Homeostasis and endocrine
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
Homeostasis meaning
regulation of internal conditions of a cell/organism to maintain optimum conditions for function in response to internal & external changes
How does this change occur (homeostasis)
requires a stimulus – something to respond to
picked up by a receptor
then sends signals to the coordination centre perform some action to respond to that until it bak to optimum
an effector produces response
receptor
detects stimuli (change in environment)
effector
muscles/glands that brings changes which restores optimum levels
coordination centre
receives and processes information from the receptors (eg brain, spinal cord, pancreas)
pathway of control system for body temperature
stimulus→ change in temperature
receptor → skin
coordination centre→ brain/hypothalamus
effector → skin/muscles
Pathway of control system for water content of body
stimulus- change of water content in blood
receptor - brain
coordination centre- pituitary gland
effector - kidneys
pathway control system for blood glucose
stimulus - change in blood glucose
receptor - pancreas
coordination centre - pancreas
effector - liver
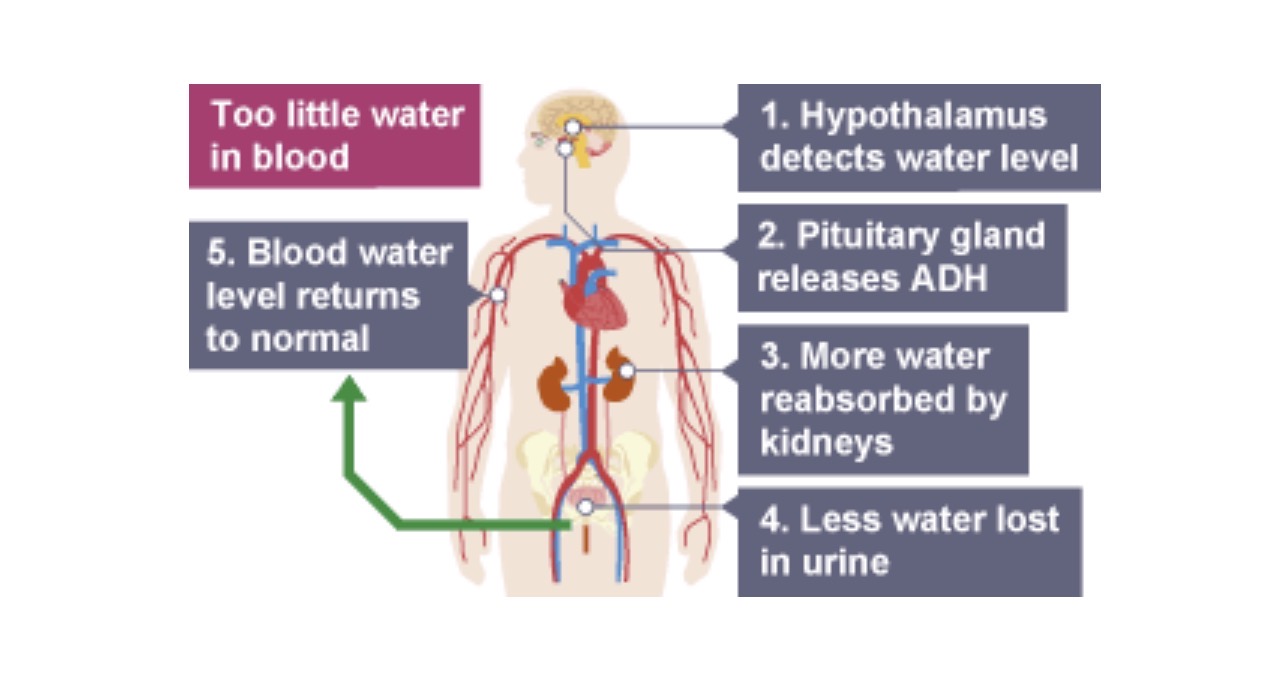
How does the body control water content
if too much water in blood
hypothalamus detects too much water in blood
pituitary gland releases less ADH
kidney absorbs more blood
so more water reaches bladder (dilutes urine)
blood level returns to normal
What controls centre coordinates body temperature
thermoregulatory centre in the hypothalamus of the brain
How does your body detect temp change?
the centre contains receptors that are sensitive to temp changes in the blood flowing through the brain
temp receptors in he skin send extra info to the thermoregulatory centre via sensory neurons
the receptors are so sensitive the can detect a 0.5 degree celsius change
cooling down
when core body temp begins to rise impulses sent via thermoregulatory centre to body so more energy is transferred to surroundings to cool you down
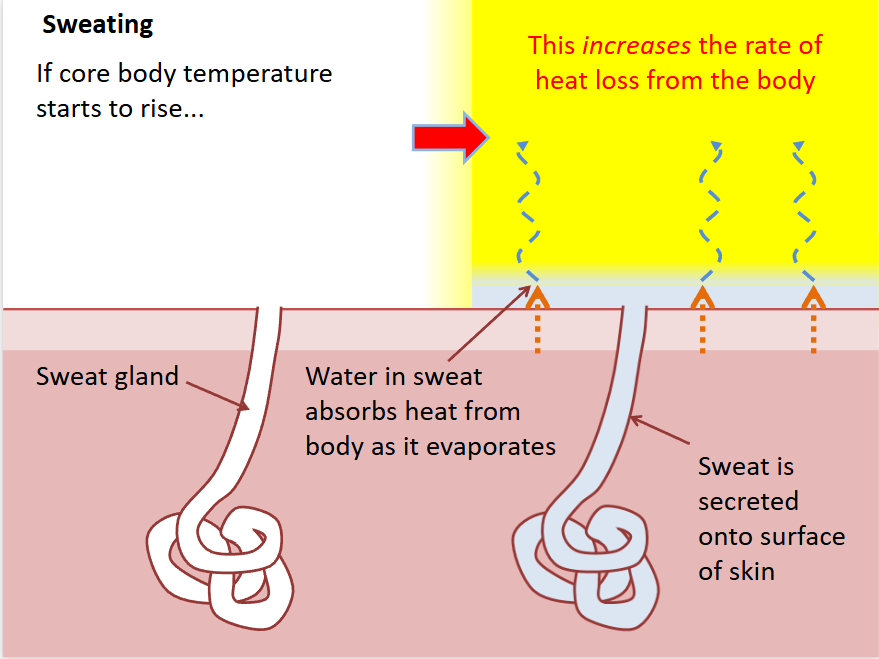
sweating
blood close to surface of skin heating it up
liquid sweat turns into gas (evaporates)
it takes heat from skin
skin loses heat it cools down
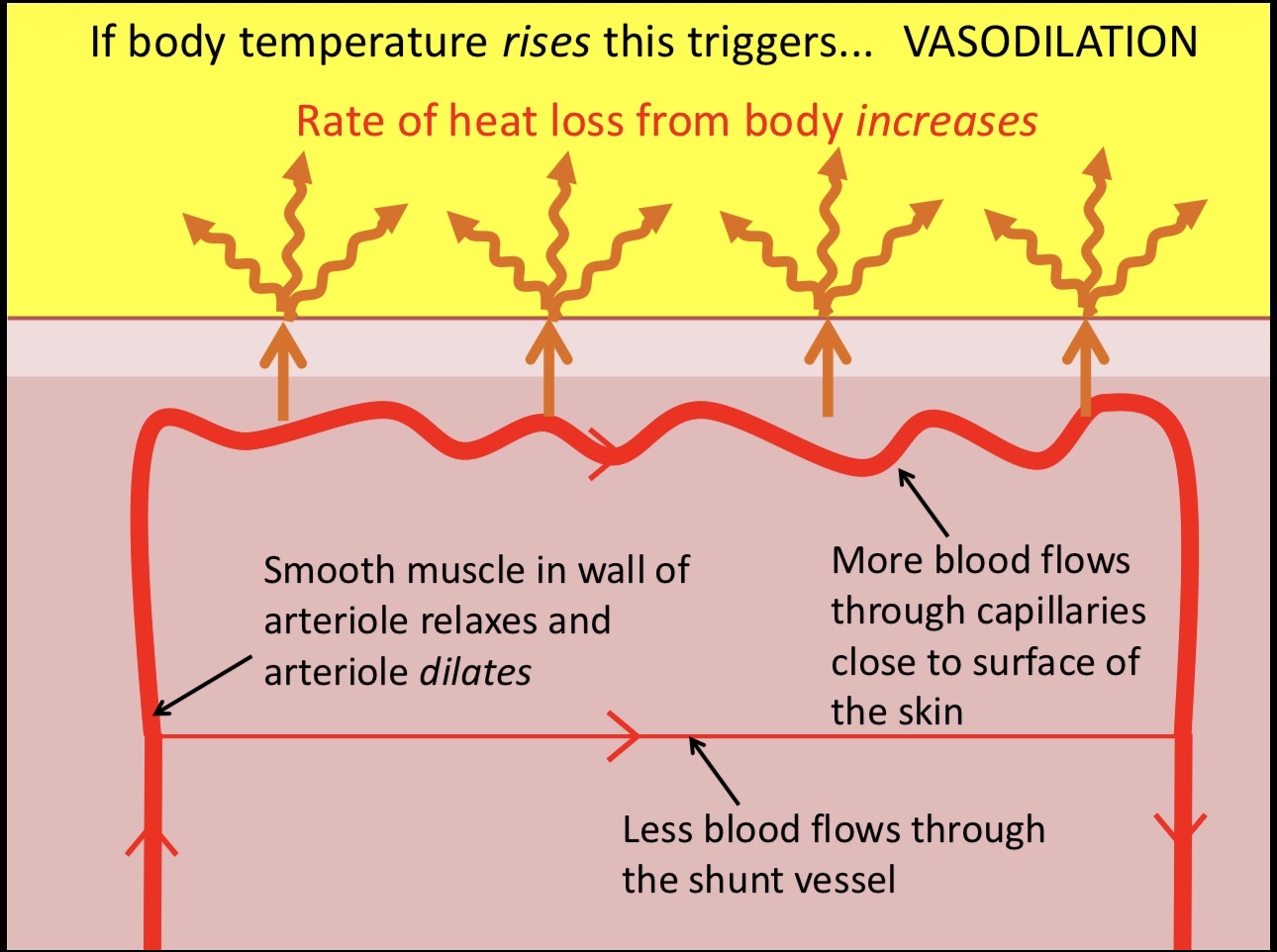
vasodilation
blood carries most of the heat energy around body
capillaries underneath skin that can be filled with blood if you get too hot
brings blood closer to surface of skin so more heat can be lost
warming up
if you get to cold the rate of enzyme controlled reactions fall too low
not enough respiration → danger of death
impulses sent to thermoregulatory system centre to prevent cooling down be preventing energy transfer to environment
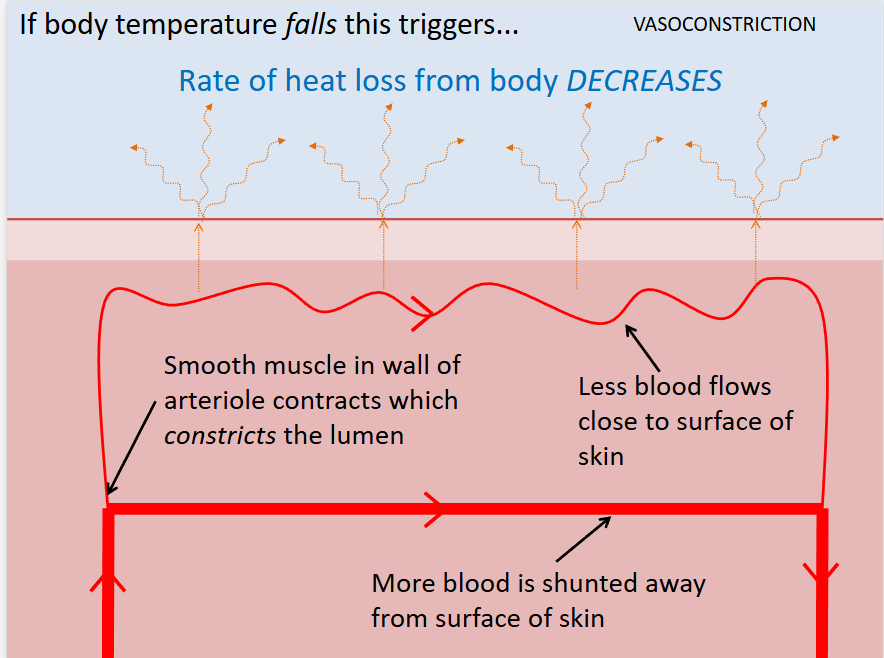
vasoconstriction
capillaries under your skin get (shut off)
takes blood away from surface of skin so less heat can be lost
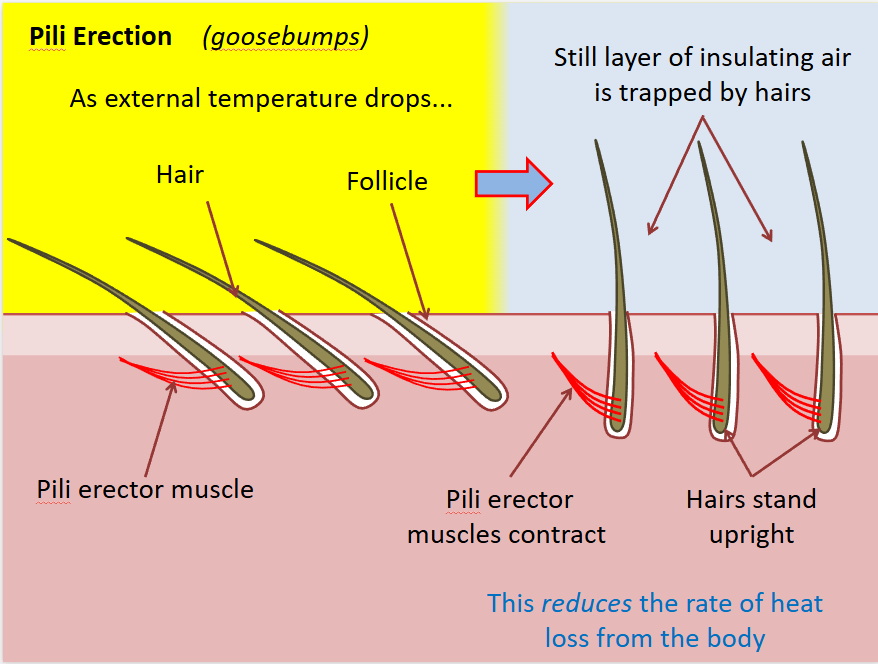
piloerection (goosebumps)
the hairs trap layer of air next to skin which is then left warmed by the body heat
the air becomes an insulating layer
shivering
muscles require energy ( from respiration) to contract
during respiration some energy is always lost as heat
Endocrine system
made up of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream
the effects are slower than nervous system but have a longer lasting effect
pituitary gland
releases hormone ADH
controls growth and stimulates other glands like thyroid, ovaries and testes
thyroid gland
releases hormone thyroxine
controls metabolic rate
adrenal gland
hormone- adrenaline
triggers fight or flight → prepares body for stressful situations
pancreas
releases hormones insulin and glucagon
controls blood glucose levels
ovary
releases hormone oestrogen
controls development of sexual characteristics & menstrual cycle
testes
releases hormone testosterone
controls development of sexualcharacteristics and sperm
hormones
chemical messages produced by gland
have an effect in target organ and travel in the blood stream
glucose
sugar
glucagon
hormone
glycogen
glucose stored (as larger molecules) in the liver/muscles
how the pancreas controls blood glucose levels
insulin moves glucose in blood into cells to be used
soluble glucose can also be turned into the insoluble carbohydrate glycogen
glucagon is a hormone that stimulates the liver to turn glycogen back into glucose
high glucose levels in blood
pancreas produces insulin to lower glucose levels in blood
glucose diffuses into liver
(glucose is used in respiration)
forms chains of glucose → glycogen
glycogen stored in liver
low glucose levels
pancreas releases glucagon
breaks up glycogen in liver
now glucose
diffuses back into blood stream
diabetes
occurs when glucose control goes wrong
type 1
pancreas doesn’t produce insulin
glucose levels are uncontrollably high
treated with insulin injections
type 2
insulin is produced but liver cells no longer responds to it
people who are obese are at risk
controlled by limiting carbs/sugar in diet and exercise
the kidney
the main job of the kidneys is to control the water balance of the body
what do kidneys do
if little water kidneys conserve it → produce very little, very concentrated urine
control concentration of mineral ions so if excess mineral ions → lost through sweat/urine
too much water so aim to excrete it → produces lots of dilute urine
What removes excess water, ions and urea from the body?
The kidneys remove excess water, ions and urea in the urine.
What happens to excess amino acids from the diet?
They are deaminated in the liver to form ammonia.
Why must ammonia be converted to urea?
Ammonia is toxic.
What do the kidneys produce by filtration and selective reabsorption?
Urine.
What useful substances are selectively reabsorbed?
Sugar and as much water as the body needs.
Which substances are excreted in urine?
Urea, excess ions and water.
What controls the water level in the body?
by the negative feedback system controlled by the hormone ADH
When is ADH released?
When the blood is too concentrated.
What does ADH cause the kidney tubules to become?
More permeable.
What does increased tubule permeability allow?
More water to be reabsorbed back into the blood.
Why does protein remain in the blood plasma rather than the filtrate?
the molecules are too large to pass through the filter
How does ADH affect production and concentration of urine by the kidneys? (4)
high levels of ADH increase water reabsorption
from kidney tubules
so) ADH increases the concentration (of urine)
(so) ADH decreases the volume (of urine)
Describe what happens to glucose, protein and urea in kidneys (4)
glucose and urea are filtered (out of the blood)
protein is not filtered (out of the blood)
all glucose reabsorbed
urea passes out in urine / not absorbed
kidney stones
high salt and minerals in your diet can lead to stones precipitating out
extremely painful
have to be excreted from the body in the urine
renal damage/failure
the kidney no longer able to filter the blood effectively
plasma not properly reabsorbed
protein and cells pass through bowman’s capsule
kidney failure
a person can survive with only one kidney
no working kidney → death
options : dialysis or transplantation
kidney dialysis
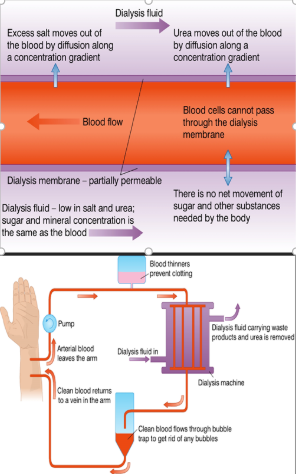
transplantation
organ removed from either dead person or living person if not an essential organ
inserted and connected to patient
damaged organs sometimes removed
donor organ not always connected into position of old organ
advantages and disadvantages of transplantation
Advantages | Disadvantages | |
can live relatively normal life | shortage of donors | |
immunosuppressant drugs are relatively cheap | need tissue match lited transplant life span (10 years) immunosuppressant drugs needed for rest of life |
advantages and disadvantages of dialysis
Advantages | Disadvantages | |
machines available | time consuming | |
no need for tissue matching | expensive longterm (30K a year) diet must be carefully controlled |
kidney disease
filtration in the kidneys doesn’t work properly so proteins are pushed out into urine as they are too big
glucose in urine = kidney failure
protein in urine = kidney failure too big to filter back into blood
negative feedback
if a factor in the internal environment increases or decreases, changes take place to reduce it and restore the original level
stimulus→ sensor → control→ effector → back to stimulus
whatever the initial change the response causes the opposite
thyroid
gland in your neck uses iodine from your diet to produce hormone thyroxine
thyroxine controls basal metabolic rate of the body
what does your basal metabolic rate determine
how quickly substances are broken down and built up, how much oxygen your tissues use and the development of the brain in a growing child
plays a huge role in growth and development
Adrenaline
important hormone for organisms
boosts the delivery of oxygen and glucose to brain and muscles
preparing body for fight or flight
how does adrenaline affect body
once adrenaline is released from adrenal glands effects include :
heart rate and breathing to increase
stored glycogen in the liver to be converted to glucose for respiration
pupils of eyes dilate to let more light
increased mental awareness
blood diverted away from digestive system to big muscles
examples of negative feedback (thyroxine + adrenaline)
if thyroxine levels begin to fall its detected by the brain
then releases TSH to increase levels (negative feedback)
adrenaline released by adrenal gland when in danger
once threat is over system returns to their resting levels
reproductive hormones during puberty
cause secondary sex characteristics to develop
ovulation (+ tests)
day egg is released
can conceive within 6 days of ovulation
ovulation test measures the levels of LH in urine
→ ovulation will occur 24-48 hrs after a positive ovulation test
menstrual cycle (hormones)
FSH -pituitary gland→ causes follicles to grow and mature then triggers ovary to make oestrogen
oestrogen-causes rise in LH, stops production of FSH, starts build up of uterus lining
LH → stimulates release of egg
progesterone→ inhibits levels of LH and FSH, maintains uterus lining, if egg fertilised prep for baby
empty follicle (yellow body) → releases progesterone
menstrual cycle days
1-7: bleeding uterus lining exits
7-13: FSH causes an egg to start to mature in one of the ovaries
14: LH causes egg to leave & go to oviduct
14-17: egg is able to be fertilised up to a day after
18-28:if not fertilised then oestrogen & progesterone causes lining to begin to break down
hormonal contraception
contraceptive pill
implant
injection
skin patch
IUS
Non-hormonal contraception
tubal ligation
condom
diaphram
IUD
Vasectomy
contraceptive pill (how it works, risks doses)
mixed pill → low doses of oestrogen and progesterone
→ inhibits production and release of FSH
→ affects uterus lining preventing implantation, makes mucus thick preventing sperm from getting through
risks → raised blood pressure, thrombosis, breast cancer
take a pill every day one week break in a month
mini pill
progestogen only pill → inhibits LH + FSH
if they don’t take pill everyday they’re at risk of pregnancy as egg will mature and be released
implant
release progesterone
lasts 3 years
99.95% effective
injections
progesterone
lasts 12 weeks
skin patch
oestrogen and progesterone
lasts 7 days
condom
collects semen
prevents STDs
diaphram
thin rubber diaphragm
prevents entry of sperm
intrauterine devices IUD
small structure inserted into uterus by doctor
last 3-5 years
contain copper and prevent any early embryos implanting into lining of uterus
IUS contains progesterone→ prevents buildup of lining which could create period problems
abstinence
some religious groups don’t accept contraception
no intercourse around ovulation
rhythm method
unreliable
ovulation indicators help
surgical methods
vasectomy→ sperm duct cut & tied prevent sperm getting out of testes
tubal ligation→ oviducts cut and tied
anaesthetic needed
surgically sterilised