Cells and membranes
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Plasma membrane
surrounds all cells that acts as a selective barrier, detects chemical signals, anchors cells to adjacent cells and the extracellular matrix
Fluid-mosaic model
Integral membrane proteins are able to move freely laterally in lipid bilayer - amphipathic molecules align with lipid bilayer
4 types of membrane juctions
integrins
desmosomes
tight junctions
gap junctions
What are integrins
Binds to specific extracellular proteins and links adjacent proteins to other cells
What are desmosomes?
Dense plaques on plasma membrane that anchor cadherins - allow elasticity e.g. skin
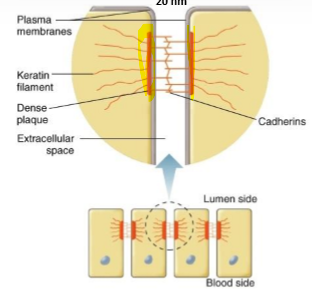
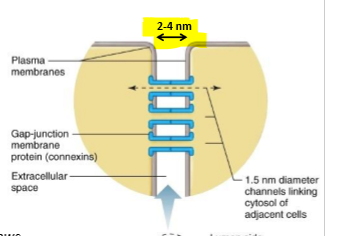
What are gap junctions?
Protein-lined channels that link two cells - small diameter links what can be exchanged e.g. small molecules and ions only
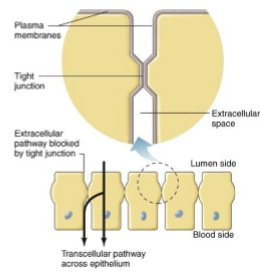
What are tight junctions?
Extracellular surfaces of adjacent plasma membranes join together - occurs in band around circumference of the cell.
This allows control in types and amount of substances absorbed as cannot pass between cells.
Osmolarity
Total solute concentration in a solution: 1 osmol = 1 mol of solute particles
What is tonicity?
Measure of ability of a solution to add or remove water from cells due to osmosis
Isotonic
No change in cell volume
Hypotonic
Lower conc. of non-penetrating solutes outside cell (high conc. ofsoluted inside) so cell will swell
Hypertonic
Higher conc. of non-penetrating solutes outside cell so cell will shrink
The possible results of a change in conformational shape of a receptor following binding of a chemical messenger are what?
1) Change in permeability/transport properties
2)Metabolism
3)Secretory activity
4) Rate of proliferation/differenciation
5)Concentration of chemicals
Properties of lipid soluble messengers
1) Can diffuse through plasma membrane
2) Have intracellular receptors
3) Receptors bind directly to recognised sequence and alter gene transcription
4) Slower response compared to membrane receptors but more sustained
Properties of water soluble messengers
1) Broad range of receptors
2) Intracellular signalling cascades
3) Can activate downstream mediators
4) Faster response but less sustained e.g. adrenaline
4 types of water soluble messengers
A: Ligand-gated ion channels (conformational change when ligand binds leading to change in membrane potential)
B: Enzymatic activity (most are protein kinases) e.g. bound messenger changes conformation → receptor auto-phosphorylates tyrosine → these become docking sites for cytoplasmic proteins → docking proteins bind and activate signalling pathways
C: Interact with cytoplasmic Janus Kinases (JAKs) (no intrinsic kinase so must use JAKs
E: G-Protein-Coupled (bound to inactive receptor protein complex, made of 3 subunits which are alpha, beta, gamma). Works by ligand binding and conformation change → activated receptor inc. aff. of alpha subunit → when bound to GTP the alpha subunit dissociates and links with another plasma membrane protein
What kind of protein does Ca2+ bind to?
Cytosolic proteins, importantly calmodulin which changes shape and allows active calcium-calmodulin to control kinase activity so control other protein activity using ATP to phosphorylate them
Why is cessation of signalling important?
Chronic overstimulation of a cell can be detrimental e.g. cancer
Eicosanoid
Intracellular messengers released locally in paracrine or autocrine manner
Agonists
Chemical messengers that stimulate a normal cellular response
Antagonists
Substances that compete with the natural ligand for that receptor
What are the 4 major features that define interactions between receptors and their ligands?
1) Specificity - receptors ability to bind only one type of chemical messengers
2) Affinity - strength with which a chemical messenger binds (strong requires lower conc)
3) Saturation - as conc of messenger inc. the response inc. as more receptors are saturated, upper limit will eventually be reached
4) Competition - ability of a natural molecule to compete with a natural ligand to bind to receptor
What determines specificity of cell membranes?
1) Pore size
2) Charge
3) Binding site
What is flux?
The amount of material crossing a surface in a unit of time
Diagram of movement of all substances
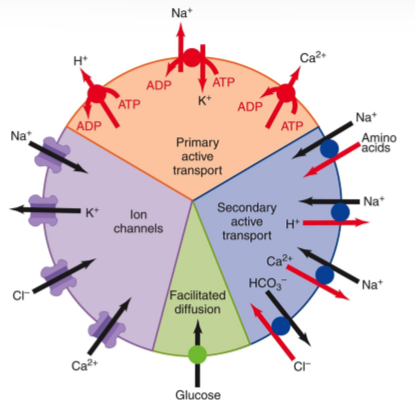
What are the three major types of protein channels that span cell membranes?
ligand gated
voltage gated
mechanically gated
What is the molarity of pure water?
55.5M
What is osmolarity?
The total solute concentration of a solution (extracellular fluid normally 285-300 mOsm
Hwat is osmotic pressure?
The ‘force’ required to prevent the flow of water into a solution
What is a semipermeable membrane?
A membrane permeable to water but not solutes
What are nonpenetrating solutes and give examples
Substances that cannot cross the plasma membrane e.g. Na+ and Cl- ions on the outside of the cell membrane or K+ on the inside of the membrane
What are 3 types of endocytosis?
pintocytosis: vesicle contains extracellular fluid with non-specific components water, ions, nutrients ect
phagocytosis: engulfing bacteria/cell debris
receptor mediated endocytosis: pathway for larger moleucles (e.g. proteins) which works when receptors bind to ligands, recruiting clathrin to form a pit and then vesicle
Describe epithelial transport
occurs in paracellular pathway through tight junctions
What effect do ligands have when bound to proteins?
Changes conformation causing function to be activated or inactivated
What two factors are needed for chemical specificity?
close proximity
complementary conformational shape
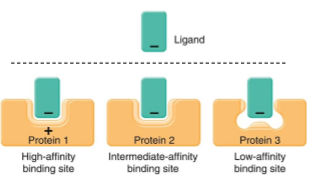
What is needed for high affinity binding site?
Correct shape and electrical charges
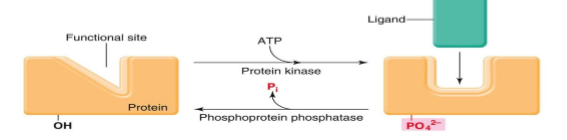
WHat are two ways to control protein activity?
1) Alter protein shape → allosteric (regulatory site binding changes functional site (active)) or covalent modulation (bonding of charged chemical groups to side chains)
2) Regulate synthesis and degradation → more or less
What is cooperativity?
Ligand binds to first of several function sites increasing affinity of other functional areas
Give an example of covalent modulation and explain how it works
Phosphorylation → kinase adds phosphate group, phosphatase removes phosphate group (not in exam)

Swell (hypo: [soln]<[cell])

The concentration of water outside the cell is initially lower than the concentration inside the cell(Hyper: [soln]>[cell])