02 adam smith
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Book 1
Establishes the idea of division of labour
Introduces prices of goods and how these are determined formed from wages, profits and rents
Book 2
Nature, accumulation and employment of stock
Book 3
Of the different progress of opulence (stages of econ development) proposes 4 stages
1st stage of human development
Humans are simply foragers or hunter/gatherers
2nd stage of human economics
By domesticating or controlling animals, humans develop a form of existence based on ‘pasturing’
3rd stage of econ development
Settled agriculture and the development of crop culture as well as rent
4th stage of econ development
‘Age of commerce’ moving to an industrial society- steel furnaces, must settle to industrialise
Book 4
Of systems of political economy- attacks mercantilists and physiocrats- if not complete ‘free trade’ then more limited internet=ventions
Book 5
Deals with taxes, the raising of state revenue and expenditure what the revenue should be sent on (defence, justice systems, infrastructure, roads, edu)
What is the division of labour
Instead of a worker producing a product from beginning to end it is broken down to separate tasks
3 reasons division of labour adds to economic productivity
Increased skill in every worker 2. Work-time saved since workers dont have to pass from one place to another 3. Leads to invention of new technology
Returns to scale- formula
Q= f(k,L)
Output is a function of capital and labour
Constant return to scale
Doubling input doubles output
Increasing returns to scale
Eg doubling input triples output
Decreasing returns to scale
Eg inputs double outputs halve
Adam smith and returns to scale
Thought agri was constant, mining was diminishing an manufacturing was increasing (due to increasing productivity)
productive vs unproductive labour
agriculture and manufacturing and the non productive sector
capital accumulation key idea
with the division of labour economic groth is driven by the accumulation of capital, rowth can only come from investment
two types of capital accumulation
fixed and circulating
circulating capital
the store of goods and materials from the last productive period, available at the beginning of the current productive period
fixed capital
the store of non consumable goods such as buildings and factories all of them necessary for the production and distribution of the national output
smith and circulating capital leading to higher productivity
‘the funds destined for the maintenance of productive labour’ feeds the labourers leading to higher productivity
prices and value quote and analysis
‘preceds both the accumulation of stock and the appropriation of land’- where there were no profits and no landlords so no rent
time and price
‘the toil and trouble of acquiring it’ the amount of time equates to the price it is valued at
relative price
the price in relation to another commodity
‘the time spent in two different sorts of work will not always alone determine this proportion’
by counting labour we are implicity assuming labour hours are equal- which is not realistic
issues with time equating to value
not all hours have the same difficulty, different commodities need to include labour value of capital used- have to make an allowance (depreciation)
labour embodied vs labour commanded
labour embodied- that used in production, labour commanded- how much labour a product can buy
labour embodied equation
labour embodied= labour + labour embodied in the capital = labour/ (1-capital)
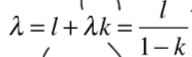
linear equation for price
price= wages + capital + profit + rent
when is there a profit
when labour commanded is greater than the embodied labour- this inceases as the difference becomes greater
what is the natural price
price of a commodity that is just enough to cover the costs of production, including the rent of land, the wages of labor, and the profits of stock
natural price link to equilibrium price
actual price might deviate but market forces would bring it back
what is the invisible hand theory
how individual self interest unintentionally promotes the overall good of society
what is the wages fund
part of the circulating capital - part of the useful goods produced in a productive cycle which is used to pay the workers in the successive cycle
landowners properties
do not own productive capital are not interested in enlargement and have no inducement to save and accumulate capital- no contribution to the growth of the nation
workers properties
only possesses their labour propensity to save is 0, no contribution to the growth of national wealth although essential to production
capitalist properties
has productive capital and aims to increase it- high propensity to save so general interest of the nation coincides with the bourgeois
critisism of ‘wages, profit and rent are ther three original sources of all exchangable value’
from equation of labour commanded can see if ages and profits are predetermined there are no more variables to determine the equation becomes overdetermined.
market price vs natural price
market price is the actual price of a good at a given moment natural is what would allow the payments of workers, capitalists and landowners at normal rates of remuneration
3 condition of competitive equilibrium
the productive system will produce those goods the consumers demand
the chosen production methods are the most efficient
the goods are sold at the lowest price possible