Bio trimester 1
1/290
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
291 Terms
Electronegativity
a measure of an atom’s ability to pull electrons away from another atom
Polar molecule
A molecule with a positive and a negative end
Example of polar molecule
Water (2 positive, 1 negative)
Nonpolar molecule
A molecule with no negative or positive end
Example of non polar molecule
Table salt(sodium chloride)
what do polar molecules do when placed in water?
They dissolve in water
What do non polar molecules do when placed in water?
they do not dissolve in water(oil)
Intermolecular bond
Bond between 2 molecules ( Hydrogen bonds)
Intramolecular bonds
within a molecule ( Holds atoms together to make a molecule) Covalent bonds
ionic bonds
chemical bond where an atom is transferred
Atomic mass - atomic number=
Number of neutrons
Covelant bond
Sharing of electrons
Polar covalent bonds
Atoms are shared unevenly
Polar hydroliphic head does what
Orient towards the water
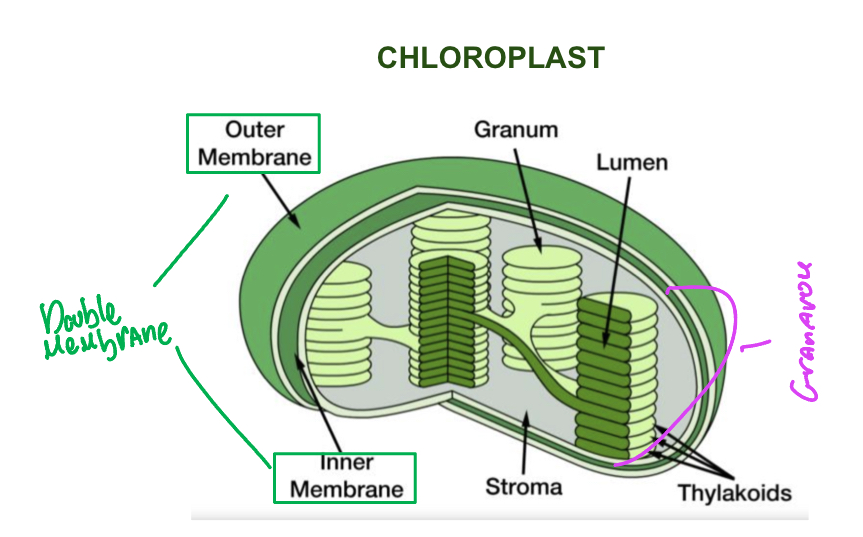
Chlorophyll
Pigment that captures and converts light energy to chemical energy to be used or stored
Where does photosynthesis take place
The chloroplast
Where is chlorophyll located
In the thylakoids
Thylakoids
Highly folded inner membrane of chloroplast
Grana
Stack of thylakoids
Stroma
Fluid that surrounds thylakoids
Picture of chloroplast
Photosynthesis equation
Carbon dioxide + water + light = glucose + oxygen
How many steps is photosynthesis
2 steps
What are the steps of photosynthesis called
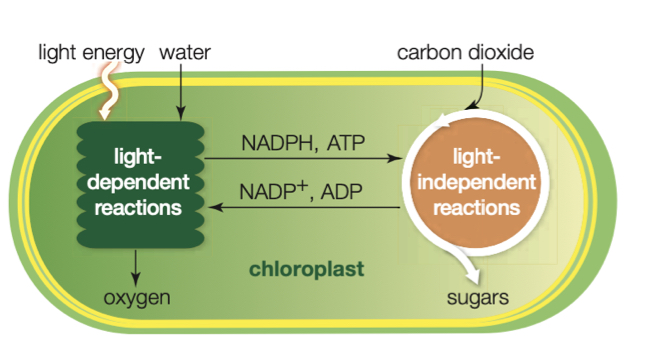
Light reactions - occur in the thylakoids
Calvin Cycle(dark phase reactions) - occur in the stroma
What goes into the light reactions
Water - providing electrons
Sunlight- energy
What comes out of the light reactions
Oxygen - Released
ATP - produced
NADPH - produced
Picture of light reactions
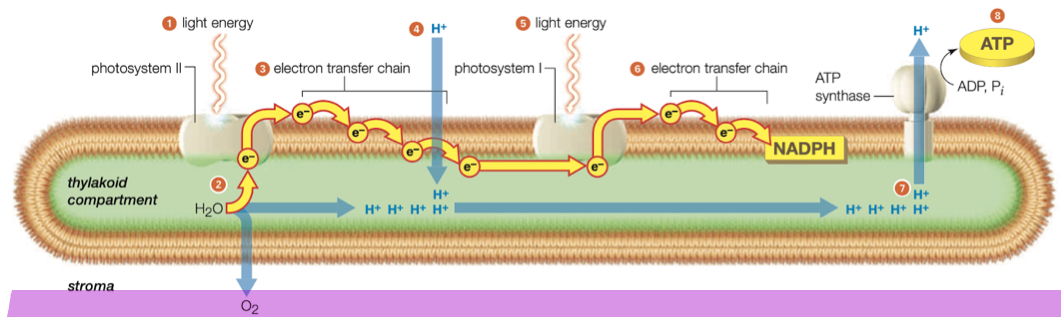
Function of light reactions
Make ATP(provides energy) And Make NADPH(provides electrons/ electron carrier) for Calvin cycle reactions
What is absorbed and released in light reactions
Light is absorbed and water is released
Where does the Calvin cycle take place
The stroma
What is absorbed in the Calvin cycle
Carbon dioxide(Co2)
What is the ATP and NADPH produced from the light reactions used for in the Calvin cycle
It’s used to create sugars for the plant.
Glucose is produced
Where does the Calvin cycle get carbon dioxide from
The air
Picture of Calvin cycle
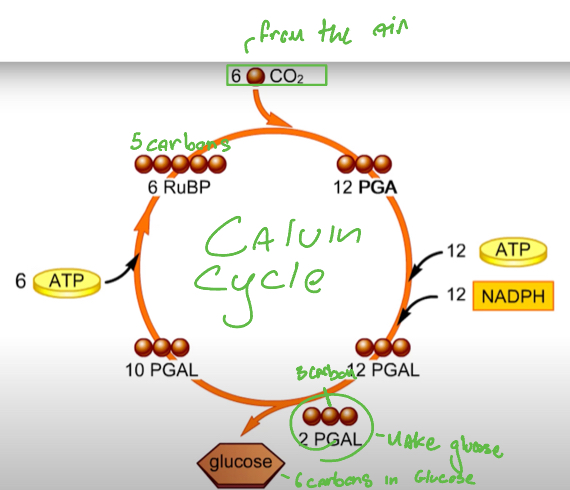
How many carbons are in glucose
6
Calvin reaction summary
____ molecules diffuse into a plant cell and chloroplast
The enzyme _________ attaches a carbon from Co2 to the 5 carbon RuBP forming an unstable 6 carbon molecule which splits into 2 molecules of PGA
Each PGA gets ___________ and ____________, forming PGAL, a 3 carbon intermediate molecule
Two PGAL’s combine to form a _______, the remaining PGAL’s regenerate RuBP
Co2 molecules diffuse into a plant cell and chloroplast
The enzyme rubisco attaches a carbon from Co2 to the 5 carbon RuBP forming an unstable 6 carbon molecule which splits into 2 molecules of PGA
Each PGA gets phosphate from ATP and electrons from NADPH, forming PGAL, a 3 carbon intermediate molecule
Two PGAL’s combine to form a glucose, the remaining PGAL’s regenerate RuBP
What goes in of the Calvin cycle
Co2
ATP
NADPH
What comes out of the Calvin cycle
Glucose
ADP
NADP+
Photosynthesis reactions summary photo
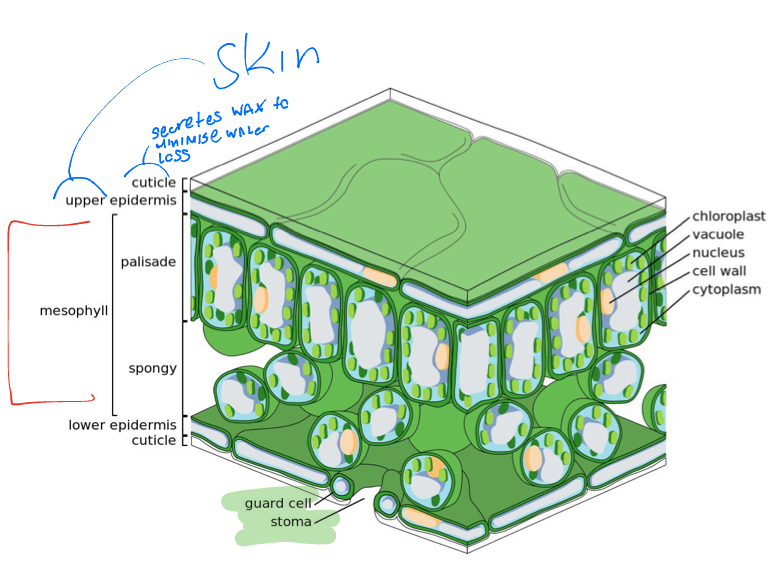
Mesophyll
Photosynthetic cells in leaves
Stomata
Openings on the leaf where gases are exchanged + transportation occurs
Guard cells
Function in pairs to open and close stomata
Picture of leaf anatomy
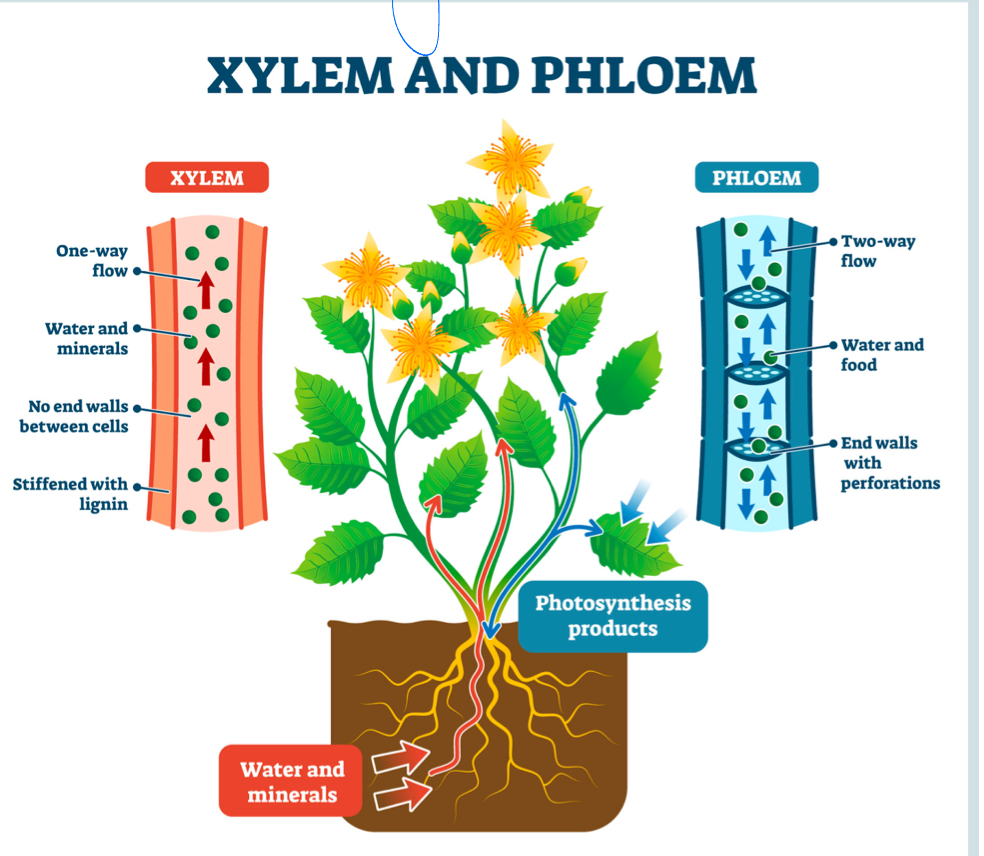
Function of Xylem
Transport of water and nutrients from the roots of the leaves
One way flow
Water and minerals
Function of Phloem
Transport glucose to where it’s needed
Two way flow
Water and food(glucose)
Function of root hairs
Increase surface areA for water and nutrient absorbtion
Photo of xylem and phloem
Meristems
Undifferentiated cells that can grow into various plant tissues
Lateral meristems
Cause secondary growth(widening of plant)
It makes it fatter
Apical meristems
Causes primary growth(lengthening of the plant)
Male reproductive plant parts
Stamen
Anther
Filament
Female reproductive plant parts
Carpel
Stigma
Style
Ovary
What part of the plant becomes fruit
The ovule
Purpose of cellular respiration
Make ATP
What are the 2 types of cellular respiration
Aerobic
Anaerobic
Aerobic respiration
Requires oxygen to make ATP, makes about 32-38
Anaerobic respiration
Doesn’t require oxygen to make ATP.
Makes 2 ATP
Occurs only in cytoplasm.
How does aerobic respiration differ from photosynthesis
Products of photosynthesis are the reactants of aerobic respiration
Aerobic respiration equation
glucose + oxygen -> carbon dioxide + water
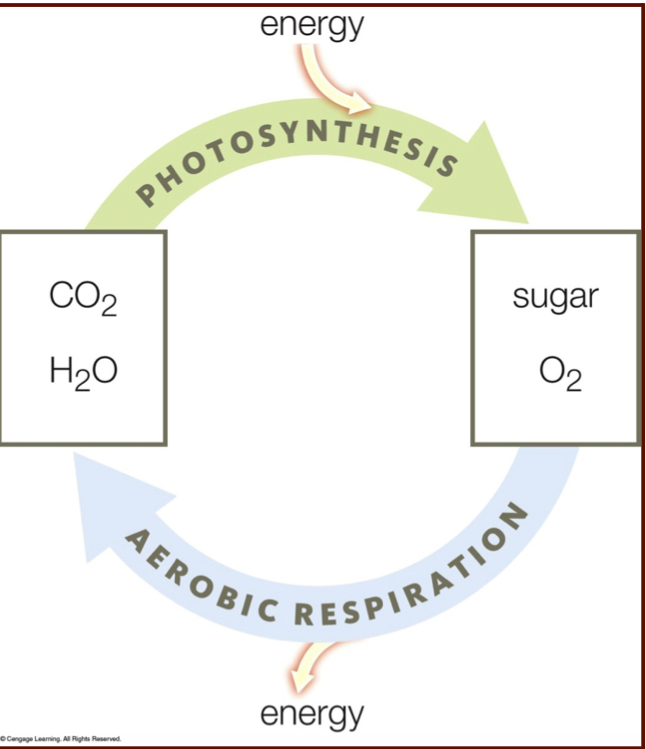
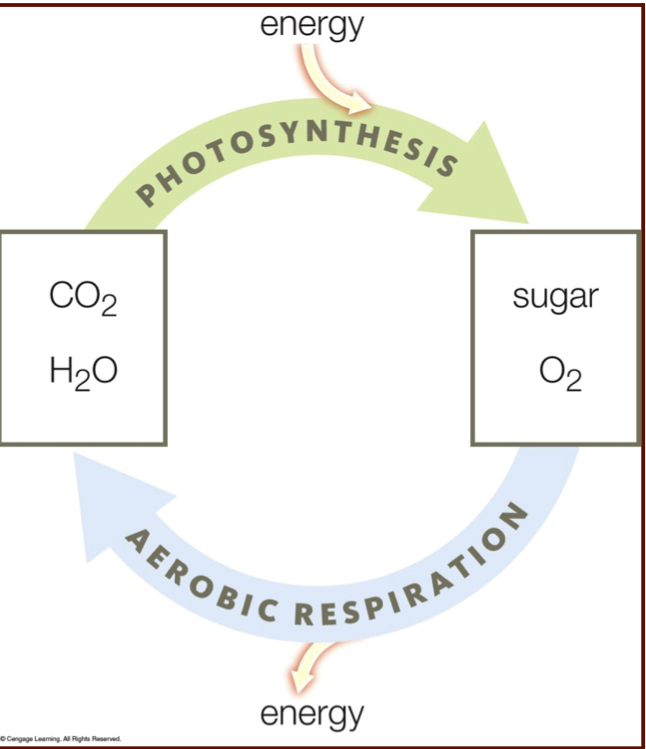
in photosynthesis, ____ splits, ___ is released, __ and ______ are produced.
in photosynthesis, water splits, O2 is released, H+ and electrons are produced
Electron carriers in aerobic respiration
NADPH
FADH
What happens in aerobic respiration
O2 accepts electrons, combining with H+ to form water.
How did electrons get transported in photosynthesis
NADPH
Where does cellular respiration occur
The mitochondria
The 3 steps of Aerobic respiration
Glycolysis
Krebs cycle
Electron transport chain
Where does Glycolysis occur
the cytoplasm
Where does the Krebs cycle occur
The mitochondrial matrix
Where does the electron transport chain occur
Occurs at the inner membrane
Krebs cycle
the Kreb's cycle occurs in the matrix and the purpose is to transfer the energy from the bonds of glucose into high energy electron carriers NADH and FADH2 which will then take those electrons to the ETC to make ATP.
Outputs of the krebs cycle
6 Co2
2 ATP
8 NADPH
2 FADH2
Glycolysis info
Net atp = 2
Electron carriers = 2 nadh
Krebs cycle info
Net atp = 2
Electron carriers = 8 NADH, 2FADH2
Electron transport chain info
Net atp = 32
Electron carriers = none
Glycolysis
Splits a glucose molecule into 2 pyruvate, 2 NADH and 4 ATP also form. An investment of 2 ATP began the reactions, so the net yield is 2 ATP
Electron Transport chain
the reduced coenzymes give up electrons and hydrogen ions to electron transfer chains in the inner mitochondrial mem-brane. Energy lost by the electrons as they move through the chains is used to move H† across the membrane. The resulting gradient causes Ht to flow through ATP synthases, which drives ATP synthesis.
Glucose’s role in aerobic respiration
Source of energy(electrons)
NADH,FADH2’s role in aerobic respiration
electron carriers that Transport high energy electrons to the ETC- electron transport chain
H+’s role in aerobic respiration
Powers ATP synthase by flowing down its concentration gradient
ATP synthase
Makes ATP when H+ flows through it
O2’s role in aerobic respiration
Final electron acceptor of the electron transport chain (etc)
H2O’s role in aerobic respiration
Created as a product when oxygen accept electrons and bonds with 2H+
How does anaerobic respiration differ from aerobic respiration
No oxygen required
Only in cytoplasm
Only makes 2 ATP
What happens to our muscles when we can’t keep up with the O2 supply?
Anaerobic respiration occurs and lactic acid builds up
Where does alcoholic fermentation occur
In the cytoplasm during glycolisis
What are the products of alcoholic fermentation
Alcohol (ethanol)
Co2
2 ATP
What is alcoholic fermentation conducted by?
Yeasts
where does lactic acid fermentation occur
In the cytoplasm during glycolysis
What is lactic acid fermentation conducted by?
Mammals, some bacteria
What are the products of lactic acid fermentation
Lactic acid
2 ATP
Ex(milk products)
Integral proteins
Embedded in cell membrane
Peripheral proteins
Not embedded in cell membrane
Cell membrane
Consists of lipid bilayer, regulates what gets into the cell.
What molecules are embedded with the lipid bilayer
Cholesterol,proteins,glycoproteins,glycolipids
Mosaic
Makes up many smaller pieces
How are phospholipids chemically bonded to one another
They aren’t
What does cholesterol do between phospholipids in the cell membrane
It helps stabilize it.
What the cholesterol in the membrane do at higher temps
Keeps it more solid, keeps it from “melting”
What the cholesterol in the membrane do at lower temps
Helps keep membrane more fluid, prevents it from “freezing”