Biology: Ch 12 Meiosis
1/55
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
What is the purpose of meiosis?
sexual reproduction
What is the process called when a sperm and an egg unite to form a new individual?
fertilization
Where are sperm cells made?
testicles
Where are egg cells made?
ovaries
_____________ is the nuclear division that precedes the formation of gametes (egg & sperm) and results in a halving of chromosome number.
meiosis
How many distinct chromosomes does a human have?
23
How many total chromosomes does a human have at the end of fertilization?
46
Another term for reproductive organs?
Gonads
Each daughter cell (sperm or egg) are genetically ____________ from the parent cell.
different; not identical
What happens in meiosis?
process of mitosis happening twice; duplicate genes separate into daughter cells, those daughter cells separate again
What does haploid mean?
“one” or n
What is a karyotype?
the number and types of chromosomes present in an organism; “chromosome spread”
What do sex chromosomes determine?
sex of the individual
Chromosomes 1-22 are _____________.
autosomes
Chromosomes of the same type (or code for the same gene) are called _______________ ______________ or _______________.
homologous chromosomes or homologs
What do homologs carry?
the same genes in the same locations; may contain different versions or alleles
What is an allele?
different versions of a specific gene
What does the haploid number (n) indicate?
number of distinct types of chromosomes present
What does the ploidy (coefficient to n) indicate?
number of each type of chromosome present
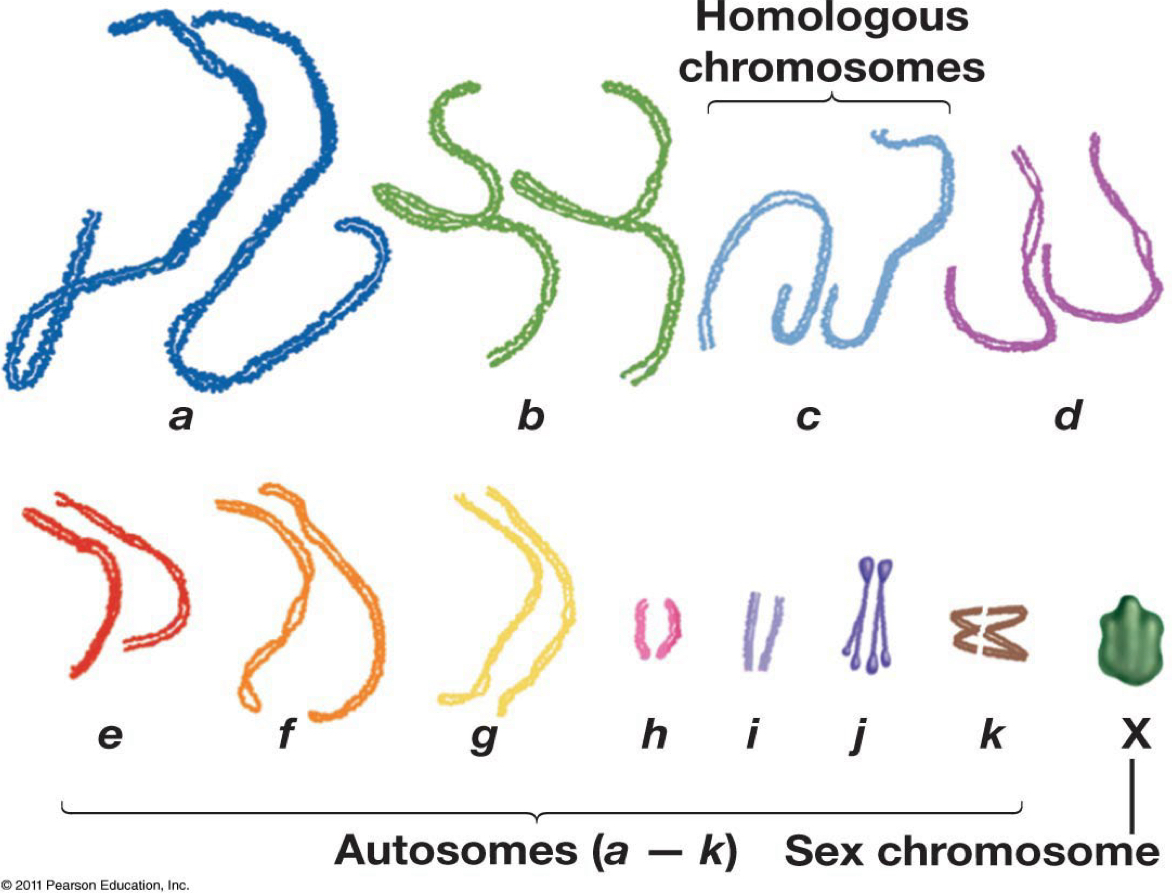
What is the haploid number?
n = 12
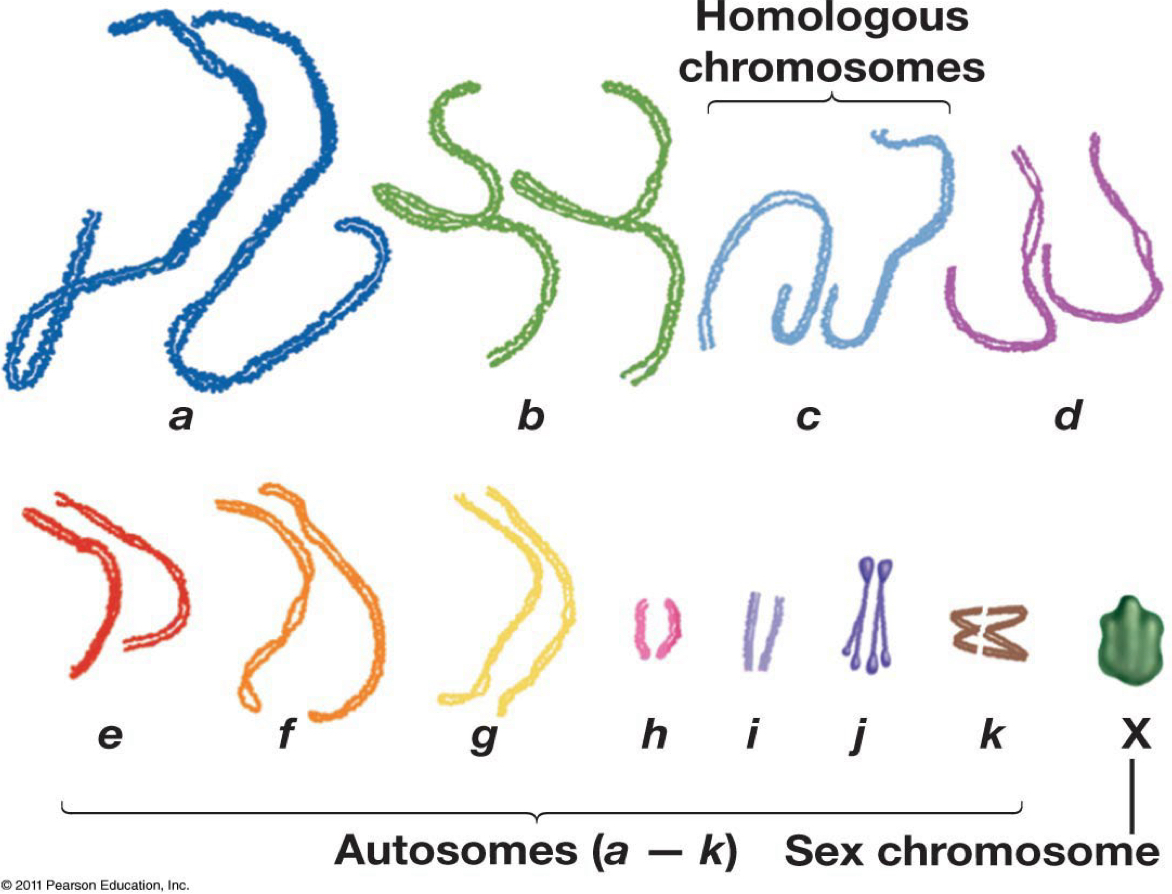
What is the ploidy number?
= 2
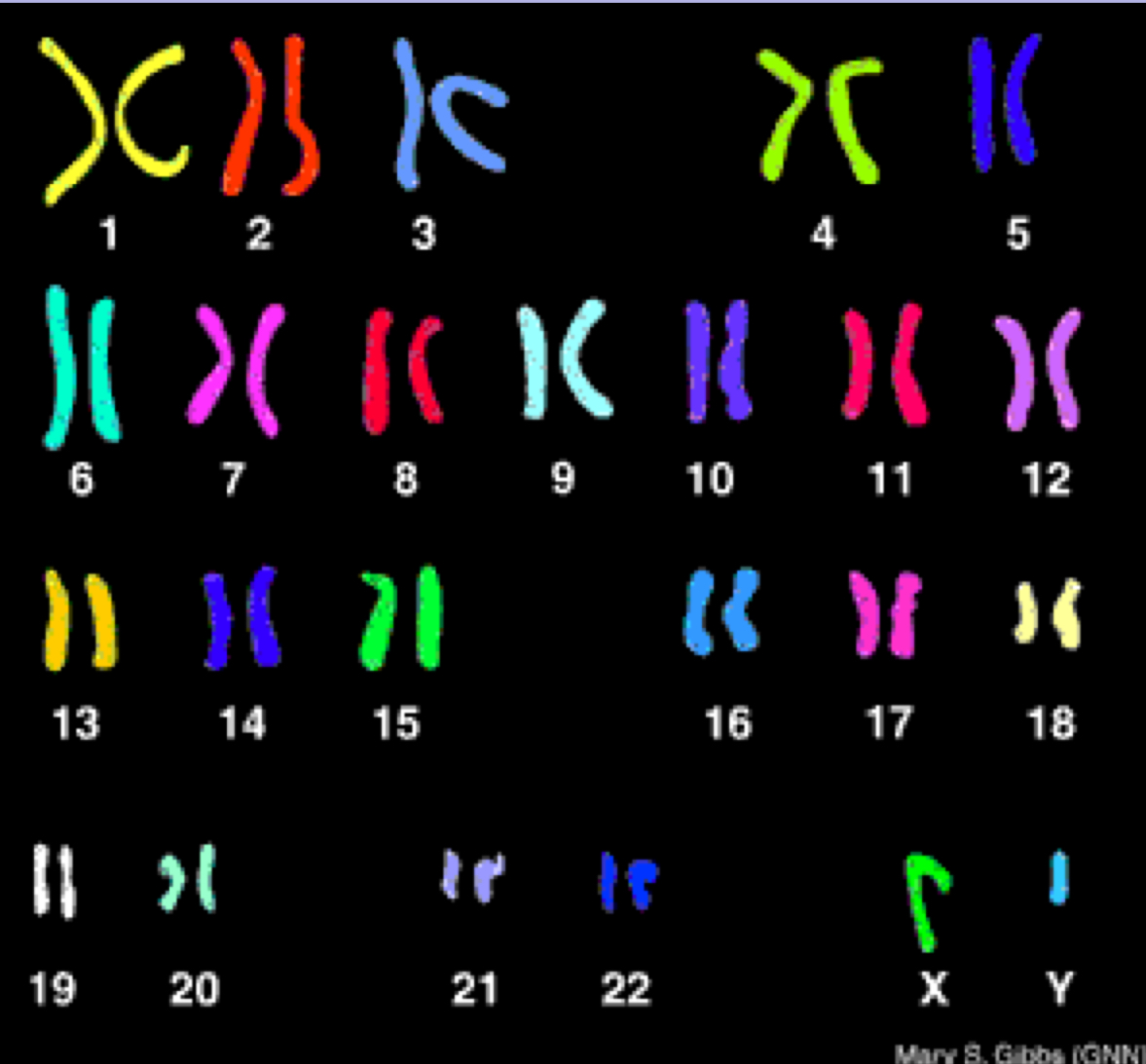
what is the human haploid (n) number?
n = 23
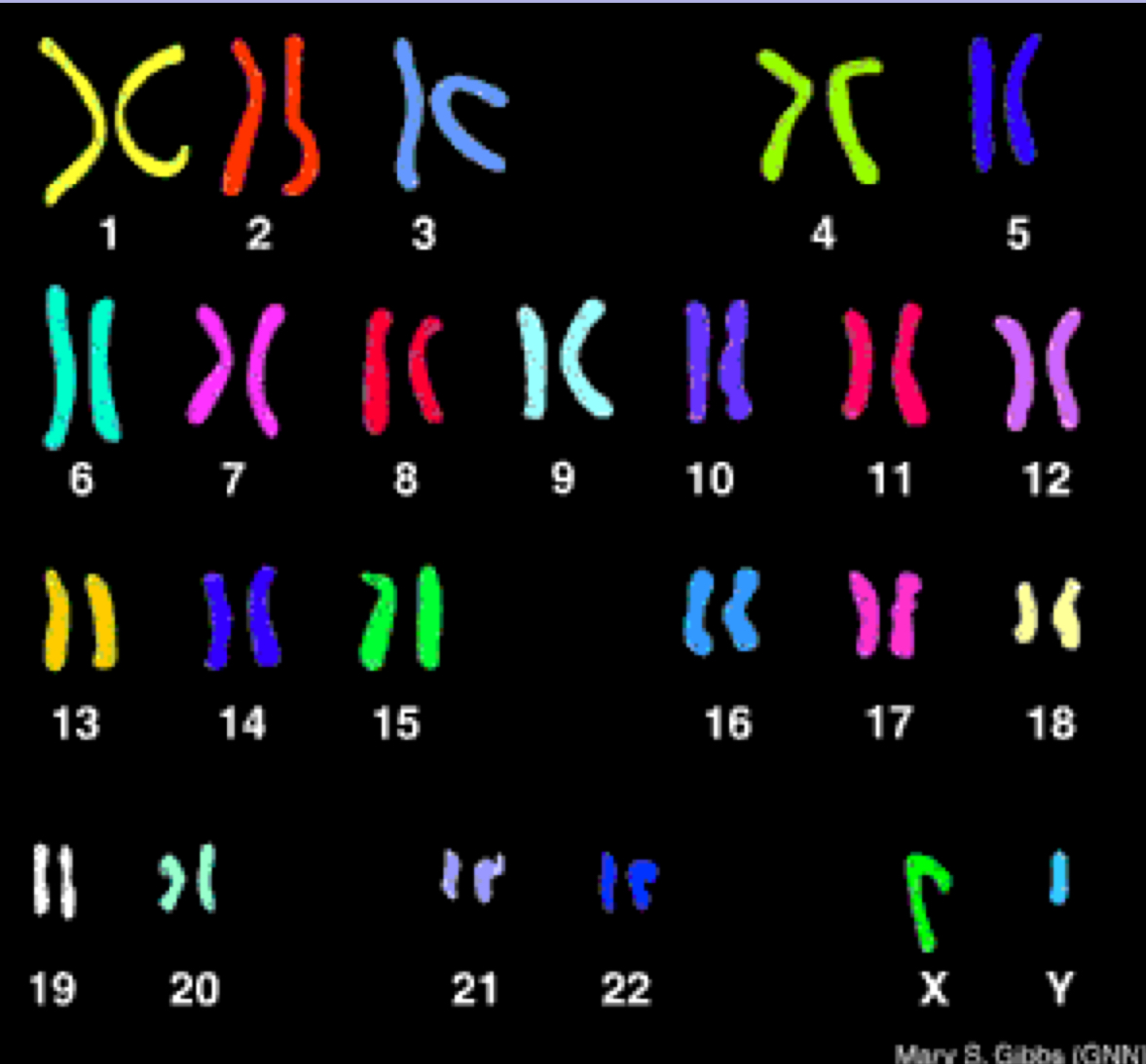
What is the ploidy number?
2
Organisms whose cells contain just one of each type of chromosome are called __________ (n)
haploid
Those whose cells contain two versions of each type of chromosome are termed _________ (2n)
diploid
What do diploid cells have?
one paternal chromosome and one maternal chromosome
Organisms with three or more versions of each type of chromosome are called ___________ (3n, 4n, etc.)
polyploid
What is the product of a diploid organism undergoing meiosis?
haploids
Meiosis reduces chromosome number by _________
half
What happens before a diploid undergoes meiosis?
each chromosome in the diploid parent cell is replicated; when replication is complete, each chromosome consists of two identical sister chromatids attached at the centromere
What is meiosis I associated with?
separation of homologous chromosomes
what is meiosis II associated with?
separation of sister chromatids
Meiosis II is similar to what other process?
mitosis
What occurs in early prophase I?
Homolog pairs come together in a pairing process called synopsis
What is the term for the structure that results from synapsis?
tetrad: consisting of two homologs (4 sister chromatids)
The chromatids of the homologs are called _____________
non-sister chromatids
What occurs in late prophase I?
crossing over between homologous non-sister chromatids occurs where chiasmata are formed
What occurs in metaphase I?
the tetrads line up at the metaphase plate
what occurs in anaphase I?
paired homologs separate and begin to migrate to opposite ends of the cell
what occurs in telophase I?
homologs finish migrating to the poles of the cell and then the cell divides in the process of cytokinesis
What is the end result of meiosis I?
one chromosome of each homologous pair is distributed to a different daughter cell
a reduction division: daughter cells of meiosis I are haploid and are still in the form of sister chromatids (duplicated)
How many distinct phases does meiosis I have?
5
How many distinct phases does meiosis II have?
4
What occurs in prophase II?
spindle apparatus forms and one spindle fiber attaches to the centromere of each sister chromatid
what occurs in metaphase II?
replicated chromosomes line up at the metaphase plate
what occurs in anaphase II?
sister chromatids separate; resulting in daughter chromosomes begin moving to opposite sides of the cell
what occurs in telophase II?
chromosomes arrive at the opposite sides of the cell
nuclear envelope forms around each haploid set of chromosomes
each cell undergoes cytokinesis
what is the result of meiosis II?
four haploid cells, each with one of each type of chromosome
one diploid cell with replicated chromosomes gives rise to four haploid cells with unreplicated chromosomes
What is considered the genetically distinct from the parental diploid cell?
the 4 unreplicated haploid cells
what causes diversity?
crossing over
mutations
fertilization randomness
What is nondisjunction?
uneven separation that typically occurs in anaphase I
both homologs or sister chromatids move to the same pole of the parent cell
What is considered an aneuploid zygote?
those with too few or many chromosomes
What condition is caused by a defect on chromosome 21 or the sex chromosomes?
down syndrome
What can sex chromosome aneuploidy cause?
Klinefelter syndrome: XXY males
Trisomy X
(karyotype XXX)
Turner syndrome: monosomy
karyotype is XO (lacking a secondary X)
What gamete determines the gender of a zygote?
sperm; carries either a “x” or “y”
What happens if nondisjunction occurs in meiosis I?
two gametes will have an extra copy of a chromosome (causing a condition called trisomy)
two gametes will lack that chromosome (monosomy)