Speech Production
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What is speech production?
A cognitive and motor process beginning with the speaker formulating a message in their mind and transmitting it through speech.
What kinds of information can speech convey?
Meaning (semantic content)
Emotions
Individual cues (identity, personality, intent)
What are the stages involved in producing spoken words?
Selecting the words
Formulating their phonetics
Articulating them via the motor systems in the vocal apparatus
Why are tongue‑twisters particularly difficult to say?
They involve sounds requiring similar vocal tract movements (e.g., sss vs shh).
Their brain representations overlap.
They need rapid sequencing of overlapping neural patterns that overwhelm the system.
What did Freud believe speech errors indicate?
That errors arise from unconscious repressed thoughts, not simple sound confusion.
What are limitations of Freud's explanation?
Some slips fit repression explanations, but many do not.
Research suggests most errors arise from language system processes, not unconscious thoughts.
What is a semantic substitution error?
Replacing the intended word with another of similar meaning.
What is a word‑exchange error?
Two intended words switch positions, showing advance planning of sentences.
What is a morpheme‑exchange error?
Inflections/suffixes attach to the wrong words, showing that inflection placement is handled separately from stem placement.
What is a spoonerism?
A phoneme‑exchange error where initial sounds of two words swap (e.g., “hissed my mystery lecture”).
Are speech errors random?
No — they cluster into categories based on linguistic units (phonological, morphemic, syntactic).
Why do similar units get exchanged (e.g., noun→noun)?
Because slips reflect misapplied rules at a specific level (phonological/morphemic/syntactic).
What do speech errors show about speech planning?
Speech is planned before articulation. Multiple linguistic units compete during planning.
What is an anticipation error?
A feature from a later unit appears early (e.g., leading list instead of reading list).
What are speech disfluencies?
Breaks and irregularities in fluent speech.
false starts
fillers
What characterises stuttering?
Involuntary repetition or prolongation of sounds, syllables, words
Silent blocks where the speaker cannot produce sound
can cause fear, anxiety and social isolation
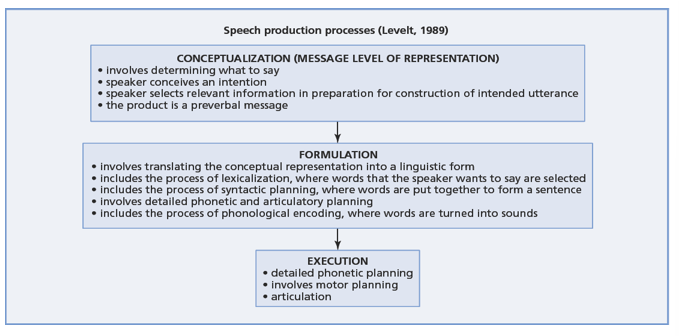
what is the speech production process (Levelt, 1989)
WEAVER Model (Levelt, Roelofs & Meyer, 1999)
Word‑form Encoding by Activation and Verification.
describes speed production as a serial, feed-forward, each stage completes before the next begins
What are the three levels in the WEAVER model?
Conceptual Level – lexical/semantic concepts → highest level of network
Lemma Level – abstract word forms with grammatical properties (and sematic specification of words)
Lexeme Level – morphemes and phonemic word forms (spoken output)
What evidence supports the WEAVER model?
The tip‑of‑the‑tongue state: the lemma is activated but the lexeme (word form) cannot be retrieved.
Spreading Activation Theory (Dell, 1986)
Planning happens in parallel across
semantic → the meaning of what is to be said
syntactic → the grammatical structure of the words planned to be said
morphological → the morphemes (basic units of meaning or word forms) in the planned sentence
phonological levels → the phonemes or basic units of sound within the sentence
How does spreading activation explain speech errors?
Errors occur when an incorrect item becomes more activated than the intended one.
Parallel activation leads to anticipation errors.
Exchange errors only occur between units close in processing.
What are discourse markers?
Words/phrases that clarify intention without adding semantic content (e.g., “well”, “so”, “you know”).
What are prosodic cues?
Rhythm, stress, and intonation patterns that shape meaning.
What is the egocentric heuristic?
Listeners interpret speech based on their own knowledge rather than shared knowledge.
Study: Horton & Keysar (1996)
A director instructed a builder to assemble a Lego model.
39% errors when interaction was not allowed
5% errors when interaction was allowed
→ Interaction helps establish common ground.
What is the monitoring & adjustment model?
Speakers first plan from their own perspective
Then adjust based on the listener’s needs
→ This model is used most of the time.
Establishing Common Ground (Bard et al., 2007)
Two stratergies:
Shared responsibility – expecting the listener to signal confusion
Cognitive overload – tracking both speaker and listener knowledge
→ Speakers mostly rely on shared responsibility.