G7 Q4: The Age of Enlightenment and Revolutions
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
Revolution
A forcible overthrow of a government or social order in favor of a new system.

Ancient Regime
old order; system of government in pre-revolution France

Authority
The power or right to give orders, make decisions, and enforce obedience.

Corruption
Dishonest or fraudulent conduct by those in power, typically involving bribery.

Treason
the crime of betraying one's country

Guillotine
a machine with a heavy blade sliding vertically in grooves, used for beheading people.

Monarchy
A government ruled by a king or queen

Clergy
A body of officials who perform religious services, such as priests, ministers or rabbis.

Social Contract
An agreement between the people and their government signifying their consent to be governed

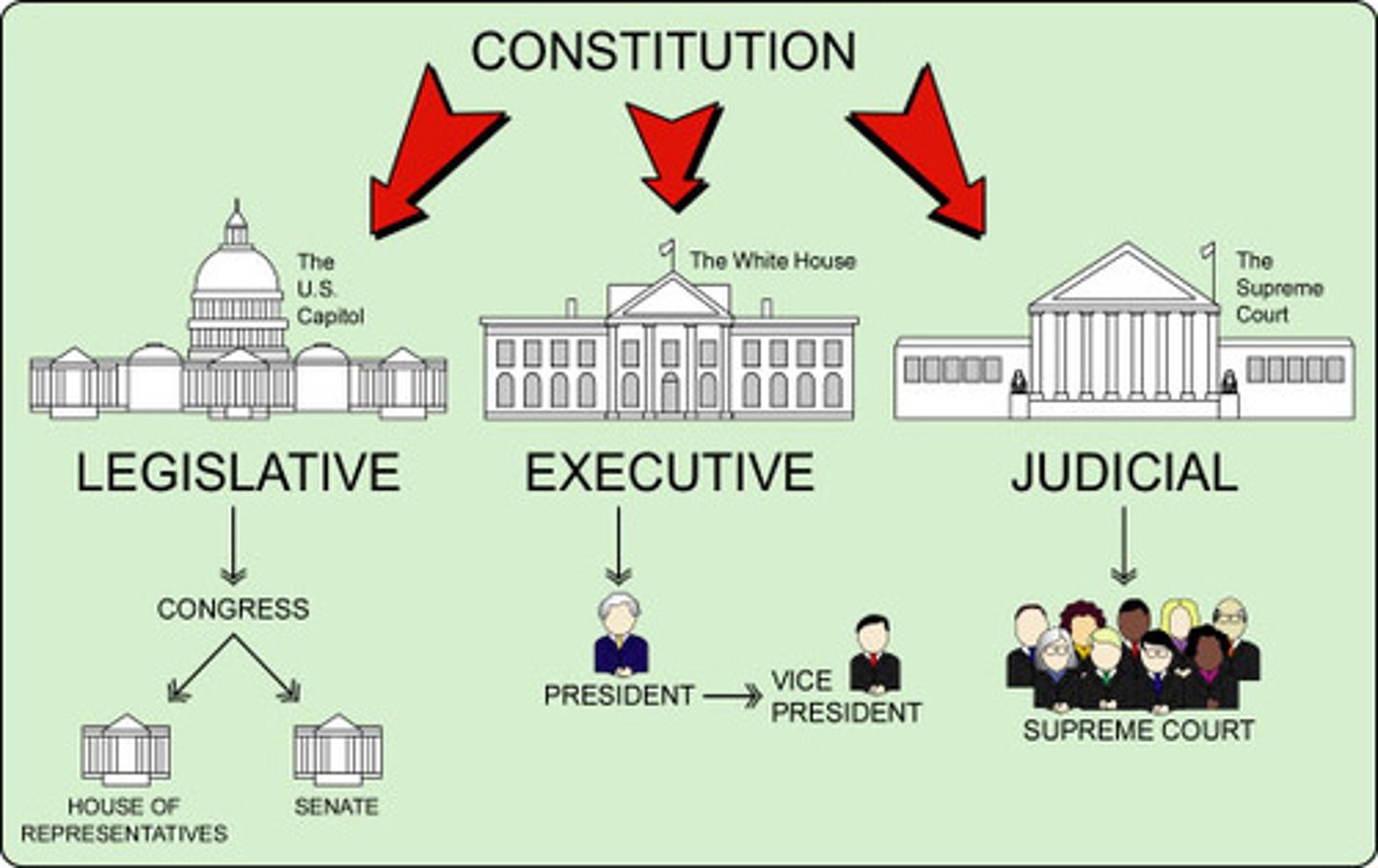
Separation of Powers
The division of power among the legislative, executive, and judicial branches of government
Enlightenment
A movement in the 18th century that advocated the use of reason in the reappraisal of accepted ideas and social institutions.
Democracy
Government by the people which involved electing your leader.

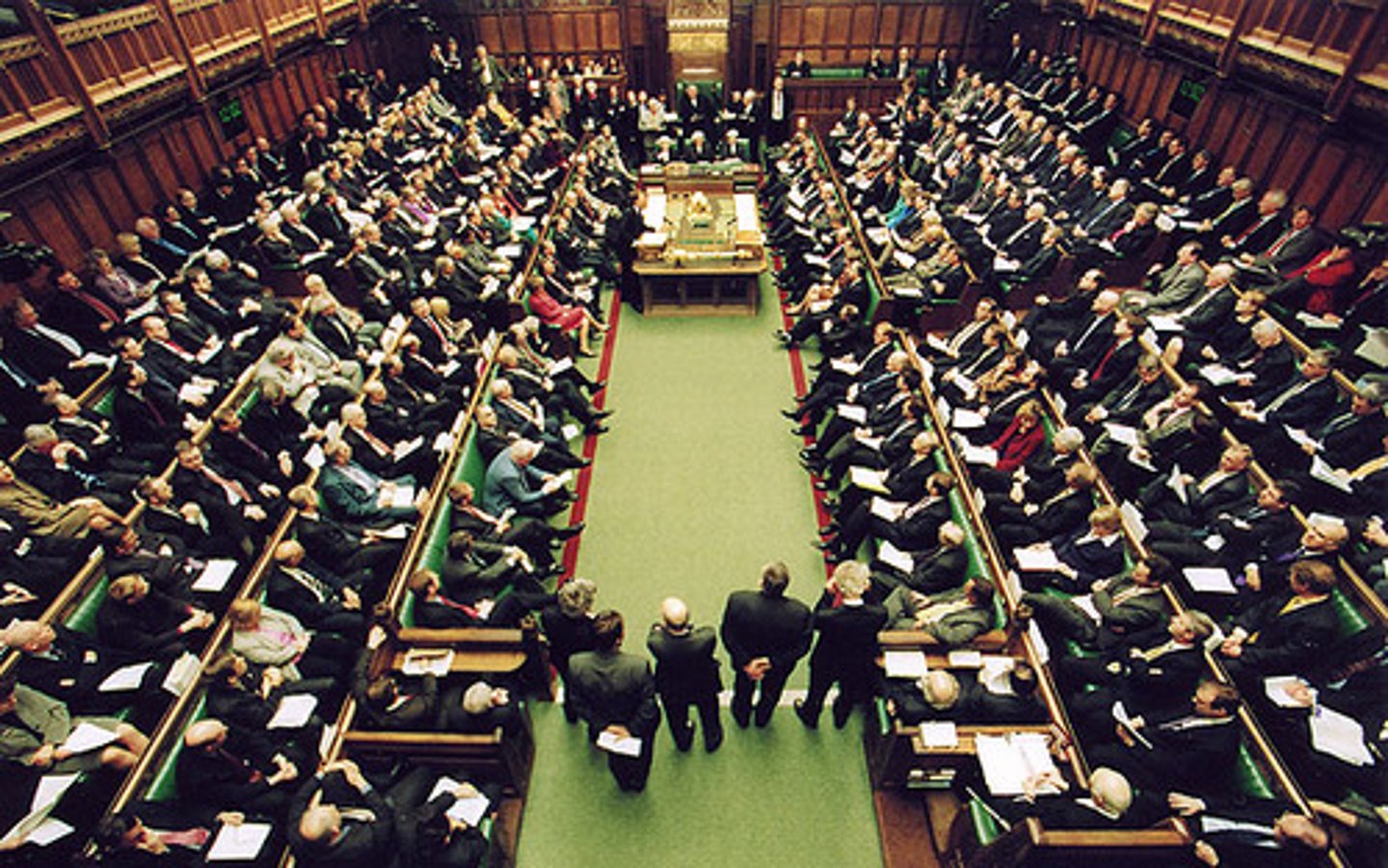
Parliament
A body of representatives that makes laws for a nation

Constitution
A written plan of government

Amendment
A change to the Constitution

Liberty
Freedom from government control

Reason
logical thinking
Scientific Method
A logical, systematic approach to the solution of a scientific problem

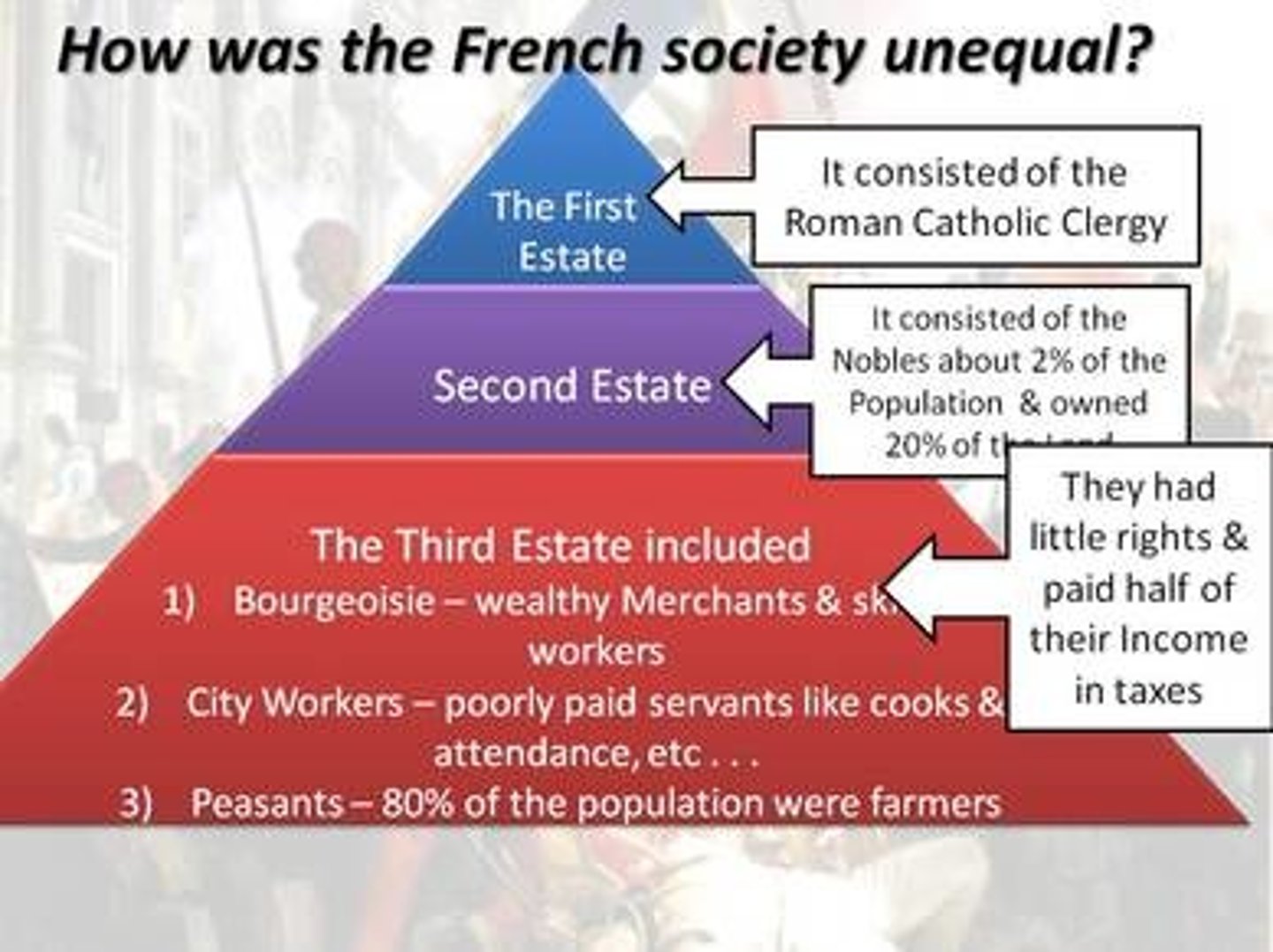
Third Estate (France)
By far the largest social group in France. Making up nearly 97% of the population. Members of this estate had few rights, and little political power.

Human rights
a right that is believed to belong justifiably to every person.

Fraternite Liberte Egalite
The French Revolution motto: Fraternity, Liberty and Equality
Bastille
Fortress in Paris used as a prison; French Revolution began when Parisians stormed it in 1789

Hereditary power
Passing power down by inheritance; this is the way who determined who would rule next

Censorship of the Press
the governments would censor the press because they didn't want citizens to see war damages/loses.

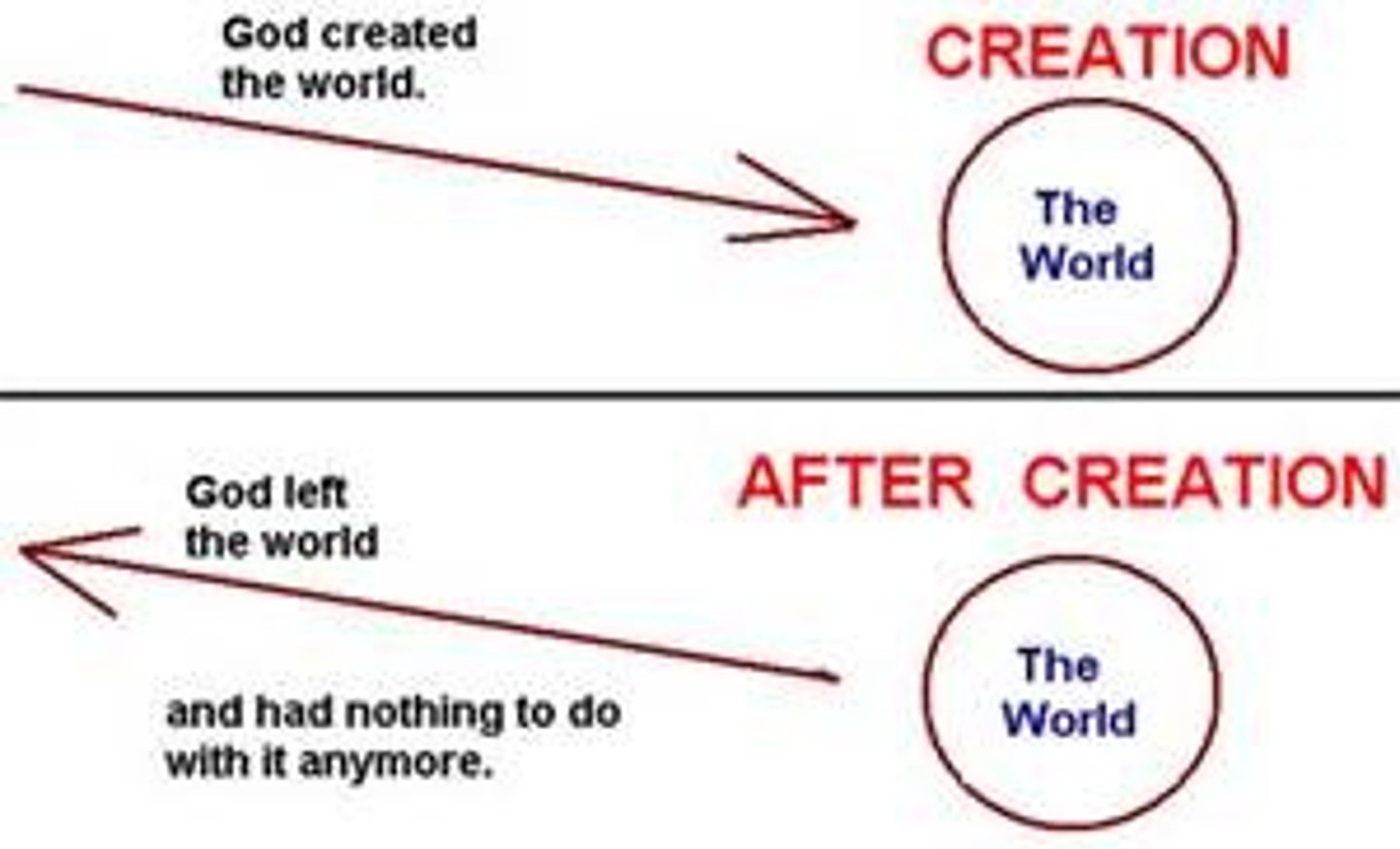
Deism
The religion of the Enlightenment (1700s). Followers believed that God existed and had created the world, but that afterwards he left it to run by its own natural laws.
Bourgeoisie
The middle class, including merchants, industrialists, and professional people
Death penalty
The punishment of execution, administered to someone legally convicted of a capital crime

Reign of Terror (1793-1794)
Ten-month period of brutal repression when some 40,000 individuals were executed as enemies of the French Revolution.

National Assembly of France
Governing body of France that succeeded the Estates-General in 1789 during the French Revolution. It was composed of the delegates of the Third Estate. Created the Declaration of Rights of Man and citizens and changed France into a constitutional monarchy.
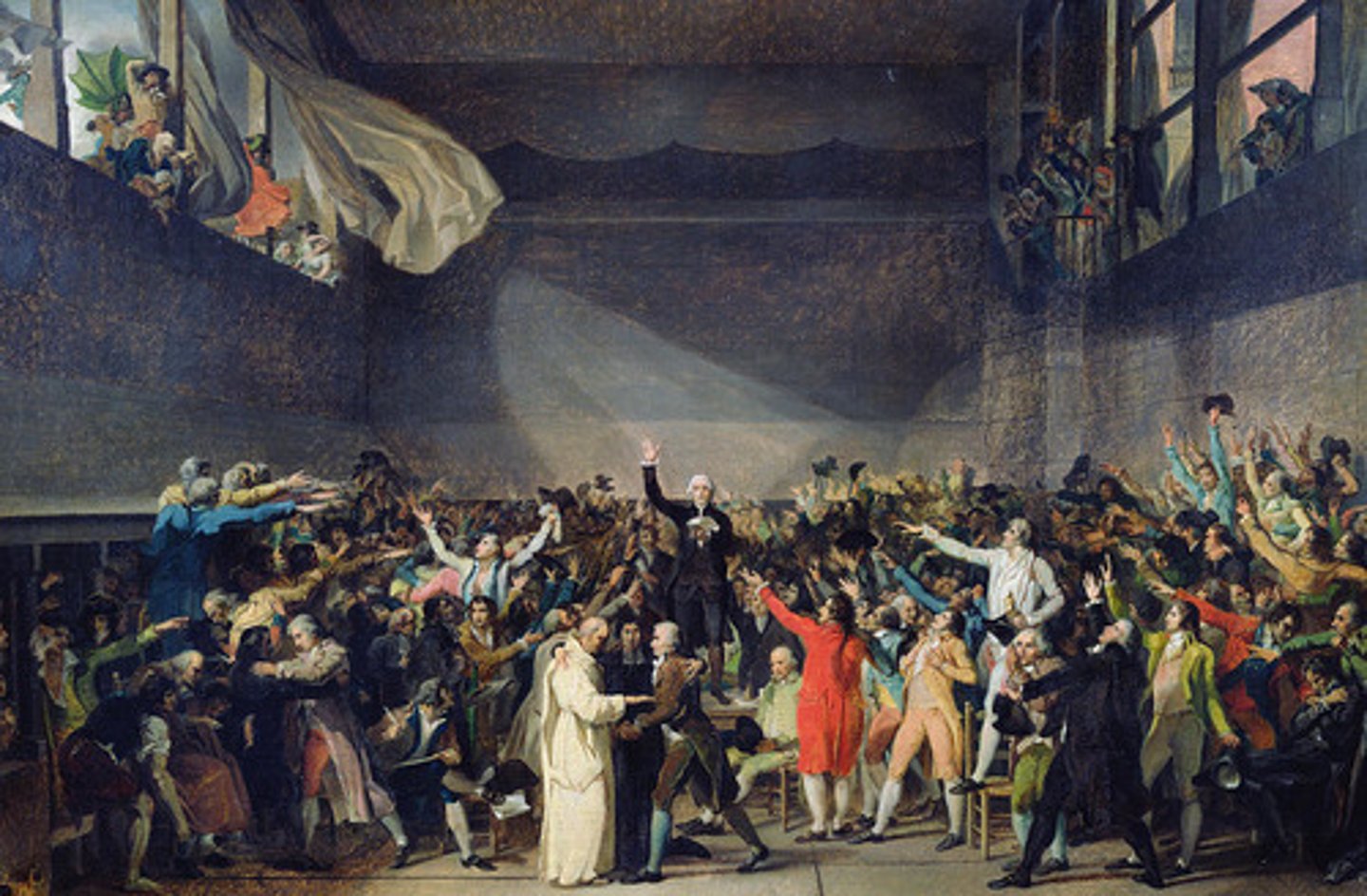

Declaration of the Rights of Man and Citizen
Adopted August 26, 1789, created by the National Assembly to give rights to all (except women).

Nation
A group of people with a common culture, language, religion and tradition living in a territory and having a strong sense of unity.
State
A group of people living in a defined territory (national borders) who have a government with the power to make and enforce law.
Sovereignty
Recognition by other states of the existence and legitimacy of an independent state.

Citizen security
The ability of a state to guarantee public and private security to its citizens.

Separation of church and state
Constitutional principle which prevents a government from favouring or setting up an official church, from providing support for religious institutions, or from requiring church to enter politics.
Authoritarianism
A political system that denies the people participation in government

Equality of individuals
Equality in opportunity, equality before the law, equal people under the law, no person should be held back on arbitrary

Private property
property owned by individuals or companies, not by the government or the people as a whole

Legitimate government
A government trusted by its people (or other states): they believe its use of power is popular, right and proper.

Despotism, tyranny
Government ruled often by an illegitimate and cruel ruler

Secularism
An indifference to religion and a belief that religion should be excluded from civic affairs and public education.

Civil Liberties
Constitutional freedoms guaranteed to all citizens

Aristocracy
The highest class in certain societies, especially those holding hereditary titles or offices.

Suffrage Movement
the movement organized around gaining voting rights for women
Industrial Revolution
A period of rapid growth in the use of machines in manufacturing and production that began in the mid-1700s
Hippies
Young people who rebelled against the mainstream culture of the 1960s
Velvet Revolution
The term given to the relatively peaceful overthrow of communism in Czechoslovakia; the label came to signify the collapse of the East Bloc in general in 1989 to 1990.
Slavery
The condition of being owned by another person and being made to work without wages
Innocence
The state of being free from sin or moral wrong