Lipids
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
What are lipids?
A macromolecule
Made of C, H and O
Can exits as fats, oils and water
Insoluble in water, soluble in alcohol and other lipids
Good source of energy (44J/Kg)
Produce more ATP than glucose during lipid respiration, they can also be stores of energy
Poor conductors of heat
Most fats and oils are triglycerides
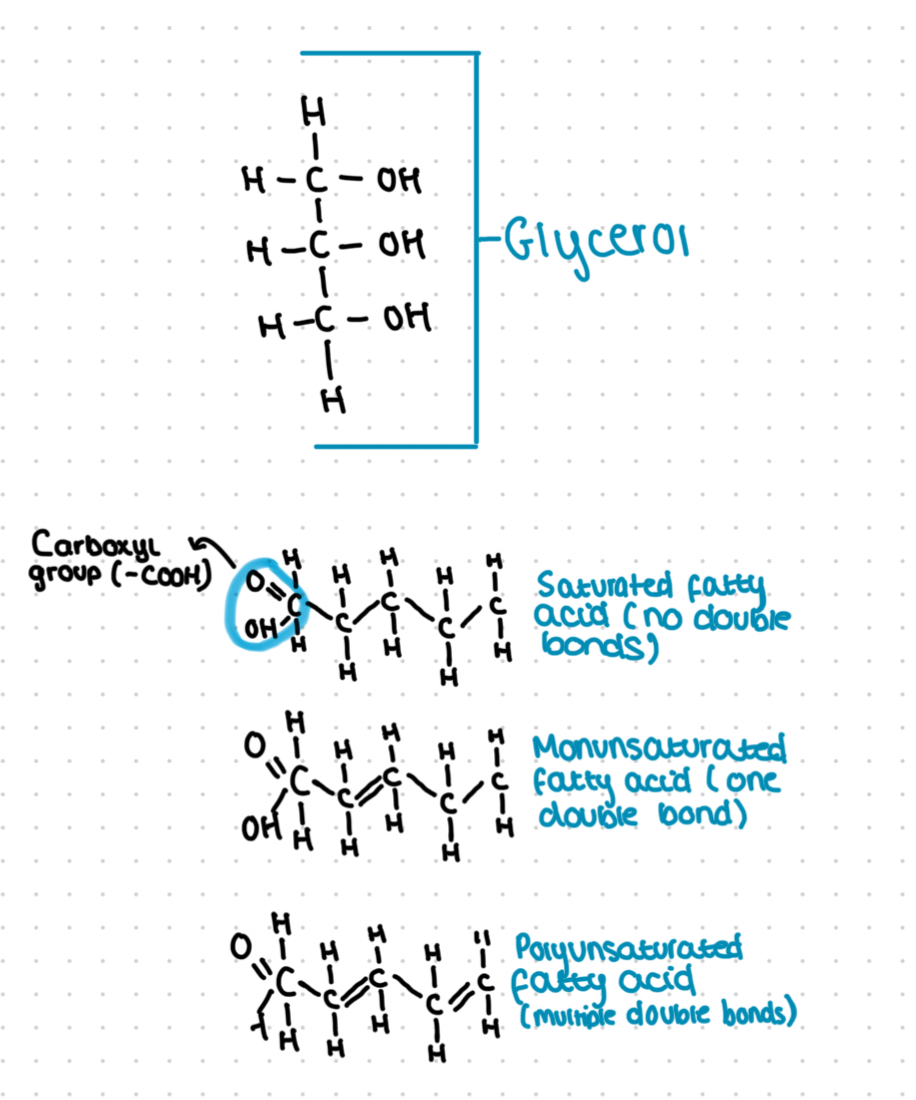
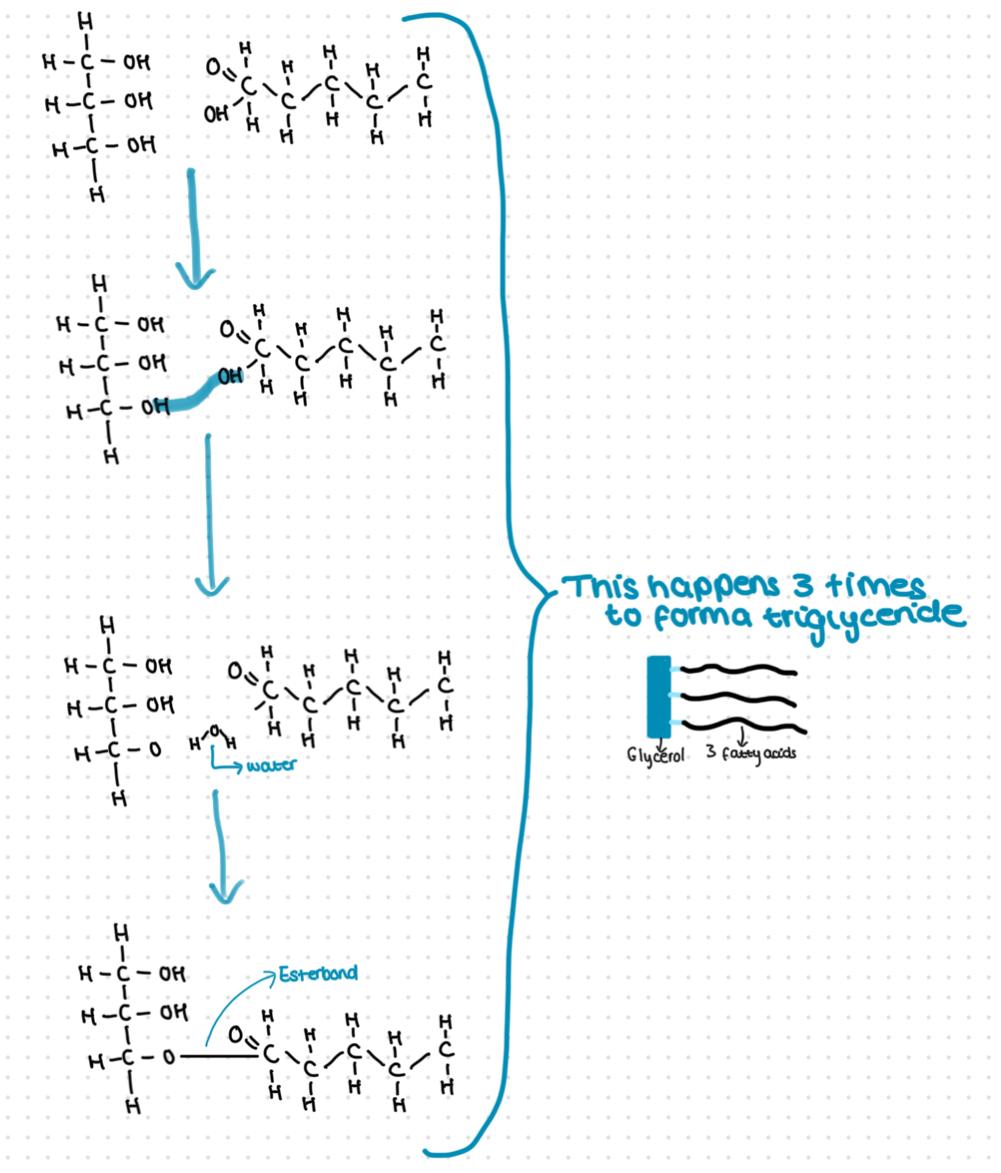
What is a triglyceride?
Formed by a condensation reaction between 4 components:
3 fatty acids
1 glycerol
Fatty acid:
Carboxyl group (-COOH)
Attached to a long, non-polar hydrocarbon
Saturated (C-C)
Unsaturated (C=C)
What is the effect of saturation on a triglyceride?
More saturated = more dense
Increasing double bonds introduces ‘kinks’ into the molecules, this reduces density as there will be more space between the hydrocarbons
Animal fats tend to be saturated and plant fats tend to be unsaturated
Condensation reaction between glycerol and a fatty acid
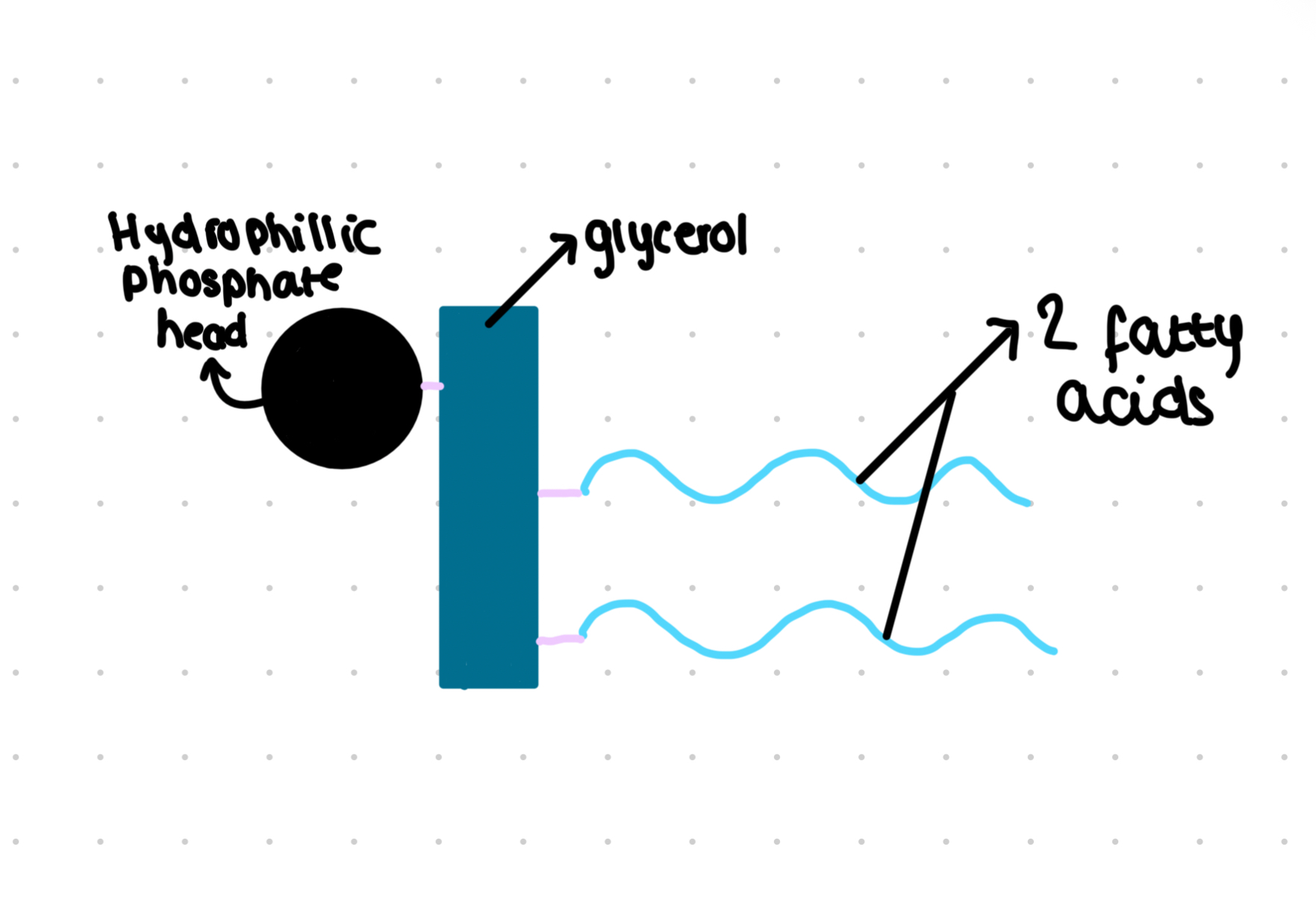
Phospholipids
One fatty acid can be replaced by a polar phosphate group
Hydrophilic head
Hydrophobic tail
Membrane lipids are a amphipathic
Partially permeable helps control movement of substance across the cell
Function of lipids
Protection of vital organs- acts like a shock absorber
Some bacteria have a lipid layer to act as a protective capsular layer
Prevent evaporation in plants and animals
Insulate the body- as a heat insulator
Form the myelin sheath around some neurones- electrical insulators
As a water source (respiration of lipids- which provides a lot of ATP)
Metabolic water- water produced by respiration
Component of cell membranes
Makes some hormones e.g testosterone
Cholesterol
Used to synthesise steroid hormones: testosterone and oestrogen
Synthesises vitamin D
Regulates fluidity of cell membranes and acids mechanical stability
Made up of 4 isoprene rings
Not based on fatty acids and glycerol
Plant membranes have a cholesterol derivative called stigmasterol
Food test for lipids
Emulation test:
Add water and ethanol to the solution
Shake vigorously for 10 seconds
Positive- milky white emulsion appears
Negative- emulsion doesn’t for, it’ll look like separate layers if liquids are of different densities