1.5-1.8 APAAS Quiz
1/39
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
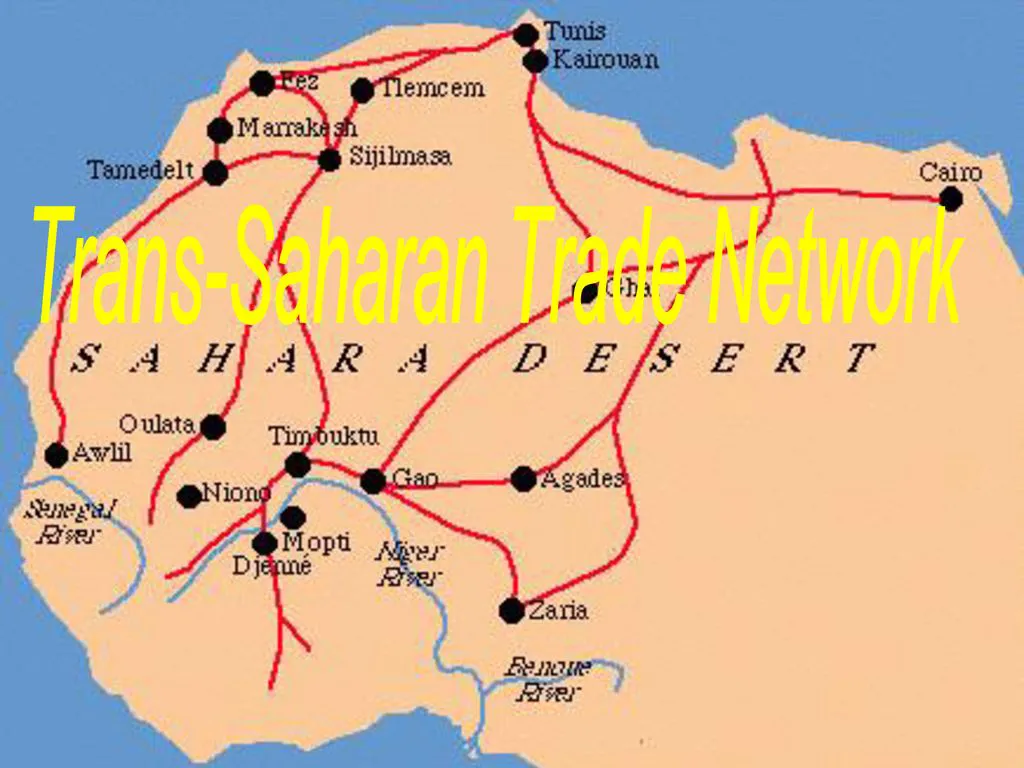
What is the Trans-Saharan Trade?
Trading that occurred between sub-Saharan Africa and North Africa mainly from the 8th to 17th century that required travel across the Sahara; it supplied gold, ivory, and slaves. The most common places that used this trade route were Ghana, Mali, Songhai, and Timbuktu.
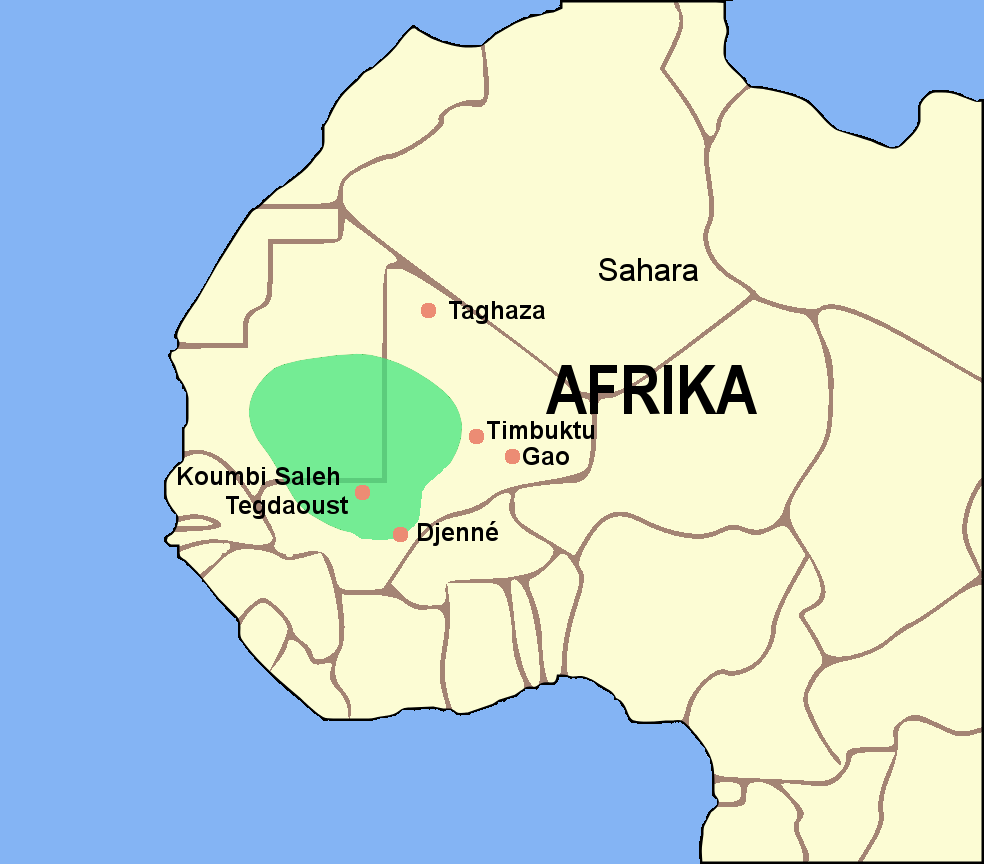
What is Ghana (kingdom)?
The first of the Sudanic empires in West Africa, flourishing in the 7th-13th century, they facilitated most of the trade across the Sahara Desert and were known for gold trade. Their central religion was a blend of traditional African religion and Islam. Their decline was because of military defeats and loss of trade.
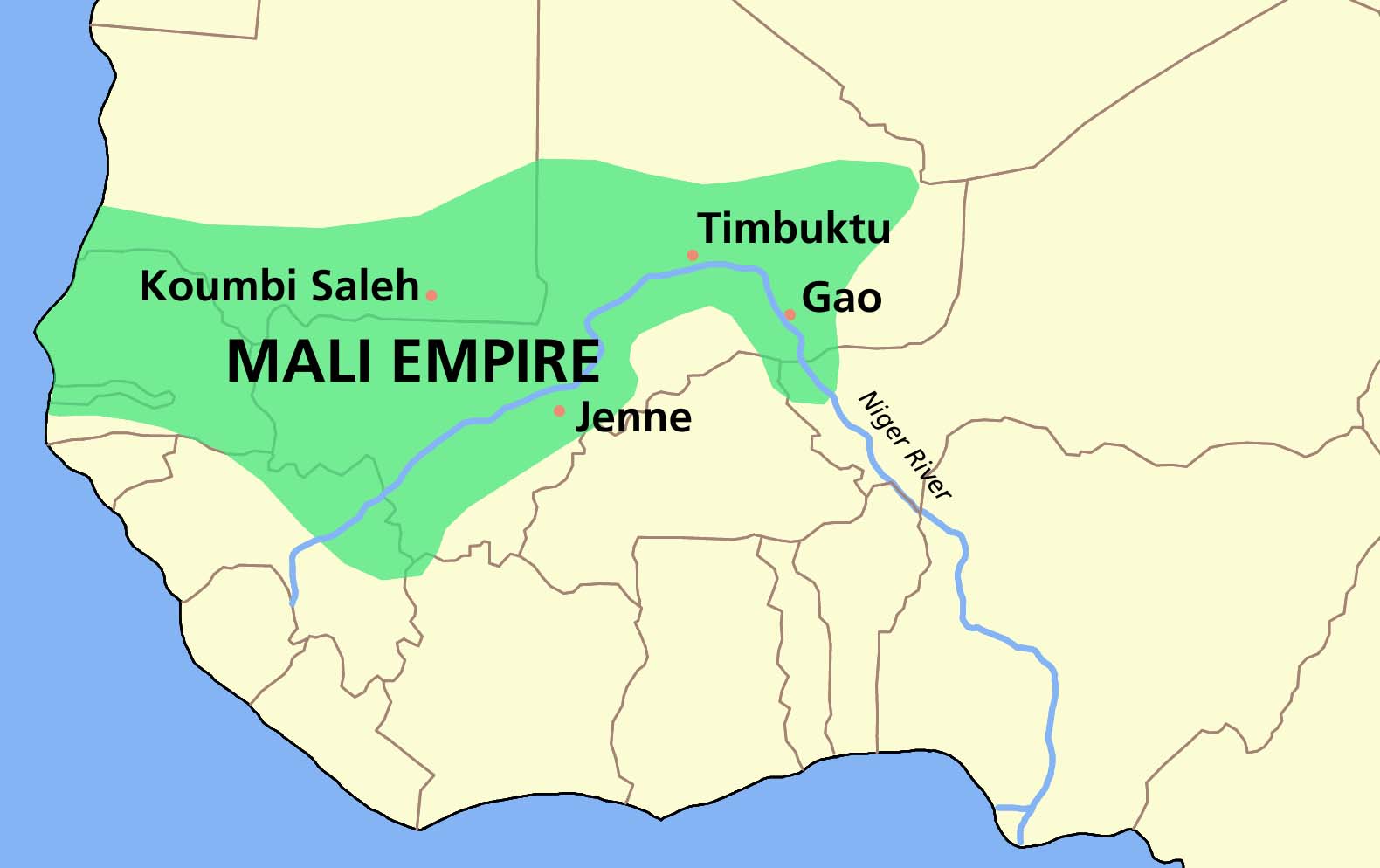
What is Mali (kingdom)?
The second of the Sudanic Empires in West Africa, going from the 13th to the 17th century, was a very rich empire due to their monopoly over the gold trade. Their main religion was Islam, and it was ruled by Mansa Musa. After Mansa Musa’s death they struggled because they had a lack of leadership, which caused their empire to weaken and get conquered by Songhai
What is Timbuktu?
A city originating in the Mali Empire around the 14th century, it was the center of Islamic scholarship, attracting scholars throughout the region and being home to many libraries. These libraries had sacred Muslim texts, medicine, astronomy, mathematics, and law.Mansa Musa played a pivotal role in making it an empire for trade.

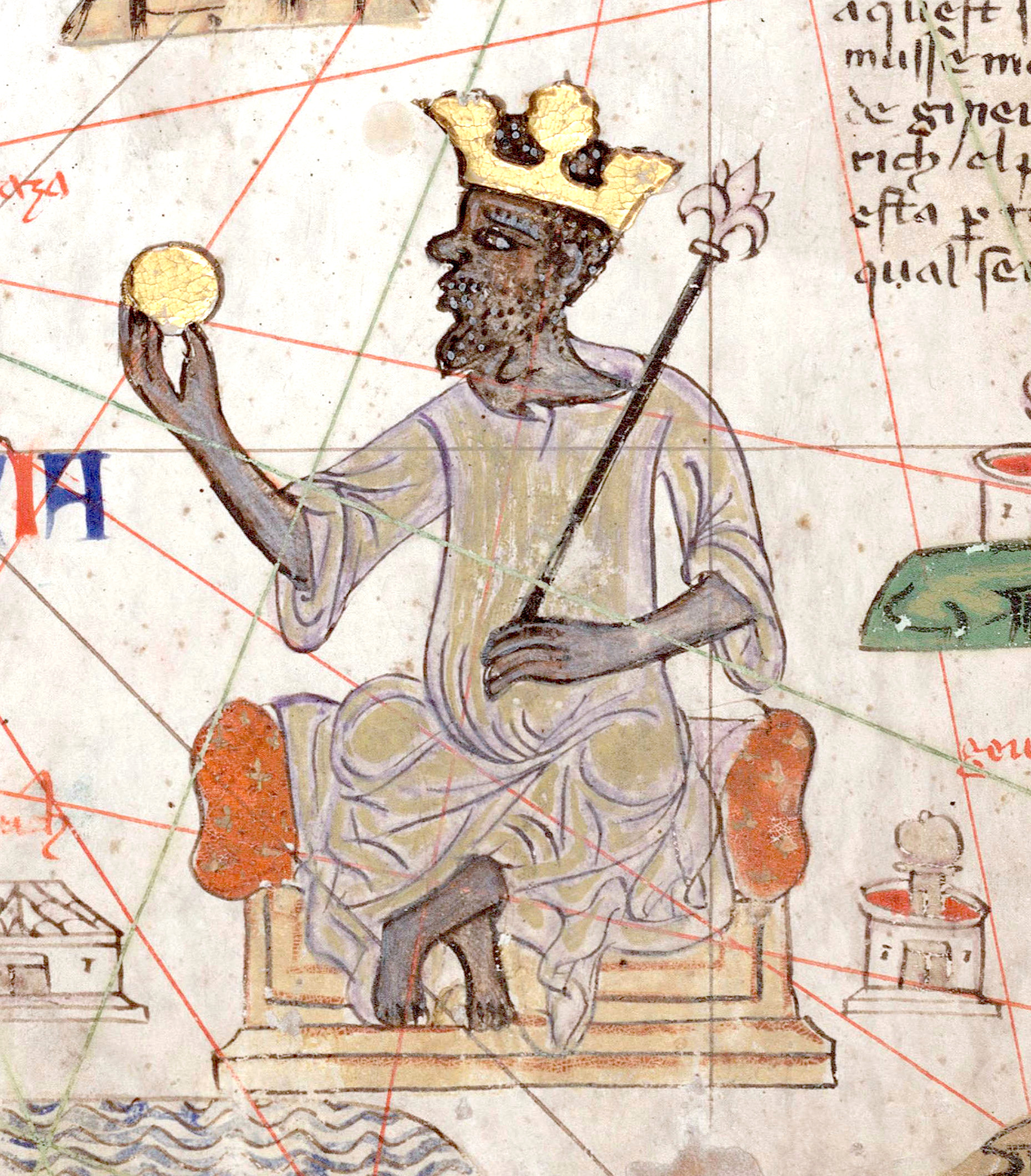
Who was Mansa Musa?
King of Mali from 1312 to 1337, believed to be the richest person in the world, with his wealth today estimated to be $400 billion, was a devout Muslim and traveled to Mecca, causing inflation wherever he went, which caused him to be well known. Built the Great Mosque at Timbuktu, established Mali as a place of trade and cultural exchange.
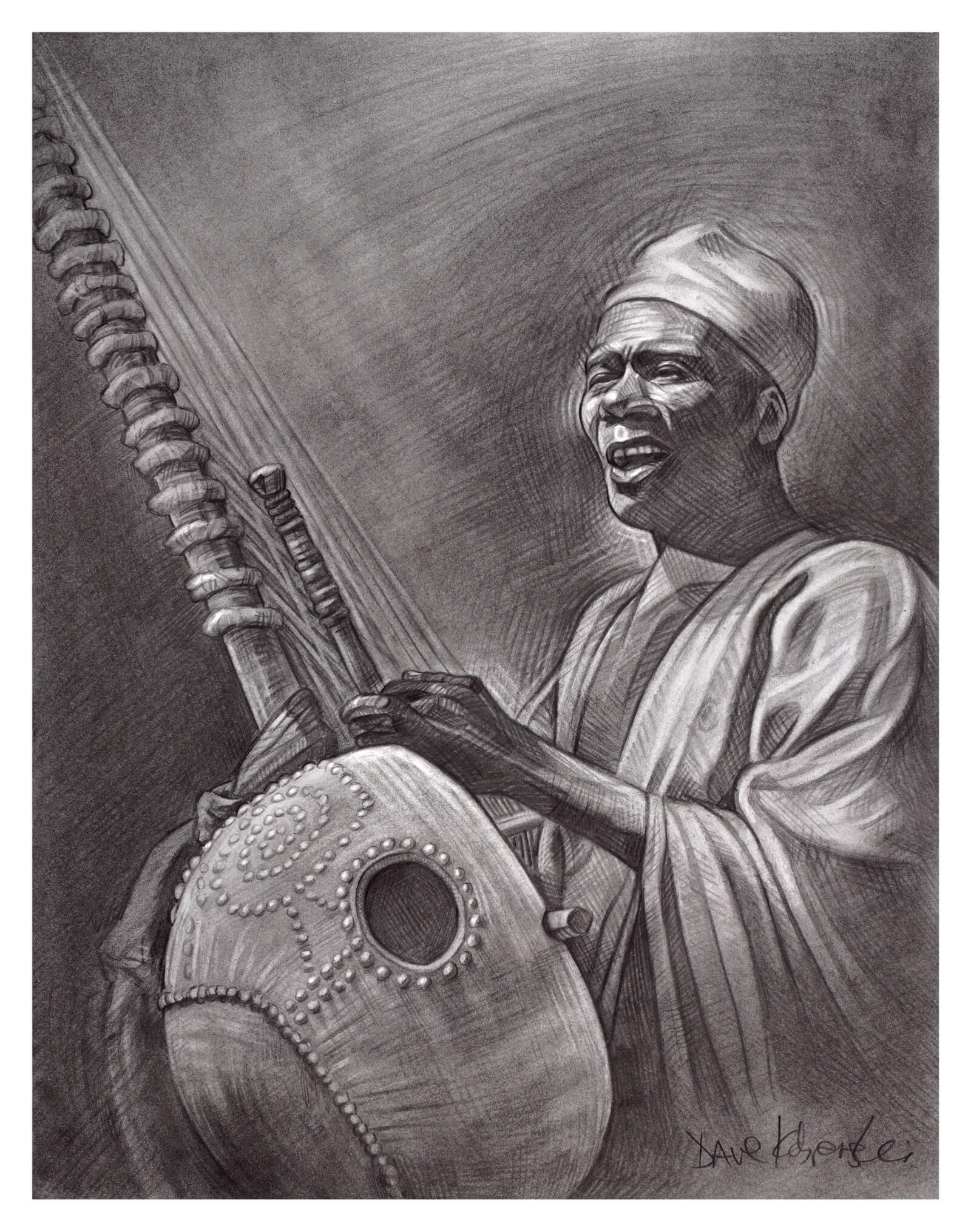


Who are the Griots?
A West African who is born into their respected position of being a storyteller, poet, historian, or musician. They only communicate their stories orally, and they accompany their storytelling with instruments like the kora. They preserve knowledge of their community’s history in their stories, and they include both African women and men.
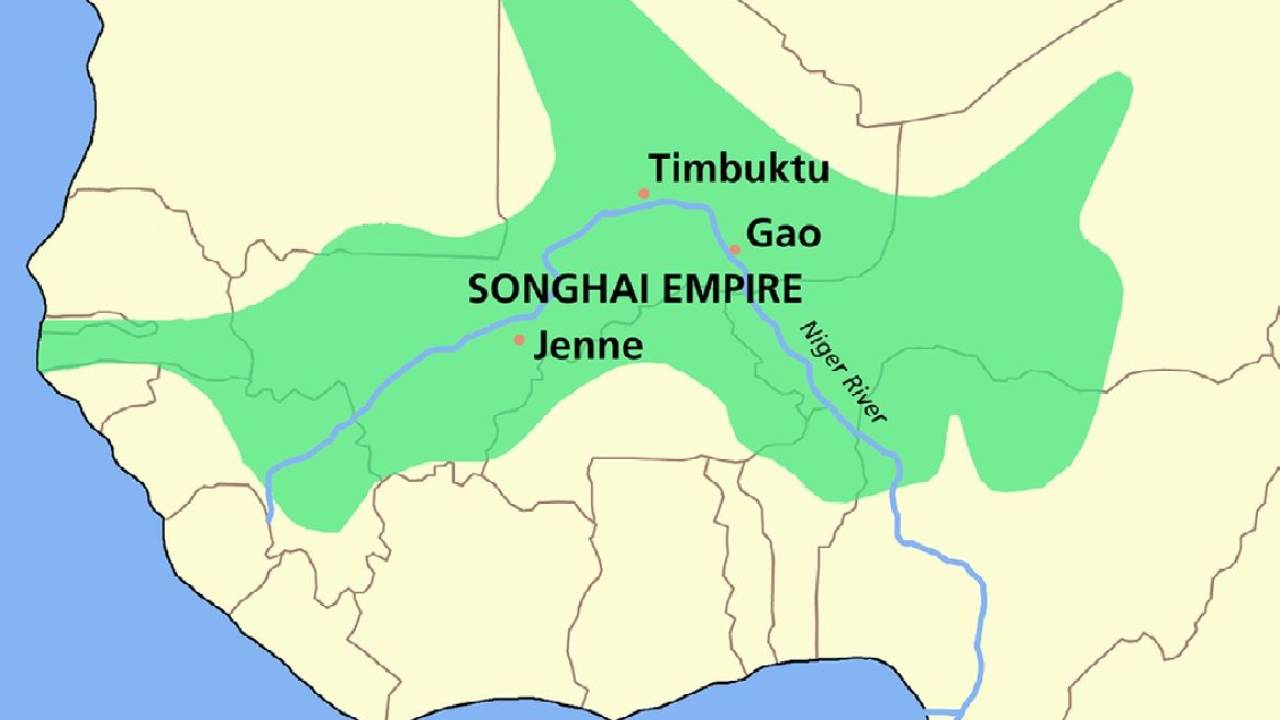
What is the Songhai (kingdom)?
The last and the largest of the Sudanic empires, lasting from the 15th to 16th century in Western Africa, their primary religion was Islam, and they specialized in gold trade. Didn’t last long because the Portuguese diminished their wealth by taking over their trade. They were ultimately conquered by the Moroccan Empire in 1591.

What is the Epic of Sundiata?
It’s a poem about the origin of the Mali Empire, which was created by the Mande people, named after Sunjata Keita who found the Mali empire, and it's an oral tradition that is constantly evolving. The story of the hero Sundiata Keita, who died in 1255 and united the twelve kingdoms of Mali, making it more powerful, and it has themes of family and loyalty.
What is the Swahili Coast?
It was a large independent trade network that traded gold, ivory, and spices along the Indian Ocean, they were able to prosper due to their agriculture and animal husbandry; and it existed from 800 to 1600 CE. Influenced by many cultures and languages from Muslims, Egyptians, Persians, and South Asians. The Portuguese led to their decline by trying to seize their trading ports.

What was Great Zimbabwe?
Thrived from 1220 to 1450 CE; gold trade made them rich due to their geographical location for trade. Known for their impressive architecture that included the Great Enclosure, which is the largest pre-colonial structure in all of sub-Saharan Africa, and it represented power, wealth, and dignity. However, they fell in the 1420s when the Swahili merchants changed their trading routes.
What is the Yoruba?
It’s an ancient, ever-evolving religion tracing back to 1 BCE that evolves with the Yoruba people’s history. The Yoruba live in the region around the Bite of Benin. Olofin was an eternal creator god and gave life and divine energy, created orishas to manage the world directly, and said that souls join ancestors in a spiritual realm and are reborn into the family realm.
What are the Orishas?
Describes any deities in most West African religions; they are a complex multidimensional unity that comprises around 400 demigods and spirits. Each spirit has a different function and sex in different locals and has a particular place in the hierarchy. Examples include Osun of the river and Aja, who is the goddess of the forest.
What is Vodou (or Vodún)?
A religion that worships gods of natural spirits, the Iwas are spirits that represent traits and laws of nature; it represents power and rebellion. These spirits are the most involved in human life, and the most important distinction to make is that they aren’t gods. It was feared by most countries, which is why it's misrepresented everywhere today, and it was because this gave their followers the strength to fight back.
What is Louisiana Voodoo (also known as New-Orleans)?
It’s an African diasporic religion that existed in Louisiana between the 18th and 20th centuries; it emerged from West African religions, and it's connected to nature, spirits, and ancestors. The core belief is that God doesn’t interfere with daily life, the spirits do. It shares a lot of similarities with Haitian Vodou, but the main difference is that it focuses more on the individual and places a greater importance on ancestor veneration.
What is Regla de Ocha-Ifá (formerly known as Santería)?
A religion that’s Afro-Cuban with influence from Yoruba and blended with Roman Catholic Christianity. They only have one supreme being called Oludumare, who has created everything with life force, and they can’t interact with them, only the Orishas. Individuals are born with an assigned orisha that’s believed to guide believers on health and wise behavior.
What is Obeah?
It is the oldest of all of the Afro-Creole religions, and the practice is confined to the British West Indies, and it has many traditional aspects of Afro-Caribbean religions, like animal sacrifice and divination. Their followers are believed to be born with power that was passed down from generations, and they were called upon to provide protection, and if they were not born with the power, they underwent a conversion to do so.
What is Candomblé?
An Afro-Brazilian religion that takes influences from many different African religions, has been blended with Catholicism, and has a traditional style and ritual dances.and consists of gods. Every person is believed to have a guardian god, and their god can be either male or female. There are 13 different gods that all have a different function.
Who is Shango?
Defified fourth ruler of the city of Oyo
What is Yemayá (Yoruba)?
Goddess of all water Ogun River, mother goddess
Who is Yemayá (Catholic)?
Virgin of Regla (Mary)
Who is Ochún?
Our lady of charity
What religion did they practice in Swahili?
Islam
What did the Swahili Coast trade?
Ivory, gold, spices, exported $25 billion of gold
Where is the Swahili Coast located?
Shores of East Africa
What did Great Zimbabwe trade?
Elephant herds, gold, ivory, copper, cattle
When did Great Zimbabwe decline?
In 1420, when Swahili created new trade routes
What trade routes did Great Zimbabwe and the Swalili Coast use?
Atlantic Ocean
What trade routes did Mali, Songhai, and Ghana use?
Trans-Saharan
What empire crossbred horses?
Mali
When was Mansa Musa’s haji to Mecca?
1324
When did the spread of islam occur?
In the 8th CE
When did Ghana exist?
7th-13th CE (officially fell in 1235 CE)
When did Mali exist?
13 to 17th CE (1250-1545 CE)
When did Songhai exist?
15 to 16th CR (1460-1591 CE)
What was the Elmira Castle?
Located in the coast of modern-day Ghana, built by Portugal in 1482 to safeguard their slave trade and it served as a waiting ground for people awaiting their enslavement across the ocean
What did Ghana trade?
Gold, ivory, animal hides, ostrich feathers
When did Timbuktu thrive?
14-17th CE
What is syncretism of religion?
When an aspect of 2 or more distinct cultures blend together to create a new custom, practice or philosophy
What are examples of Syncretism in religion?
Mali and Songhai (Islam), Kongo (Christianity), Brazil (Candomblé), Cube (Santeria)
What is divination?
Communicating with the spirit world