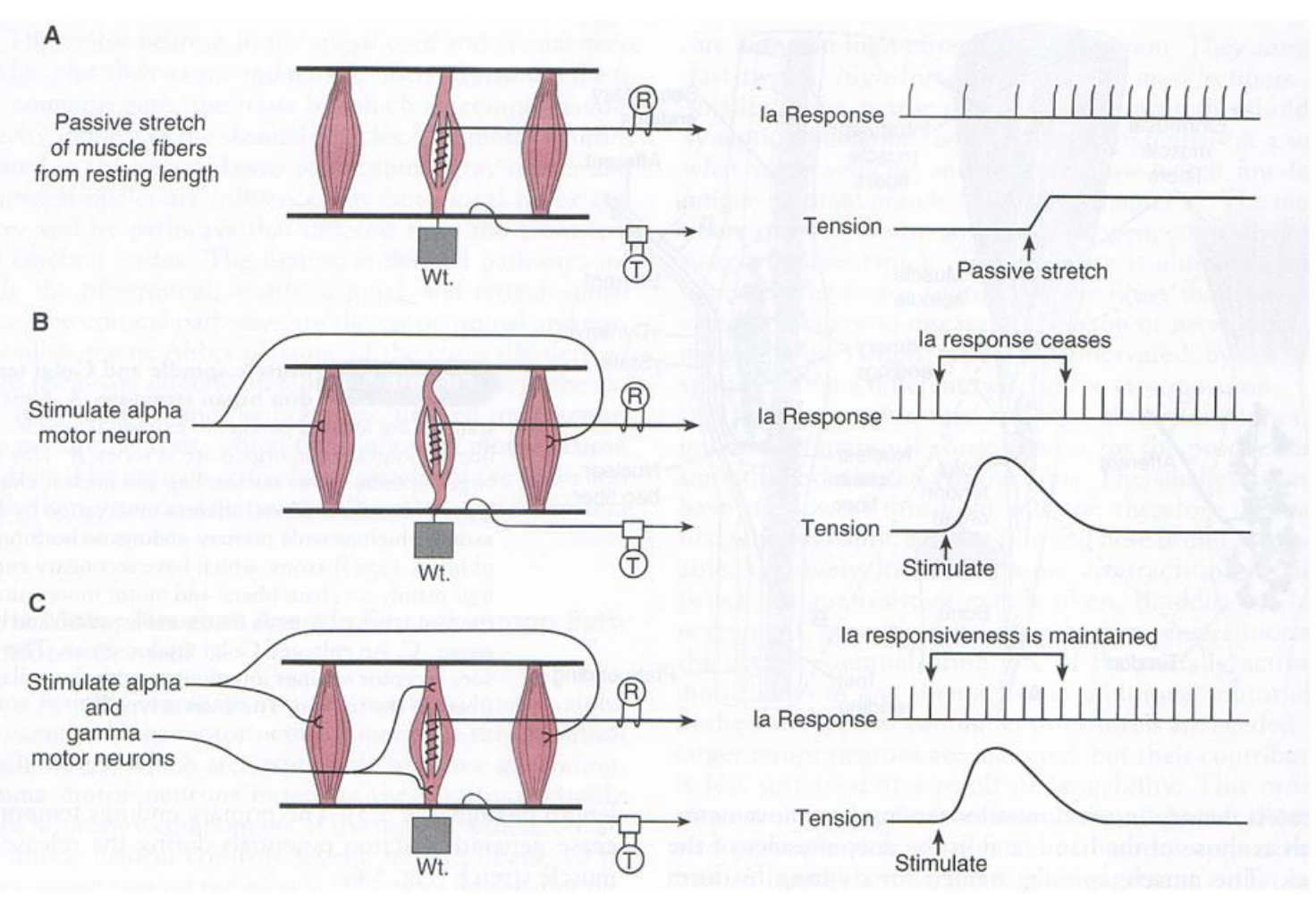
what happens when the alpha motor neuron is stimulated and what about if both alpha and gamma are?
la response ceases and is maintained if both.