IB Chemistry HL Unit 20: Organic Chemistry
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Nucleophilic substitution
A type of substitution reaction in which a nucleophile is attracted to an electron-deficient centre or atom, where it donates a pair of electrons to form a new covalent bond.
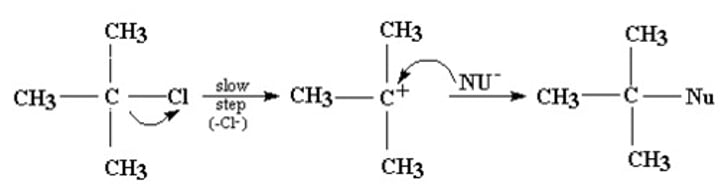
SN1 substitution
Unimolecular nucleophilic substitution
- Two steps (with intermediate)
- Tertiary (and secondary halogenalkane)
- Carbocations
- Best with protic, polar solvent
- Faster than SN2
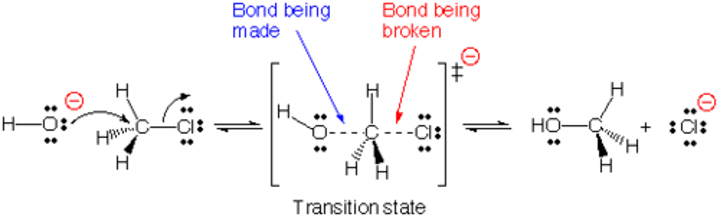
SN2 substitution
Bimolecular nucleophilic substitution
- One step concerted reaction
- Primary and secondary halogenalkane)
- Has transition state
- Best with aprotic, non-polar solvent
Rate = k(halogenalkane)(nucleophile)
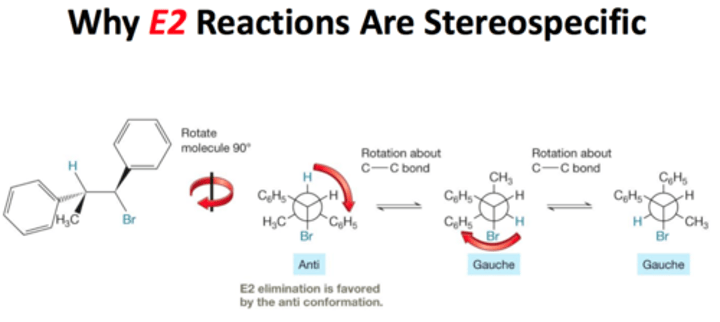
Stereospecific reaction
A reaction in which different stereoisomers react to give different stereoisomers of the product
Steric hindrance
The prevention of a reaction at a particular location in a molecule by substituent groups around the reactive site.
Protic solvent
Solvents with protons in solution, e.g. water or alcohol.
Large atoms tend to be better nucleophiles in here because they can shed the solvating protons around them and are more polarizable
Aprotic solvent
Solvent that cannot donate protons (hydrogen ions) in an acid-base reaction
Suitable for SN2 reactions, cannot solvate nucleophile therefore leaving the nucleophile to be effective in the transition state
Factors of rate of nucleophilic substitution
- Reactivity of halogen
- Bond enthalpy
- Class of halogenalkane
- Type of solvent
- Primary/Secondary/Tertiary Alcohol
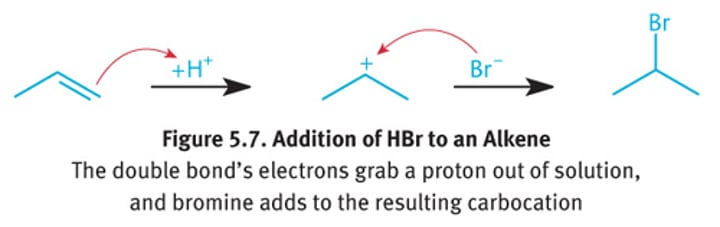
Electrophillic addition reaction
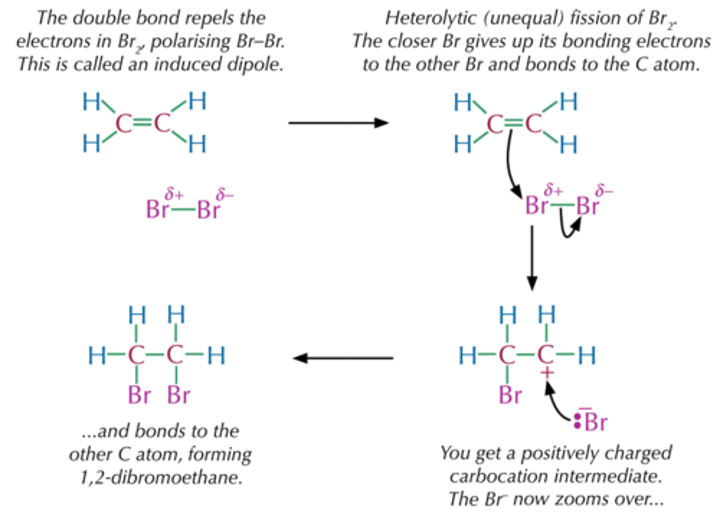
Markovnikov's Rule
The H atom from an electrophile will preferentially add to the carbon atom of the double bond that has the most H atoms
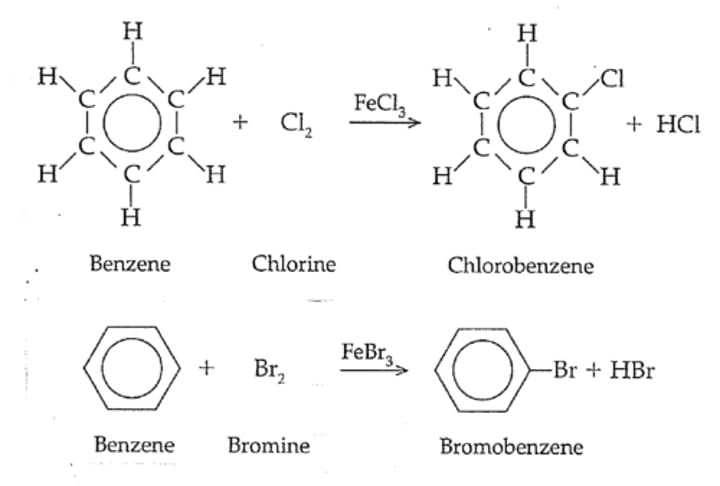
Electrophillic substitution reaction
A type of substitution reaction in which an electrophile is attracted to an electron-rich centre or atom, where it accepts a pair of electrons to form a new covalent bond.
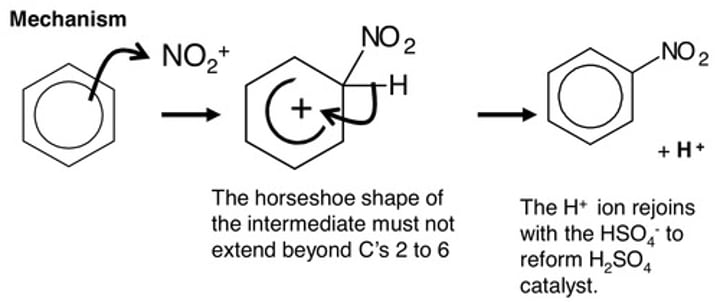
Nitration of benzene
Carbonyl
carbon double bonded to an oxygen
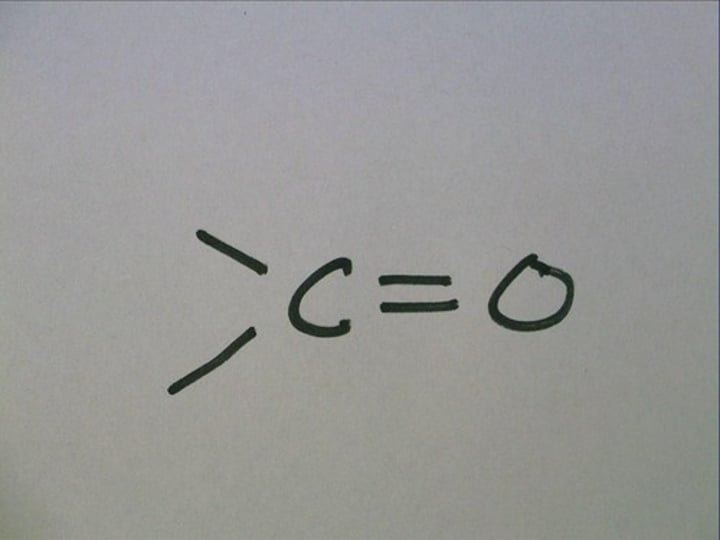
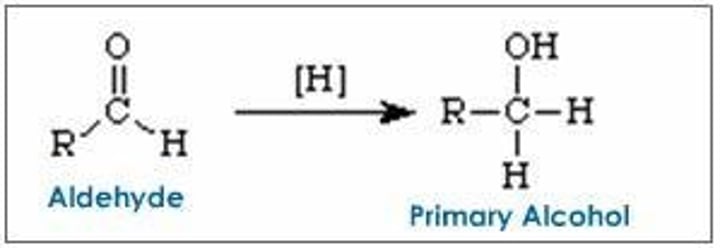
Reduction of Aldehydes
Reduced to primary alcohols.
Reduction of Ketones
Reduced to secondary alcohols.

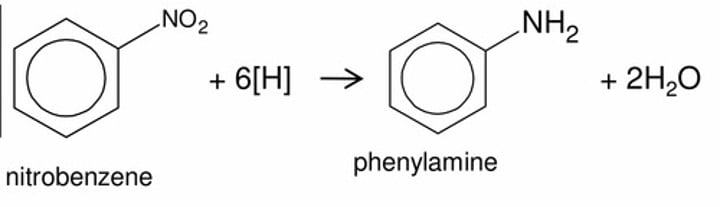
Nitrobenzene to Phenylamine
Step 1:
- Heated under reflux with zinc and concentrated HCl
Step 2:
- Add sodium hydorxide
- Formation of aniline (Deprotonation of ammonium salt)
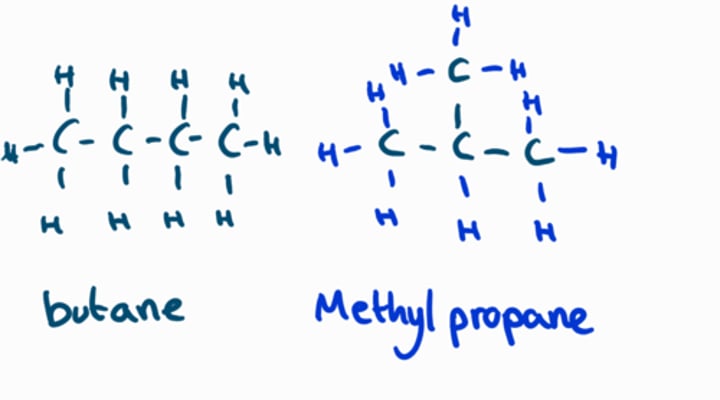
Chain isomerism
The same molecular formula, but a different arrangement of carbon atoms in the chain
Positional isomerism
The same molecular formula, but the functional group in a different position
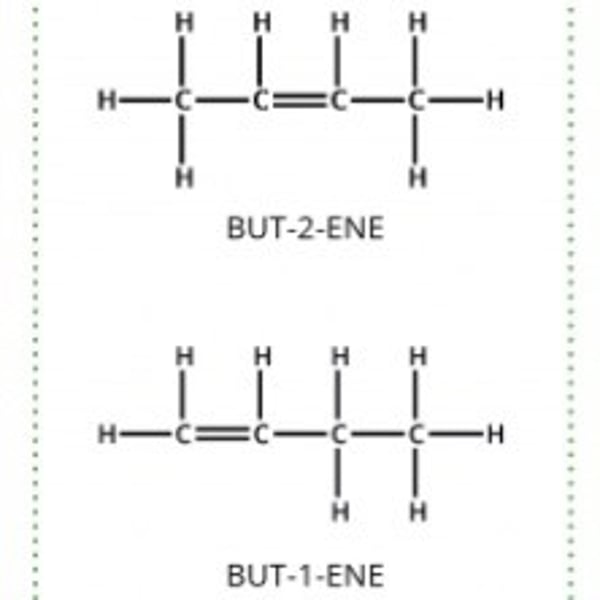
Functional group isomerism
Same molecular formula but different functional group
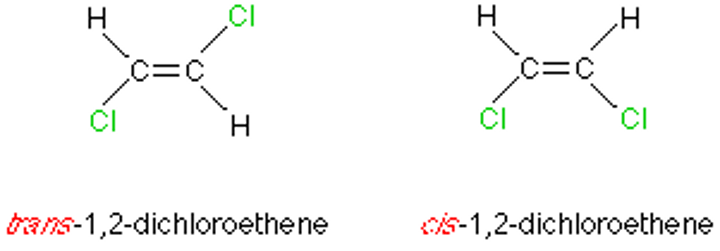
Stereoisomerism
Compounds with the same structural formula but a different arrangement of atoms in space
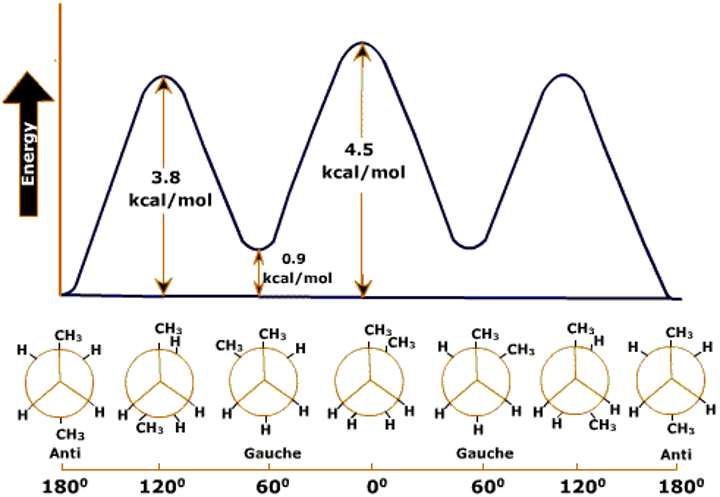
Conformational stereoisomerism
- Differ by arrangement of atoms around a single bond
- Interconvert by rotation about a sigma bond
- Changing the 3D shape of molecule
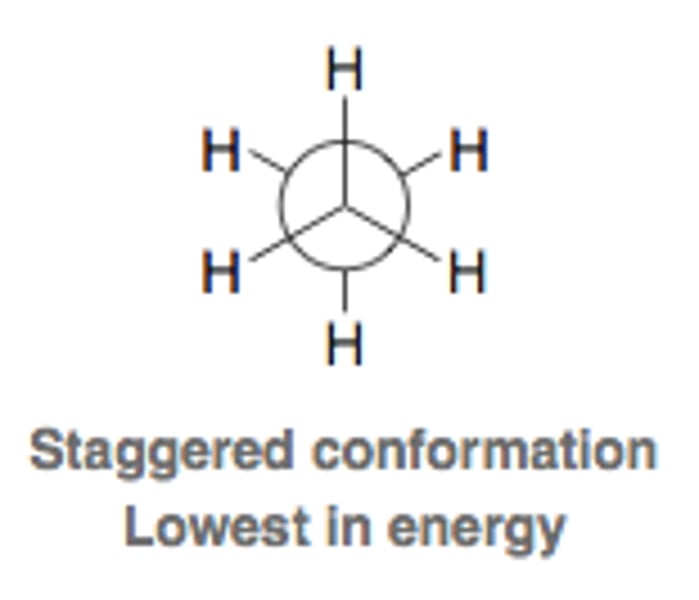
Staggered conformation
- H atoms as far apart as possible
- More stable
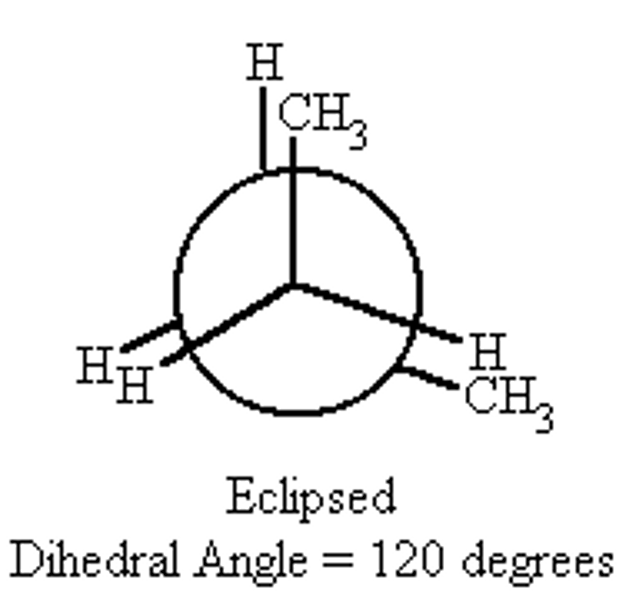
Eclipse Conformation
- H atoms close to each other as possible
- Has higher energy
- Less stable due to repulsion between electrons of C-H bonds
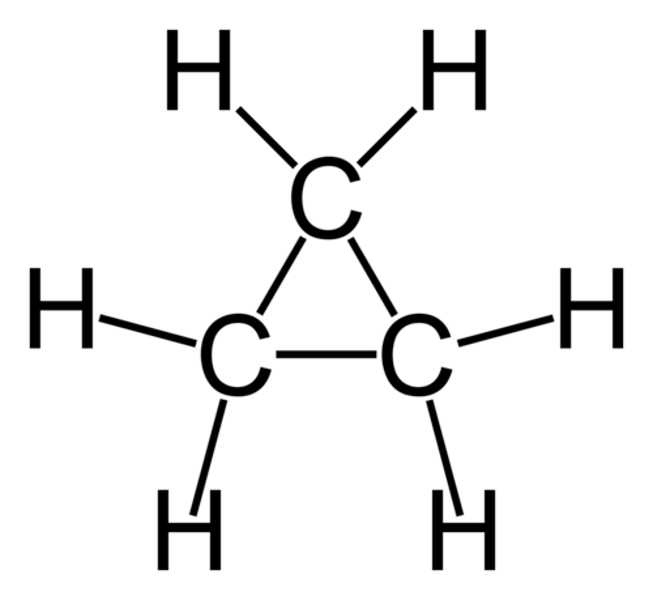
Cyclopropane
- Lacks stability due to ring strain
- Torsional strain from repulsion of adjacent bonding electrons
- Angle strain is much less than orbital tetrahedral angle
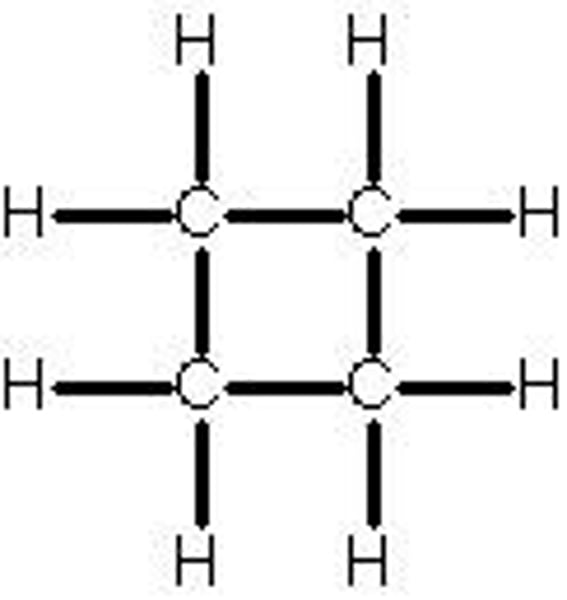
Cyclobutane
- Angle strain of 90⁰
- Torsional strain from eclipse arrangement
- One of the carbon atom moves out of plane
Configurational stereoisomerism
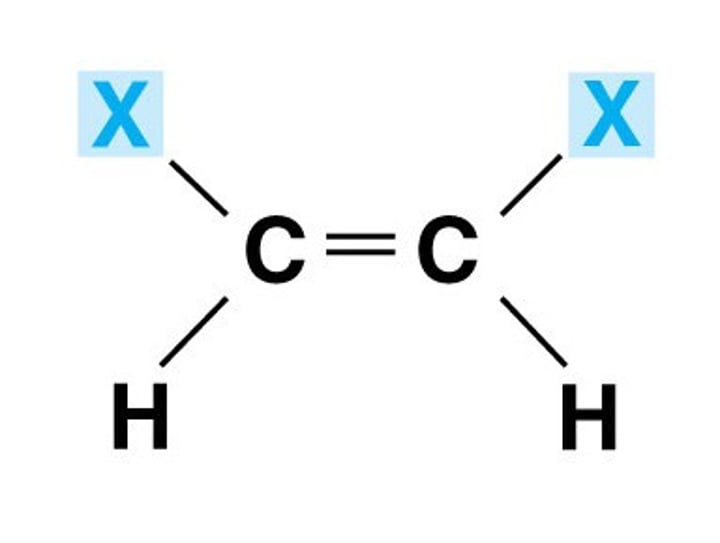
Cis configuration
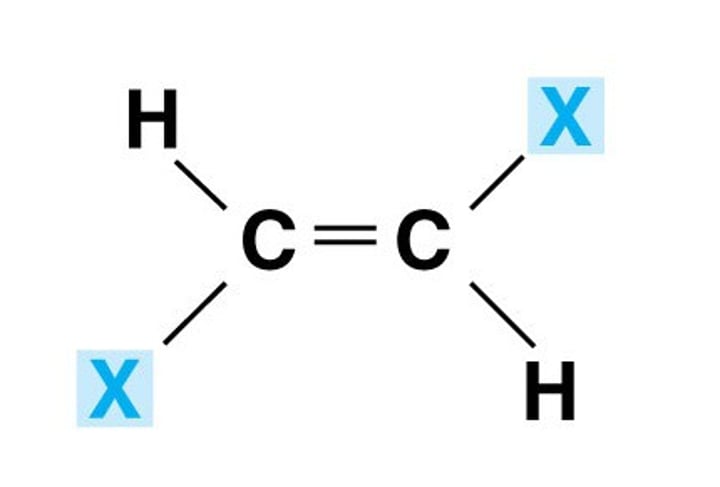
Trans configuration
E-Z notation
When the sterioisomer has different atom/s opposite or next to each other, we can no longer use cis or trans.
-Choose which atom/s on the left and which on the right has priority (the heavier one has priority). If the priority atom/s are opposite each other it's an E isomer (Entgegen) or if they are next to each other it's a Z isomer (Zusammen)
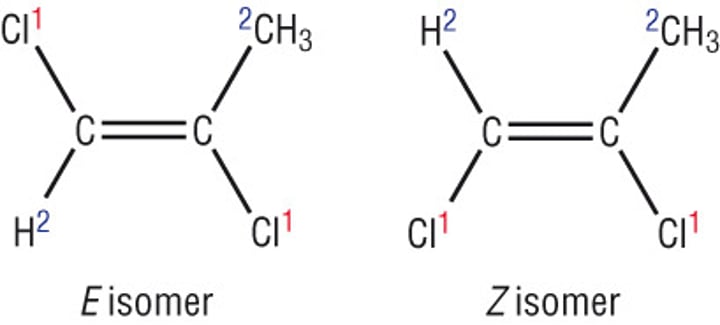
E-Z priority
- Highest atomic number = Highest priority
- Double bond = Count atom twice
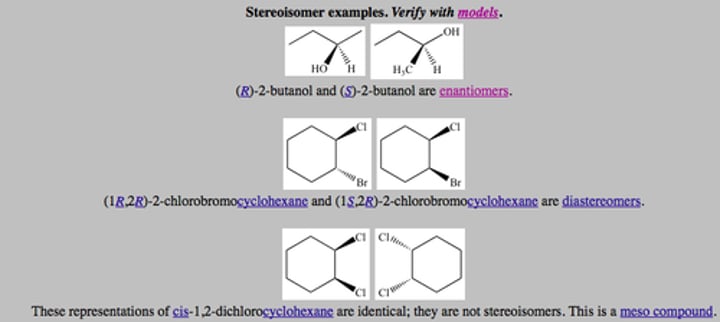
Optical isomers
Stereoisomers that are non-superimposable mirror images of each other
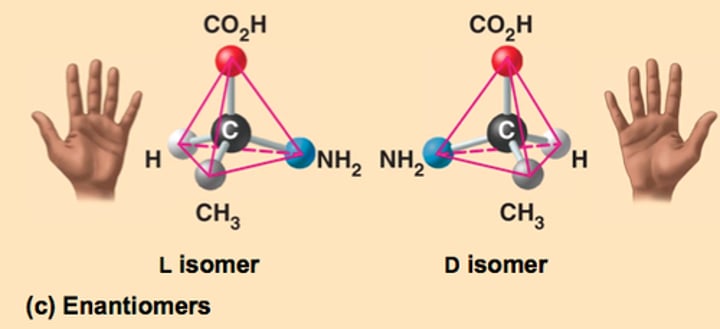
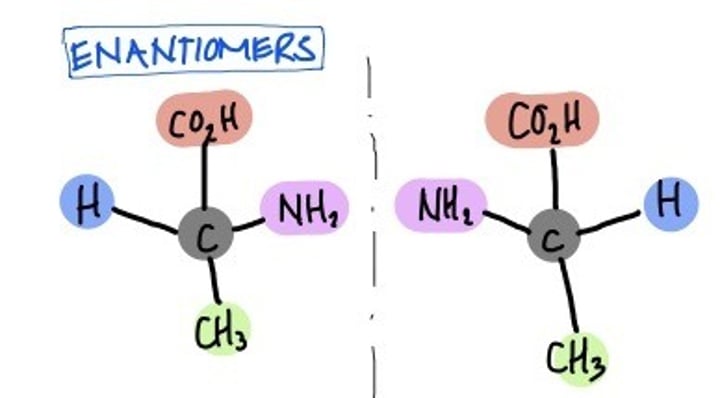
Enantiomers
Isomers that are mirror images of each other (Optical isomers)
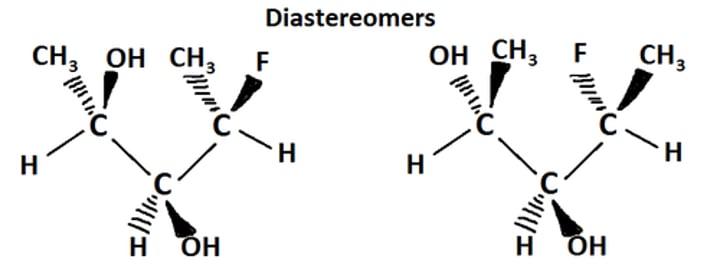
Diastereomers
Stereoisomers that are not mirror images
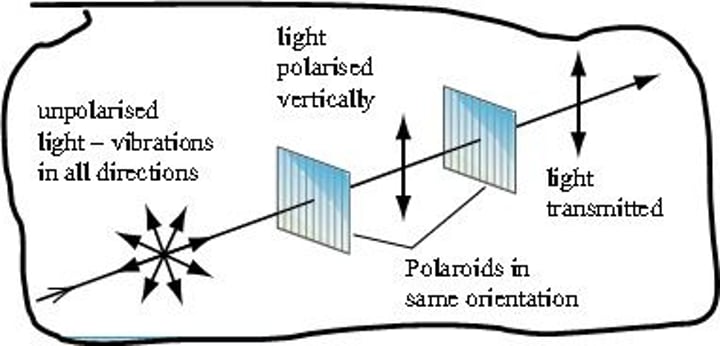
Polarised light experiment
An optically active compound can rotate the plane of polarized light (vibrating in one plane)
Thalidomide
A mild tranquilizer that, taken early in pregnancy, can produce a variety of malformations of the limbs, eyes, ears, and heart.

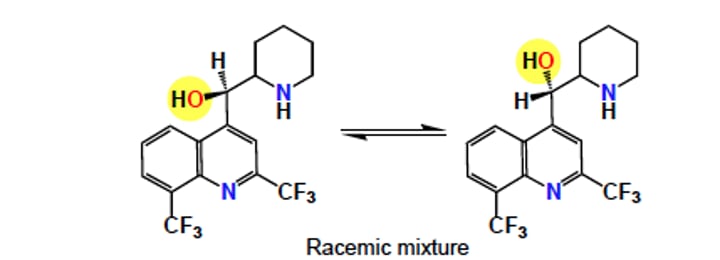
Racemic mixture
A mixture that contains equal amounts of the (+) and (-) enantiomers. Racemic mixtures are not optically active.