25. Viral genetics and Genomics
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Positive-sense (+) viral RNA
is like mRNA and can be immediately translated by host ribosomes
Negative-sense (-) viral RNA
is complementary to mRNA and must be converted
to (+) RNA before it can be translated
Baltimore groups 1 and 2 DNA viruses require
RNA polymerase to transcribe genome and a DNA polymerase to replicate genome
Baltimore group 7 DNA viruses require
RNA polymerase to transcribe genome AND a virus encoded RT to replicate genome
Large DNA viruses vs small DNA viruses:
Which ones DO NOT encode their own polymerases?
Small DNA viruses do not encode their own polymerases.
Baltimore group 6 and 7 (DNA) viruses require
a virus-encoded reverse transcriptase (RT) to replicate their genomes,
Baltimore groups 3, 4, and 5 RNA viruses require:
Virus-encoded RdRp (an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase) to both transcribe and replicate their genome
When is RdRp required following infection by a virus with a (+) ssRNA genome?
RdRp is not packaged within the virion. Instead, the viral genome is directly translated by the host cell's machinery to produce RdRp after infection
When is RdRp required following infection by a virus with a (-) ssRNA genome?
RdRp must be packaged within the virion because the host cell cannot directly translate the (-) ssRNA genome. The RdRp transcribes the (-) ssRNA into (+) ssRNA, which can then be translated into viral proteins and serve as a template for genome replication
Quasispecies
Virus populations are not identical, even within a single host, rather they exist as dynamic distributions of nonidentical but related replicons
How do latent herpesviruses persist in the host cell nucleus without being detected?
combination of histone modifications and regulatory RNAs inhibit viral transcription to limit expression of viral proteins
Marek's disease virus (MDV)
Herpes virus that infects chickens
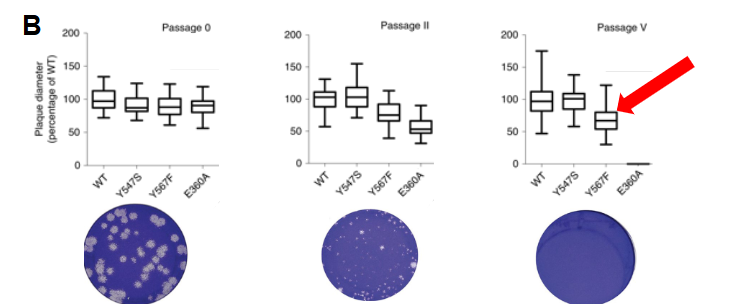
How would you interpret the cell culture data below?
Disrupting MDV DNA pol exonuclease activity reduces plaque size so MDV shows dependency on DNAP proofreading for effective infection.
provirus
dsDNA moves into the nucleus and inserts into the host genome
Quasispecies in regard to HIV
It takes 5-10 years to develop AIDS, during which time
HIV evolves into patient-specific quasispecies
Early stage (R5; Macrophage trophic) HIV virions
can infect dendritic cells and macrophage that display
CD4 (with CCr5 as co-receptor), and T cells that
display the same
Evolved late stage (X4; T-cell trophic) HIV
initiate infection using CD4 with CXCr4 as a co-receptor (only T cells)
What happens when viruses replicate above
their error threshold?
(1) The population contains too many mutations
and results in dead viruses.
(2) The population does not contain mutations
and results in live viruses.
(3) The population contains too many mutations
and produces more pathogenic viruses.
(4) The population cannot undergo reassortment
and produces less pathogenic viruses.
(5) The population does not contain mutations
and produces more pathogenic viruses
The population contains too many mutations
and results in dead viruses
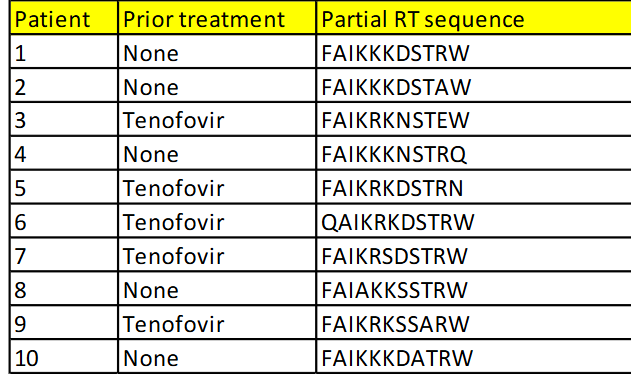
The table shows HIV genotyping data
from ten patients. HIV in the five
patients previously treated with
tenofovir have become resistant to this
base analogue inhibitor of RT. HIV in
the five new patients (untreated) are
sensitive to tenofovir. What is the RT
amino acid change that is associated
with the development of resistance?
Which of the following describes an activity provided by reverse transcriptase?
(A) It has protein-dependent RNA polymerase activity
(B) It has DNA-dependent RNA polymerase activity
(C) It has RNase H activity that hydrolyzes the RNA strand in an RNA/DNA hybrid
(D) It converts select proteins into their specific mRNA sequence
(E) It has RNA-dependent RNA polymerase activity
It has RNase H activity that hydrolyzes the RNA strand in an RNA/DNA hybrid
Which 3 functions does RT have
RNA-dep DNA pol
DNA-dep DNA pol
RNAse H activity