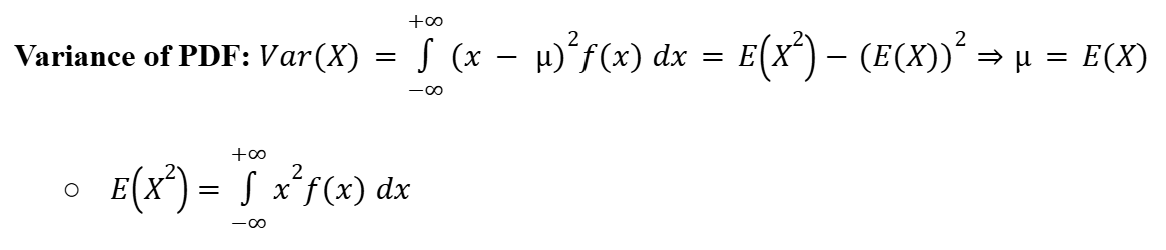UNIT 4: Statistics and Probability
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Formulae (SL & HL)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Arithmetic Mean (Ungrouped Data)
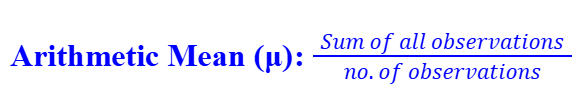
Median (Ungrouped Data)
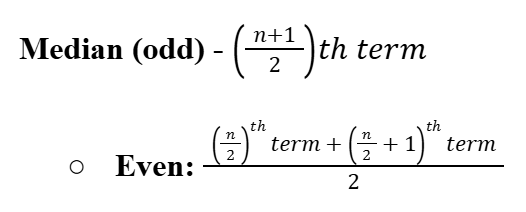
Mode
The most common term/class in a given data set.
Range
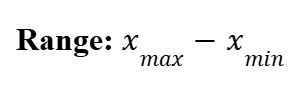
First Quartile (Q1)
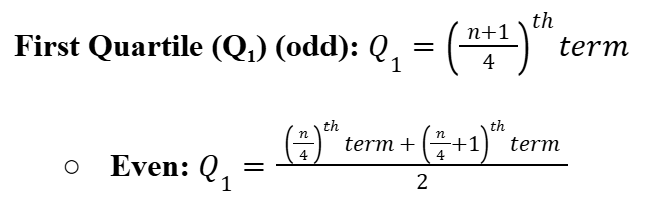
Third Quartile (Q3)
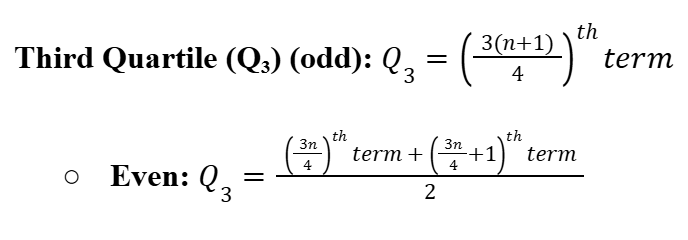
Interquartile Range (IQR)

Midpoint of a class (xmid)
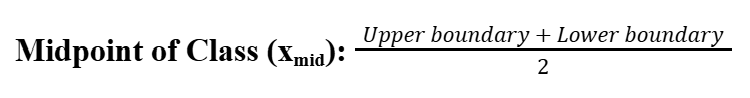
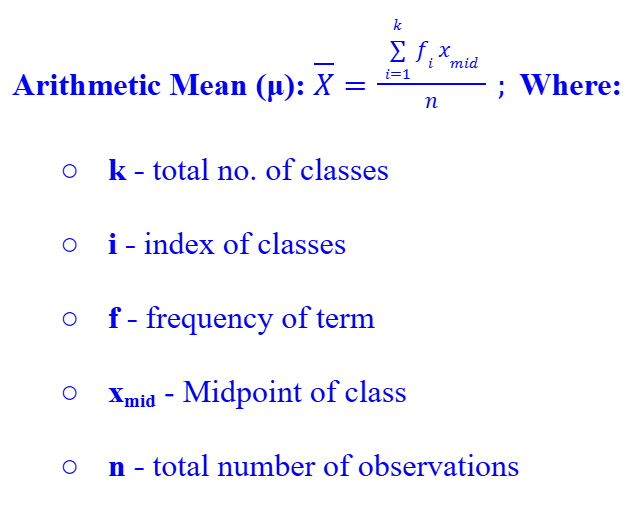
Arithmetic Mean (Grouped Data)
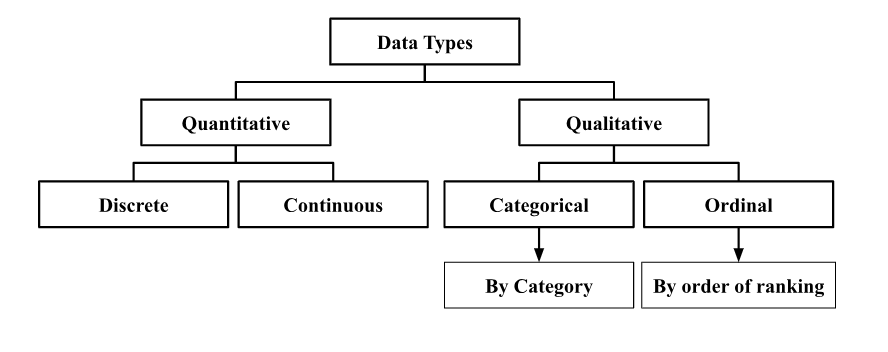
Data Classification (Statistics)
Outlier
A data point is considered an outlier if it lies more than 1.5 IQR above Q3 or lies under 1.5 IQR below Q1.
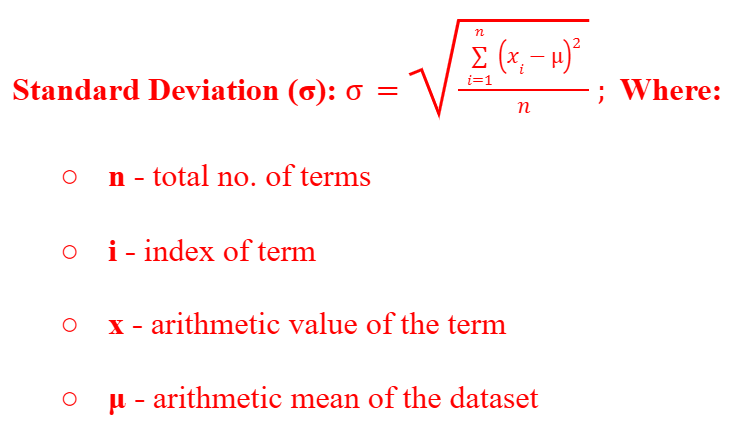
Standard Deviation
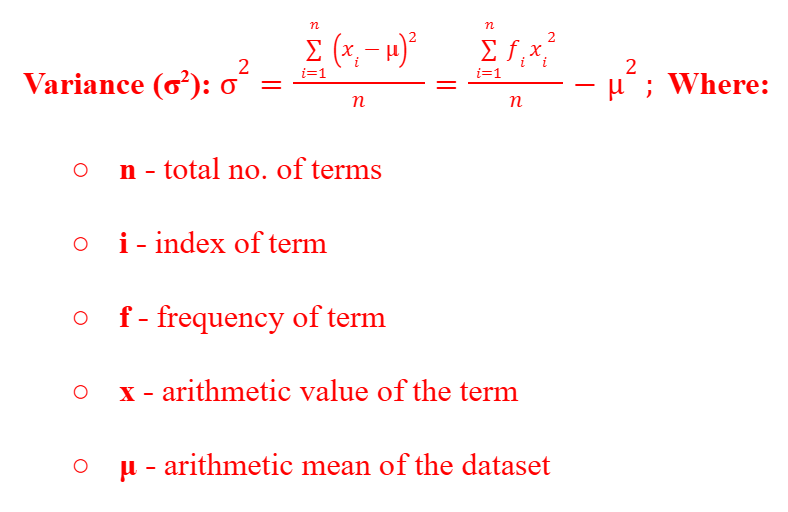
Variance
Simple Random Sampling
When you randomly choose the samples, such as drawing names from a hat.
Systematic Sampling
When you choose your samples from a fixed starting point and with a uniform interval from a data set. Eg. when sampling students in a school, you might choose every 10th person as your sample.
Stratified Sampling
When you divide the data set into classes defined by a certain trait or characteristic. Then you choose samples from each strata with the same percentage of samples available in each strata as compared to the dataset. Eg. when sampling pizza in a restaurant you might use the toppings as a stratum. The percentage of the pizzas in each topping would then decide the percentage of samples to choose from each stratum.
Quota Sampling
When you choose your samples in a specific quota (percentage ratio) to mirror real life. Eg. when sampling the same pizza in a restaurant, you might use the percentage of meat pizzas to the percentage of vegetarian pizzas to choose your samples. Then you would choose your samples in the same ratio or quota as found above.
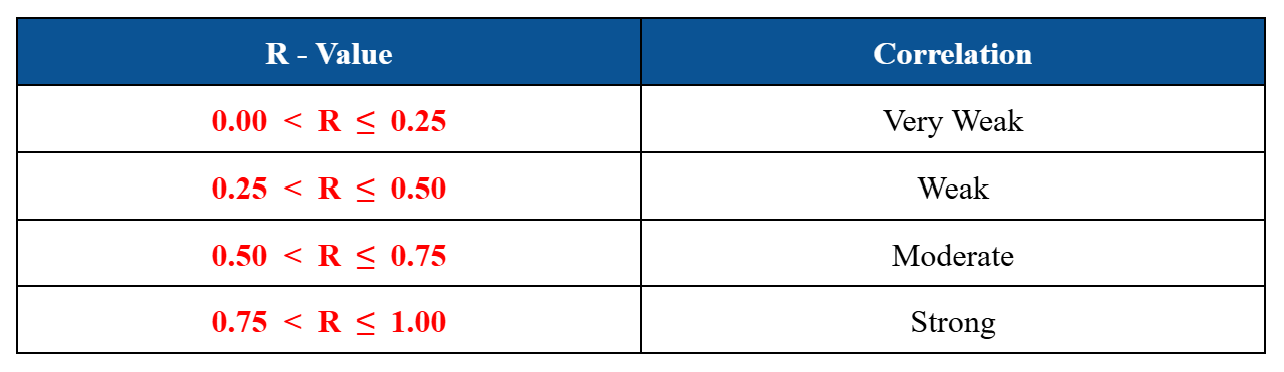
Pearson Correlation Coefficient (R-Value)
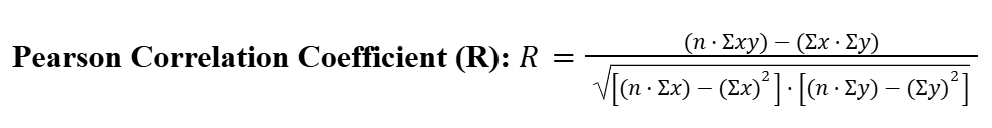
R-Value and Correlation
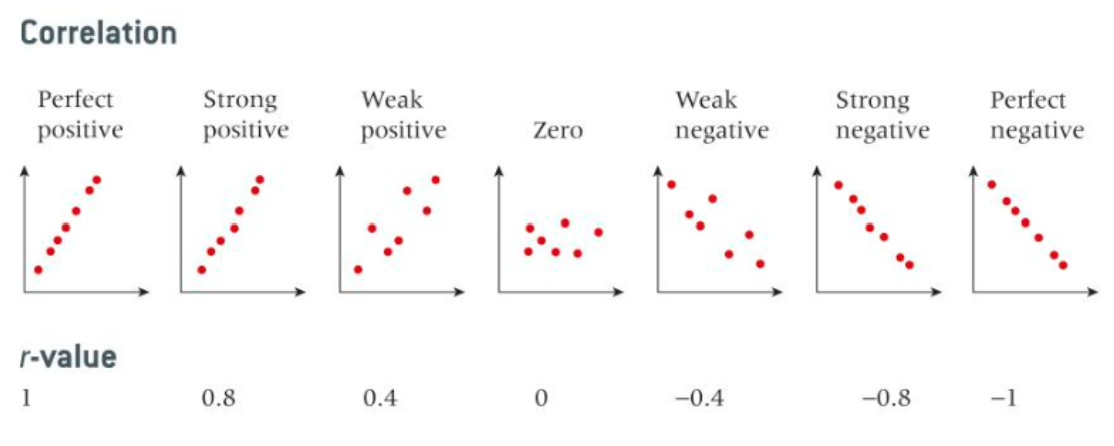
Positive and Negative Correlation
Line of Best Fit (by eye)
The line must pass through the mean point of the dataset (not necessarily part of the dataset) and there must be an equal amount of points on both sides of the line (up and down).
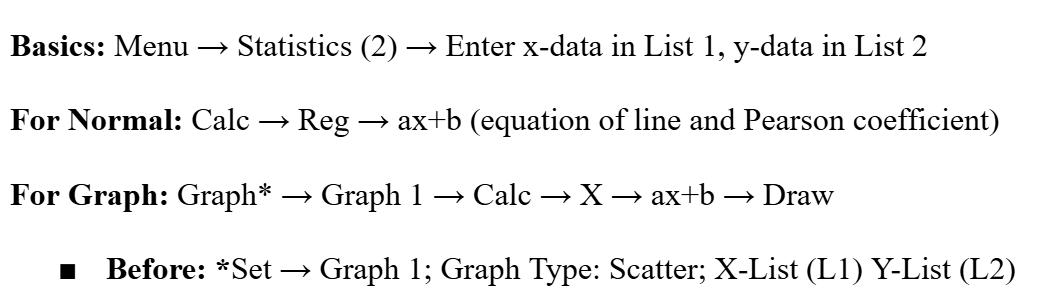
Line of Best Fit (Linear Regression)
Calculated by minimizing the distance of the squares of the residuals of each data point from the trendline (done by computer/calculator) in the form (y=ax+b) or (y=a+bx).
Residuals
A residual is the distance of the data point from the trendline or line of best fit.
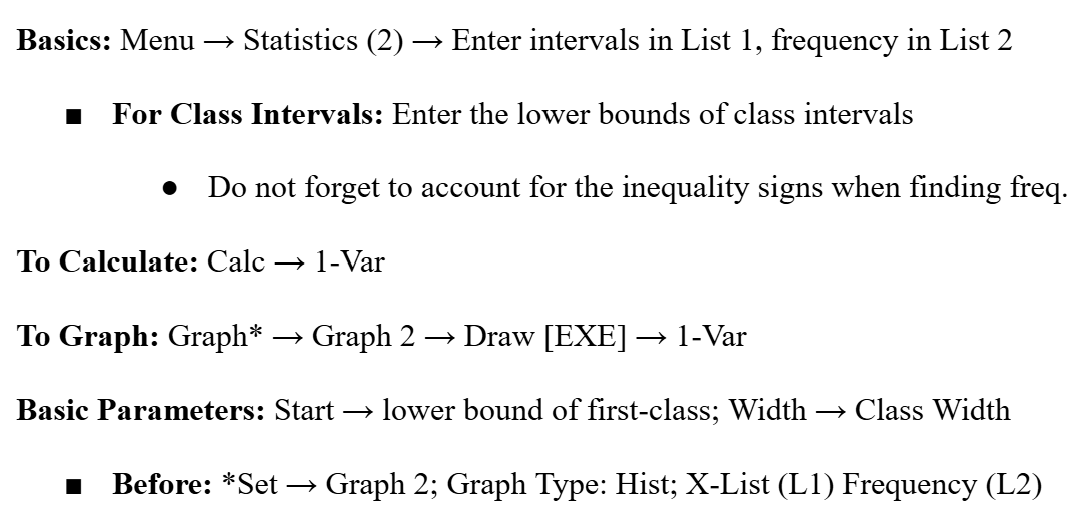
Histogram
Bar Graph constructed from grouped frequency data with continuous data (class intervals). Unlike bar graphs, histograms have a continuous scale for the x-axis and the width is the class interval.
Plotting Histograms (Casio Fx-CG50)
Probability
Probability: Measure of the likelihood of an event to occur.
Probability is always less than or equal to 1, the probability of an impossible event is 0, and the probability of a guaranteed event is 1.
Sample Space: A sample space contains all possible outcomes.
Probability of an event ‘A’
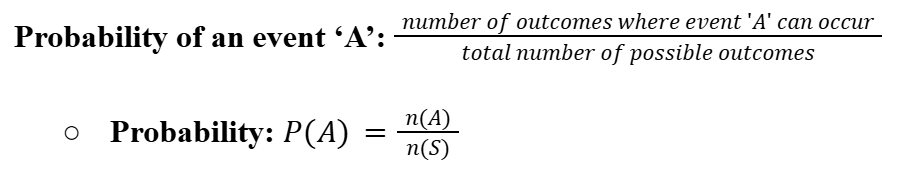
Complementary Factor (Probability)

Independent Events
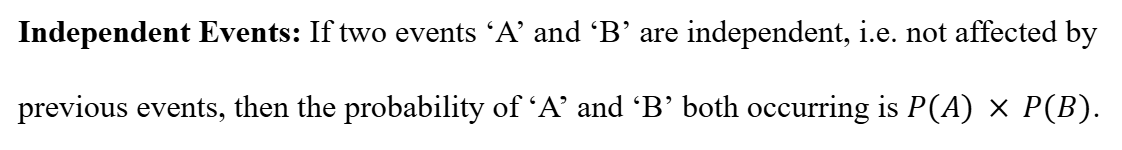
Two-Way Table (Probability)
A two-way table is a tabular list of all possible outcomes of any event.
Probability Tree
A probability tree is a representation of the sample space when multiple events occur and branch out. The final probability at the end of each branch is the multiple of all the probabilities corresponding to that branch.
Dependent Events
For dependent events, where the probability of the event occurring is based on past events, the probability will change based on the outcome of the previous event.
Venn Diagram
A Venn Diagram represents the similarities and differences between two or more sample spaces.
Union (Probability)
All the terms in both sets.
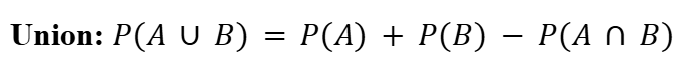
Intersection (Probability)
All the common terms in both sets.
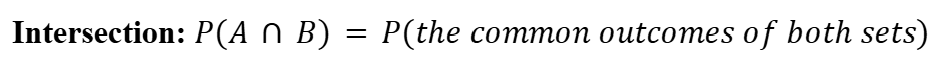
First Axiom of Probability
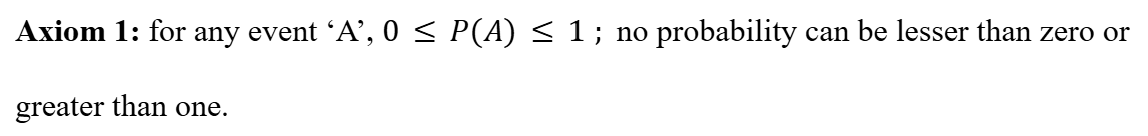
Second Axiom of Probability
For a sample space ‘S’, P(S) = 1 i.e. the probability of all occurrences is one.
Third Axiom of Probability
In probability, two events are mutually exclusive if only one event can occur at a given time in a particular experiment.
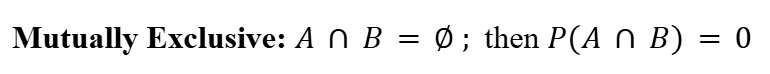
Fourth Axiom of Probability
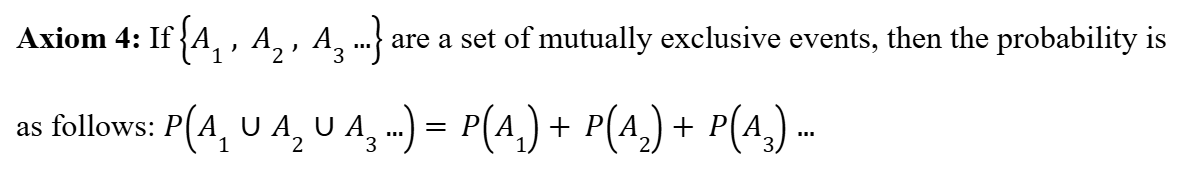
Direct Random Variable
A random variable is a quantity whose value depends on the outcome of a probability experiment. Random variables are represented using capital letters.
Example of Direct Random Variables
If ‘X’ represents the number of sixes obtained when a dice is rolled three times, then the probability is P(X=x) where ‘x’ is the outcome of the experiment, in this case, either 0, 1, 2, or 3.
Properties of Random Variables
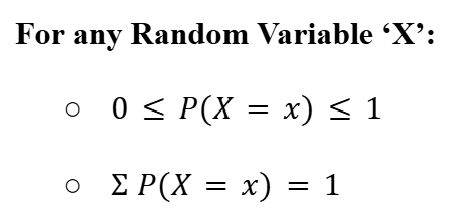
Expected Value (Direct Random Variables)

Binomial Distribution
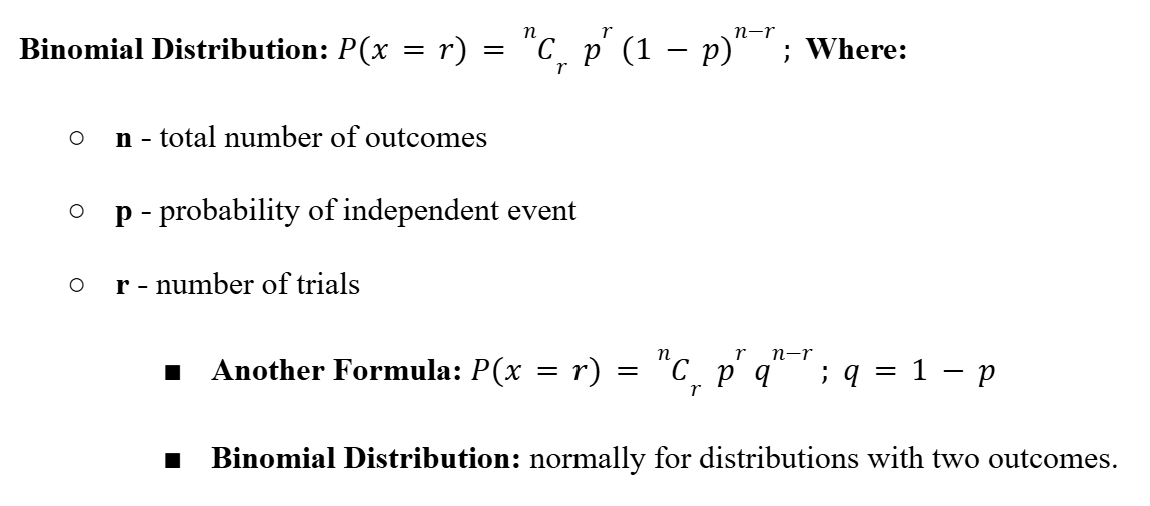
Expectation (Binomial Distribution)
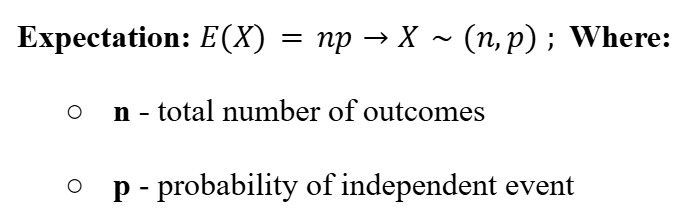
Variance (Binomial Distribution)

Normal Distribution
Normal Distribution: A normal distribution follows a “bell-shaped” curve, with most values grouped around a central value.
Perfect Normal Distribution: Perfectly symmetrical around the mean. The mean, median, and mode are then all the same.
Formula for Normal Distribution (Not Needed)
Standard Normal Distribution
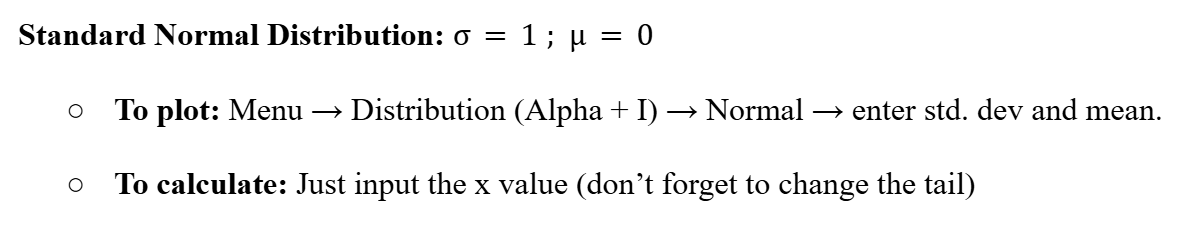
Standardization (Normal Distribution)
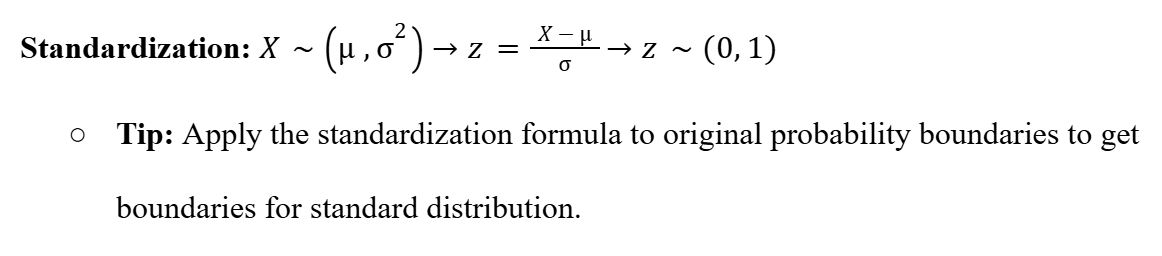
Inverse Normal Distribution
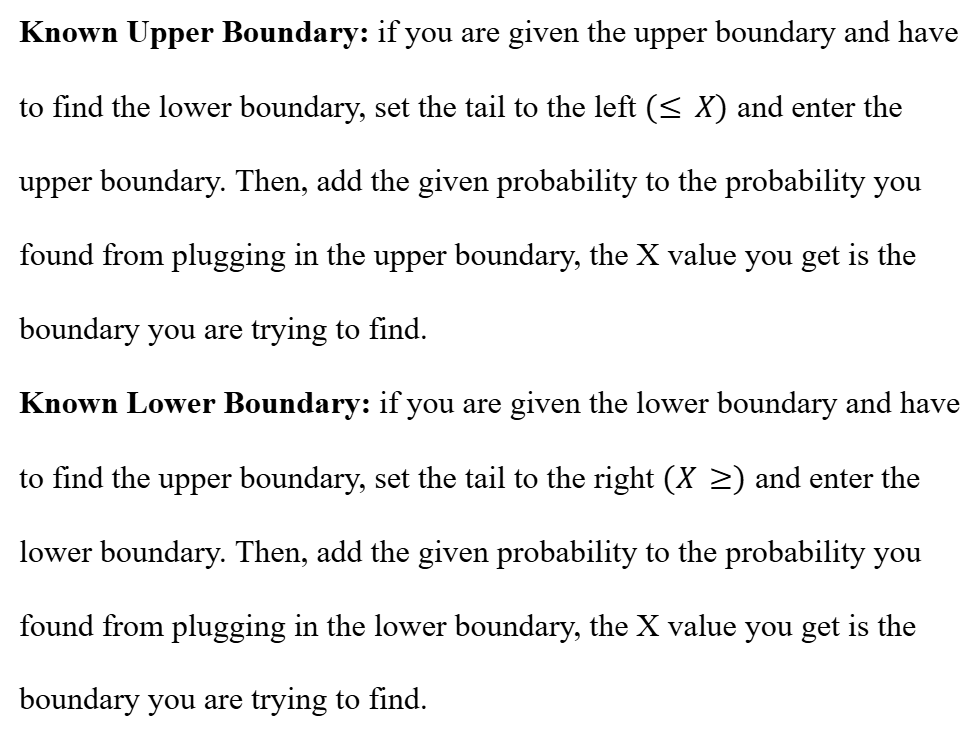
To find the inverse, a.k.a. the ‘X’ value, simply create the normal distribution with the given mean and standard deviation, move over to the probability, and enter the given probability to find X based on your boundaries.
Tricks for Inverse Normal Distribution
Probability Density Function (PDF)

Probability from a Probability Density Function (PDF)
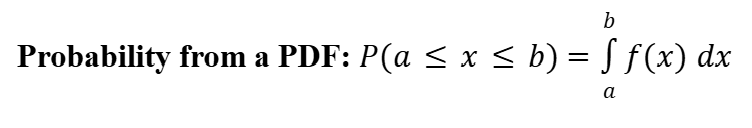
Mode (Probability Density Function)

Arithmetic Mean (Probability Density Function)
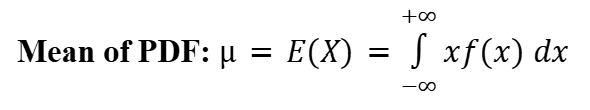
Median (Probability Density Function)
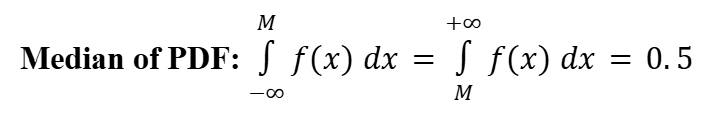
Variance (Probability Density Function)