Economics test 1
1/50
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
scarcity
something is scarce when it’s both desirable and limited
choice
as people do not have infinite incomes, they must make choices on what goods/services to purchase
oppertunity cost
what is given up to get something else (never expressed in monetary terms). “trade-off”
Factors of production
Land,Labour,Capital,Entrepreneurship
positive statement
concerned with the facts what is actually happening
normative statement
what should be done, contains subjective value judgement
potential output
The maximum quantity of both products that can be produced
utility
usefulness/pleasure a consumer gets when consuming a product
Marginal utility
benefit of consuming one more
merit goods
goods that are healthy for us, gov wants us to consume more(fruits,veg), usually underprovided/underconsumed
demerit goods
products that are bad for us, gov wants us to consume less (alcohol,tobacco), usually overproduced/overconsumed
rationing
since recources in an economy are relatively scarce, there must be a way of rationing those recources and the goods/services that come from them
types of economy (rationing systems)
planned, free market, mixed
planned economy (command economy)
what/how/for whom to produce controlled by gov, all recources collectively owned
free market economy
Prices used to ration goods/services. All production in private hands and demand/supply are left free to set wages/prices in economy. Works relatively efficient, with lesser surpluses/shortages, self righting system
disadvantage free market economy
demerit goods overprovided, recources used up to quickly, people burden unemployment, monopolies
disadvantage planned economy
miscalculation causes shortge/surplus, distorted incentives, govt dominance
circular flow of income model
simple two-sector model that can illustrate the interdependence that exists between key economic decision-making
running a budget deficit
when governments are able to spend more money than they earn in taxes by borrowing money
Market
any place where transactions take place between buyers and sellers
Four types of market
product,factor, stock, internation
demand
the quantity of a good or service that customers are both willing and able to buy at a given price, per period of time
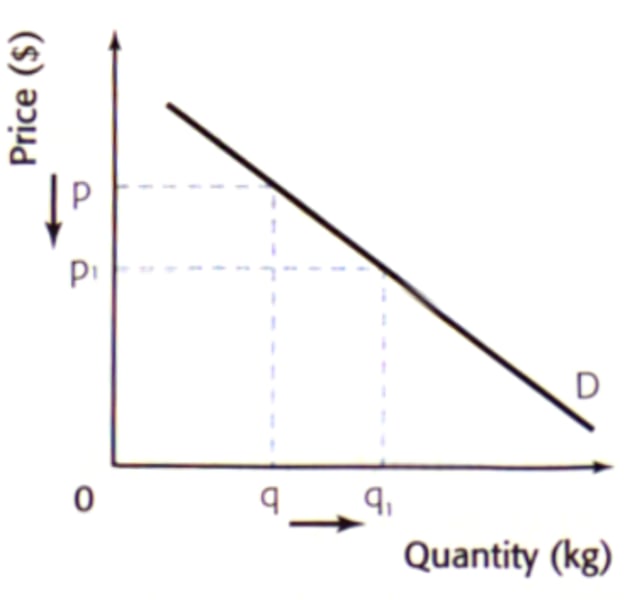
Law of Demand
as price of a product falls the quantity demanded of a product will usually increase, ceteris paribus
income effect
when price of a product falls, increase in ‘real income’
substitution effect
as price of one product falls, the product will be more attractive than competitor
Non-price determinants of demand
various factors other than the price of the good or service that affect the demand for the product. This causes a leftwards or rightwards shifts in demand
normal goods
products that customers tend to buy more of as their real income level increases. This includes both necessities and luxury goods and services.
Inferior goods
products with a negative income elasticity of demand. In other words, the demand for such products tends to fall when consumers real incomes rise.
non-price determinants
change in income, substitutes, complements, unrelated, taste/preferance, future price predictions
Complements (complementary goods)
products that are jointly demanded; for example, torches and batteries, or printers and ink cartridges.
Substitutes
products that are in competitive demand because they can be used in place for each other; for example, butter and margarine, tea and coffee, or Honda and Toyota cars.

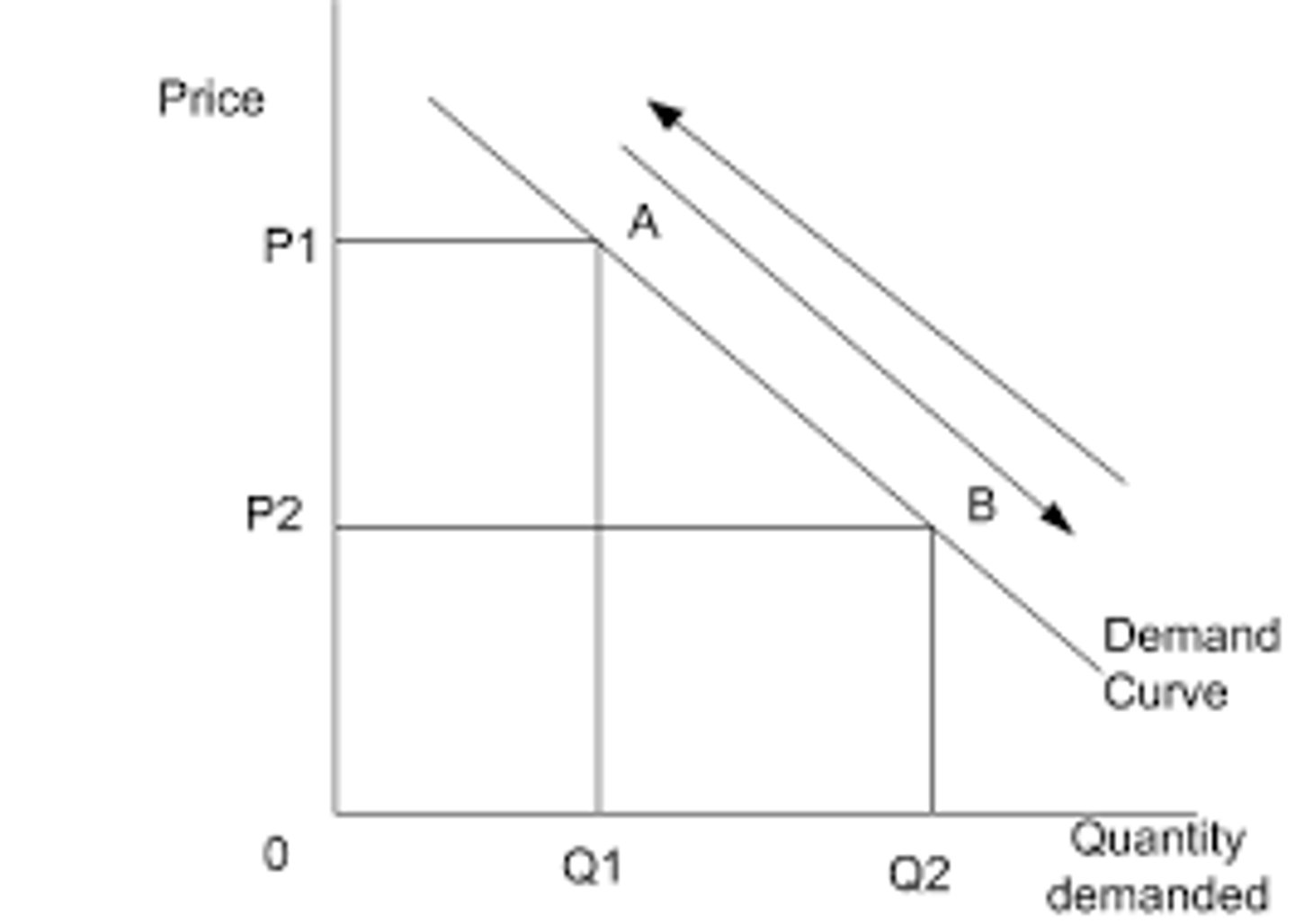
movement along the demand curve
movement along a demand curve is caused by price changes only. A fall in price causes quantity demanded to expand while an increase in price causes quantity demanded to contract
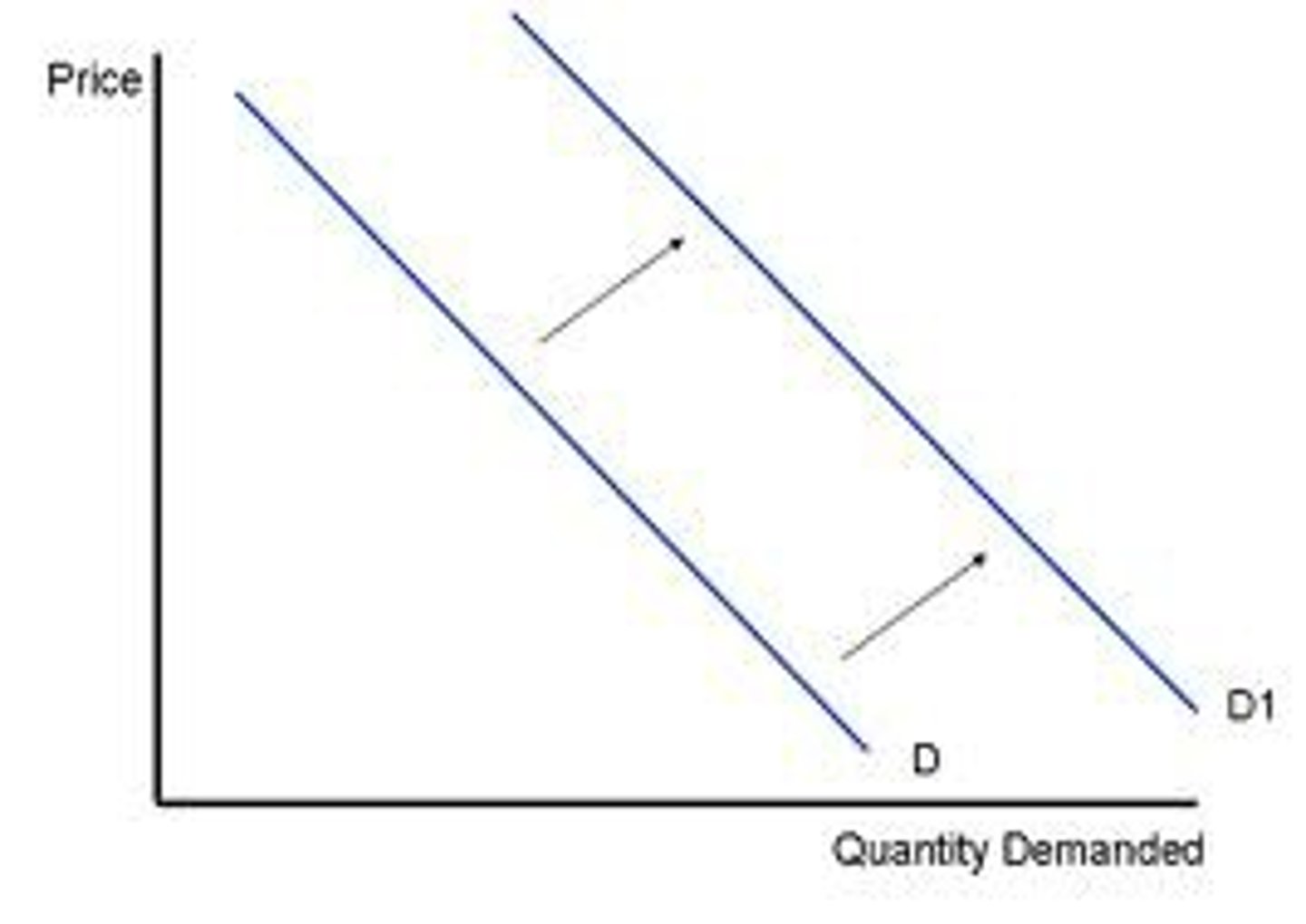
increase in demand
rightwards shift of the entire demand curve for a product, caused by favourable changes in non-price factors that affect demand.
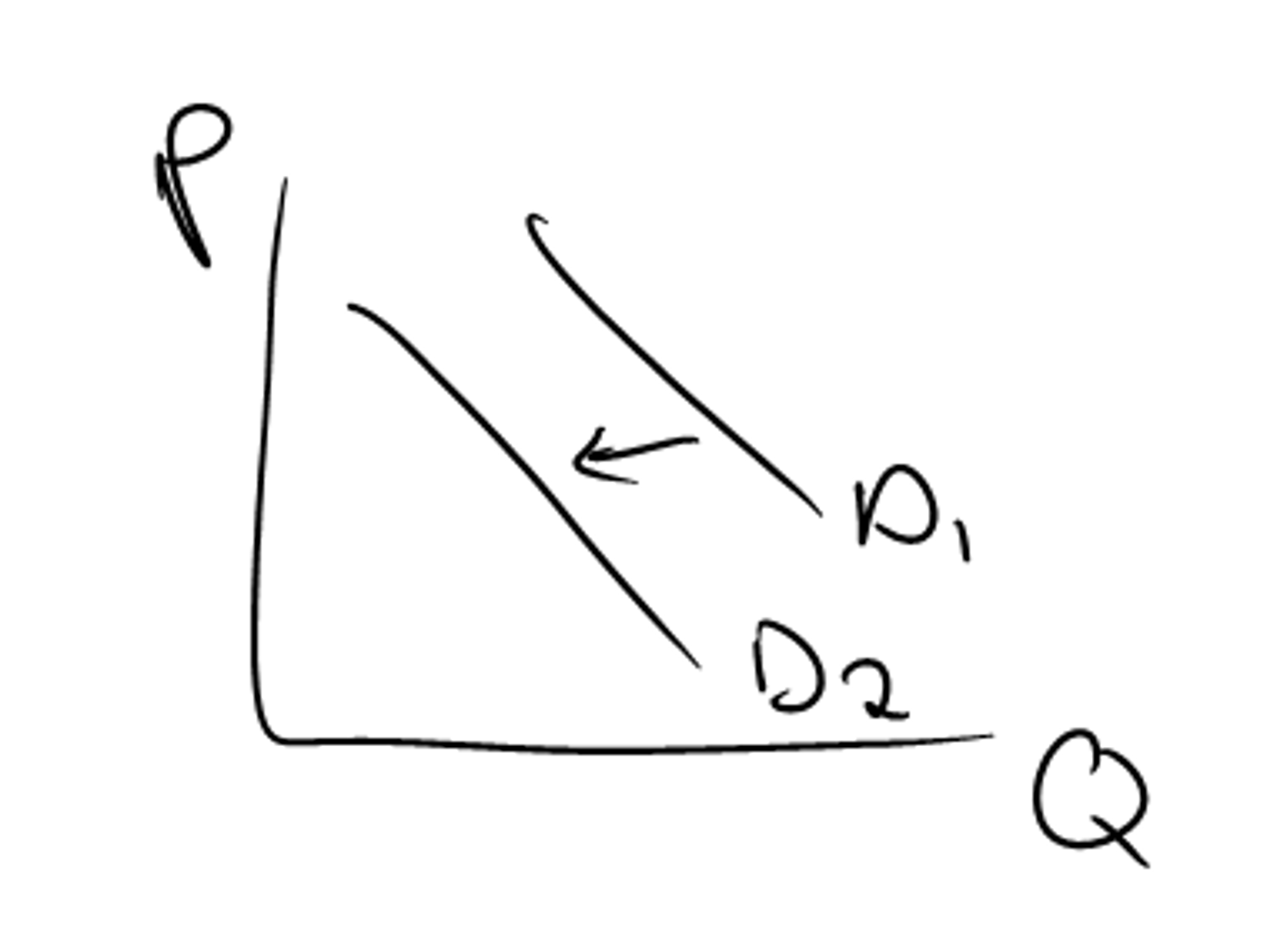
decrease in demand
leftwards shift of the entire demand curve for a product, caused by unfavourable changes in non-price factors that affect demand.
Shift
occurs when there is a change in any non-price factor that affects the demand for a product. The entire demand curve shifts to the left if there are unfavourable changes affecting demand, and vice versa.
veblem goods (snob value goods)
demand increases as price rises, gain more utility from consuming expensive products
Giffen good
a low-income, non-luxury product for which demand increases as the price increases and vice versa
key assumptions of law of demand
consumer is rational, has perfect information, is very intelligent, is selfish ect
horizontal summing
adding together the total demand you can create a demand curve for the total market
dual system model
automatic, reflective
system 1- automatic
fast decisions that are essentially subcontious
system 2- reflective
slow decisions that are much more controlled
cognitive biases that affect decision-making
availability bias,anchoring bias, framing bias, social conformity, status quo, losses aversion bias, hyperbolic discounting
availability bias
the availability of recent information/examples tend to over-influence people’s decision making, consumers are quite poor at assessing risk/probabilities
anchoring bias
given a value, use that value as a reference point to influence future decision/choices
status quo/inertia bias
with many choices, consumers would prefer to do nothing and stick to what has always been done
losses aversion bias
consumers feel the losses far more than the gains
hyperbolic discounting
humans prefer smaller short-term gains than larger long-term ones
Choice architecture
The theory that the decisions that we make are heavily influenced by the ways in which the choices are presented to us
nudge theory
suggests that the choice architecture offered to people can be carefully designed to gently encourage (nudge) the people to voluntarily choose the option that is better for them
consumer sovereignty
the consumer’s right to choose, maintained by nudge theory