Biology - Chapter 8 (Unit 2)
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
109 Terms
Plants have adaptations for? f
Terrestrial life
What sets algae and plants apart?
Plants have adaptation for terrestrial life. They can live on land, while algae cannot.
What is the name of the Kingdom of plants?
Plantae
Are plants eukaryotic or prokaryotic?
Eukaryotic
Are plants unicellular or multicellular?
Multicellular
From who did plants “possibly” evolve from?
Green algae ancestors
What type of tissues do plants have?
3-dimensional tissues
Why do plants have 3-dimensional tissues?
Increased ability to avoid water loss
What are the growth tissues in plants and where are they found?
Meristems, and they are found at the tips of roots and stems.
Plants have thick, ____ bodies?
Thick, robust bodies
How many different types of plants species are on Earth?
435,000 types of plant species
What is the closest living species to land plants?
Algae
Similarities between algae and land plants:
have chloroplasts.
have chlorophyll with stacks of thylakoids.
store starch in plastids (a cell that stores food).
have cellulose (helps to protect, stand-up, and grow up straight in plants) in cell walls.
go through Alternation of Generations Life Cycle.

What type of habitat is this?
Terrestrial habitat

What type of habitat is this?
Aquatic habitat
When plants live in aquatic environments, what helps support them?
Water
From where do aquatic plants receive their nutrients?
They receive their nutrients from water.
Why do aquatic plants stay near the surface of the water?
They stay near the surface for light.
When aquatic plants try to fertilize in order to reproduce…what does the sperm do?
The sperm swims to the egg of a plant.
Do aquatic plants dry out?
No, since they are surrounded in water.
If a terrestrial plant needs minerals, what can be a solution?
The roots will absorb H20 & minerals.
If a terrestrial plant is facing gravity issues, what can be a solution?
Lignin and cellulose in cell walls can help a plant stand up straight.
If a terrestrial plant is small in height which causes them to not get light, what can be a solution?
Lignin and cellulose in cell walls can help a plant grow in height in order to get light.
What helps plants survive in a dry environment?
A plants waxy cuticle will prevent water loss, helping them to survive. A stomata allows gas exchange while minimizing water loss.
Why do plants have a waxy cuticle?
To help prevent water loss.
Why do plants have cutin?
Helps to block out pathogens from entering plants (bacteria, fungi, viruses, worms, and etc.).
Why do plants have stomata?
Pores that open up to allow gas exchange while minimizing water loss, during dry environments.
Are plants unicellular or multicellular?
Multicellular
Are plants autotrophic or heterotrophic?
Autotrophic, since they produce their own food.
What do plants use to harvest energy?
Plants use chlorophyll in thylakoid membranes.
What do the cell walls in plants contain?
Cellulose
What do plants store?
Plants store starch in plasmids (are food storing cells)
Diploids have how many sets of chromosomes?
2 complete sets
Haploids have how many sets of chromosomes?
1 complete set
Diploid (mitosis) is what stage?
Sporophyte stage
Haploid (meiosis) is what stage?
Gametophyte stage
During plant reproduction, what type of embryo forms and what protects it?
A multicellular embryo forms, which is protected inside a multicellular haploid tissue.
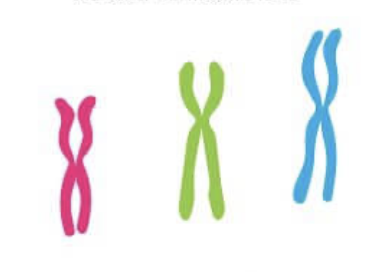
What type of chromosome is this?
Diploid

What type of chromosome is this?
Haploid
Plants are divided into 2 groups? What are they?
Non-vascular
Vascular
What are non-vascular plants often referred to?
Bryophytes
Do non-vascular plants have vascular tissue?
They do not have vascular tissue for support or condition of materials.
What type of environments do non-vascular plants need to survive?
They need a moist/wet environment.
How tall do non-vascular plants grow?
They can’t grow as tall.
Non-vascular plants grow VERY tall. True or False?
False. They don’t grow as tall.
Non-vascular plant CELLS need to be in contact with moisture/wetness. True or False?
True. Non-vascular plant cells need to be in direct contact with moisture/wetness.
How do water and dissolved materials move through non-vascular plants?
By diffusion (can also move with osmosis).
In non-vascular plants, what does the sperm need to go through to get to the egg?
Sperm needs to swim through water droplets.
What are the 3 types of non-vascular plants?
Mosses
Liverworts
Hornworts
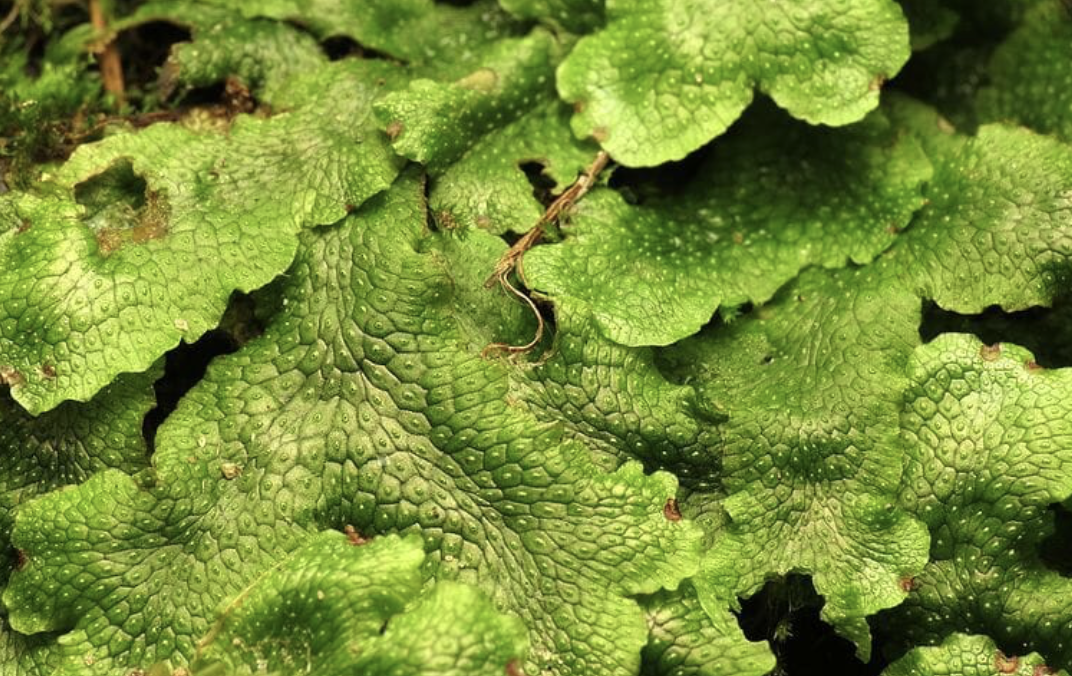

What type of plant is this?
Liverworts
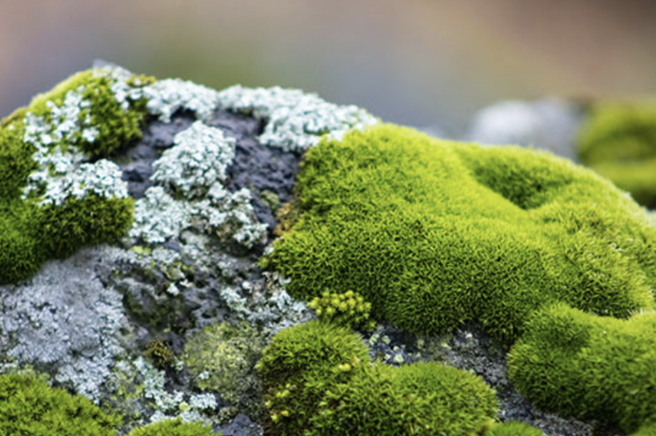

What type of plant is this?
Mosses
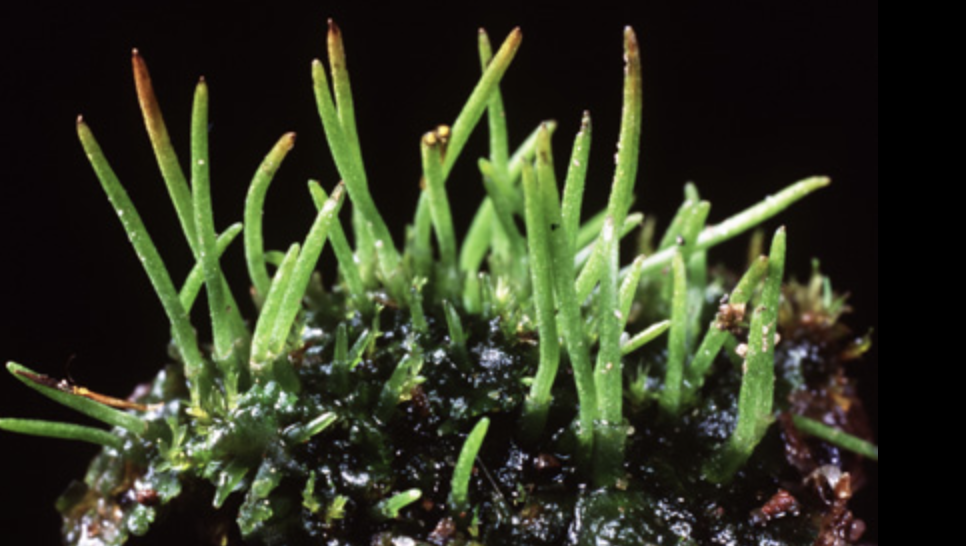

What type of plant is this?
Hornworts
Hornworts are under what phylum?
Antherophyta
Mosses are under what phylum?
Bryophyta
Liverworts are under what phylum?
Hepatophyta
What are vascular plants often referred to?
Tracheophytes
Vascular are divided into 2 groups. What are they called?
Seedless vascular
Seed-bearing vascular
What are 4 types of seedless vascular plants?
Lycophytes - Club moss
Pterophytes - Ferns
Equisetum - Horsetails
Psilophytes - Whisk ferns

What type of plant is this?
Equisetum - Horsetails

What type of plant is this?
Pterophytes - Ferns

What type of plant is this?
Psilophytes - Whisk ferns
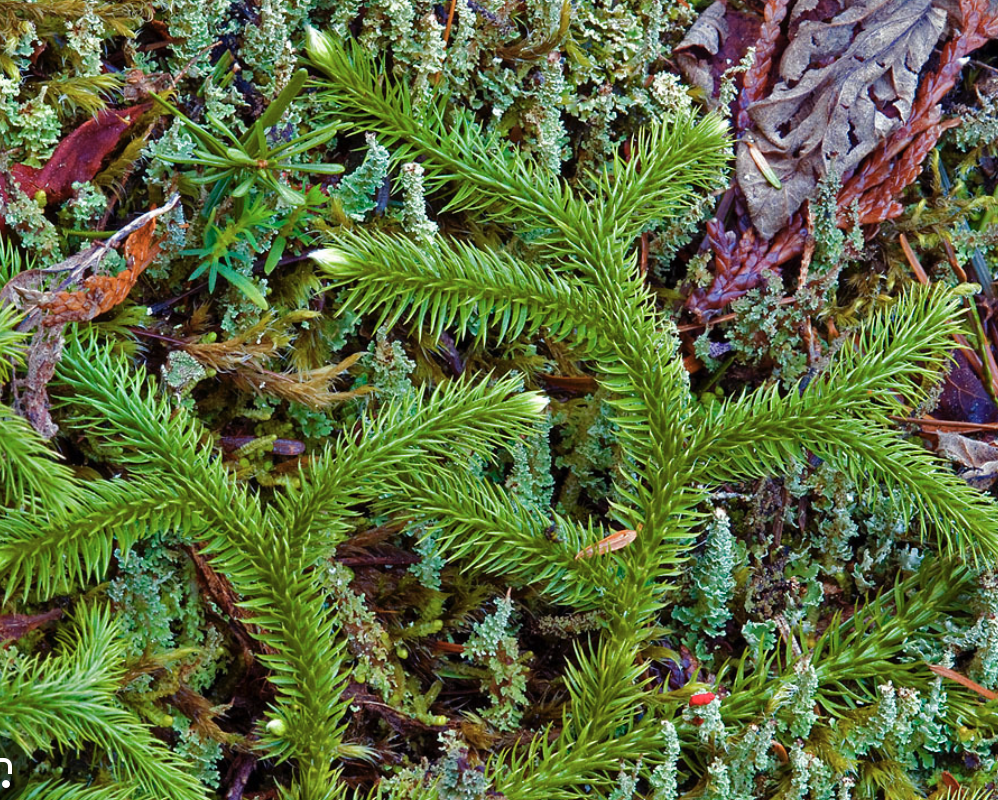

What type of plant is this?
Lycophytes - Club mosses
Seed-bearing vascular plants are divided into 2 groups. What are they called?
Gymnosperms
Angiosperms
Out of the 2 groups of seed-bearing vascular plants. Which one have naked seeds in cones?
Gymnosperms
Out of the 2 groups of seed-bearing vascular plants. Which one have flowers that produce seeds to attract pollinators and produce seeds.
Angiosperms
What are the 3 types of KNOWN gymnosperms?
Conifers - Coniferophyte
Cycads - Cycadophyte
Ginkgo - Ginkgophyte
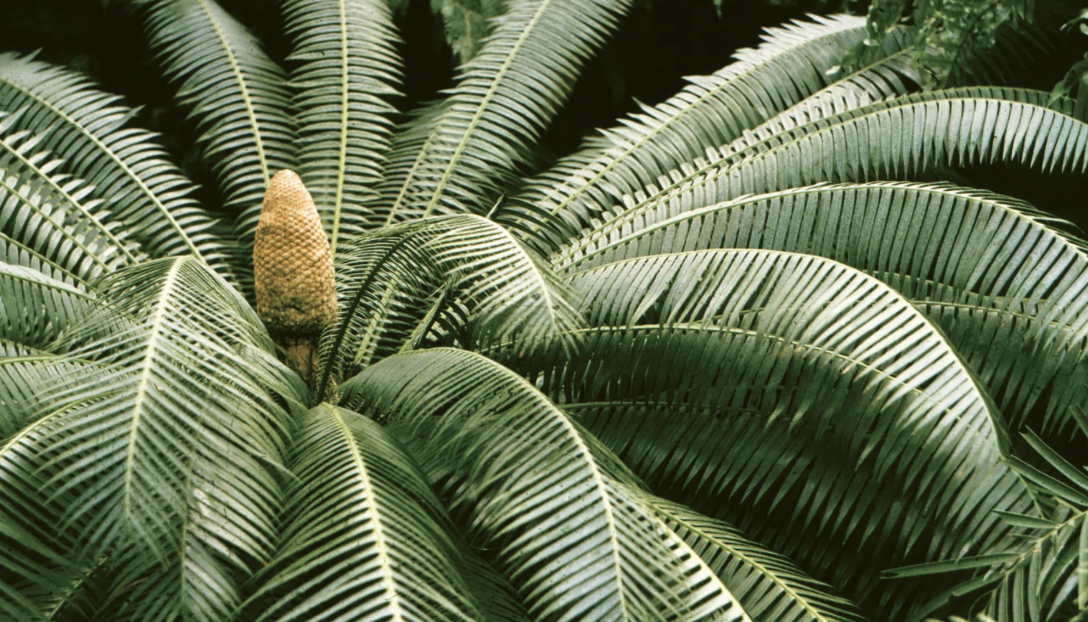

What plant is this?
Cycads
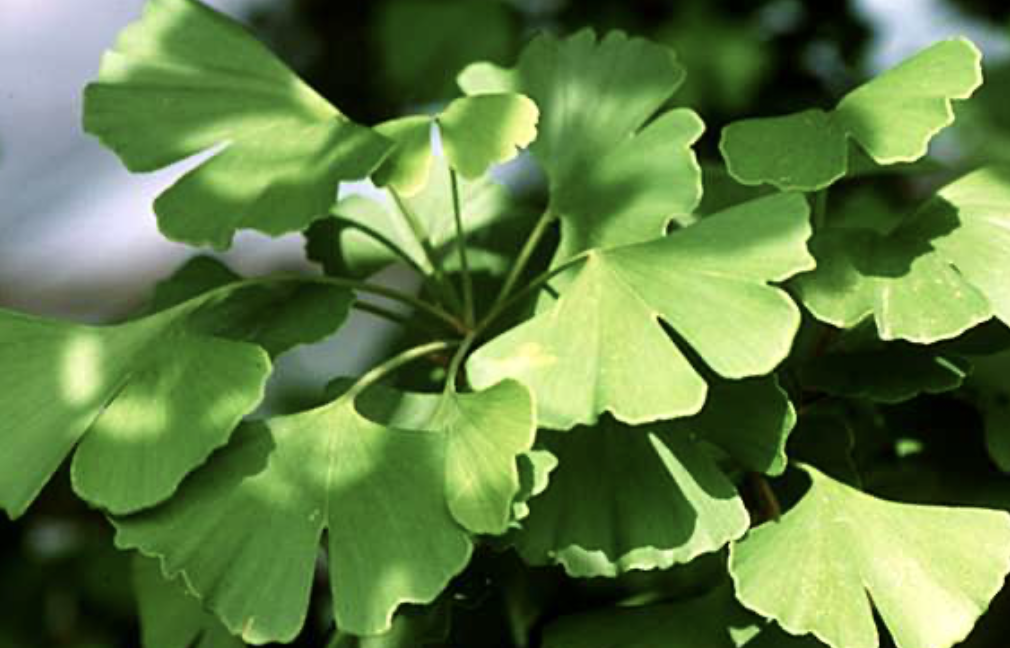

What plant is this?
Ginkgo
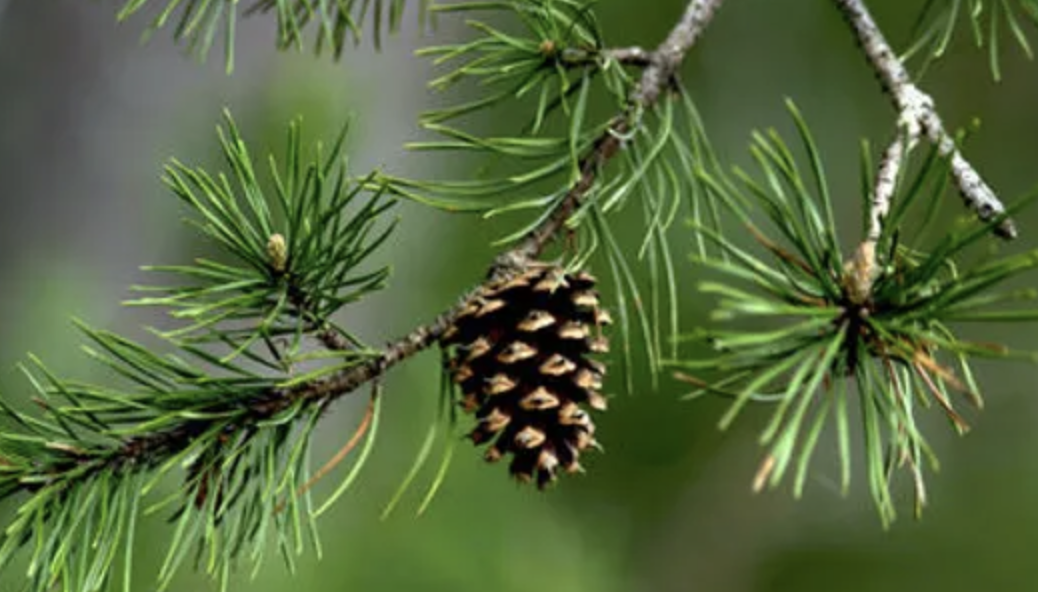

What plant is this?
Conifers
What gymnosperm is the oldest living plant? [Hint: tree]
Bristle cone pine
What gymnosperm is the tallest living plant? [Hint: tree]
Sequoia OR Redwood
What type of seed-bearing vascular plant, contain flowers or fruit?
Angiosperms
How are angiosperms produced?
An egg or ovule is fertilized by pollen in the ovary.
Where is the ovary?
Deep, within a flower
What part of a flower anatomy is male?
Stamen
What part of a flowers anatomy is female?
Ovary
Fruits are frequently produced from what part of a flowers anatomy?
Ovary
There are 2 types of angiosperms. What are they?
Monocots
Dicots
What type of angiosperm have two seed cotyledons?
Dicots
What type of angiosperm have a single seed cotyledon?
Monocots

This type of angiosperm have flower parts in multiples of 3…
Monocots
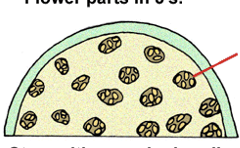
This type of angiosperm have vascular tissue that is scattered in cross section of the stem…
Monocots
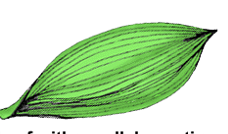
This angiosperm have parallel venation in leaves…
Monocots

This type of angiosperm have flower parts in multiples of 4 or 5…
Dicots
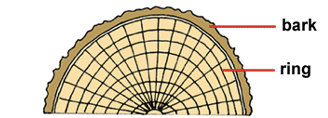
This type of angiosperm have vascular tissue that in rings in cross section of the stem…
Dicots

This angiosperm have net variation in leaves…
Dicots

What type of angiosperm is this?
Monocot

What type of angiosperm is this?
Dicot
A billion years ago, how was the land surface on earth?
Bare
The origin of land plants were essential for what 3 things?
Development of true soils
Evolution of modern plants
Provided food source for animals
What were the 3 steps for plants to conquer land?
Had to have an adaptation to terrestrial life
Seedless plants helped to transform the earths ecology
Mass distinctions which led to the diversification of modern angiosperms
In non-vascular plants, the sporophyte dominates? True or False?
False. Gametophytes dominate.
In vascular plants, the sporophyte dominates? True or False?
True.
In ferns, are the spores haploid or diploid?
Haploid
How many types of fern species are there?
12,000
Vascular plants appeared how long ago?
420-429 million years ago
Vascular plants converted hug amount of atmospheric CO2 into decay-resistant organic material? True or False?
True
The removal of large amounts of greenhouse gas C02 from the atmosphere by vascular plants had a health effect on the climate?
False. It had a cooling effect. Since plants take in C02, it helped climate stay cool.
How did we determine early vascular plant fossils?
By the plants liginin and cutin.
Extensive forests dominated by tree-sized lycophytes, pteridophytes, and early lignophytes occurred in widespread swampy regions during the warm. What period is this?
Carboniferous period