Macro Chapter - 1
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What is national income accounting used for and what are the 3 measures
National income accounting is used to measure a nation’s level of economic activity. The 3 measures are
total expenditure
total income
total output of goods and services
Circular flow of income
shows the flow of money between different stakeholders of an economy and is also used to illustrate the three methods of national income.
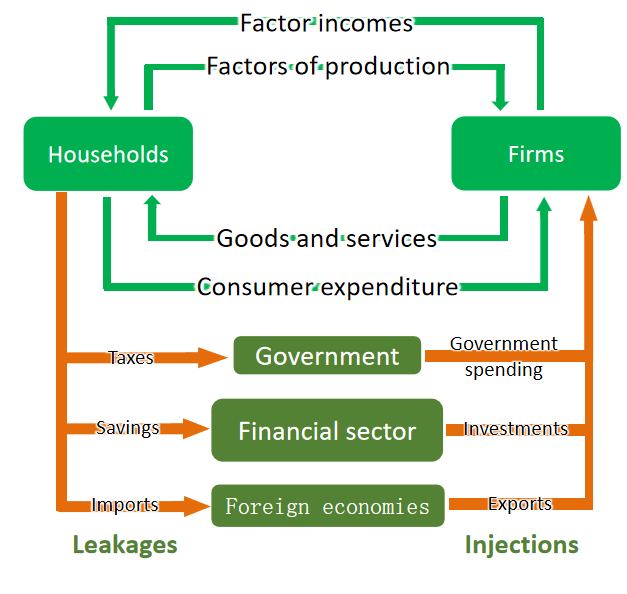
Factor income?
this is just the reward for each factor of production. land has rent. labour has wages. capital has interest. entreprenurs have profit
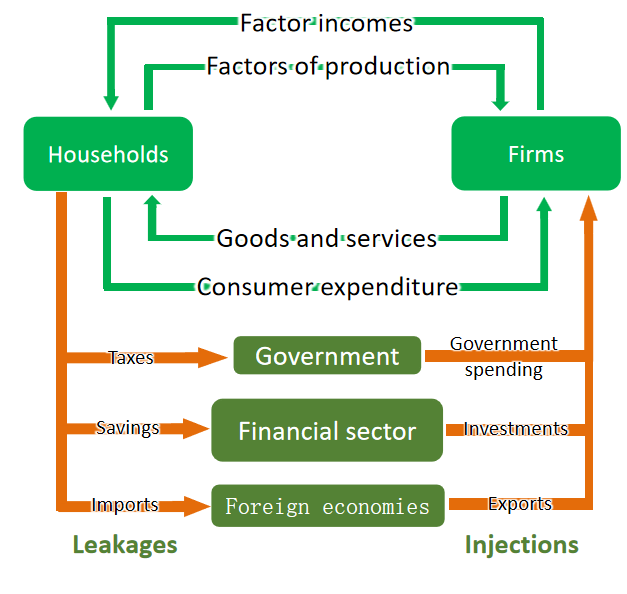
Explain each approach with the diagram
Expenditure approach : this is measuring the total expenditure by all stakeholders in the economy. which would be C + I + G + (X-M) and therefore the same as GDP of the country
Income approach : this just takes all the things earned by each factor of production and adds it up so rent + wages + interest + profit
Output approach : measures the total output in the economy so goods and services. measured using GDP
Main formula for Circular flow of income
The total expenditure = The total income = Total Output
Firms use the factors of production to produce goods and services. Therefore, the total value of output of goods and services is equal to the factor incomes used to purchase the factors of production, which is equal to the total expenditure of all stakeholders.
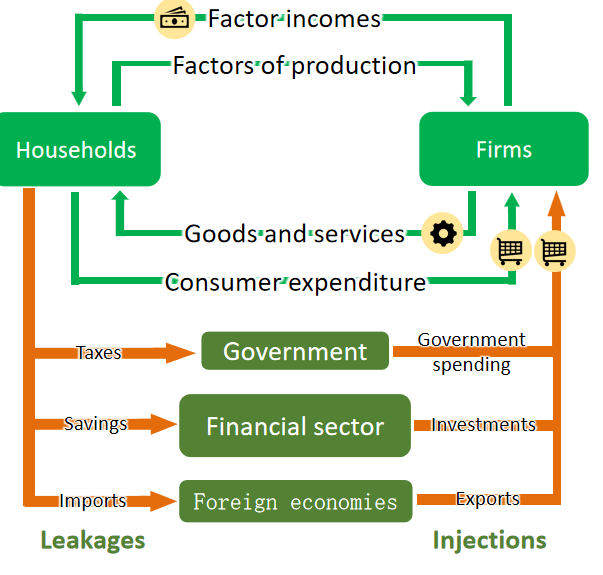
Injection
An injection refers to the additional money added into the circular flow of income.
leakage
A leakage refers to a withdrawal of money from the circular flow of income
National income Increase or decrease
The national income increases if the injections are more then leakage and if leakage is more then injection then national income decreases
Nominal GDP
measures the value of all final goods and services produced in an economy within a given time period using current price levels
Gross national income (GNI) & its formula
measures the value of all income earned by the country’s citizens including income earned from abroad.
GNI = GDP + net income from abroad
Net income from abroad = Income from abroad – Income sent abroad
Real vs Nominal
Real simply means that the value is adjusted for inflation and are calculated on constant prices
Nominal means not calculated by adjusting for inflation, using the current prices
Real to nominal conversion for GDP and GNI
Real GDP = (Nominal GDP/GDP deflator) * 100
Real GNI = (Nominal GNI/GDP deflator) * 100
What does it mean if Nominal GDP is increasing but Real GDP is decreasing
This means a recesion as the actual output of the country decreased but the nominal GDP still went up which means that there is inflation
Real GDP/GNI per capita
Real GDP/Population
Real GNI/Population
Purchasing power
refers to the amount of goods and services that can be bought with one unit of a currency.
Purchasing power parity (PPP)
refers to the exchange rate needed to buy the same basket of goods and services in different countries using the same amount of money
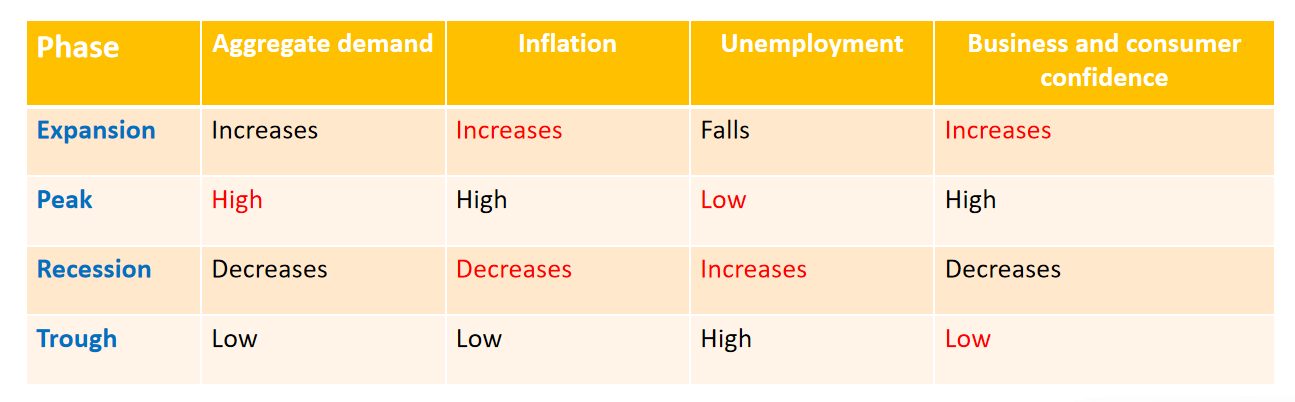
business/economic cycle and its stages
A business/economic cycle illustrates the short-term fluctuations of real GDP over time.
Expansion Peak Recession and Trough
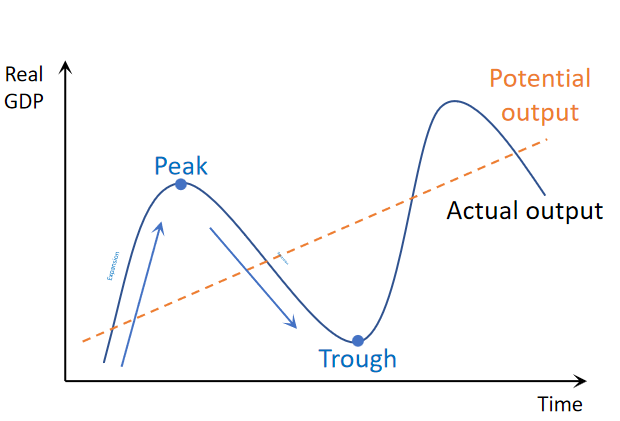
Explain each part of the Cycle with respect to AD, Inflation, Unemployment and Confidence
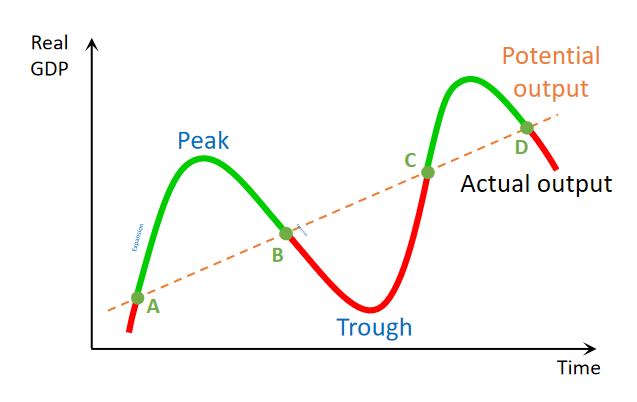
Explain the Green part of business cycle with reference to inflation and unemployment
Also explain full employment
The green part is an inflationary gap, where the real GDP > potential GDP. At potential GDP an economy reaches natural rate of unemployment. so in the green portion Unemployment is lesser then Natural rate of Unemployment.
An economy achieves full employment when real GDP = potential GDP (A, B, C, D). unemployment = NRU.
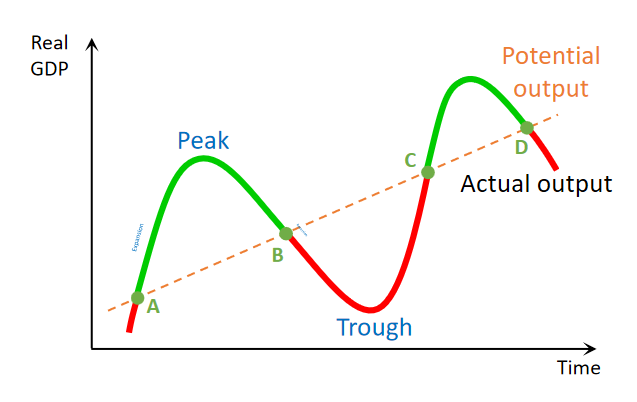
Explain the red part of business cycle with reference to inflation and unemployment
The red part is a deflationary gap, where the real GDP < potential GDP. so in the red portion Unemployment is more then the Natural rate of Unemployment.
GDP/GNI for economic wellbeing Pro
A higher real GDP/ GNI per capita value usually corresponds to a higher standard of living, as the average person will be able to purchase more goods and services.
GDP/GNI for economic wellbeing Cons
Does not take into account Leisure time so not an accurate representation of economic wellbeing
Negative externalities : GDP and GNI statistics do not account for the negative externalities. As a result, economic well-being may be overstated as environmental costs are not considered.
Informal activities : GDP/ GNI statistics may be understated as they do not account for informal activities involving non-marketed goods and those in the hidden/ underground economy (Kirana stores)
Green GDP
Green GDP is a measure of economic activity which accounts for environmental degradation and the depletion of natural resources.
Green GDP = GDP - environmental costs of production