Med Surg 1 - Test 1/Quiz 1
1/165
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
166 Terms
Nystagmus
Involuntary rapid eye movements
Strabismus
crossed eyes
Myopia
nearsightedness (can't see things far away)
Astigmatism
distortion caused by irregularity of the cornea
Mydriatics
Dilate the eye (contraindicated for narrow angle glaucoma)
CANNOT GIVE TO PATIENTS TAKING MAOI's OR TRICYCLIC ANTIDEPRESSANTS
Glaucoma
increased IOP causes mechanical damage
risk increases with age
Aqueous production and drainage are not in balance
signs/symptoms: vision loss, blurring, halos, difficulty focusing,
aching/discomfort around the eyes, or headache.
tested with: tonometry, ophthalmoscopy, and central vision field testing
treated with: miotics, beta-blockers, alpha1-agonists, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, and prostaglandins
Cataracts
opacity or cloudiness of the lens
risk factor: increased age
traumatic, congenital, and senile
signs/symptoms: painless, blurry vision, surroundings dimmer. reduced visual acuity. sensitivity to glare.
tested with: ophthalmoscope, slit lamp, or inspection
treated with: surgery
- phacoemulsification: the lens is sucked out through a tube
- lens replacement: surgeon inserts an intraocular lens implant
DONT BEND OR STOOP AFTER SURGERY
Retinal detachment
two layers of the retina separate from each other
- assess visual acuity
- ophthalamascope, slit lamp, tomography, and ultrasonography
scleral buckle
compress sclera
Weber test
detects unilateral hearing loss through bone conduction
Rinne test
bone vs air hearing conduction
sensorineural hearing loss
caused by damage to the cochlea or vestibulocochlear nerve
Mixed hearing loss
both conductive and sensorineural
Functional (psychogenic) hearing loss
caused by emotional problem
Cerumen impaction
buildup of ear wax blocking ear canal
- removal through irrigation, suction, or instrumentation
- mineral oil or peroxid may be used to soften the ear wax
External otitis
inflammation of the external ear
- commonly caused by bacteria or fungus
- also called swimmers ear
- pain, purulent discharge, tenderness
Otalgia
pain/fullness in the ear
Meniere Disease
disorder of the labyrinth of the inner ear; elevated endolymph pressure within the cochlea and semicircular canals
FALL RISK - ask for assistance, call light, bed alarm, get rid of rugs
- signs/symptoms: vertigo, tinnitus, fluctuating sensorineural hearing loss
- treatment: low sodium diet, meclizine, valium, and surgical management
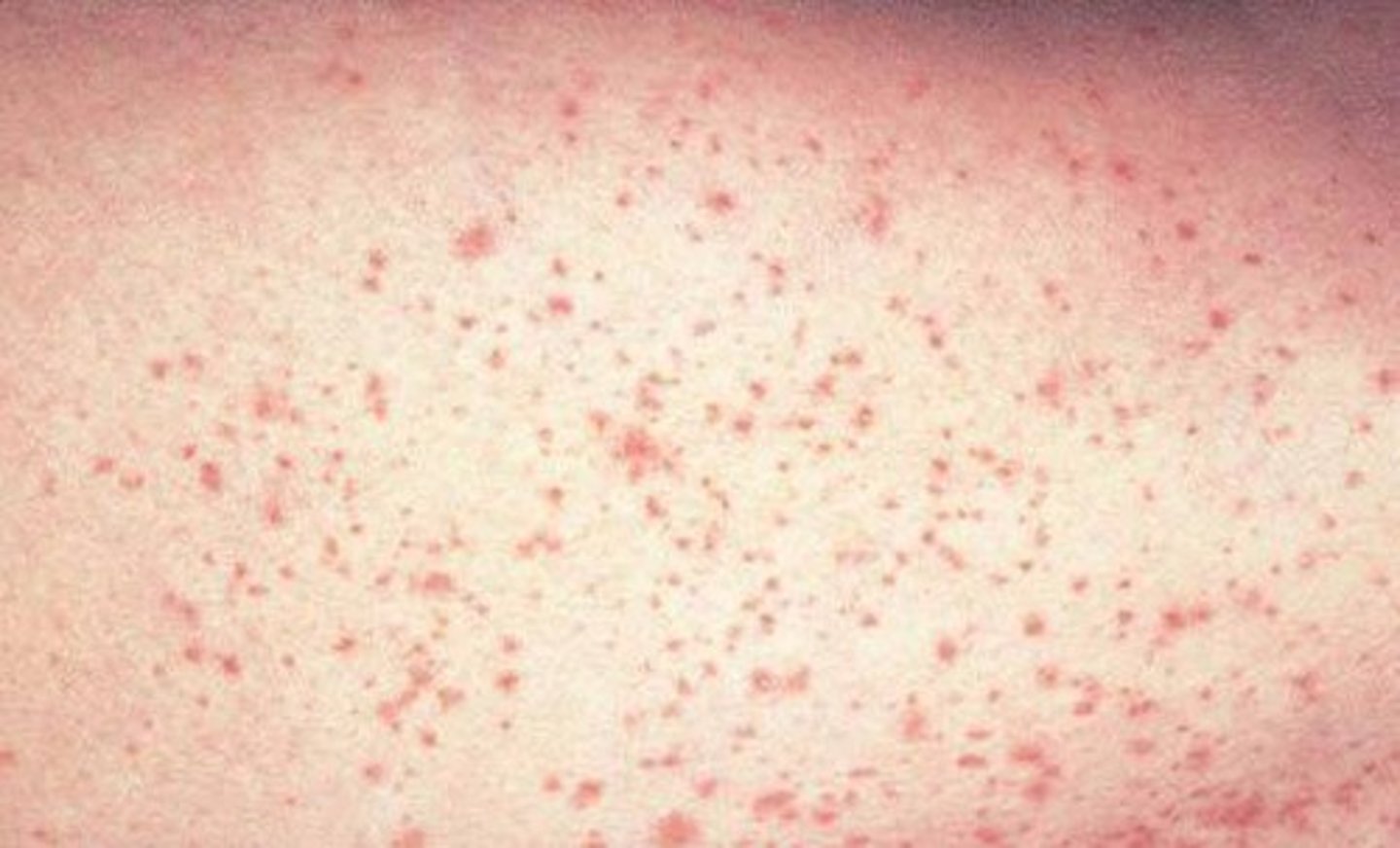
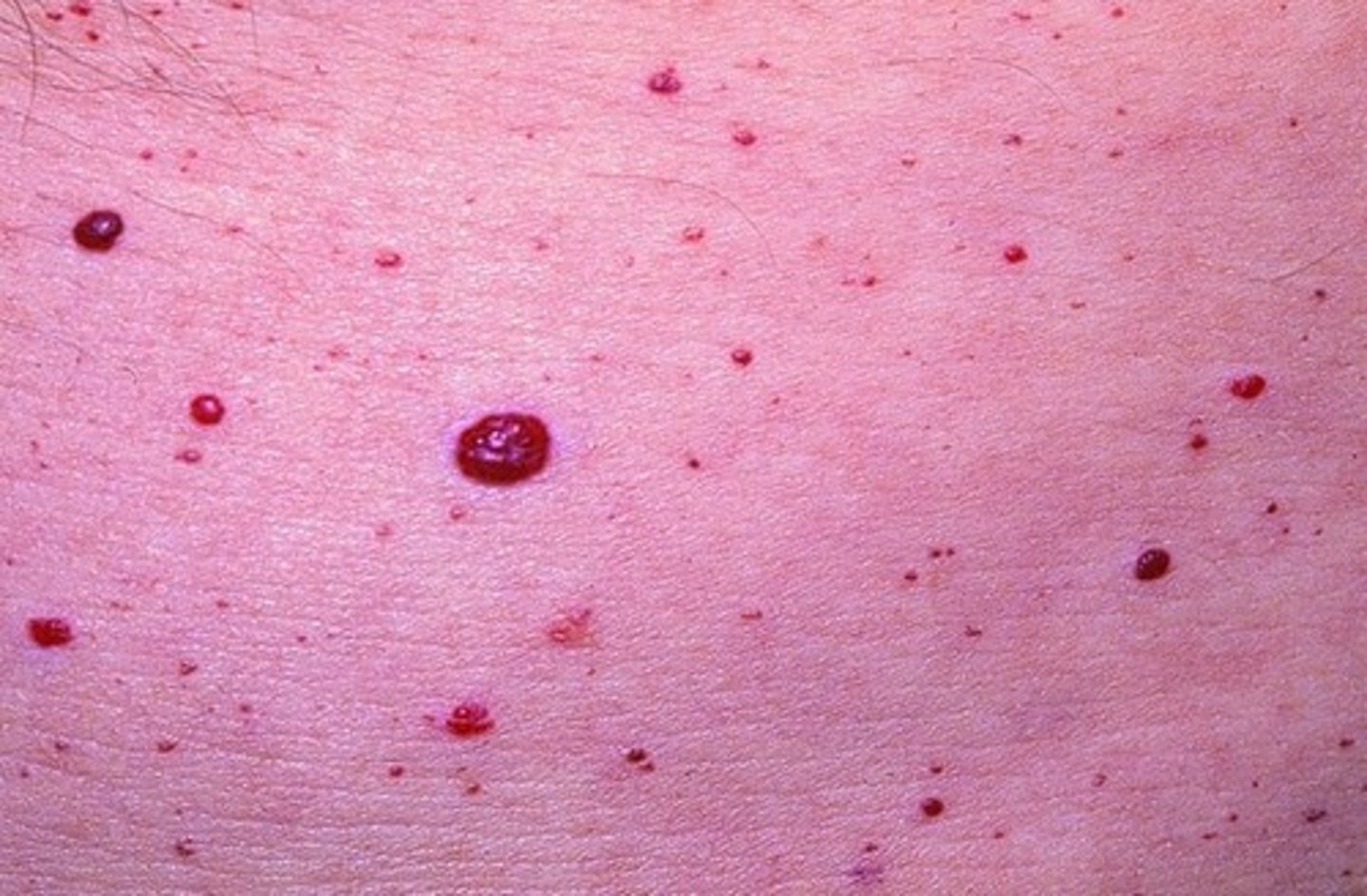
Petechiae
small, pinpoint hemorrhages from capillaries
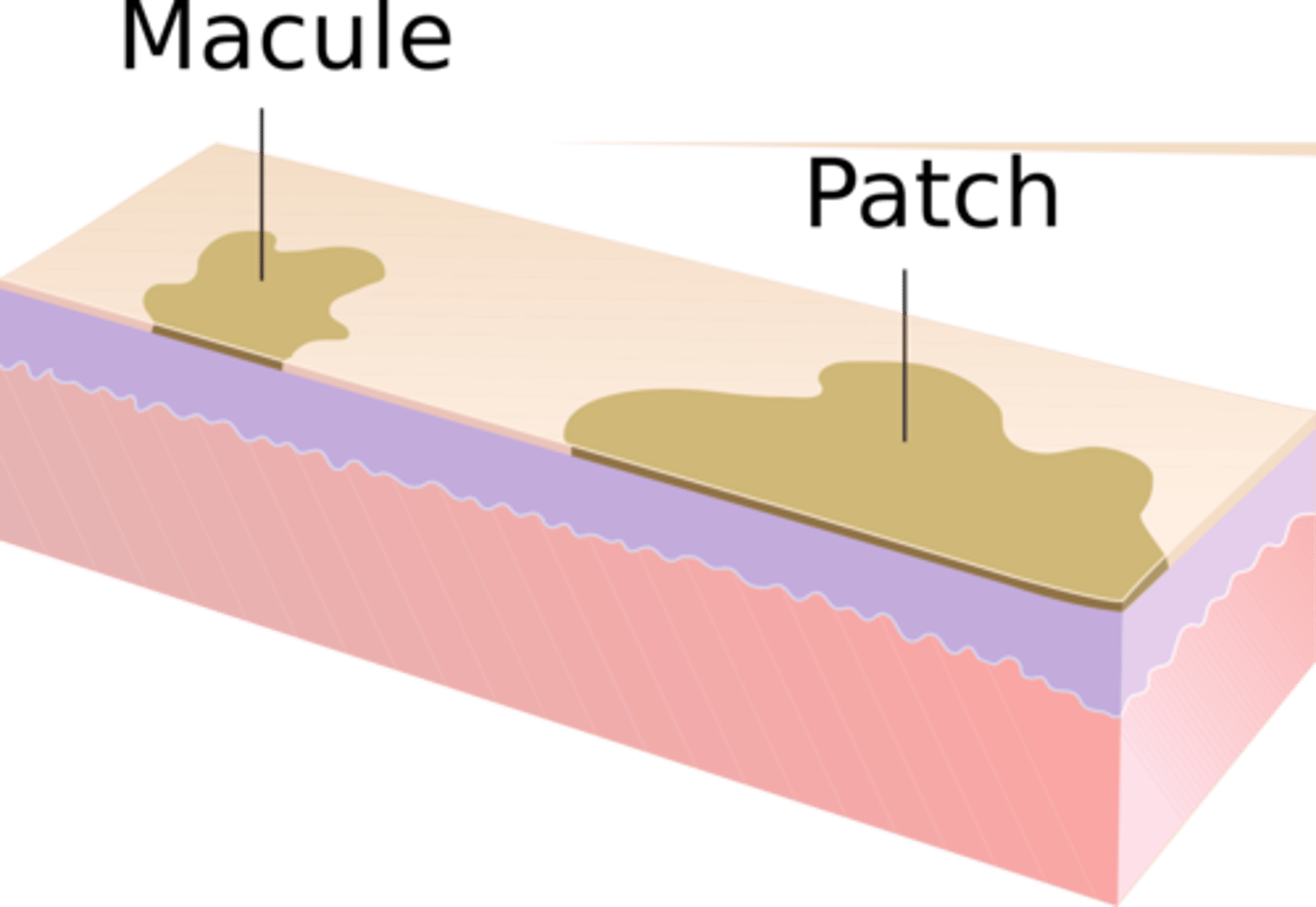
Patch (primary)
a flat, discolored area on the skin larger than 1 cm (bigger than a macule)
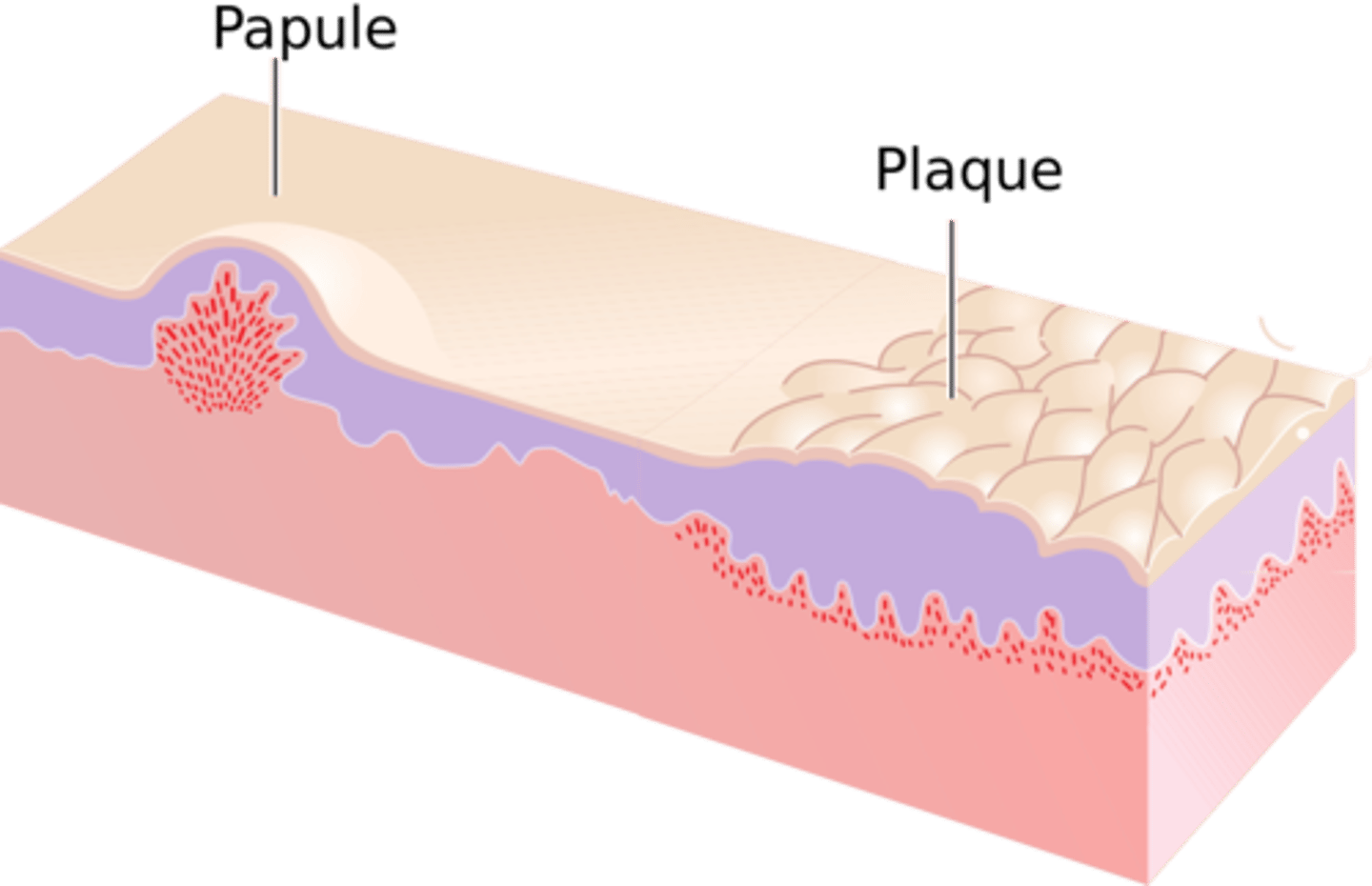
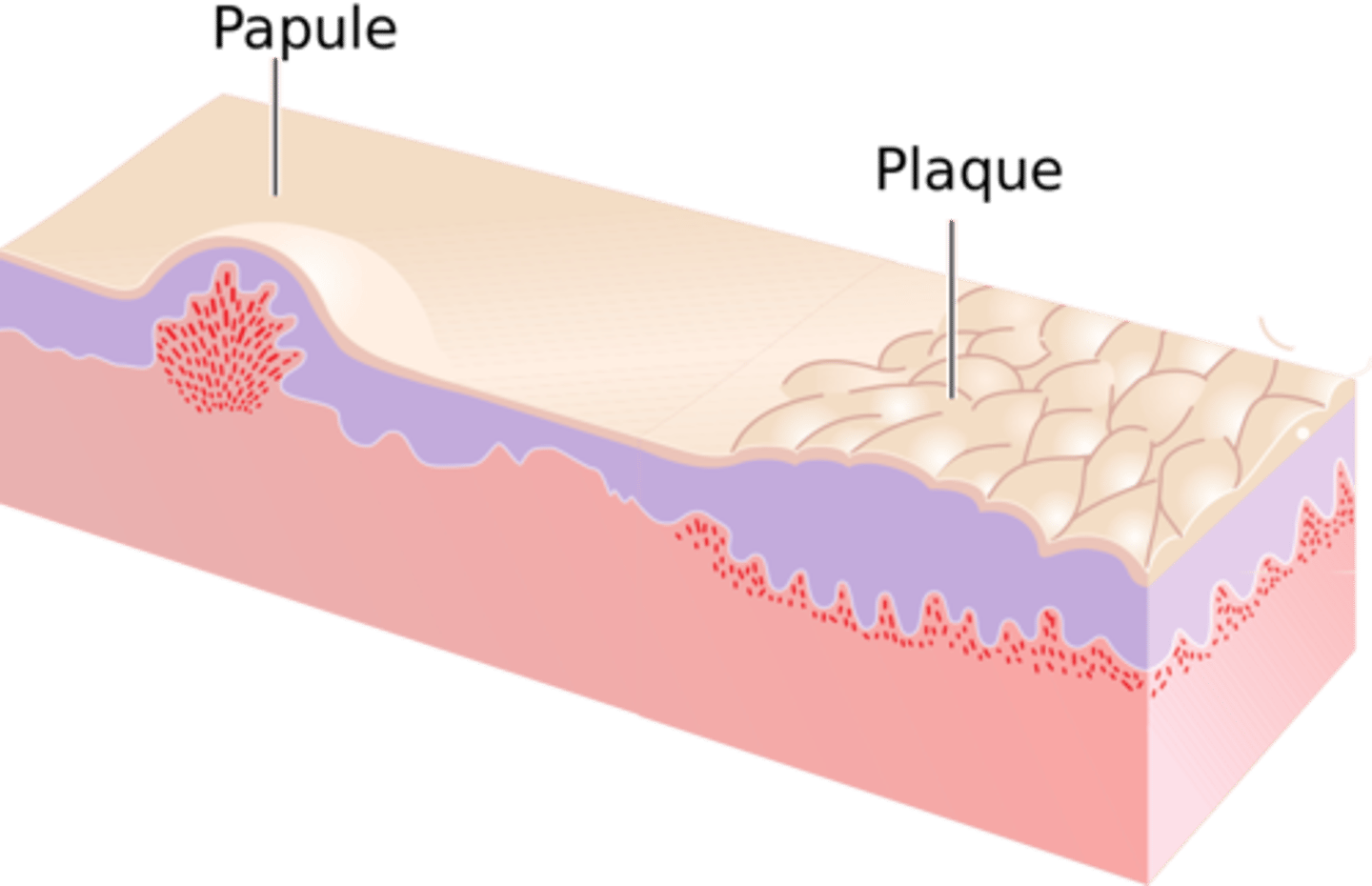
Papule (primary)
Superficial, elevated lesion up to 1 cm
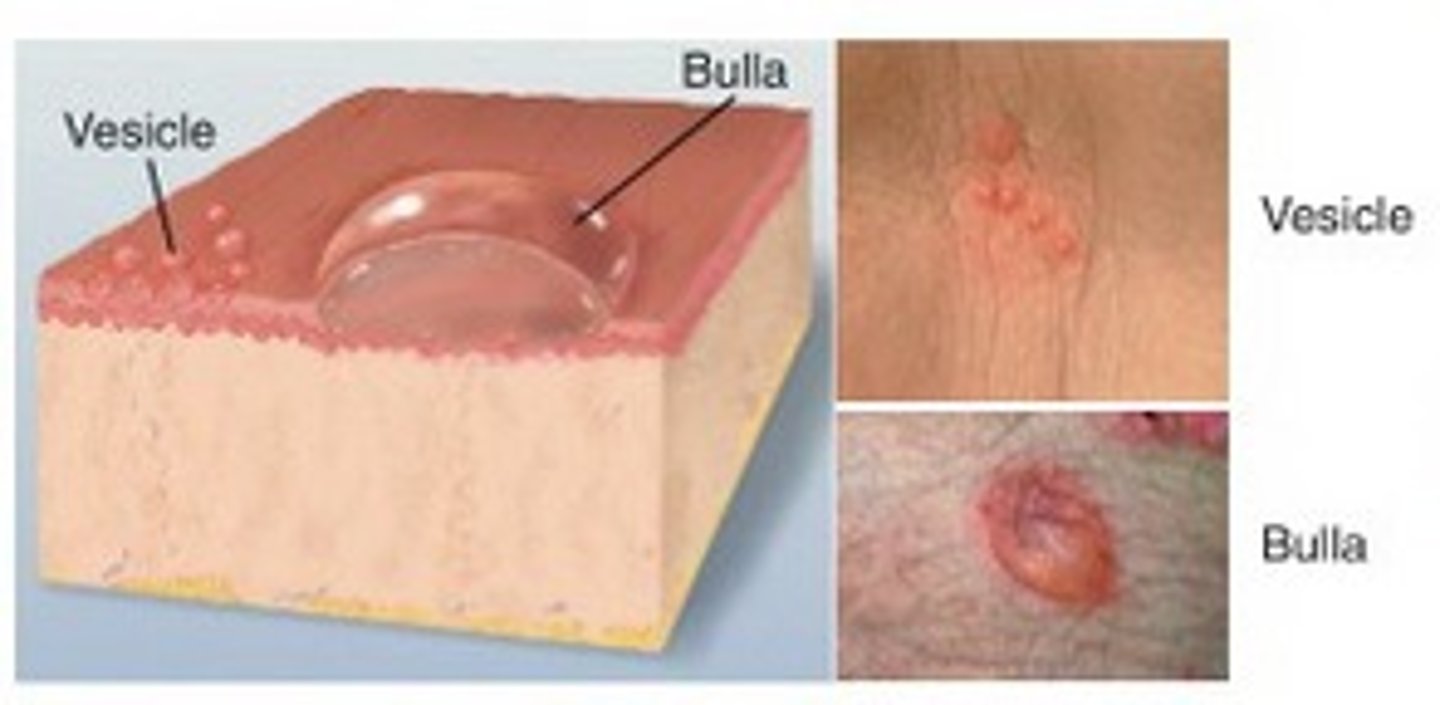
Vesicle (primary)
- small blister
Elevated < 1 cm; a "blister", clear serum flows if wall is ruptured ex. herpes simplex, chickenpox, shingles
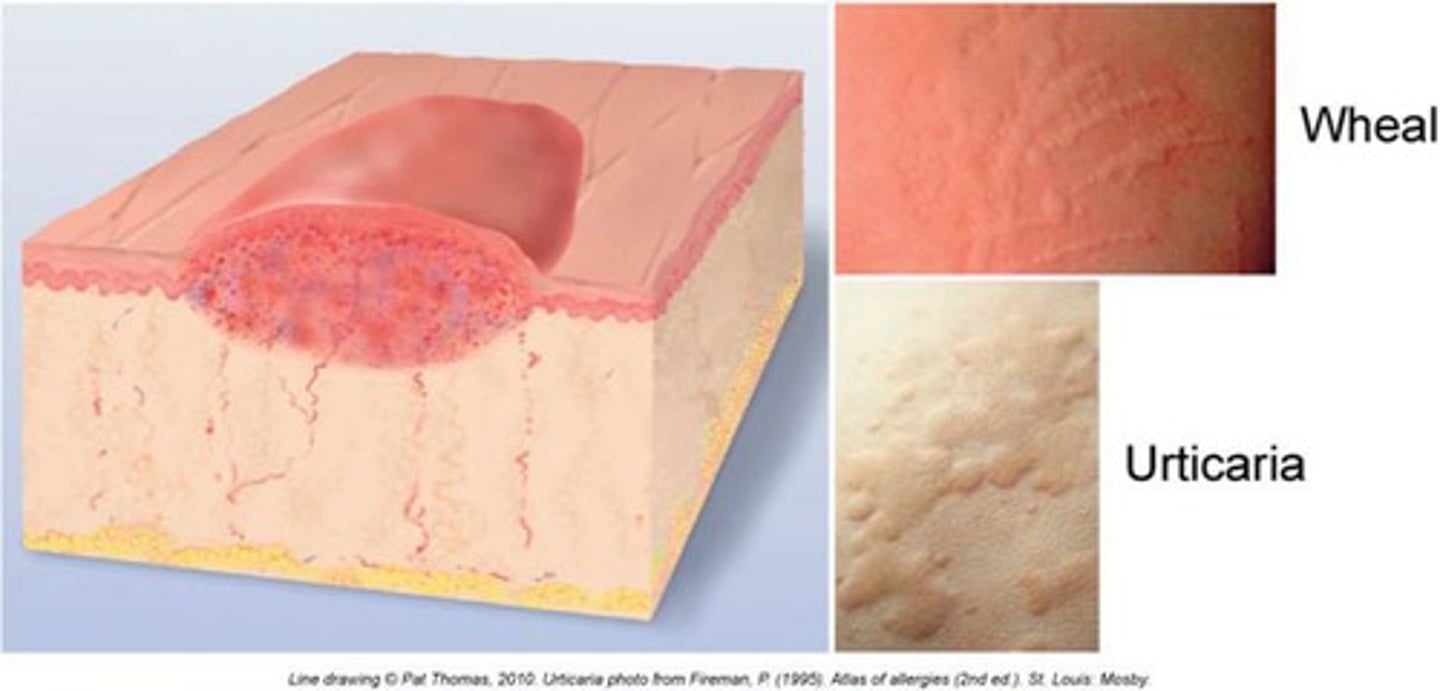
Wheal (primary)
Irregular, transient, superficial area of localized skin edema
urticaria = more than 1 skin wheel
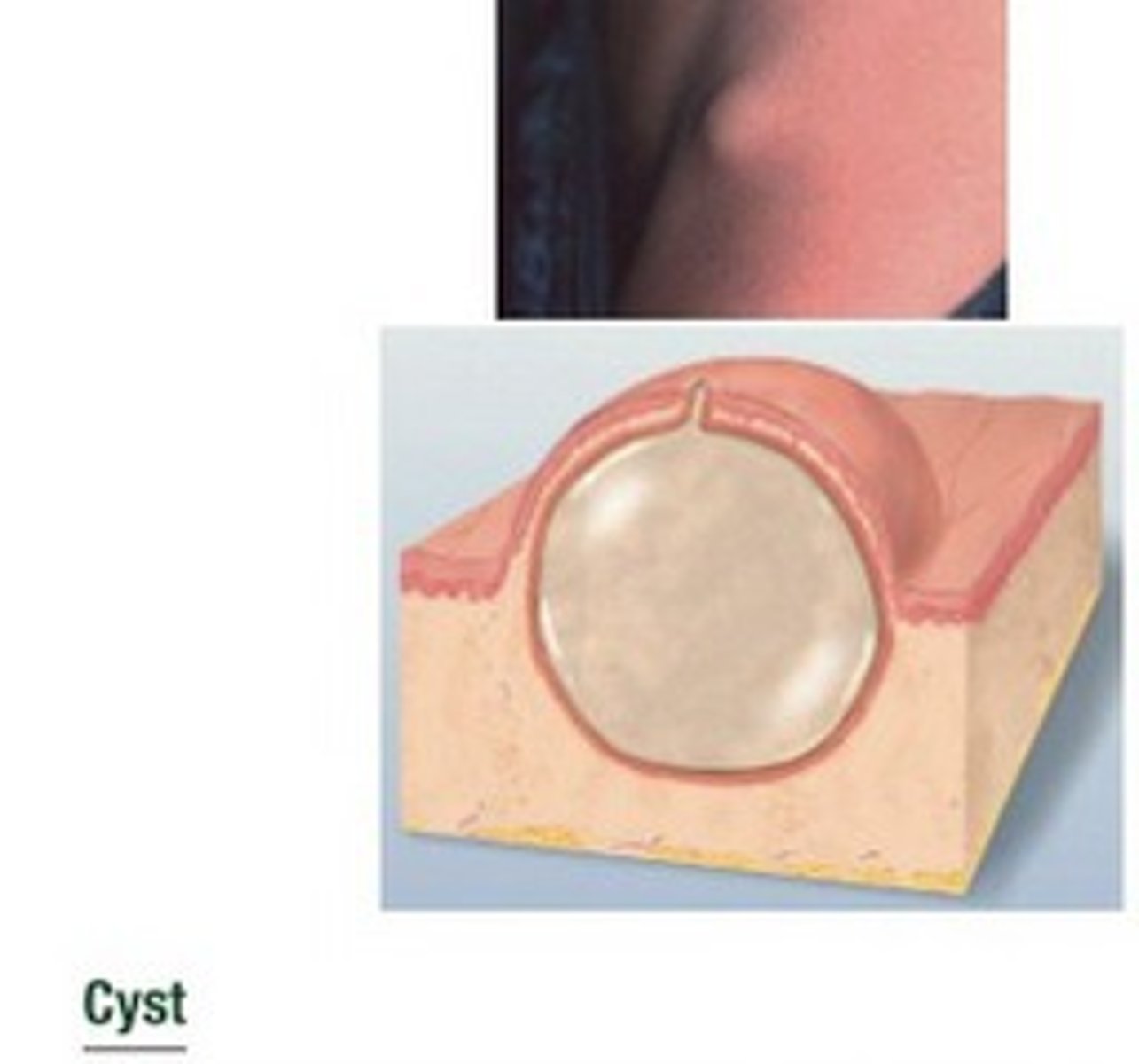
Cyst (primary)
encapsulated fluid-filled cavity in dermis or subcutaneous layer, tensely elevating skin
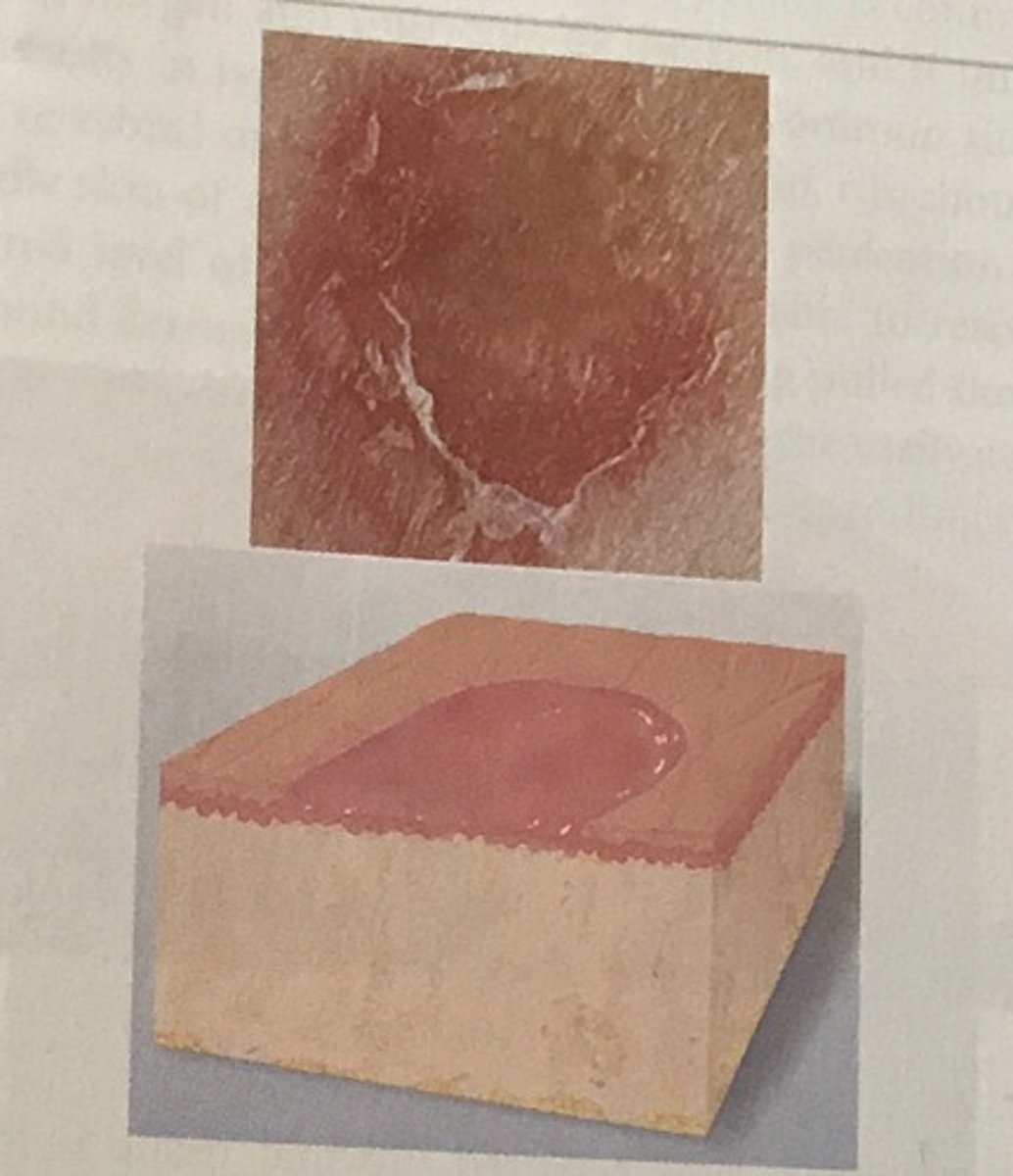
Erosion (secondary)
Scooped out but shallow depression. Superficial; epidermis lost; moist but no bleeding; heals without scar because erosion does not extend into dermis.
Scar (cicatrix) (secondary)
Skin mark left after healing of a wound or lesion; represents replacement by connective tissue of the injured tissue
Young scars: Red or purple
Mature scars: White or glistening
petechiae
small, pinpoint hemorrhages
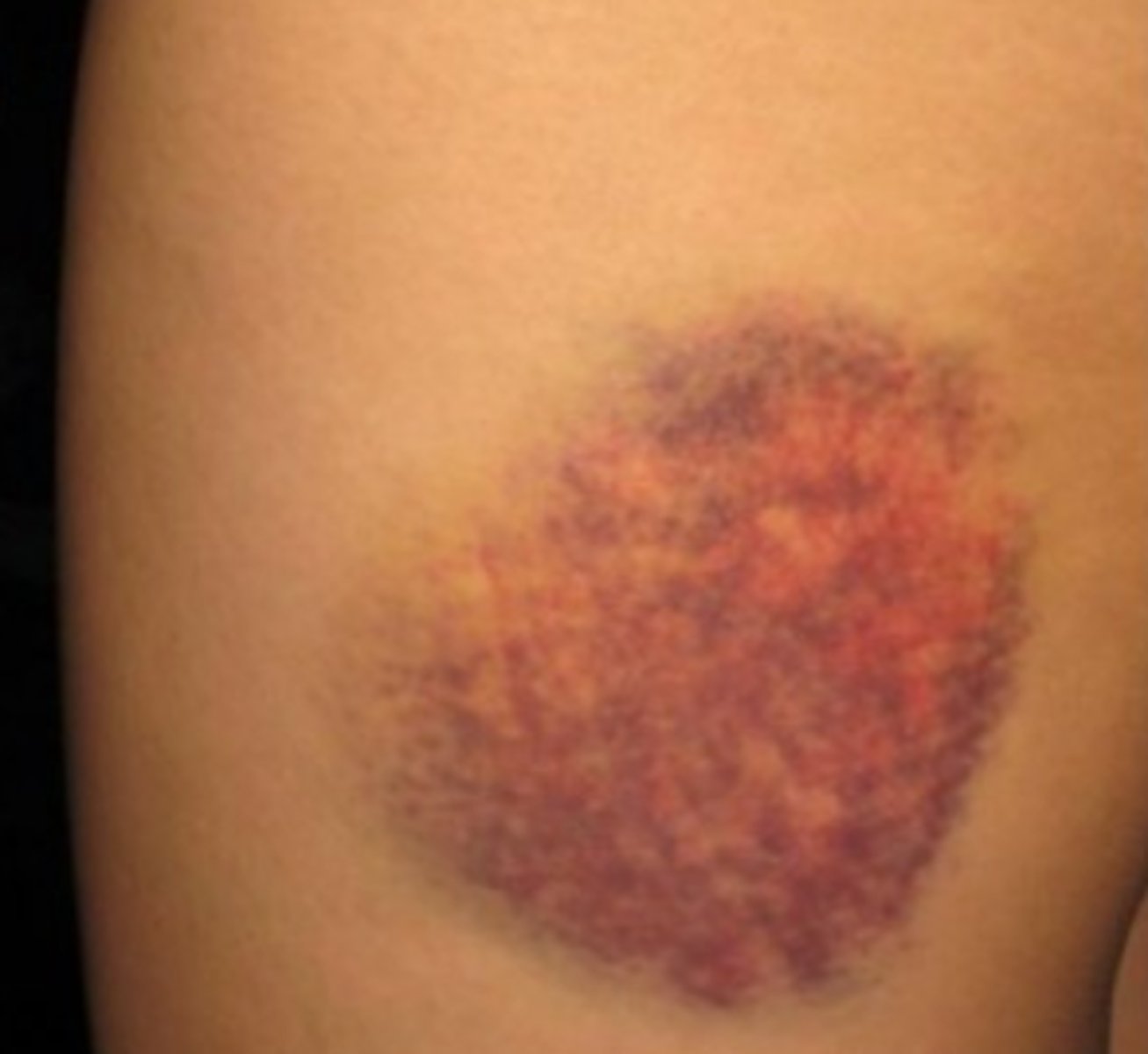
Ecchymosis
bruise
Skin scrapings
used to diagnose fungal lesions
Tzanck smear
used to diagnose blistering skin conditions ex. chickenpox, herpes zoster/simplex, varicella
Impetigo
bacterial infections (staph, strep, MRSA) CONTAGIOUS
family cannot touch/share items
treatment: antibiotics
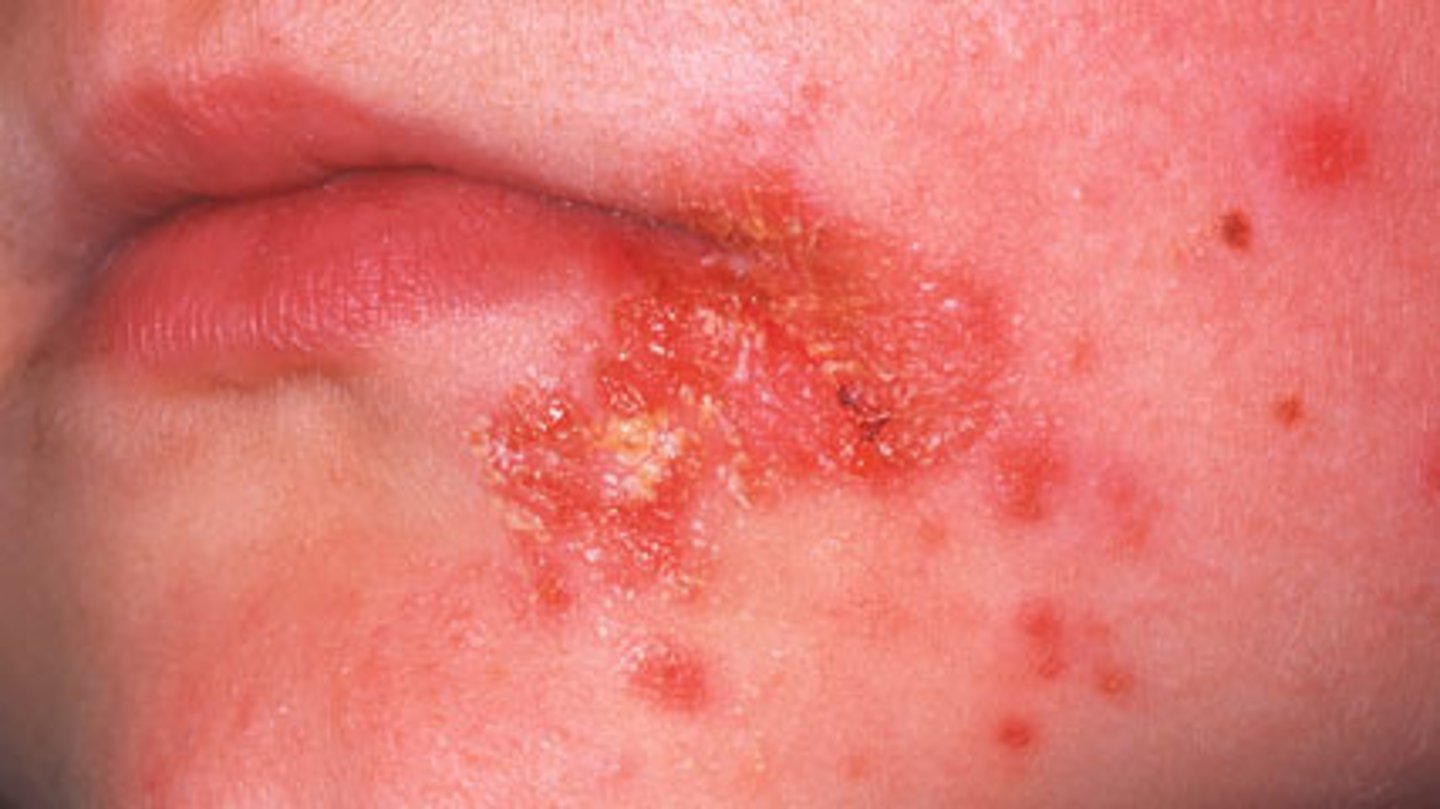
herpes simplex
simplex 1 = cold sore
simplex 2 = genital blisters
CONTAGIOUS
treatment: antiviral medications and prophylactic medications
dont kiss babies
Pediculosis
Pediculosis capitis- treatment: lindane (kwell), pyrethrin (RID) and heat
Pediculosis corporis- bath in soap and water and apply scabicide
Pediculosis pubis-check for coexisting STDs
Vitamin C
vital for collagen synthesis
Rhinitis and Rhinosinusitis
Rhinitis (runny nose) and Rhinosinusitis (full sinus)
acute, chronic, bacterial, and viral
treatment: PUSH FLUIDS. hot pack to reduce congestion
Neck stiffness (nuchal rigidity): If it turns into bacteria--there is a risk of meningitis
medicamentosa: drying of the nose caused by overuse of nasal spray
Laryngitis
voice loss
Epistaxis
nose bleed
treatment: AFRIN (phenylephrine) spray = vasocontriction, pressure. ice collar to reduce inflammation and bleeding
Eosinophils and Basophils
allergic reactions
Neutrophils
mature, first line of defense
bands (baby neutrophils): shift left--sign of immediate/new infection
iron deficiency anemia (hypoproliferative)
diagnosed with labs: hemoglobin and hematocrit, RBC, iron studies, bone marrow asp.
signs/symptoms: fatigue, weakness, malaise, pallor/jaundice, resp/cardia symptoms, pica, nail changes
treatment: eat more iron and vit. C
can cause black bowel movements
DECREASE FATIGUE AND MAINTAIN NUTRITION
Megaloblastic anemia (turn big due to defect in factory)
folic acid and B12 deficiency (cells get stuck on conveyor belt and grow large)
Pernicious anemia = B12 anemia could possibly be a vegetarian
diagnosed with labs: hemoglobin and hematocrit, RBC, iron studies, folic acid and B12, bone marrow asp.
signs/symptoms: fatigue, weakness, malaise, pallor/jaundice, resp/cardia symptoms, pica, nail changes
sodium-potassium pump
ACTIVE TRANSPORT (requires energy)
keeps the cell in electrolyte check
Every 3Na+ out = 2 K+ in (and vise versa)
There should always be more potassium in the cell
Fluid Volume Deficit (FVD)
hypovolemia
mostly caused by:
- hemorrhage=loosing blood (1st reason)
- diarrhea/vomiting=loosing electrolytes (2nd reason)
- may be caused by burns
symptoms: low temp, high HR, low BP, lab levels, elderly: congusion/cognition
treatment: I&Os every 8 hr and daily weights
dehydration is not the same of FVD
ORAL FLUIDS ALWAYS PREFFERED
Fluid Volume Excess (FVE)
hypervolemia
mostly caused by:
- kidney disease
- too much intake of sodium
- heart failure
symptoms: edema, distended neck veins, crackles in the lungs, decreased concentration of HCT and BUN (more fluid=diluted)
treatment: I&Os every 8 hr and daily weights (output > input), diuretics (flush out the fluid) and dietary restriction of fluids and sodium
look for signs of cerebral edema
Hypokalemia
low potassium (<3.5) caused by:
- diarrhea
- hyperaldosteronism
manifestations: heart problems (ECG changes and dysrhythmias)
treatment: oral/diet intake of potassium or IV. monitor ECG and ABGs
hypophosphatemia
low phosphate (<2.7) caused by:
- bowel problems and lots more
manifestations: confusion and muscle pain
treatment: oral supplements/diet, IV (CHECK IV SITE for tissue damage or necrosis)
metabolic alkalosis
caused by vomiting and NG
respiratory acidosis
caused by major lung issues, puncture, PE
MOST LIKELY VENT
respiratory alkalosis
always caused by hyperventilation
Vertigo
the illusion of motion or a spinning sensation
Benign positional veritgo (BBPV): triggered by specific changes in position and the loosening/movement of calcium crystals in the ears
Acoustic neuroma
tumor of the VIII cranial nerve (vestibulocochlear)
Laryngectomy
surgical removal of the larynx to avoid cancer
(still have vocalization and the ability to eat)
Amblyopia
lazy eye
Emmetropia
normal vision 20/20
Hyperopia
farsightedness (can't see things close up)
Blindness
Legal blindness = 20/200
Low Vision
visual impairment that requires the use of devices and strategies in order to see--often accompanied by functional impairment
- placement of items in room
- clock method on tray
- braille and service animals
MAY ALSO BE CAUSED BY RETINAL VEIN OR ARTERY OCCLUSION
Blinking
lowers the size of the conjuntival sac = less absorption
Apnea
temporary cessation of breathing. Weight of the chest pushes on the lungs
major risk: obesity
signs/symptoms: open mouth breathing and snoring. groggy (daytime sleepiness), short of breath, weak, headache
Cycloplegics
paralyze the eye
CANNOT GIVE TO PATIENTS TAKING MAOI's OR TRICYCLIC ANTIDEPRESSANTS
Glaucoma meds
increase aqueous outflow or decrease aqueous production
may constrict the pupil.
example: atropine
Tonometry
the measurement of intraocular pressure
Corneal Dystrophies
deposits in the corneal layers (keratoconus and fuchs)
Retinal vascular disorders
-Central retina vein occlusion
-Branch retinal vein occlusion
-Central retinal vein occlusion
-Macular degeneration
vitrectomy
surgical removal of all or part of the vitreous humor (bubble)
age related macular degeneration (AMD)
a condition in which the macula degenerates, gradually causing central vision loss and blindness (leading cause of blindness)
slow break down of retina layers. (wet type: proliferation of blood vessels under retina)
conjunctivitis
inflammation of the conjunctiva (pink eye)
classified by cause
viral and bacterial conjunctivitis are contagious
symptoms: hyperemia
uveitis
inflammation of the uvea
orbital cellulitis
An infection within the eye socket.
diabetic retinopathy
damage to the retina as a complication of uncontrolled diabetes=blindness
Flushing
only flush when the corneal surface is intact
Conductive hearing loss
caused by external of middle ear problem
Tinnitus
perception of sound (often called ringing in the ears)
Foreign bodies
- removal through irrigation, suction, or instrumentaiton
- objects that may swell (vegetables or insects) should not be irrigated
Malignant otitis externa
rare. effects external auditory canal and surrounding tissues/skull
Dizziness
any altered sense of orientation in space
Labyrinthitis
inflammation of the labyrinth
Ototoxicity
damage to the organs of hearing by a toxic substance (induced by drugs)
Cochlear implant
prosthesis for people with bilateral sensorineural hearing loss who cannot use conventional hearing aids
ABCDEEFG
Asymmetry
Borders
Color
Diameter
Evolving
Elevated
Firm
Growing
Corticosteriods
anti-inflammatory agents that treat skin inflammation (can decrease wound healing)
Erythema
reddness
Pruritus
itching
Primary lesions
initial lesions that are characteristic of a disease
Secondary lesions
lesions that result in changes in primary lesions
- scratching, trauma, infections, wound healing
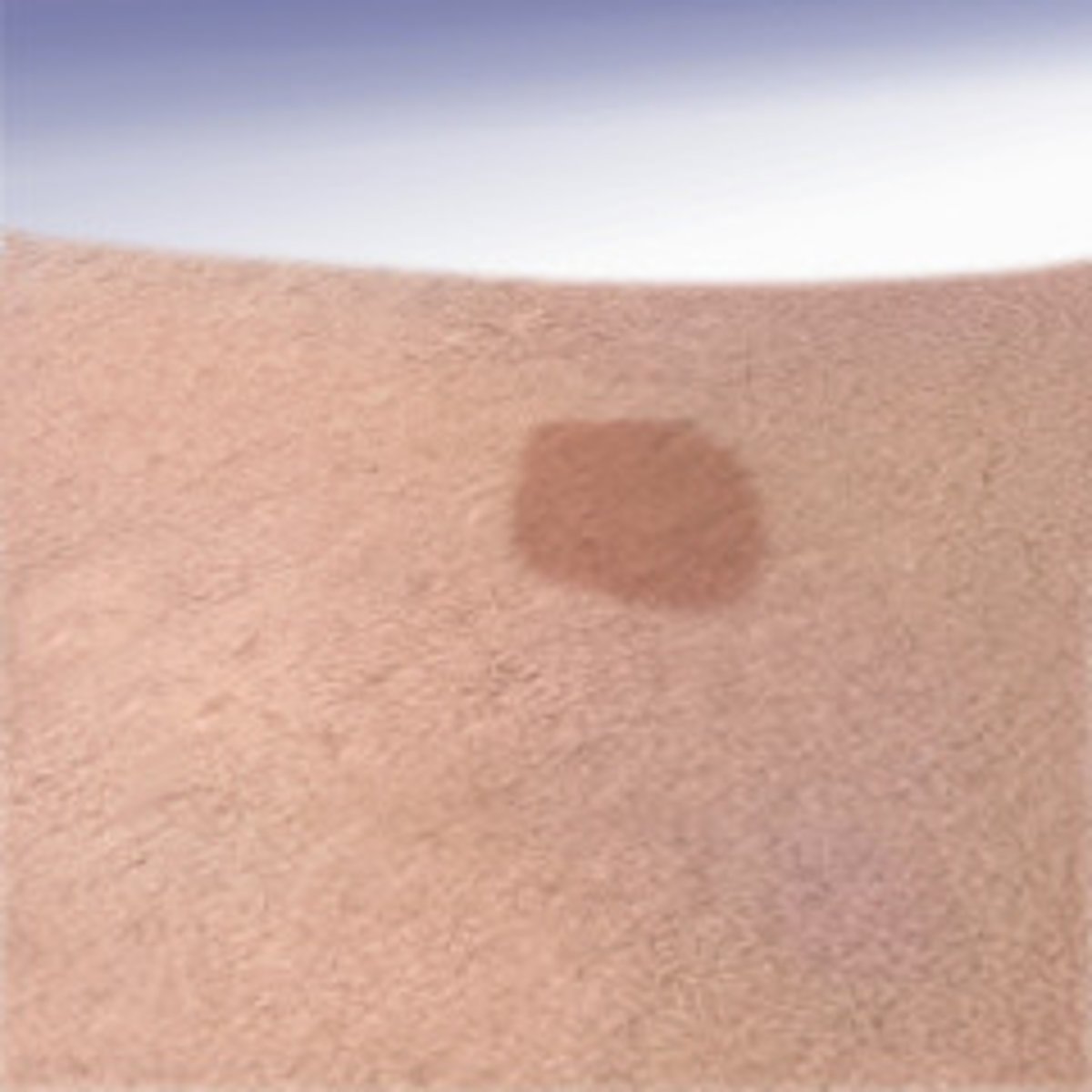
Macule (primary)
flat, discolored spot on the skin
ex. port wine stains

Plaque (primary)
Superficial elevated lesion, 1cm or larger
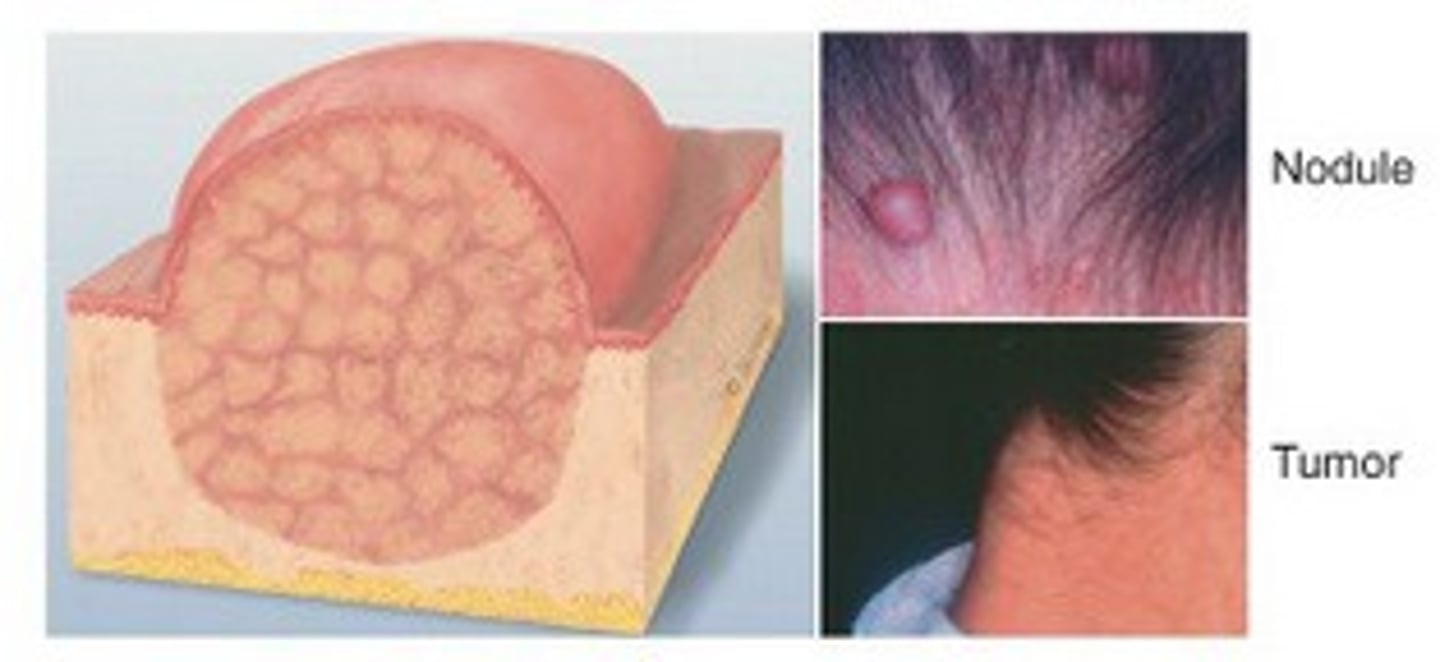
Nodule/tumor (primary)
elevated, solid, palpable mass with irregular border- may be malignant (cancerous) or benign ex. tumor
Bulla (primary)
- big blister
Elevated blister > 1 cm, clear serum inside
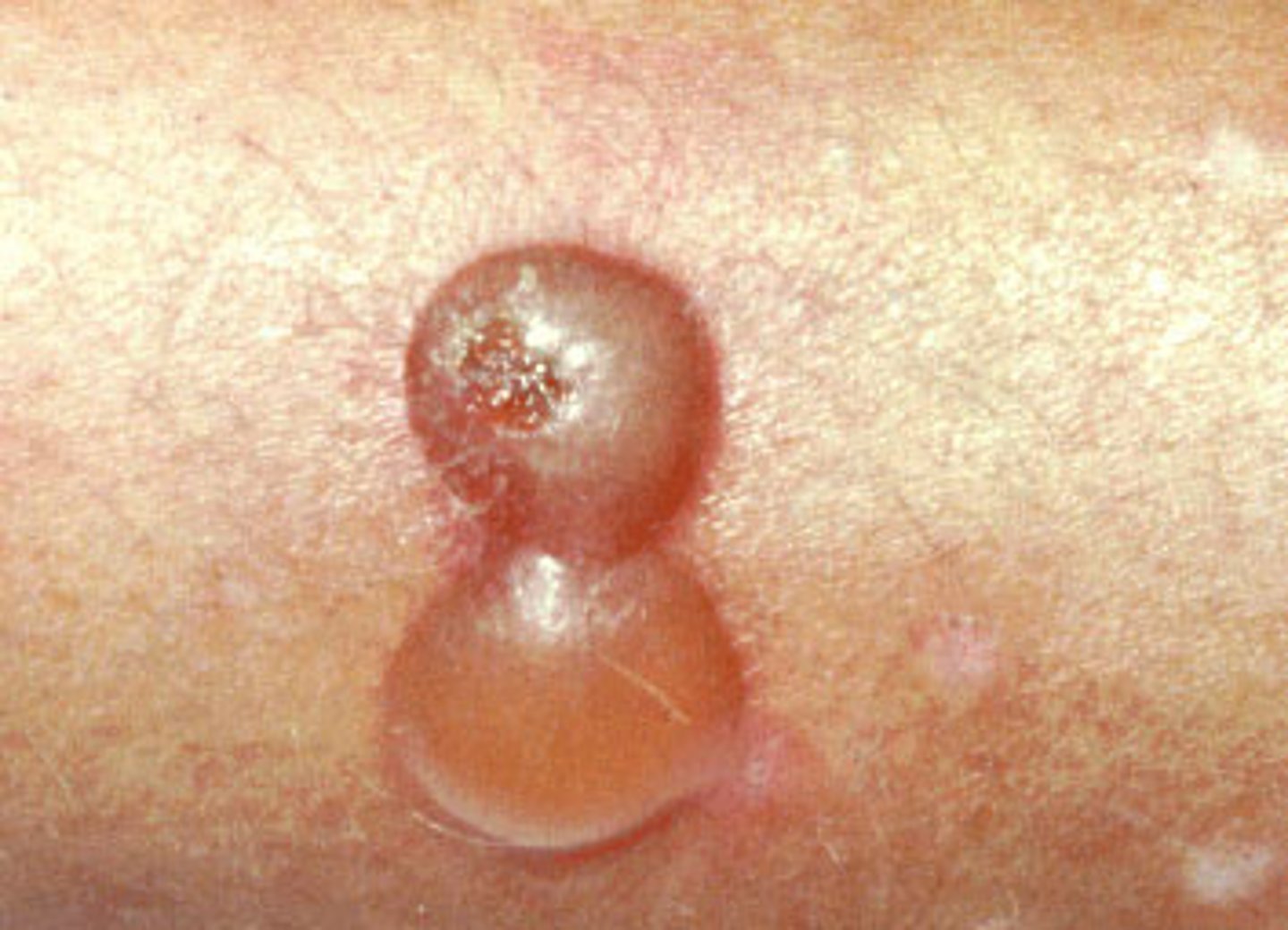
Pustule (primary)
turbid fluid (pus) in cavity; circumscribed and elevated; ex - impetigo, acne
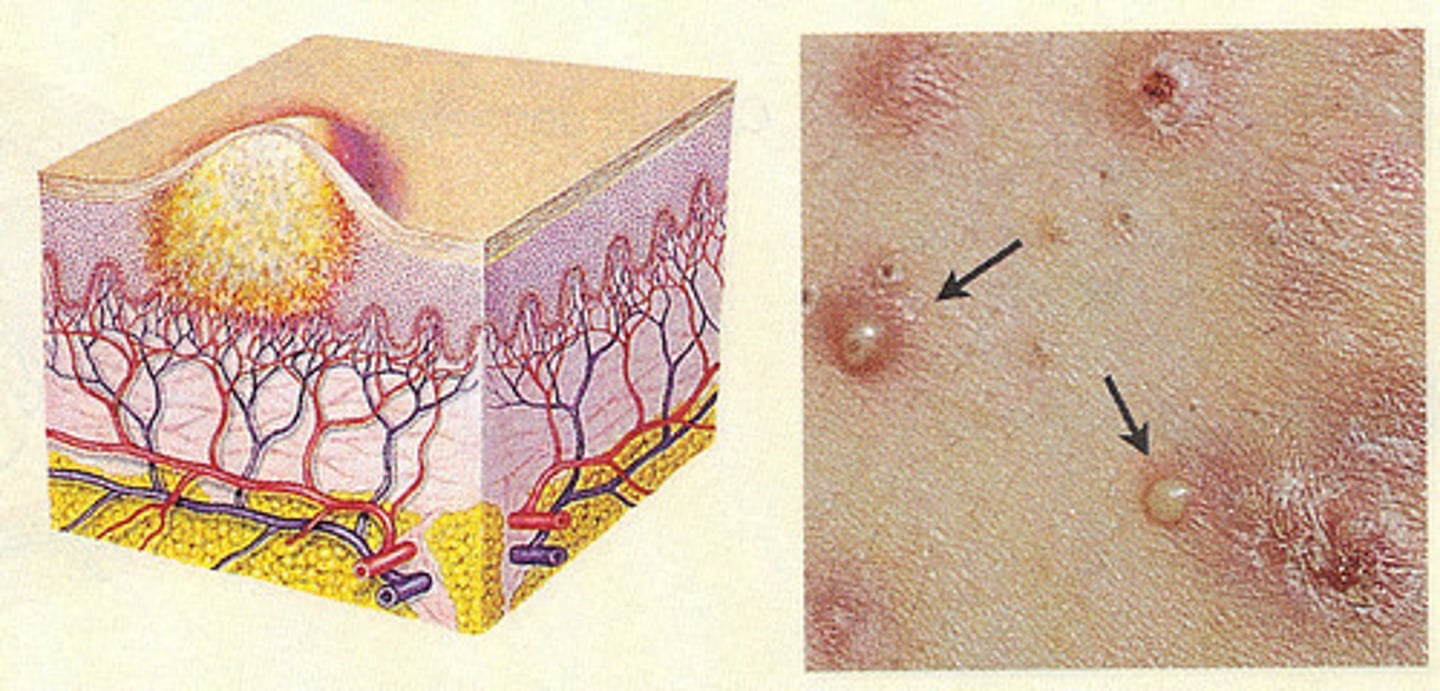
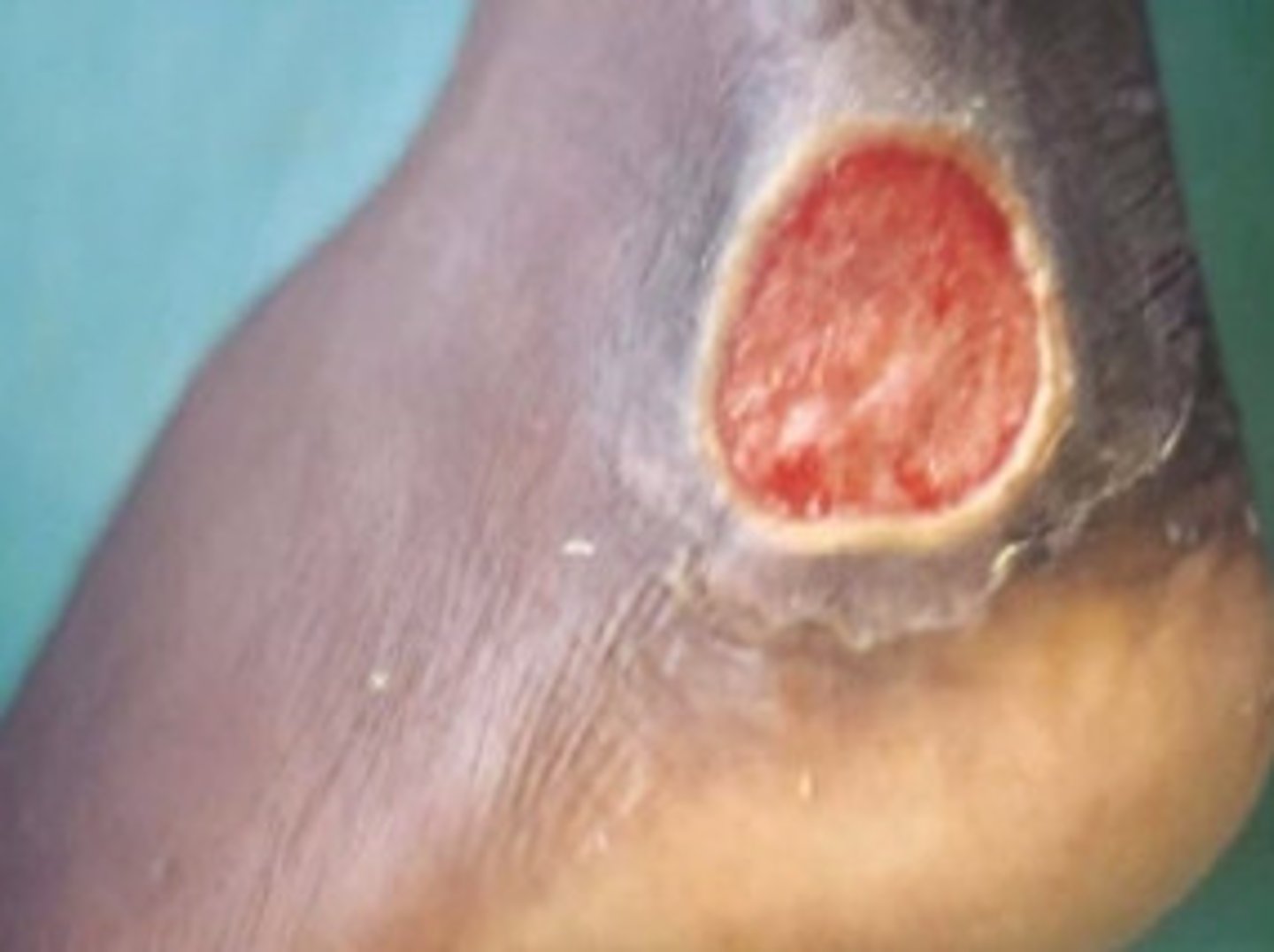
Ulcer (secondary)
deeper depression extending into dermis, irregular shape; may bleed; leaves scar when heals
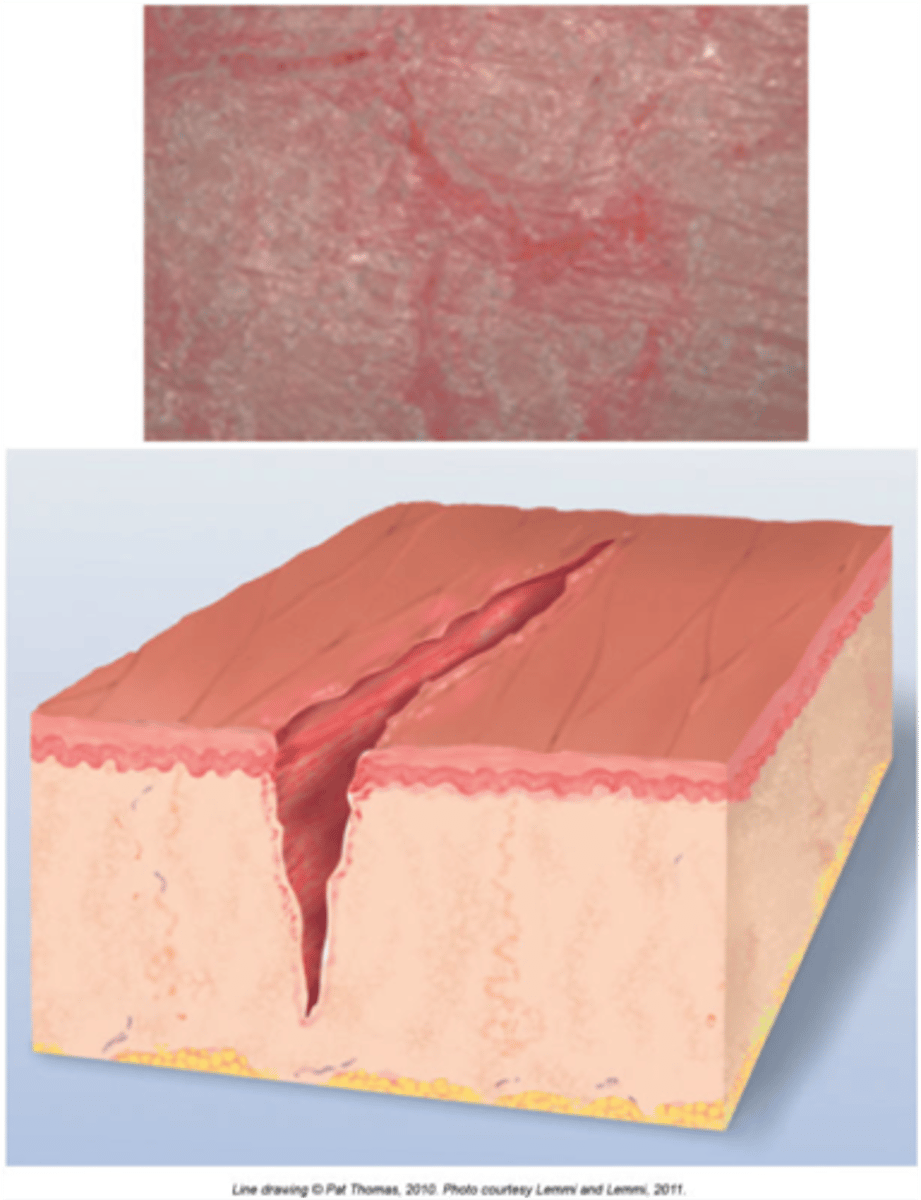
Fissure (secondary)
a linear crack in the skin
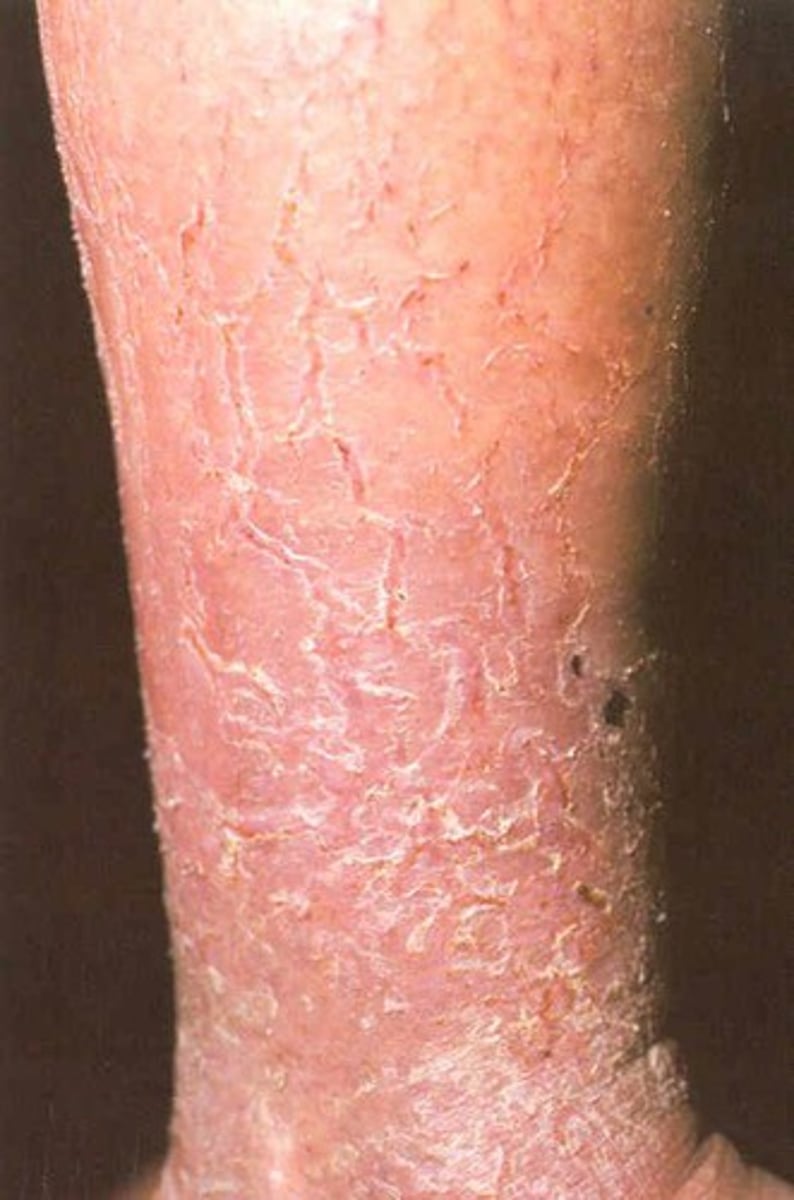
Scales (secondary)
flakes of skin, sheds excess keratin (eczema)
Crust (secondary)
dried residue of skin exudates such as serum, pus, or blood
impetigo = yellow crust
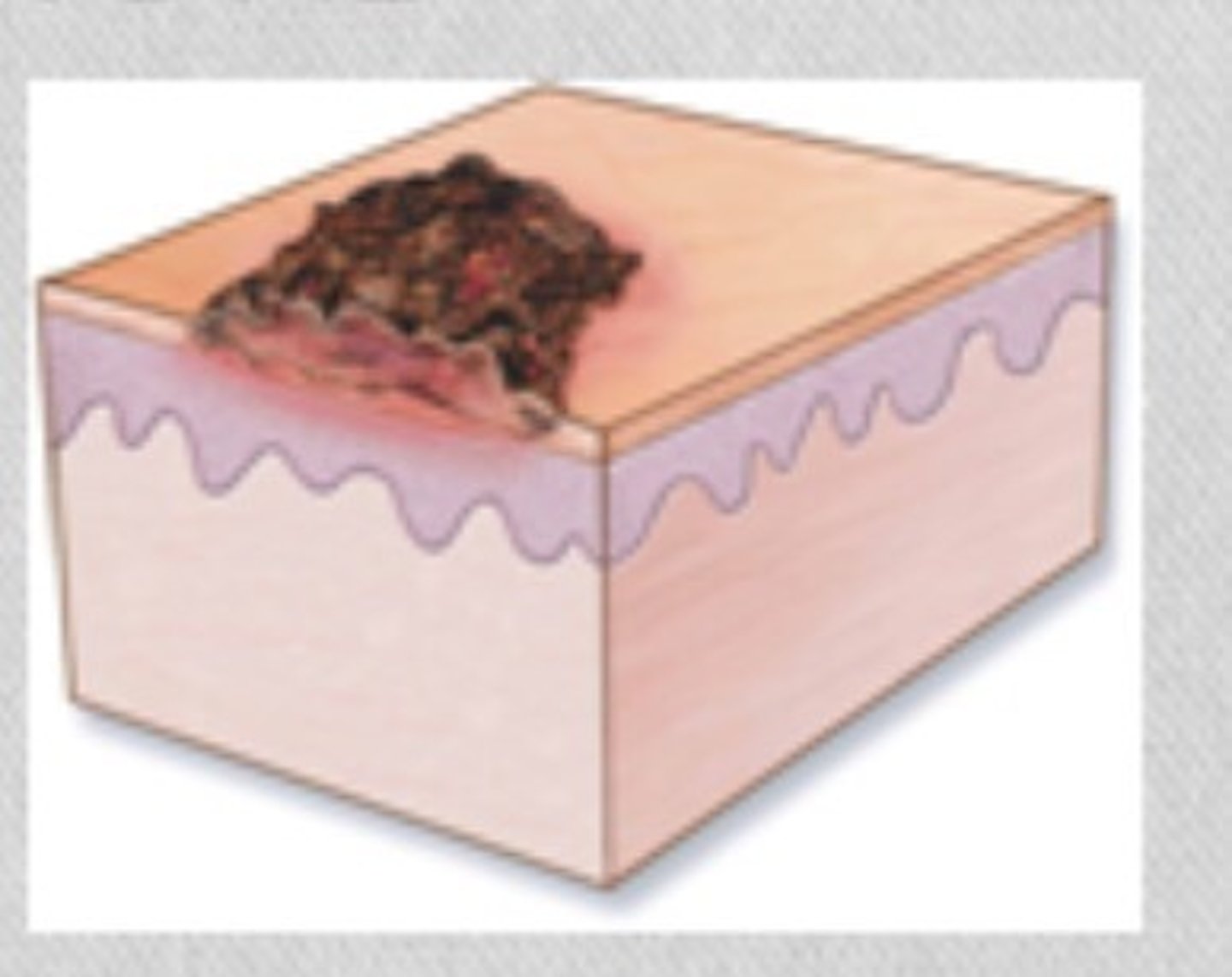
Keloid (secondary)
Thick scar resulting from excessive growth of fibrous tissue
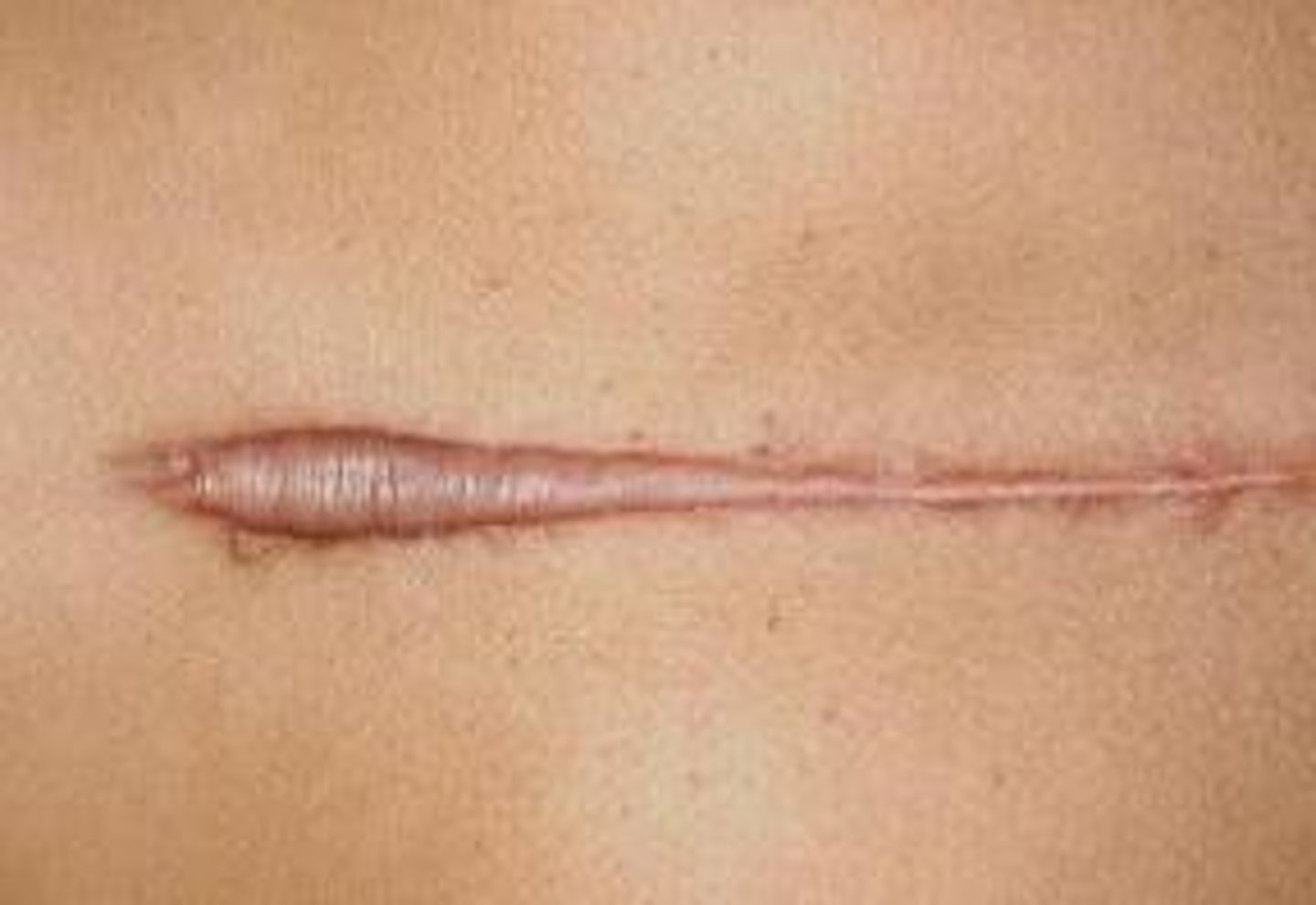
Atrophy (secondary)
Thinning of the dermis or epidermis causing depression in the skin. (happens in old age)
Lichenification (secondary)
prolonged, intense scratching eventually thickens skin and produces tightly packed sets of papules; looks like surface of moss
psoriasis and eczema
Cherry angioma
a small, round, bright red blood vessel tumor on the skin, often on the trunk of the elderly
Pruritis
Itching associated with most forms of dermatitis.
treatment: reduce heat and humidity! Hygiene. Corticosteroids and antihistamines
herpes zoster (shingles)
viral infection affecting peripheral nerves caused by previous varicella (reactivation and distribution along the nerve symplex)
3 phases: pain, vesicle formation (raised, red, and pussy), and nerve pain
signs/symptoms: vesicles (blisters), pain, linear formation
treatment: antiviral medications, pain medication
complications: is disease is close to eye = trigemenal nerve complications