6.2.5 Organic synthesis
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
how to prepare organic compounds
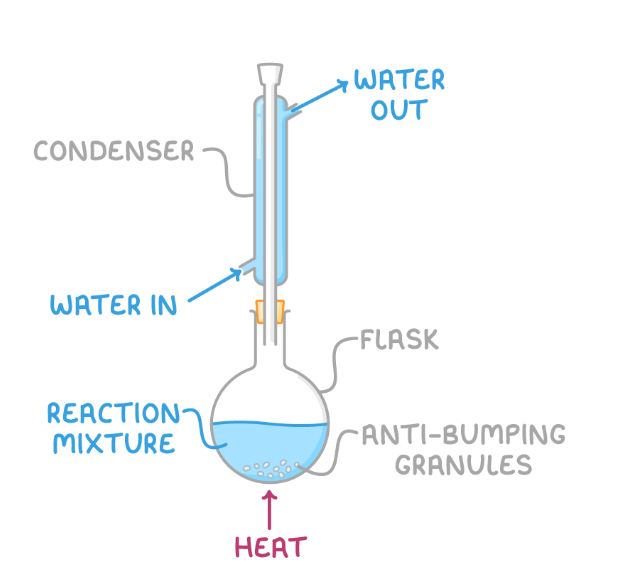
reflux
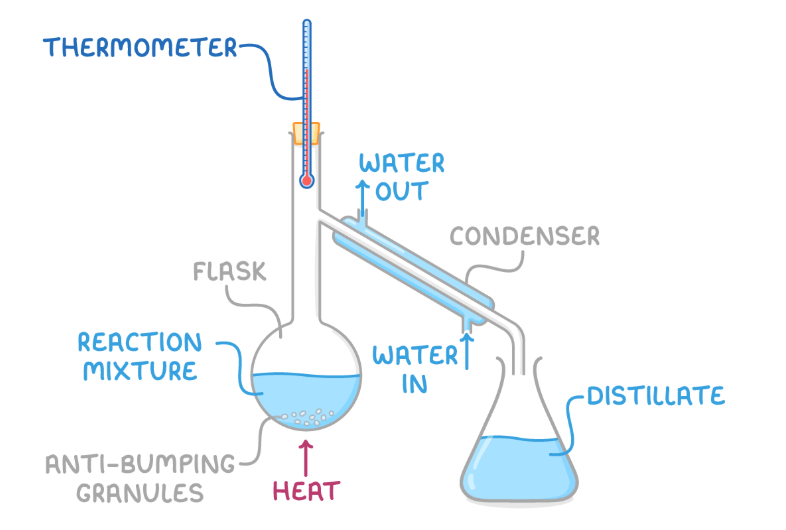
distillation
heating under reflux
Involves heating the reaction mixture in a round-bottomed flask equipped with a Liebig condenser.
As the mixture boils, vapours condense in the condenser and return to the flask, preventing the escape of reagents.
problem with reflux
a drawback of reflux is that desired products may undergo further reactions if heated for too long.
reflux apparatus
distillation
Involves gently heating the mixture so that components evaporate according to their boiling points.
This is particularly useful if the desired product has the lowest boiling point, allowing it to be selectively evaporated and condensed, thereby avoiding unwanted side reactions.
Distillation is most effective when the product's boiling point is lower than that of the reactants.
distillation apparatues
how to purify an organic solid
filtration under reduced pressure
recrystallisation
measurements of melting point
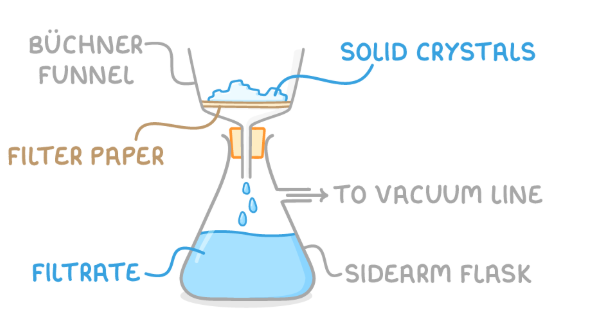
steps for filtering solids under reduced pressure
Transfer the reaction mixture into a Büchner funnel with a piece of filter paper. The funnel is positioned on top of a flask connected to a vacuum line.
Apply suction to quickly draw the liquid through the filter, leaving the dry solid on the filter paper while the filtrate containing liquid impurities is collected in the flask below.
filtration under reduced pressures
technique for separating a solid product from liquid impurities in a reaction mixture
filtration under reduced pressures apparatus
recrystallisation steps
Dissolve the impure solid in a minimal amount of hot solvent to create a saturated solution.
Allow the solution to cool slowly, which encourages the formation of pure crystals while impurities remain in the solution.
Filter the mixture under reduced pressure to collect the crystals, and wash them with a small amount of cold solvent to remove any residual impurities on the crystal surface.
Dry the purified crystals.
what should the ideal recrystallisaiotn solvent do
Fully dissolve the solid at high temperatures.
Promote crystallisation of the solid as the solution cools.
if solubility i to low when hot when recrystallising
The product does not fully dissolve, even upon boiling.
This prevents recrystallisation since crystals cannot form from a solution.
if solubility i to high when cold when recrystallising
The product remains dissolved in the cold solution.
Crystals fail to form, leading to product loss during filtration rather than impurity removal.
how cna you test purity
The melting point of a compound is a valuable indicator of its purity. Pure substances melt at precise temperatures, while impure substances melt over a range of temperatures.
how to determine melting pointof an organic solid
The melting point of a compound is a valuable indicator of its purity. Pure substances melt at precise temperatures, while impure substances melt over a range of temperatures.
aromatic compounds functional group,properties and typical reactioms
stable delocalised ring of electrons,electrophilic substitution
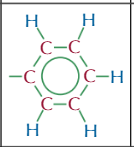
haloalkane functional group,properties and typical reactioms
-x
polar c-x bond
nucleophilic substituion
elimination
amine functional group,properties and typical reactioms
-N-
lone pair on nitrogen can act as a base or nucleophile
neutralisation
nucleophilic substitution
amide functional group
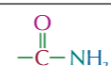
nitrile functional group,properties and typical reactioms
electron deficient carbon centre
reduction,hydrolysis

ester unctional group,properties and typical reactioms
electron deficient carbon centre
hydrolysis
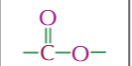
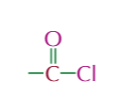
acyl chloride functional group,properties and typical reactioms
electron deficient carbon centre
nucleophilic substitution
condesation
friedal crafts acylation
acid anyhdride functional group,properties and typical reactioms
electron deficient carbon centre
esterification
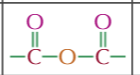
alevel syntehsis routes for aliphatic compounds
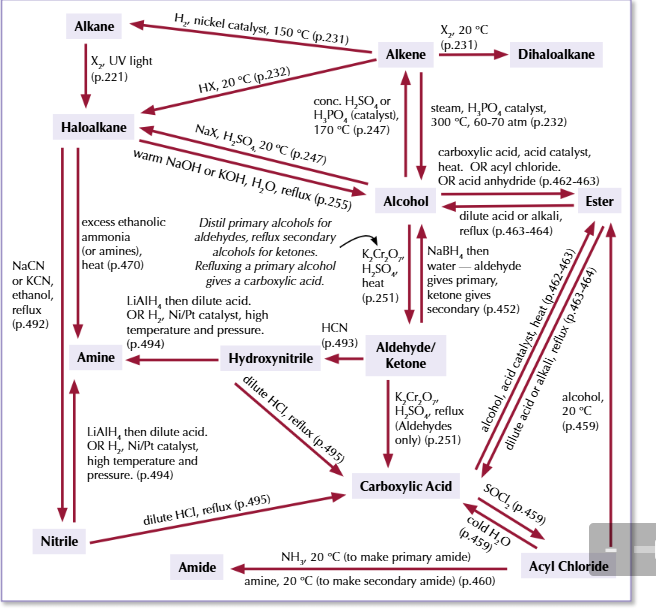
alevel syntehsis routes for benzene
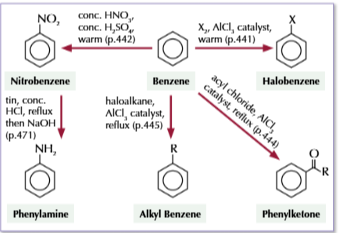
alevel syntehsis routes for henol
alkane to haloalkane
X2
UV light
haloalkane to amine
excess ethanolic ammonia
heat
haloalkane to nitrile
NaCN or KCN
ethanol
reflux
haloalkane to alcohol
warm NaOH or KOH
H2O
reflux
alcohol to haloalkane
NaX
H2SO4
20C
alcohol to ester
carboxylic acid,acid catalyst,heat
or acyl chloride
or acid anhydride
ester to alcohol
dilute acid or alkali
reflux
alcohol to alkene
conc H2SO4 or H3PO4
170C
alkene to alcohol
steam
H3PO4 catalystt
300C
60-70 atm
alkene to dihaloalkane
X2
20C
alkene to alkane
H2
nickel catalyst
150C
Alkene to haloalkane
HX
20C
alcohol to aldehyde/ketone
Acidified pottasium dichromate
distil primary alcohols to aldehydes
reflux secondary alcohols to ketones
aldehyde/ketone to alcohol
NaBH4 with water
aldehyde gives primary
ketone gives secondary
aldehyde/ketone to hydroxy nitrile
HCN
aldehyde to carboxylic acid
acidified pottasium dichromate reflux
hydroxynitrile to amine
LiAlH4 then dilute acid
or H2 Nickle catalyst high temp and pressure
hydroxy nitrile to carboxylic acid
dilute HCL
reflux
nitrile to carboxylic acid
dilute HCl
reflux
carboxylic acid to ester
alcohol
acid catalsyt
heat
ester to carboxylic acid
dilute acid or alkali
reflux
carboxylic acid to acyl chloride
SOCl2
acyl chloride to carboxylic acid
cold H2O
acyl chloride to ester
alcohol
20
acyly chloride to amide
NH3 20C to make primary
amine 20 to make secondary
benzene to nitrobenzene
conc HNO3
conc H2SO4
warm
phenyl amine
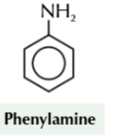
nitrobenzene to phenylamine
tin
conc HCL
reflux then NaOH
benzene to alkly benzene
haloalkane
AlCl3 catalyst
reflux
phenyl ketone
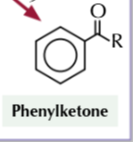
benzene to phenyl ketone
acyl chloride
AlCl3 ctalyst
reflux
benzene to halobenzene
phenol to 2,4,6-tribromophenol
bromien water Br2
20C
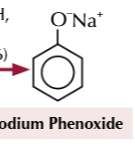
phenol to sodium phenoxide
NaOH
20C
sodium phenoxide
phenol to 2-nitrophenol or 4-nitrophenol
dilute HNO3
20C
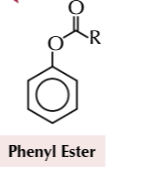
phenol to phenyl ester
acyl chlirde
20C
phenyl ester