IB Computer Science Paper 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/76
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 11:46 PM on 5/7/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
1
New cards
What is inheritance
an ‘is-a’ relationship. using regular arrow. inherits the attributes and behaviours of the container. “class mountain bike **extends** bicycyle'“
2
New cards
what is association
one to many, one to one, many to many. a relationship between classes of objects that allows one object instance to cause another to perform an action on its behalf.
3
New cards
what is aggregation
‘has-a’ relationship. container and contained = customer and bank account. using blank diamond arrow, pointing towards container (opp of inheritance) (container has contained as an attribute)
4
New cards
what is composition
when contained cannot exist without its container. Bank account and sub account, sub account cannot exist w/o bank account. filled-in diamond arrow pointing towards container.
5
New cards
what is a pure association
neither classes have each other as an attribute. a line and 0…n on both ends
6
New cards
what is an object diagram
have actual real-world examples or values. show how a system will look like at a given time
7
New cards
what is an object
* representation of a real world entity.
* instance of a class.
* abstract entity and its components(data and actions).
* contains attributes and behaviours
* has 2 components: attributes(like lists) and behaviours (functions)
* instance of a class.
* abstract entity and its components(data and actions).
* contains attributes and behaviours
* has 2 components: attributes(like lists) and behaviours (functions)
8
New cards
what is a class
template for creating an object. identifies what data needs to be stored for objects of this type and what methods are available to allow access to this data.
9
New cards
advantages of subprograms and objects
* support abstraction
* facilitating ease of debugging
* future maintenance (only need to work through one subprogram instead of whole thing)
* reusability of code
* modularity
* facilitating ease of debugging
* future maintenance (only need to work through one subprogram instead of whole thing)
* reusability of code
* modularity
10
New cards
what is abstraction
ignore the irrelevant and focus on the essential qualities of something rather than sticking to one specific example that illustrates our idea
objects are abstracted into a class
objects are abstracted into a class
11
New cards
what is polymorphism.
methods (behaviours) have the same name but different parameter lists and processes
12
New cards
what is encapsulation
technique of making the states in a class private and providing access to those states via public behaviours (methods)
* private = cannot be accessed by any method outside the class, thereby hiding the states within the class
* private = cannot be accessed by any method outside the class, thereby hiding the states within the class
13
New cards
what is dependency
when one class’ methods use a different class. a dotted arrow, from dependent part to the required part.
14
New cards
difference between an object and instantiation
15
New cards
why are dependencies bad
* decrease reuse.
* reuse helps development speed cuz developers can work on it at the same time.
* increases maintenance overheads
* changing one line of code could have big impact on all classes involved.
* greater room for error and takes lots of time to fix error
* reuse helps development speed cuz developers can work on it at the same time.
* increases maintenance overheads
* changing one line of code could have big impact on all classes involved.
* greater room for error and takes lots of time to fix error
16
New cards
explain the need for different data types to represent data items
* data is stored as a combination of binary values in the computer
* data types are used to store different kinds of data
* needed because they specify to the computer how to interpret the binary values in the storage
* So computer uses minimum RAM, and the program is more efficient
* data types are used to store different kinds of data
* needed because they specify to the computer how to interpret the binary values in the storage
* So computer uses minimum RAM, and the program is more efficient
17
New cards
different types of data and the memory they take up
* boolean = data that’s only 2 values (true/ false, on/off). 1 byte
* integers = represent whole numbers, 4 bytes bits to store information
* real = decimal numbers, 8 bytes
* string = sequence of characters like a name, each character takes up one byte
* integers = represent whole numbers, 4 bytes bits to store information
* real = decimal numbers, 8 bytes
* string = sequence of characters like a name, each character takes up one byte
18
New cards
what is declaration
variable declaration with a variable name with an object type
19
New cards
what is instantiation
‘new’ key word used to create the object
20
New cards
what is a super class
class whose features are inherited is known as a super class
21
New cards
what is sub class
* class that inherits the other class is known as sub class
* can add its own states and behaviours
* can add its own states and behaviours
22
New cards
what are parameters
* allows us to pass information or instructions into functions and procedures
* names of the information we want to use in a function or procedure
* values passed in are called arguments
* names of the information we want to use in a function or procedure
* values passed in are called arguments
23
New cards
what is overloading
* in a class, different methods have the same name
* different signatures where signature can differ but number of input parameters or type of input parameters (or both).
* different signatures where signature can differ but number of input parameters or type of input parameters (or both).
24
New cards
what is overriding
* allows child class to provide a specific implementation of a method that is already provided by the parent class
* same function, same parameters but different classes
* always invokes the more specialized behaviour.
* same function, same parameters but different classes
* always invokes the more specialized behaviour.
25
New cards
overloading vs overriding
* overloading = same function but different parameters
* overriding = same function, same parameters but different classes connected through inheritance
* overriding = same function, same parameters but different classes connected through inheritance
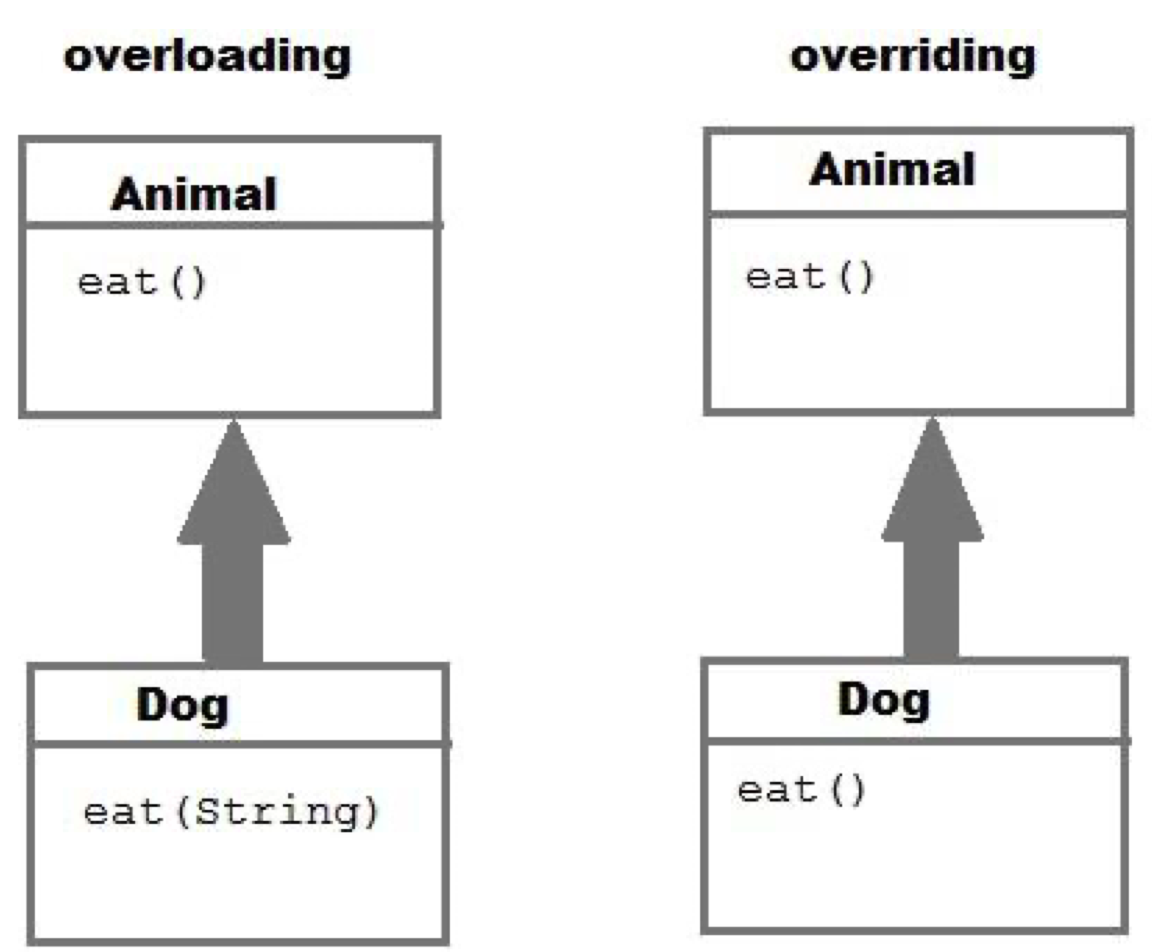
26
New cards
advantages of encapsulation
1. data hiding
2. increased flexibility
3. reusability
4. testing code is easy
27
New cards
what is data hiding as an adv of encapsulation
* secure because user can’t see the inner information of the class
* not visible to the user how the class is storing values in the variables
* only know that we are passing the values to a setter method and variables are getting initialized with that value
* not visible to the user how the class is storing values in the variables
* only know that we are passing the values to a setter method and variables are getting initialized with that value
28
New cards
what is reusability as an adv of encapsulation
* encapsulation also improves ability for code to be used many times
* can be copied to different/new classes and help meet new requirements
* can be copied to different/new classes and help meet new requirements
29
New cards
what is ‘testing code is easy’ as an adv of encapsulation
* allows unit testing (automated testing that tests many different types of data quickly
* easier to fix larger programs if you know which method is returning the wrong response
* easier to fix larger programs if you know which method is returning the wrong response
30
New cards
what is increased flexibility as an adv of encapsulation
* can make variables of the class as read-only or write-only, depending on our requirement
* if we wish to make the variables as read-only then we can omit the setter methods
* or for variables as write-only then, we omit the get methods
* if we wish to make the variables as read-only then we can omit the setter methods
* or for variables as write-only then, we omit the get methods
31
New cards
main advantage of inheritance
* minimizes amount of duplicate code in an application by sharing common code amongst several subclasses
* reduces time and effort to recreate classes by moving that common code up to a common superclass
* reduces time and effort to recreate classes by moving that common code up to a common superclass
32
New cards
other advantages of inheritance
1. minimize amount of duplicate code in an application
2. better organization of code
3. code more flexible to change
33
New cards
what is better organization of code as an adv of inheritance
moving common code to a super class result in better organization of code (better abstraction)
34
New cards
what is code more flexible to change as an adv of inheritance
in inheritance classes can be used interchangeably
35
New cards
advantages of overriding
* allows a parent class to specify methods that will be common to all of its derivatives
* while allowing sub classes to define the specific implementation of some or all of those methods
* allow us to call methods of any of the parent classes without even knowing the specifics of the parent class
* while allowing sub classes to define the specific implementation of some or all of those methods
* allow us to call methods of any of the parent classes without even knowing the specifics of the parent class
36
New cards
advantages of overloading
* don’t have to create and remember different names for functions doing the same thing
* like would have to make many methods names for ever possible combination of parameters being used
* like would have to make many methods names for ever possible combination of parameters being used
37
New cards
advantages of libraries of objects
* time saving
* sorting algorithms do not have to be re-invented (like u dont have to reinvent the wheel)
* complex algorithms and processes can be reused
* sorting algorithms do not have to be re-invented (like u dont have to reinvent the wheel)
* complex algorithms and processes can be reused
38
New cards
disadvantages of OOP
* increased complexity for small problems
* unsuited to particular classes of problems
* unsuited to particular classes of problems
39
New cards
what is increased complexity in disadvantages of OOP
* involves more lines of code than procedural programs
* slower than procedure-based programs, as they require more instructions to be executed
* slower than procedure-based programs, as they require more instructions to be executed
40
New cards
what is unsuited to particular problems as disadvantages of OOP
* problems can be easily solved by functional programming style, logic programming style, or procedure-based programming style and applying OOP in those situations will not result in efficient programs
* ex. why make an object when using a String will do
* ex. why make an object when using a String will do
41
New cards
why is working in a team better
1. Speed of completion faster
2. information hiding to reduce module dependencies
3. expertise in a narrow field
42
New cards
what is speed of completion as an adv of teams
tasks can be completed concurrently, so project completed in shorter amount of time
43
New cards
what is information hiding as an adv of teams
* developers only need to know the name and required parameters to use a behaviour
* can use code without needing to understand how it functions
* security benefit to coders not having access to actual data items
* can use code without needing to understand how it functions
* security benefit to coders not having access to actual data items
44
New cards
what is expertise in narrow fields as an adv of teams
* assembling a complex project needs many skills
* each part can be programmed by an expert in that field, so quality of final product is significantly higher than expecting one person to know it all
* each part can be programmed by an expert in that field, so quality of final product is significantly higher than expecting one person to know it all
45
New cards
disadvantages of teams
* Communication and coordination issues
* Groupthink: diffusion of responsibility; going along
* Working by inertia; not planning ahead
* Conflict or mistrust between team members
* Groupthink: diffusion of responsibility; going along
* Working by inertia; not planning ahead
* Conflict or mistrust between team members
46
New cards
explain the advantages of modularity in program development
* easier debugging and testing
* speedier completion
* code blocks reusable
* speedier completion
* code blocks reusable
47
New cards
what is easier debugging and testing as adv of modularity
* smaller modules to test means easier to find and fix bugs
* number of tests that have to be run to confirm the module is operational is reduced
* number of tests that have to be run to confirm the module is operational is reduced
48
New cards
speedier completion as adv of modularity
* breaking the project into smaller modules, can save time by using modules that already exist from libraries that do the function you want
* each module can be worked on concurrently, so speedier completion of the overall project
* each module can be worked on concurrently, so speedier completion of the overall project
49
New cards
what is reusable code blocks as adv of modularity
* some problems are common and possible occur in multiple programs (like needing a text box)
* can reuse blocks of code, so development time is slashed
* can reuse blocks of code, so development time is slashed
50
New cards
define an identifier
* named pointer that explicitly identifies an object, class, method or variable
* allows programmer to refer to the item from other places in the program
* allows programmer to refer to the item from other places in the program
51
New cards
define primitive
* most basic data types available within Java language
* boolean, byte, char, short, int, long, float, double
* building blocks of data manipulation
* purpose: contain pure, simple values of a particular kind
* boolean, byte, char, short, int, long, float, double
* building blocks of data manipulation
* purpose: contain pure, simple values of a particular kind
52
New cards
define a variable
* named storage location for a value that a program can manipulate
* must be declared before they can be used
* must be declared before they can be used
53
New cards
define instance variable
* non -static variables and are declared in a class outside any method, constructor or block
* created when object of the class is created and destroyed when object is destroyed
* can use access modifiers for instance variables
* created when object of the class is created and destroyed when object is destroyed
* can use access modifiers for instance variables
54
New cards
define parameter variable
* parameter allows us to pass information or instructions into functions and procedures
* names of the information we want to use in a function or procedure
* values passed in are argument
* names of the information we want to use in a function or procedure
* values passed in are argument
55
New cards
define a local variable
* variable defined within a block or method or constructor
* created when the block is entered or the function is called and destroyed after exiting from the block or when the call returns from the function
* only accessible within its block
* created when the block is entered or the function is called and destroyed after exiting from the block or when the call returns from the function
* only accessible within its block
56
New cards
define method
* set of code referred to by name and can be called at any point in a program simply by utilizing the method’s name
* described as a subprogram that acts on data and returns value
* each method had its own name
* described as a subprogram that acts on data and returns value
* each method had its own name
57
New cards
define accessor
* type of method returning the value of a private instance variable
* getter method
* getter method
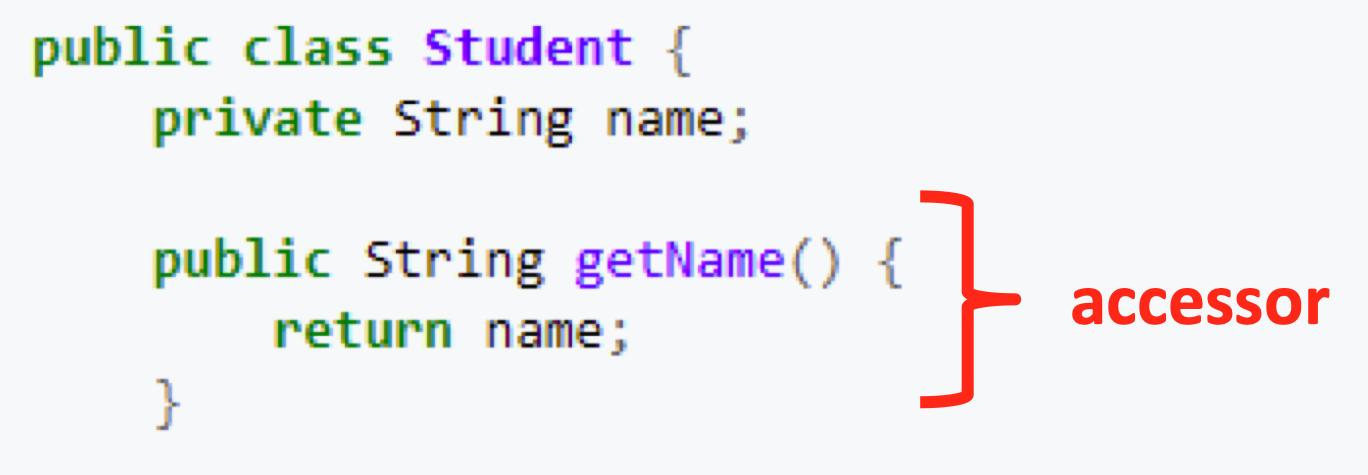
58
New cards
define mutator
* setter method
* used to control changes to an encapsulated instance variable
* used to control changes to an encapsulated instance variable
59
New cards
define constructor
* instance method invoked when object of that class is created (using the **new** keyword)
* same name as class, no return type
* class name, object name = **new** constructor();
* same name as class, no return type
* class name, object name = **new** constructor();
60
New cards
difference between constructors and methods
* method can be any user defined name
* constructor must be class name
\
* method should have return type
* constructor doesn’t have any return type
\
* method called explicitly either with object reference or class reference
* constructor called automatically whenever object is created
* constructor must be class name
\
* method should have return type
* constructor doesn’t have any return type
\
* method called explicitly either with object reference or class reference
* constructor called automatically whenever object is created
61
New cards
what is a signature
* part of the method declaration
* combination of the name and the parameter list
* _____(___)
* combination of the name and the parameter list
* _____(___)
62
New cards
define return value
* return = reserved keyword in Java, not an identifier
* exits from a method, with or without a value
* exits from a method, with or without a value
63
New cards
difference between procedures and functions
* procedures dont return any value (void)
* functions return value
* no method can return more than one value at a time in Java
* functions return value
* no method can return more than one value at a time in Java
64
New cards
what is an access level modifier
* determines whether other classes can use a particular field or invoke a particular method
65
New cards
what is public as a modifier
* visible to all classes everywhere
66
New cards
define private as a modifier
* can only be accessed within the declared class itself
* most restrictive access level
* can be accessed outside of class if public getter methods are present
* using the private modifier is main way an object encapsulates itself and hides data from the outside world
* most restrictive access level
* can be accessed outside of class if public getter methods are present
* using the private modifier is main way an object encapsulates itself and hides data from the outside world
67
New cards
define protected as a modifier
* can be accessed only by subclasses
* prevents non related classes from trying to use it
* prevents non related classes from trying to use it
68
New cards
define extends
keyword used in a sub class to inherit the properties of a parent class
69
New cards
define static
means shared between all instances of that class is it belongs to the type, not the actual objects themselves.
takes up less memory cuz only 1 memory allocation for all instances vs 1 per instance
can access the static member without first creating a class instance
takes up less memory cuz only 1 memory allocation for all instances vs 1 per instance
can access the static member without first creating a class instance
70
New cards
how is internationalization done
* common character sets among many platforms and languages like Unicode
* platform independent high level languages enable code to run on many platforms
* platform independent high level languages enable code to run on many platforms
71
New cards
what is a moral issue
has the potential to help or harm anyone, including oneself
ex: not testing a product that then fails and causes harm, product failing and causing commercial harm, stealing other programmers’ work
ex: not testing a product that then fails and causes harm, product failing and causing commercial harm, stealing other programmers’ work
72
New cards
what is an ethical issue
requires you to choose between choices that are right or wrong
ex. responsibility for computer failure, protection of computer property, records and software
ex. responsibility for computer failure, protection of computer property, records and software
73
New cards
what is open source movement
supports the use of open-source licenses for some or all software
voluntarily writing and exchanging programming code for software development
voluntarily writing and exchanging programming code for software development
74
New cards
what is a byte
* Byte data type is an 8-bit signed two's complement integer.
75
New cards
what is long type
* Long data type is a 64-bit signed two's complement integer.
76
New cards
what is double data type
* 64-bit floating point
77
New cards
what is a char data type
* single 16-bit Unicode character