DPT 745- (Lecture 1)
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Explain to me weight distrubution is important when it is transmitted down the vertebral column and down into the Ilium, Femur, and Pubic region?
It helps with the center of gravity
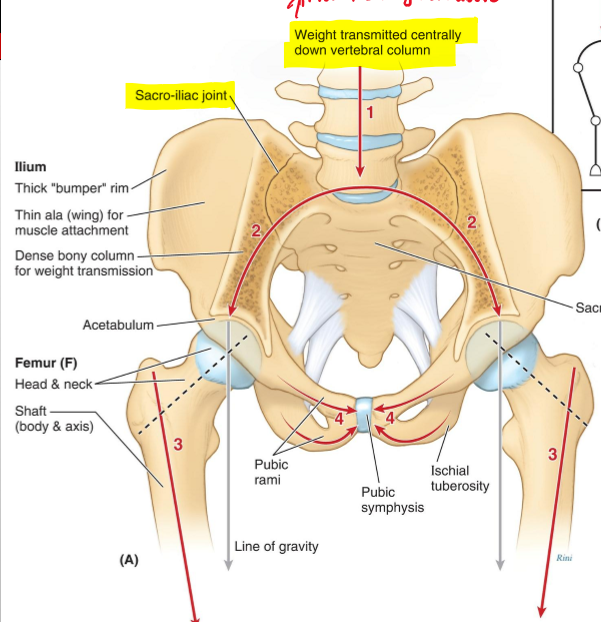
Why are the lumbar vertebras bigger?
Because weight is transmitted centrally down the vertebral columns.
When regarding the hip bone it can be also reference as what?
“Os Coxa”, which can consist of the ilium, Ischium, and Pubis.
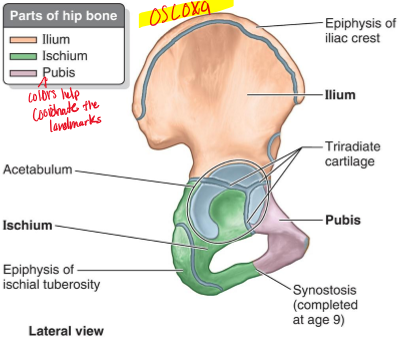
If you break a certain surface of the hip bone, which one is it and what does it affect?
Symphysial Surface, if broken is hard to bare weight
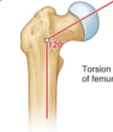
What is Angle of Inclination?
refers to the femur and the angel between the femoral shaft and the vertical axis of the femur
What is the angle of inclination of a 3 year old?
135 degrees
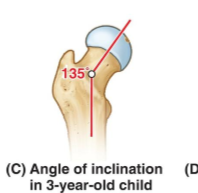
What is the angle of an adult and older age individual?
125 is normal for adults, and 120 degrees for older age
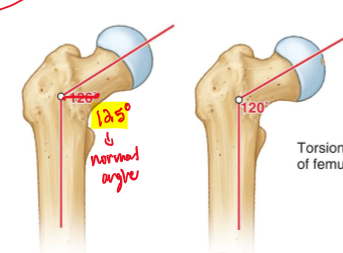
Why does the inclination angle seem to decrease over time?
Mainly due to load being put through the hips and femur which leads to decreased angles
Regarding (Inclination angle) What defines Coxa Vara and what angle is coxa vara considered severe?
A femoral neck–shaft angle < 120° & Neck–shaft angle ≤ 90°
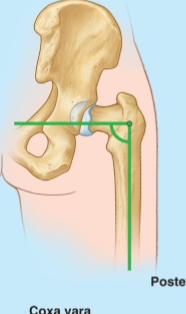
Regarding (Inclination angle) How does coxa vara affect shear forces, and what injury is more likely to occur?
As the neck approaches 90°, the angle decreases and shear forces on the femoral neck increase; Greater chance for fracture
Regarding (Inclination angle) What is Coxa Valga and
Femoral neck–shaft (CCD) angle > 135°
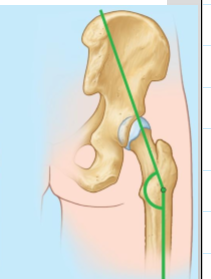
Regarding (Inclination angle) How does coxa valga affect force distribution in the hip? and this causes what injury to most likely to occur?
Increases stress through the femur and reduces load transfer through the acetabulum. Increases chance of a hip dislocation
What is angles of torsion in the hip?
It's the angle between the femoral neck (where the head of the femur connects) and the femoral condyles (at the knee). (meaning if you lay the femur flat, you would see the femoral neck at an angle.
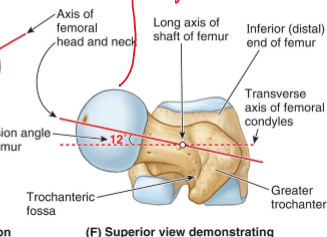
What is the typical angle (angle of torsion)?
10-20 degrees
Regarding (angle of torsion) What is anteversion?
The femoral neck is rotated forward relative to the shaft (MORE ANTERIORLY)
What gait result does femoral anteversion cause?
Internal hip rotation → “toe‑in” or in‑toeing
What is retroversion when is comes to angle of torsion?
The femoral neck decreases angle meaning the femoral head “leans backward”
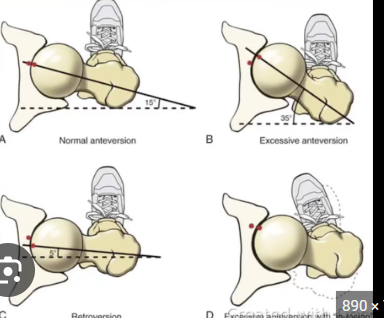
What gait result does femoral anteversion cause?
This can lead to an "out-toeing" gait (walking with feet turned outward)
When there is patella tracking issue is the issue usually medial or lateral tracking
laterally because of the angle of the quads and patella creating an outward pull
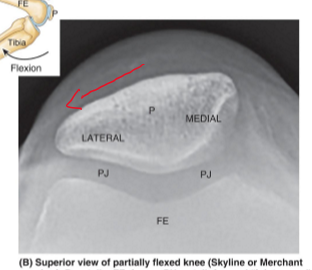
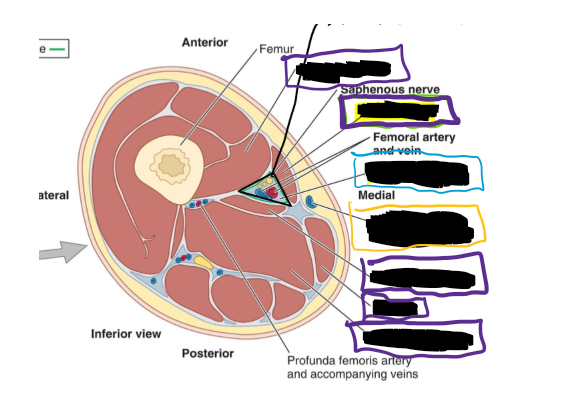
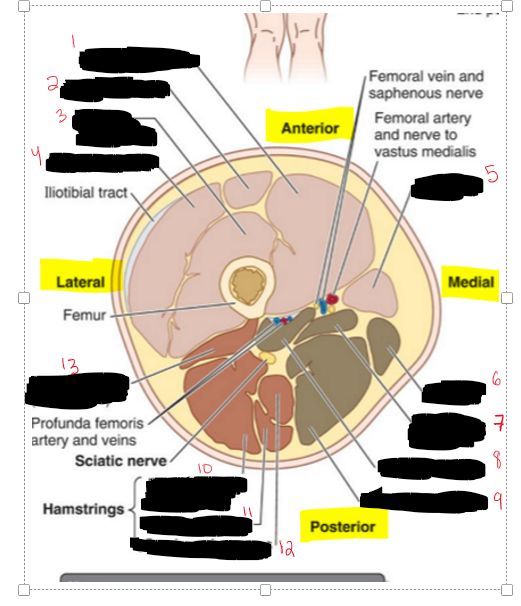
When looking at a transverse view of the anterior, medial, and posterior compartment, what is the best way to know if laying prone or supine?
Is to look at the femur and see what the point part is doing (that references the POSTERIOR SIDE)
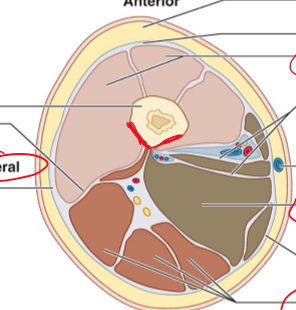
Is this individual laying supine or prone and why?
They are laying supine because the pointy part is facing the posterior on the bottom and it’s an inferior view so feet to head.
Where does the sacrotuberous ligament originate and insert
Posterior inferior iliac spine + sacrum + coccyx… ischial tuberosity
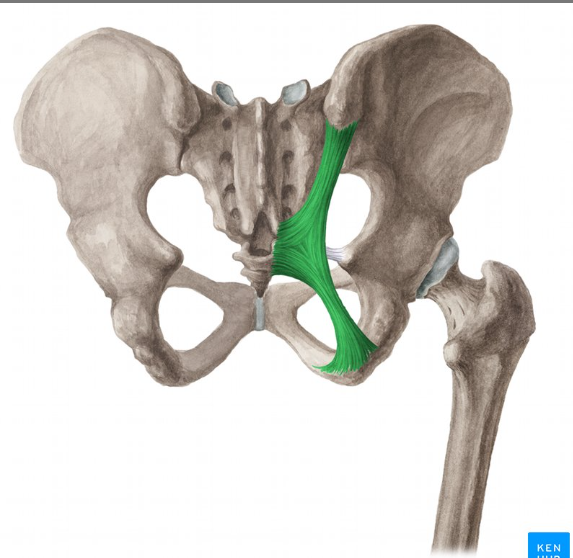
Where does the sacrospinous ligament originate and insert? also is it anterior or posterior to the Sacrotuberous ligament?
From sacrum & coccyx → to ischial spine…. ANTERIOR
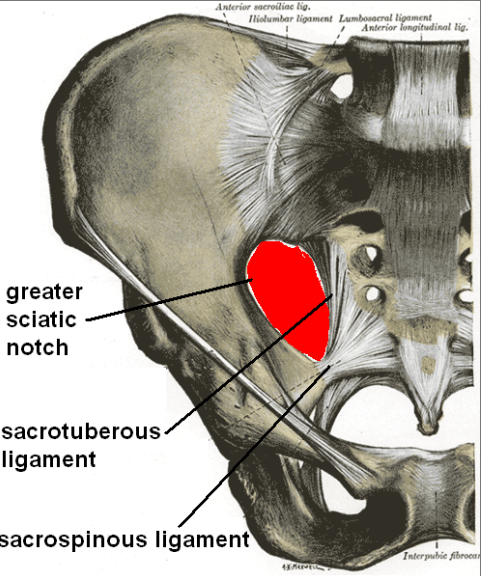
The Sacrotuberous and Sacrospinous ligament transfer what?
The greater and lesser sciatic notches into foramina
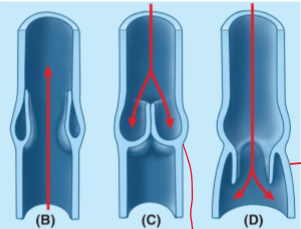
Briefly explain this image by explaining (B), (C), and (D)
(B)- valves open up to allow blood to pump back up from the legs to the heart (this is down when we contract our muscles)
(C)- The valves close to prevent backflowing of blood back down the legs
(D)- This is considered a malfunctioning value as it is allowing blood to flow back down the leg.
what does the adductor hiatus form?
allows the femoral artery and vein to pass from the anterior thigh to the posterior thigh, specifically into the popliteal fossa
The Pudendal nerve can effect what kind of athletes?
Can effect cyclist because of the prolonged sitting on the seat.
Where is the femoral triangle located?
Anterior thigh, just below the inguinal ligament
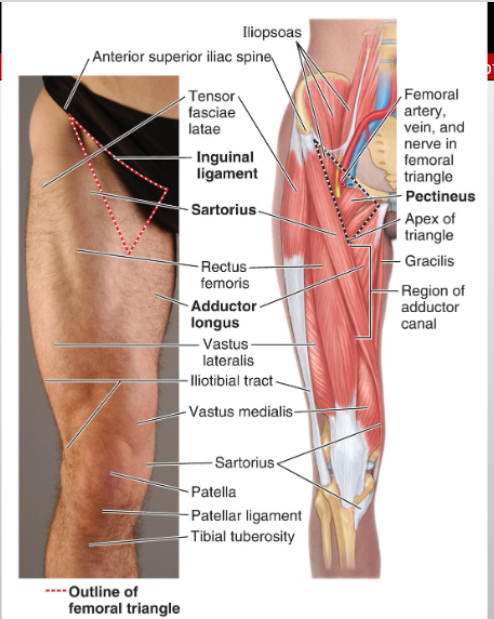
What are the three borders of the femoral triangle?
Superior = inguinal ligament; Lateral = sartorius; Medial = adductor longus
What forms the roof and floor of the femoral triangle?
deep fascia (fascia lata) and Lateral = iliopsoas
Which cutaneous nerve lies at the femoral triangle?
Lateral femoral cutaneous n.
Which nerve and its branches lie outside the femoral sheath?
Femoral nerve and its terminal branches
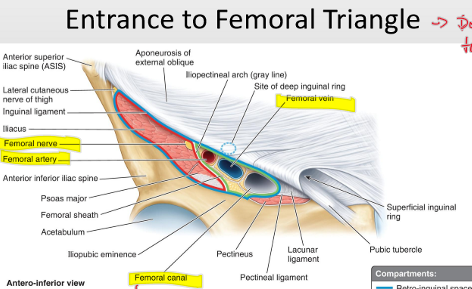
What major artery and branch run through the femoral sheath?
Femoral artery and profunda femoris artery (branching to circumflex femoral arteries)
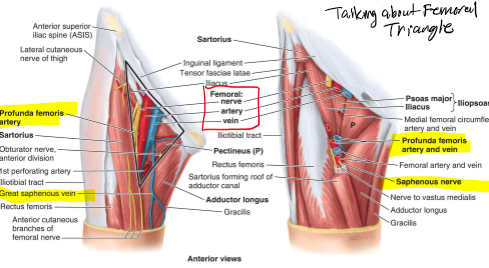
Which vessels accompany the femoral vein within the sheath of the femoral triangle
Femoral vein plus proximal tributaries: great saphenous & profunda femoris veins
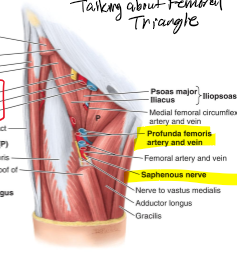
Which arteries mainly supply the femoral head and neck?
Medial and lateral femoral circumflex arteries (branches of profunda)
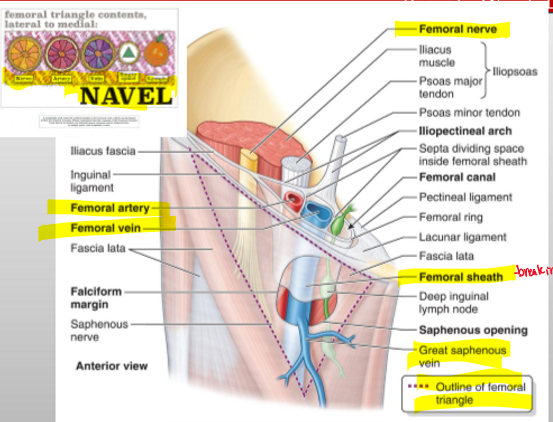
What is the order of structures from lateral to medial in the femoral triangle?
NAVEL: Nerve → Artery → Vein → Empty space (canal) → Lymphatics
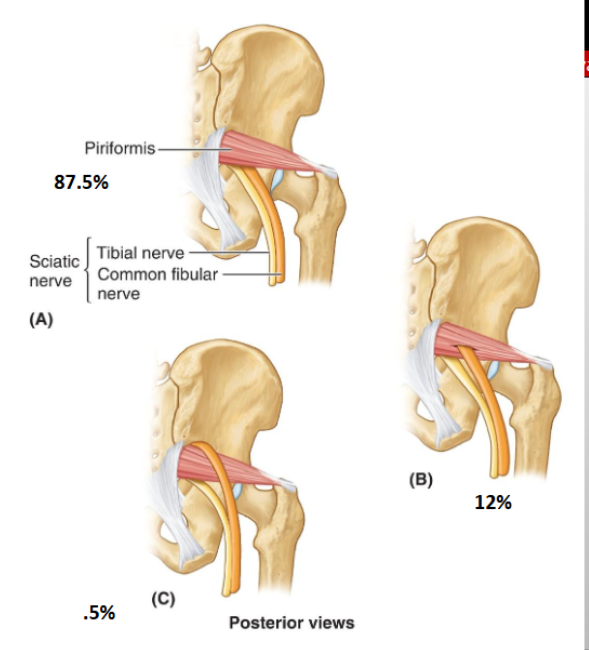
Is it possible for the sciatic nerve to through the piriformis different ways, if so explain.
Yes, most sciatic nerves (tibial nerve and common fibular n.) will both go under the piriformis m.
Sometimes the common fibular n will pierce through the sciatic n.
Rarely the common fibular n will go over the piriformis m.
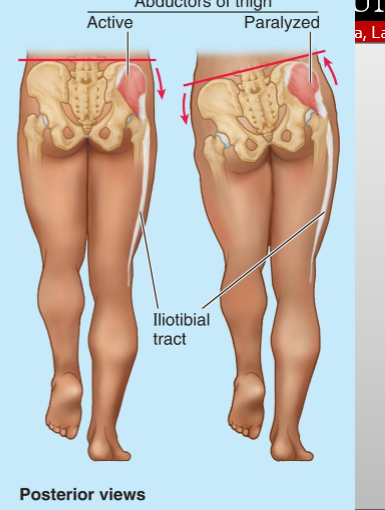
What is Trendelenburg gait and what causes its characteristic pelvic drop?
An abnormal gait from weak hip abductors (gluteus medius/minimus). During stance, pelvis drops on the unsupported side (during single leg); trunk leans to the affected side to maintain balance
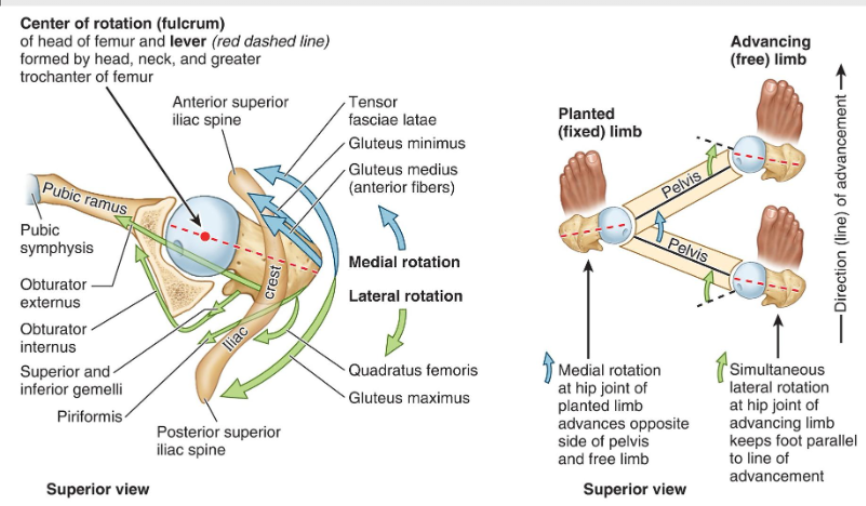
When walking how does the hip move within the hip joint?
When walking the advancing limb moves in lateral rotation and the planted limb moves in medial rotation, if hips didnt rotate you couldnt walk well.
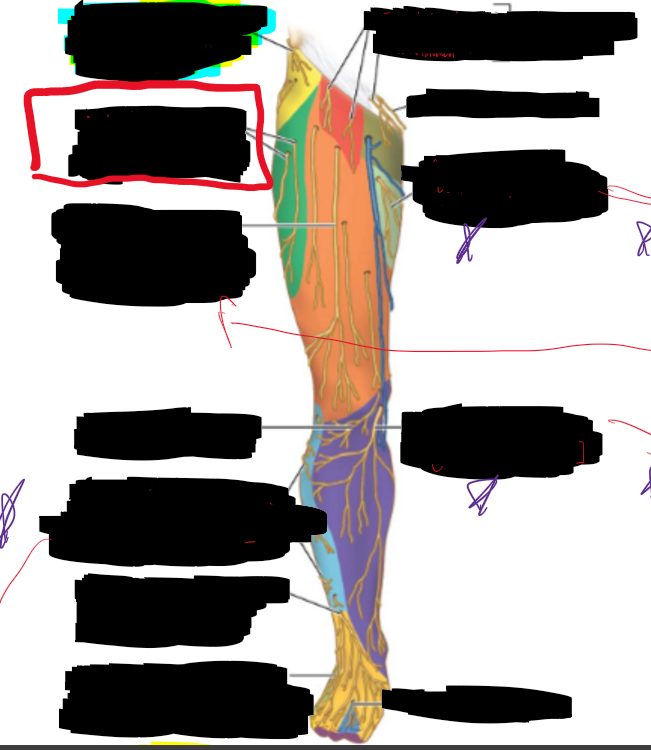
How is the thigh divided and what are the compartments?
The fascia lata sends three intermuscular septa into the femur, creating:
Anterior compartment (extensors; innervated by femoral nerve)
Medial compartment (adductors; innervated by obturator nerve)
Posterior compartment (hamstrings & some extensors; innervated by
What is the adductor canal?
A narrow fascial tunnel in the anterior thigh that carries femoral vessels to the popliteal fossa.
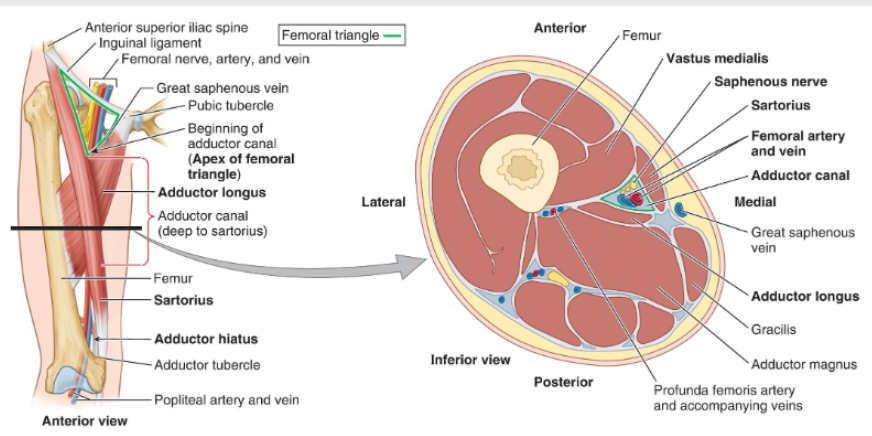
Where is the adductor located?
It begins where sartorius crosses adductor longus and ends at the adductor hiatus in adductor magnus.
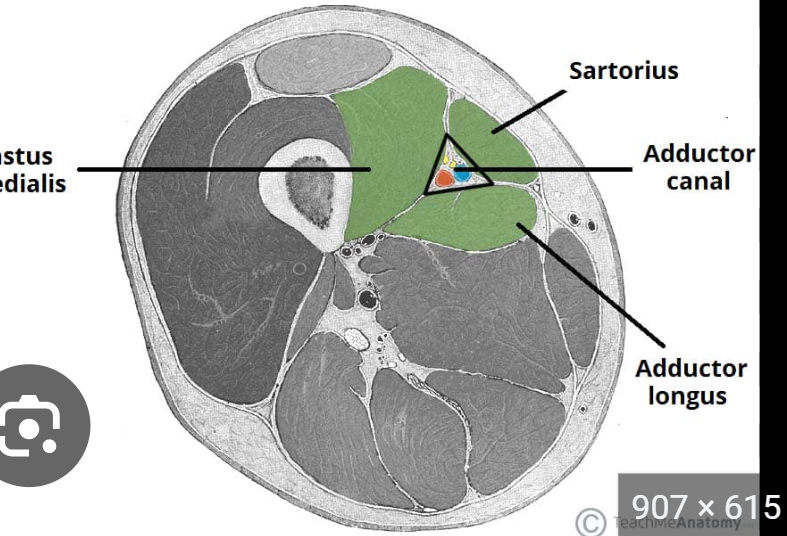
What are the contents of the adductor canal?
Femoral artery and vein (become popliteal vessels after exiting adductor hiatus)
Saphenous nerve (cutaneous branch of femoral nerve, accompanies the femoral artery and vein into the canal
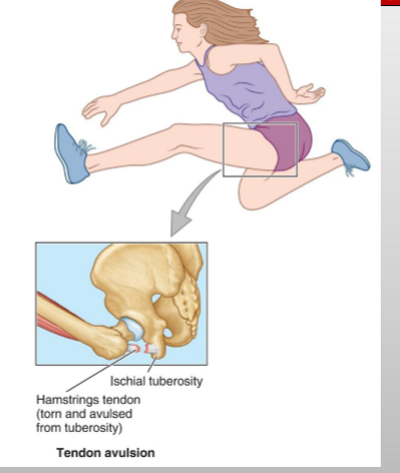
What is this?
Tendon avulsion of the hamstring tendon (where the tendon rips off the bone and takes pieces of bone with it.)
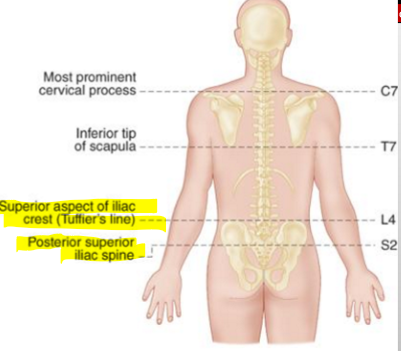
Where can you find the Superior aspect of iliac crest and what is it called?
L4 & (Tuffler’s Line) BY THE ILIAC CREST
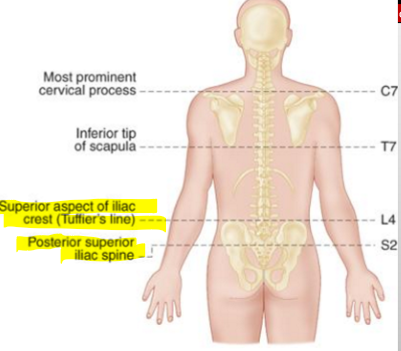
Where can you find the Posterior superior iliac spine and what is it called?
S2 & and its by the ILIAC SPINE
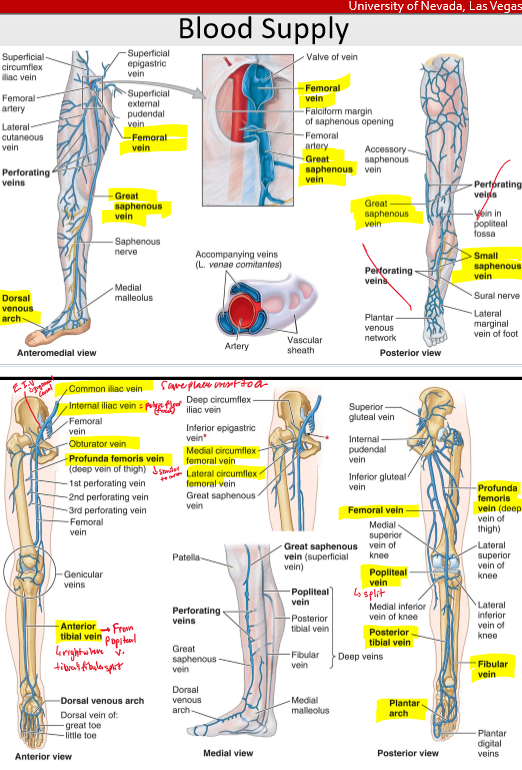
What is the order of the vein from the dorsal side?
Dorsal Venous Network- anterior tibial vein- popliteal v.- femoral v.
dorsal venous network- great saphenous- femoral v- (profunda femoris)- ext iliac v- common iliac ( which branches off the interal iliac- obtruator v.
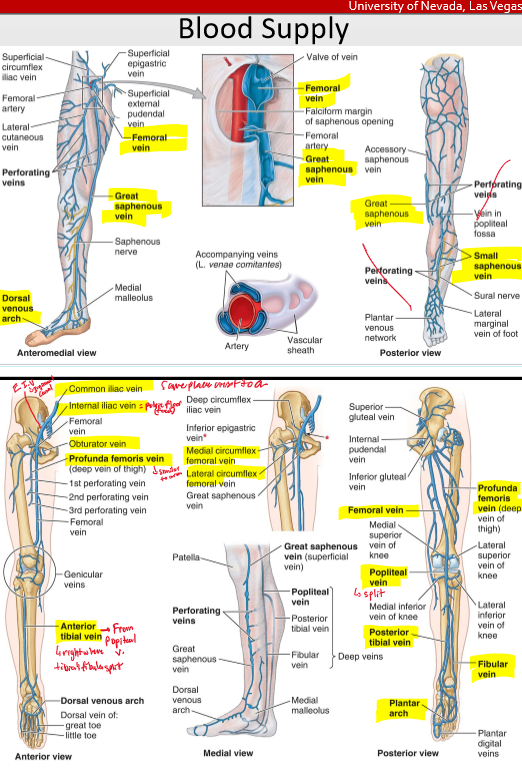
What is the order of the vein from the plantar side
Plantar venous arch- Fibular v. - post tibial v.- popliteal v.
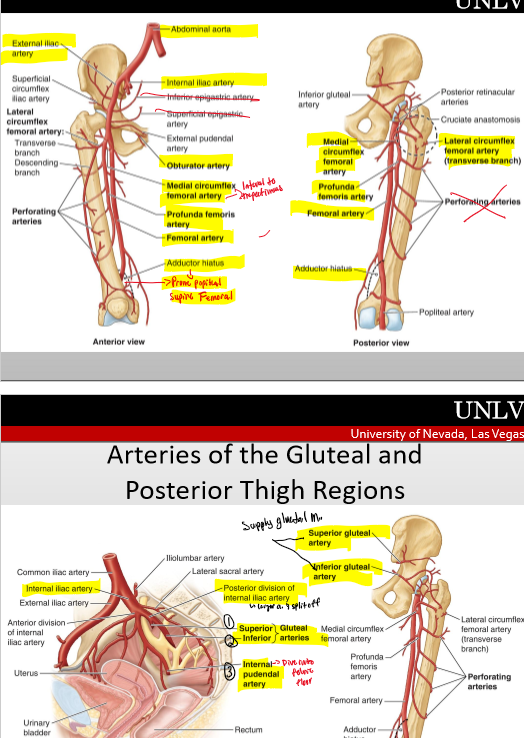
What is the order of the arteries?
abdominal aorta- common iliac a( int iliac a.- obtruatora.- superior gluteal- inf gluteal)- ext iliac a- femoral a. (profunda femoral a- med & lat circumflex a.)- popliteal a. (4 genicular anatamoses)- (ant tibial a. & post tibial a.)- (fibular a.)
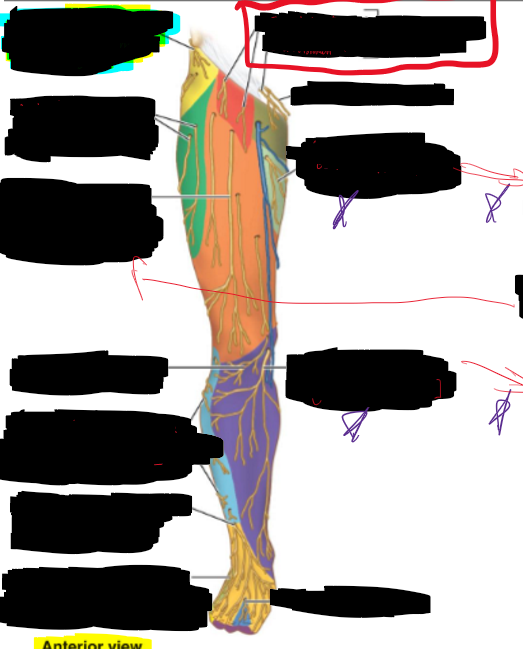
What is the structure circled?
Lateral cutaneous branch of subcostal nerve (T12)

What is the structure circled?
Lateral cutaneous nerve of thigh (anterior branches)
What is the structure circled?
Anterior cutaneous branches of femoral nerve (lateral group)

What is the structure circled?
Lateral sural cutaneous (from common fibular nerve)
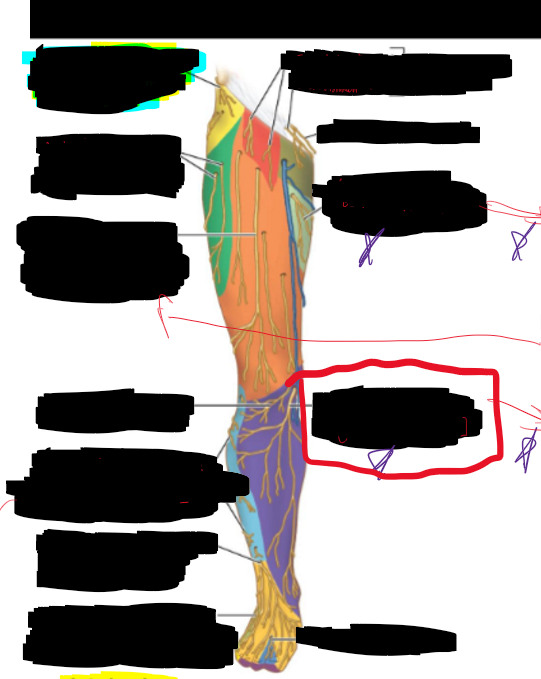
What is the structure circled?
Saphenous nerve (from femoral nerve)
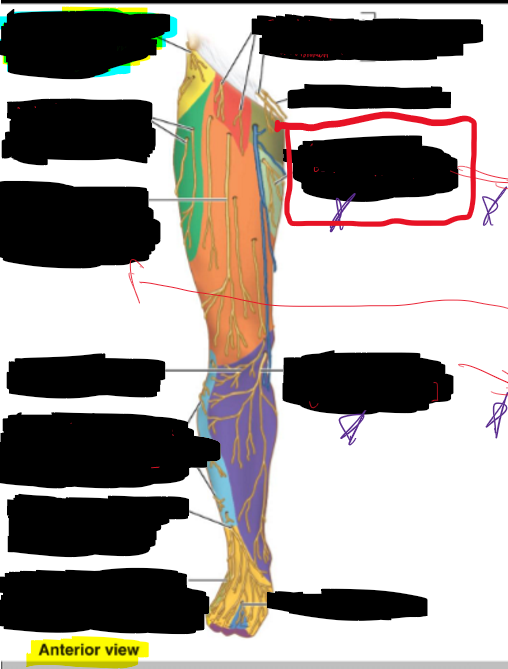
What is the structure circled?
Cutaneous branch of obtruator nerve
What is the structure circled?
Genitofemoral n.
What is the structure circled?
Posterior cutaneous nerve of thigh
What are the structured circled?
Vastus medialis
Sartorius
Adductor Longus
Gracilis
Adductor Magnus
Adductor Canal
Great Saphenous vein
Name the Structures.
Vastus Medialis
Rectus Femoris
Vastus Intermedius
Vastus Lateralis
Sartorius
Gracilis
Adductor Longus
Adductor Brevis
Adductor Magnus
Bicep Femoris (Long Head)
Semitendinosus
Semimembranosus
Bicep Femoris (Short head)
What muscle is this?
Obturator Externus
What muscles is reflected and shown?
Pectineus and Adductor magnus
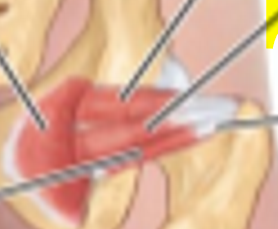
What muscle is show?
Obturator internus
Anteversion of angle of torsion increases or decreases between the femoral neck and femoral condyle?
Is increases the angle
Retroversion of angle of torsion increases or decreases between the femoral neck and femoral condyle?
It decreases the angle
During the swing phase of one leg, what happens to the pelvis on the opposite (stance) side in Trendelenburg gait?
It drops because the hip abductors on the stance leg are too weak to stabilize the pelvis.
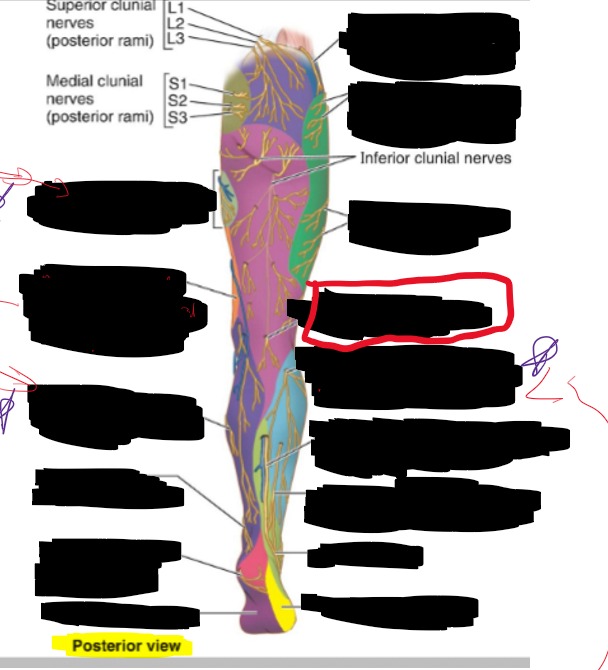
Name all the structures in the lumbar plexus and its innervation
“Star Igodola Is Great Leads Fast Offence”
Subcostal [T12]
Iliohypogastrial [T12,L1]
Ililoingineal [L1]
Genitofemoral [L1-L2]
Lateral Femoral Cutaneous [L2,L3]
Femoral [L2-L4]
Obrtuator [L2-L4]
Name the sacral plexus and their innervation
Superior Gluteal n, n. to inferior gemellus & quadratus femoris [L4-S1]
Inferior gluteal n. and n. to obtruator externus, and superior gemellus [L5,S2]
Piriformis n. [S1-S2]
Posterior femoral cutaneous n. [S1-S3]
Pudendal n. [S2-S4]
Sciatic n. [L4-S3]