8.3 Pathology of Stomach and Abomasum
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What is gastric dilation, displacement and volvulus (GDV)?
In large, deep-chested dog breeds
Gas, fluid or feed block the cardia, which prevents eructation and emesis
Gastric rotation - pylorus obstructed. prevents passage of contents into small intestine
Gas result of aerophagia or may come from carbon dioxide produced by physiologic processes
What are reasons for GDV?
Gastric rotation occurs due to recurrent dilation, overfeeding or postprandial exercise
Repeated episodes - result in stretching and relaxation of gastrohepatic ligament
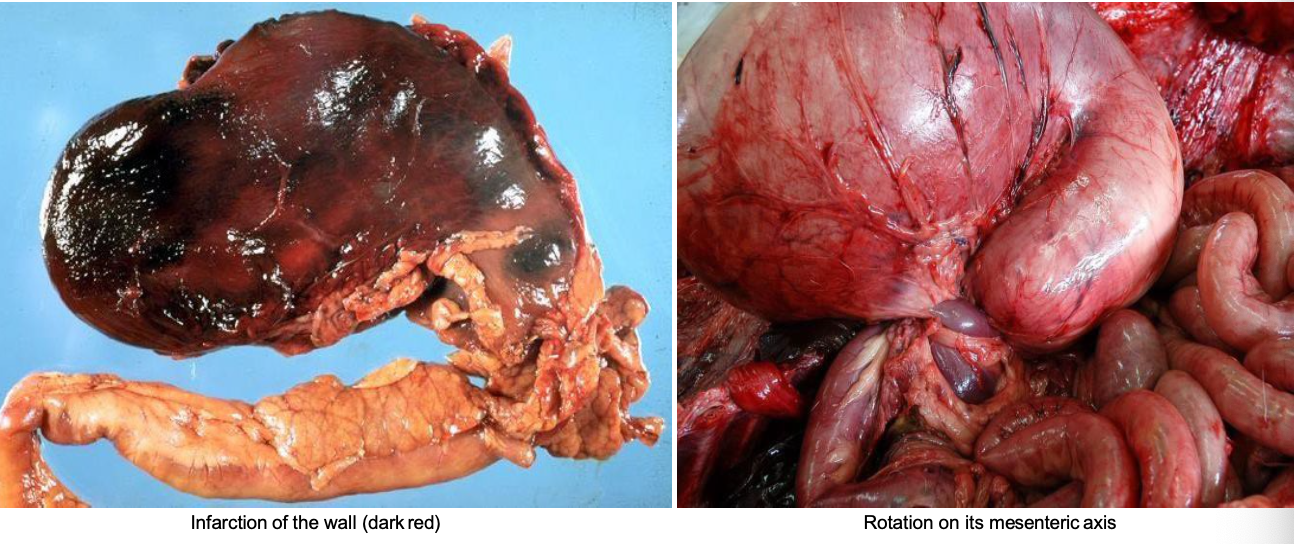
What is the rotation and infarction of GDV?
Clockwise rotation on a ventrodorsal axis - 180 or 360°
V-shaped bending or enlarged spleen
Venous infarction
Compression of diaphragm, vena cava and portal vein → decrease of venous return → decreased cardiac output and perfusion of abdominal viscera → shock → death
Rupture of the stomach
What are signs of inflammation in gastritis?
Acute/chronic
Catarrhal
Haemorrhage - clostridia, uraemia, fungal
Ulcerative/necrotising - NSAIDs. uraemia
Proliferative/hyperplastic
What are causes of of gastritis?
Dogs and cats - uraemia. parasites. allergic/immune-mediated
Pigs - infectious. colibacillosis. salmonellosis
Ruminants - clostridia. fungi. parasites
Horses - parasites
What is traumatic gastritis?
Ingestion of foreign bodies (dogs and cats)
e.g:
Corn cobs. Sticks. Stones. Bones. Toys etc
What types of gastritis are there?
Helicobacter spp. - stomach of dogs and cats
Mycotic gastritis - granulomatous inflammation by Histopplasma capsulate
Parasitic gastritis
What is Braxy?
Type of gastritis
Caused by Clostridium septicum
Haemorrhagic and necrotising abomasitis
Lambs more affected than calves
Usually associated with cold weather
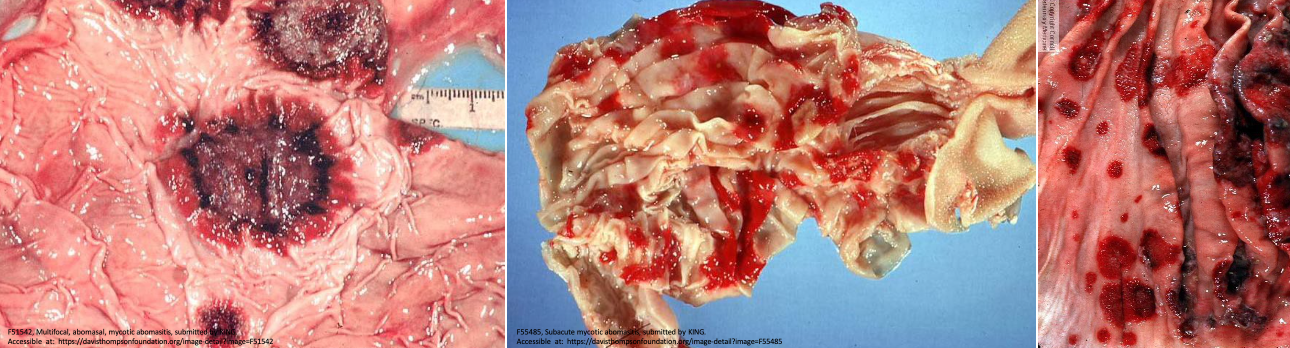
What is mycotic abomasitis?
Angioinvasive fungi such as Aspergillus, Mucor, Absidia
Results in vasculitis and thrombosis → haemorrhage infarction in the mucosa
Round, target-like lesions are typical of fungal infections
How does gastric ulceration happen?
Gastric or abomasa ulcers can be seen incidentally in any species
Stress and mucosal hyper perfusion - imbalance between necrotising effects of gastric acid/pepsin secretion and mucosal protective mechanisms
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) in high doses - depresses prostaglandin formation. leads to decreased secretion of protective bicarbonate
What causes gastric ulceration?
Local mucosal physical injury
Local hypoperfusion and ischemia
High gastric acidity - mast cell tumours release histamines. leads to acid hyperexcretion. Zoellinger-Ellison syndrome is a tumour-associated cause is gastrin-secreting pancreatic islet cell tumours or gastrinomas
NSAIDs - decreased PG → vasoconstriction → decreased mucus production → necrosis
Uraemia - damage to endothelial cells → vascular compromised increases ammonia secretion → caustic injury → necrosis
Multfactorail in pigs
Infection and inflammation - angioinvasive fungi in cattle. Helicobacter
What is gastric ulceration in pigs and horses?
Pigs - at the pars oesophageal, frequency bleed and can cause exsanguination
Horses - in foals (idiopathic). adults (NSAIDs)
What is uremic gastropathy?
Dogs and cats - due to chronic renal disease
Gross findings - oedema, haemorrhage, ulceration
Pathogenesis - vascular damage from uremic toxins → ulceration, necrosis
Mineralisation
What are the 2 types of toxic gastropathies?
Blister beetle toxicosis
Heavy metal toxicosis
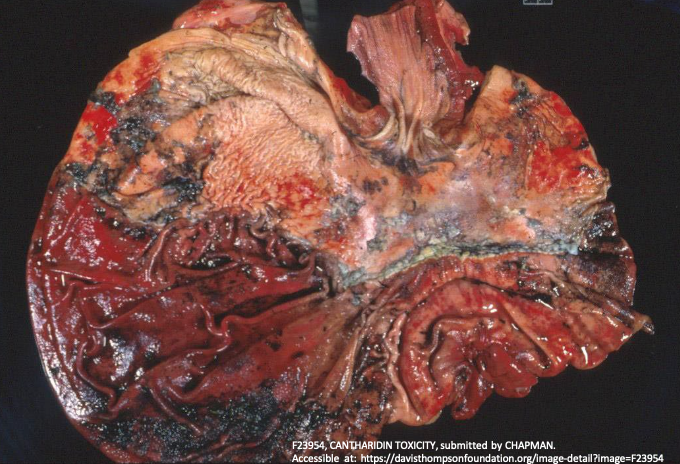
What is blister beetle toxicosis?
Horses eating alfalfa hay infested with blister beetles
Necrohaemorrhagic gastroenteritis, haemorrhage ulcers in the bladder and myocardial necrosis
Causative toxin - cantharidin
What is heavy metal toxicosis?
Arsenic, zinc
Haemorrhage, necrosis and ulceration in stomach or abomasum
How can we classify gastric neoplasia?
Epithelial - Polyp/adenoma (mucosal lining and glands). Adenocarcinoma (mucosal lining and glands). Squamous cell carcinoma (linked to equine papillomavirus-2 infection)
Mesenchymal - Leimyoma/leimyosarcoma (from muscle layer/tunica muscularis)
Round cell - lymphoma (from mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue)
What are neoplasias in the abomasum?
Lymphoma is most common
Usually associated with bovine leukosis virus