module 4 Time Value of Money
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Time Value of Money
A dollar today is worth more than a dollar tomorrow
This is the case because you can earn interest on your money’s potential earning capacity.
Future Value formula (for one period)
FV = PV (1+r)
r = the appropriate interest rate
Present Value formula (for one period)
PV = FV / (1+r)
The general formula for the future value of an investment over multiple periods:
FV = PV (1+r)^T
T = number of periods over which the cash is invested
PV for multiple periods
PV = FV / (1+r)^T
Perpetuity
A constant stream of cash flows (C) that lasts forever
Growing perpetuity
Growing stream of cash flows that lasts forever
annuity
Stream of equal cash flow for a given number of periods. Its payments stop after T periods.
Discount rate (meaning)
Discount rate r is also called the rate of return, hurdle rate, or opportunity cost of capital.
Why is the discount rate sometimes called opportunity cost of capital
Because it is the rate of return that is foregone by investing in this project rather than investing in financial markets.
Note the same level of risk must be involved
When the discount rate increases, what happens to the net present value?
The net present value decreases
Internal rate of return
Is the rate that makes a projects net present value equal to zero.
This can be thought of as a project’s inherent growth rate.
How does internal rate of return affect decision-making?
A project should be accepted if the internal rate of return is greater than the required rate of return.
If there are multiple projects to choose from, you should choose the project with the highest internal rate of return.
Annual percentage rate APR
The rate that a bank is required to quote on loans it extends
Is a simple interest rate that does not consider compounding
APR equals the periodic interest rate times the number of compounding periods in a year
What would the end of your payment be if you were offered an APR of 15% compounded monthly on a $1000 loan?
Compounding and investment m times per year for T years with stated interest rate r provide provides the end of year wealth
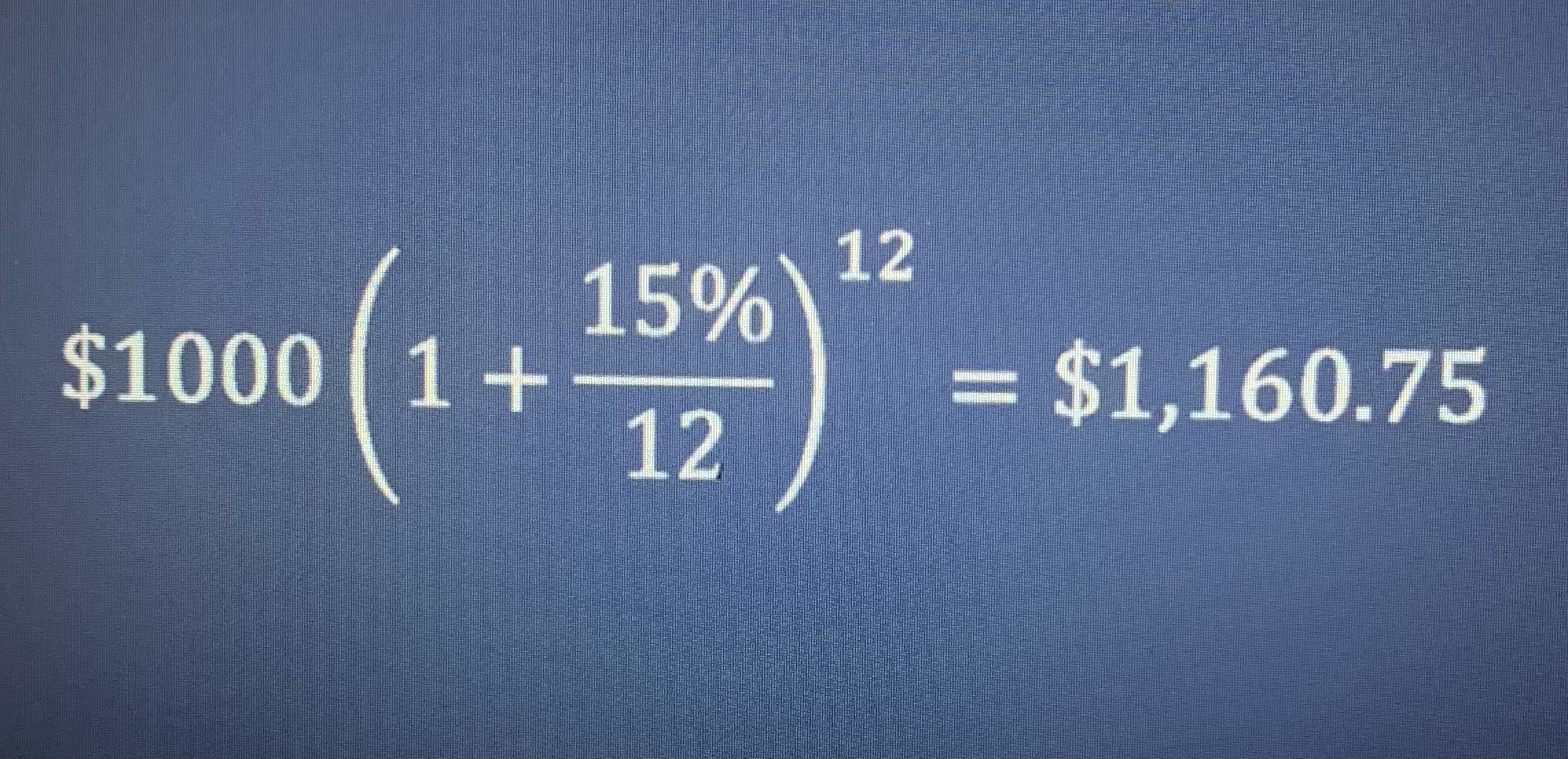
Compounding and investment m times per year for T years with stated interest rate r provide provides the end of year wealth

Effective annual rate, EAR
The true annual rate that would give us the end of investment wealth.
What is the major difference between APR and EAR?
APR ignores compounding
EAR considers the effects of compounding