Computer Security Principles and Practices Overview
1/136
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
137 Terms
Confidentiality
Protect information from unauthorized access.
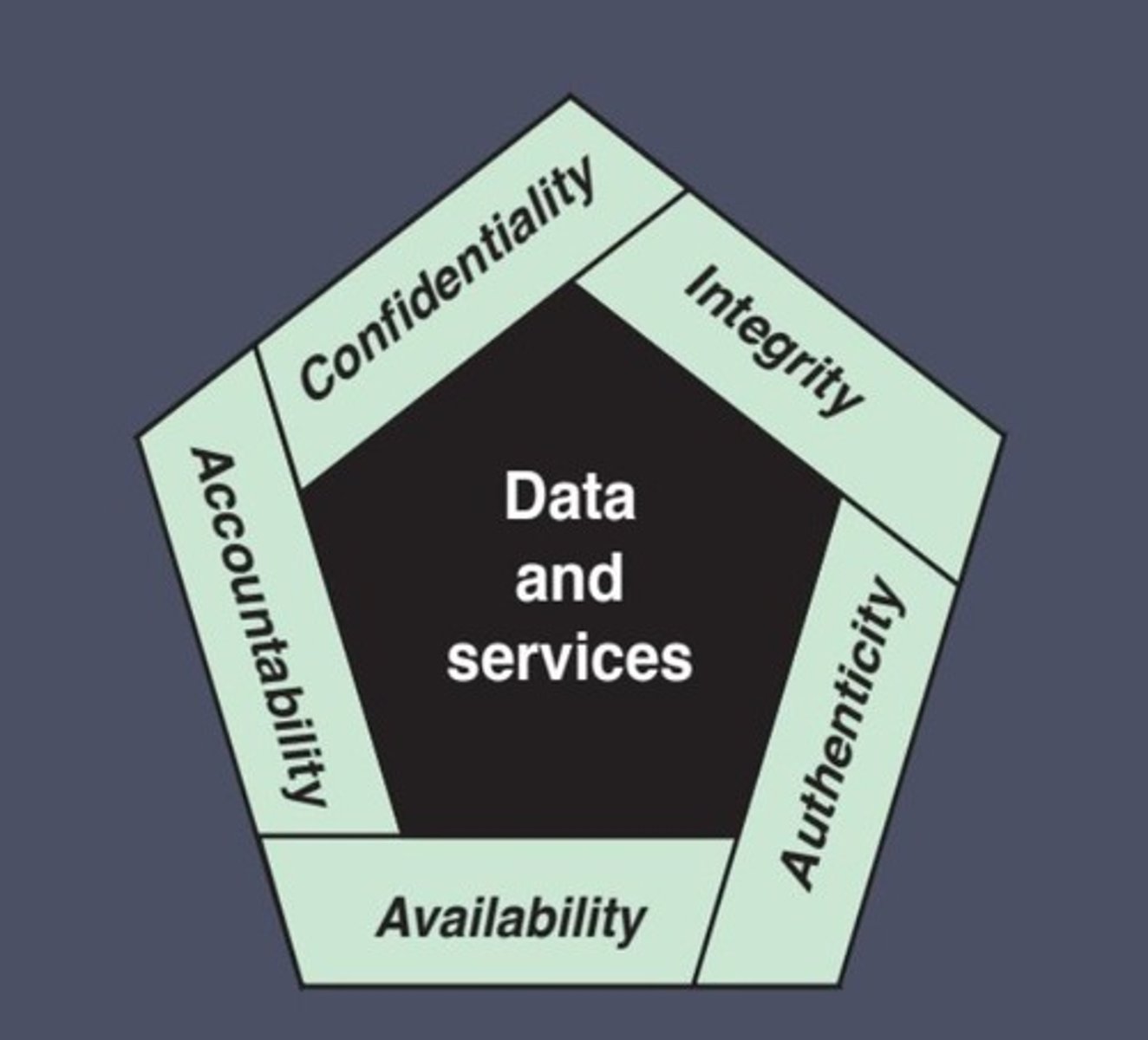
Integrity
Maintain the accuracy and reliability of information.
Availability
Ensure information and systems are accessible when needed.
Confidentiality (Key Security Concept)
Preserving authorized restrictions on information access and disclosure.
Integrity (Key Security Concept)
Guarding against improper information modification or destruction.
Availability (Key Security Concept)
Ensuring timely and reliable access to and use of information.
Low Impact Level
The loss is expected to have a limited adverse effect.
Moderate Impact Level
The loss is expected to have a serious adverse effect.
High Impact Level
The loss is expected to have a severe or catastrophic adverse effect.
Complexity of Security
Security is more complicated than it seems to novices.
Potential Attacks
Security mechanisms or algorithms must account for potential attacks.
Counterintuitive Procedures
Procedures to provide security services may not always be straightforward.
Placement Decisions
Requires careful determination of physical and logical placement.
Secret Information
Security mechanisms depend on secret information, raising concerns about creation, distribution, and protection.
Asymmetry of Effort
Attackers need only one weakness; designers must address all vulnerabilities.
Afterthought Security
Security is often added post-design instead of being integral to the design process.
Continuous Monitoring
Security requires constant and regular vigilance.
Perceived Value
Security investments are often undervalued until a failure occurs.
Efficiency vs. Security
Strong security is often seen as hindering efficiency and user-friendliness.
Adversary (Threat Agent)
An individual, group, organization, or government intending to conduct detrimental activities.
Attack
Malicious activity aimed at collecting, disrupting, denying, degrading, or destroying information system resources or data.
Countermeasure
Devices or techniques designed to impair adversarial activities and prevent espionage, sabotage, theft, or unauthorized access/use of sensitive systems and information.
Risk
Measures the threat level based on adverse impacts if an event occurs and the likelihood of the event happening.
Security Policy
A set of criteria defining how security services are provided and constrains data processing activities to maintain security for systems and data.
System Resource (Asset)
Includes major applications, systems, critical programs, personnel, equipment, or logically related systems.
Threat
Any event or circumstance with potential adverse impacts, such as unauthorized access, destruction, disclosure or modification of information, or denial of service.
Vulnerability
A weakness in information systems, security procedures, internal controls, or implementation that could be exploited or triggered by a threat.
Leakage of Information
Unauthorized individuals gain access to some or all of the information available through the network.
System Unavailability or Slowdown
The system or network becomes impossible to use or impractical due to significant delays or slow performance.
Hardware
Physical components of a computer system.
Software
Programs and applications that run on a computer system.
Data
Information processed or stored by a computer system.
Communication facilities and networks
Systems that enable data exchange between computers.
Corrupted Vulnerability
Loss of integrity.
Leaky Vulnerability
Loss of confidentiality.
Unavailable or Slow Vulnerability
Loss of availability.
Threats
Entities capable of exploiting vulnerabilities, representing potential security harm to assets.
Passive Attack
Goal: Learn or use information without affecting system resources.
Active Attack
Goal: Alter system resources or disrupt their operation.
Insider Attack
Initiated by entities within the security perimeter.
Outsider Attack
Initiated by entities outside the security perimeter.
Countermeasures
Actions or mechanisms to address security attacks.
Countermeasures Functions
Prevent: Stop attacks before they occur. Detect: Identify attacks in progress or after they happen. Recover: Restore systems and data after an attack.
Countermeasures Considerations
Countermeasures may introduce new vulnerabilities. Residual vulnerabilities might remain even after implementation.
Countermeasures Goal
Minimize the residual risk level to protect assets effectively.
Unauthorized Disclosure
An unauthorized entity gains access to data they shouldn't have.
Deception
An authorized entity receives false data and believes it to be true.
Disruption
Circumstance or event that interrupts system operation.
Usurpation
Unauthorized control of system services or functions.
Availability Threats - Hardware
Equipment is stolen or disabled, denying service.
Confidentiality Threats - Hardware
An unencrypted USB drive is stolen.
Integrity Threats - Hardware
A working program is modified to either cause failure or unintended tasks.
Availability Threats - Software
Programs are deleted, denying access.
Availability (Software)
Programs are deleted, denying access.
Confidentiality (Software)
An unauthorized copy of software is made.
Integrity (Software)
A program is altered, causing failures or unintended behaviours.
Availability (Data)
Files are deleted, denying access.
Confidentiality (Data)
Unauthorized reading of data or analysis of statistical data revealing underlying information.
Integrity (Data)
Existing files are modified or new files are fabricated.
Availability (Communication Lines and Networks)
Messages are destroyed or deleted; communication lines/networks are rendered unavailable.
Confidentiality (Communication Lines and Networks)
Messages are read; message traffic patterns are observed.
Integrity (Communication Lines and Networks)
Messages are modified, delayed, reordered, or duplicated; false messages are fabricated.
Passive Attack
Attempts to learn or make use of information from the system without affecting system resources.
Eavesdropping
Monitoring transmissions.
Goal of Passive Attack
To obtain information being transmitted.
Release of Message Contents
Unauthorized access to message contents.
Traffic Analysis
Observing the patterns of message traffic to infer details without accessing the contents.
Active Attack
Attempts to alter system resources or affect their operation.
Goal of Active Attack
Involve modifications to the data stream or the creation of a false stream.
Replay
The attacker retransmits valid data or messages to affect system operation.
Masquerade
The attacker impersonates an authorized entity to gain access or perform actions.
Modification of Messages
Altering the contents of messages to mislead or disrupt.
Denial of Service (DoS)
Disrupting the availability of the system or network, preventing legitimate access.
Access Control
Limit access to authorized users, processes, or devices and restrict the types of transactions users can perform.
Awareness and Training
Ensure managers and users are aware of security risks and related laws.
Audit and Accountability
Create and retain audit records to monitor, analyze, and report inappropriate activity.
Certification, Accreditation, and Security Assessments
Periodically assess the effectiveness of security controls.
Configuration Management
Maintain baseline configurations and inventories of hardware, software, and documentation.
Contingency Planning
Develop plans for emergency response, backup operations, and recovery to ensure availability and continuity in emergencies.
Identification and Authentication
Identify and authenticate users, processes, or devices before granting system access.
Incident Response
Establish and maintain an incident-handling capability.
Maintenance
Perform periodic and timely maintenance on systems.
Media Protection
Protect both paper and digital media.
Physical and Environmental Protection
Limit physical access to systems and infrastructure.
Planning
Develop, document, and update security plans that describe controls and rules for behaviour.
Personnel Security
Ensure trustworthy individuals occupy responsible positions.
Personnel Security
Protect systems during personnel actions like terminations.
Personnel Security
Enforce sanctions for non-compliance with security policies.
Risk Assessment
Periodically assess risks to operations, assets, and individuals from the use of information systems.
Systems and Services Acquisition
Allocate sufficient resources for security.
Systems and Services Acquisition
Incorporate security in system development and acquisition processes.
Systems and Services Acquisition
Ensure third-party providers follow security practices.
System and Communications Protection
Monitor, control, and protect communications at internal and external system boundaries.
System and Communications Protection
Use architectural and software development principles for effective security.
System and Information Integrity
Identify and correct system flaws quickly.
System and Information Integrity
Protect against malicious code and monitor security alerts.
Economy of Mechanism
Keep the design as simple as possible to reduce the number of security mechanisms, which makes it easier to analyze and maintain.
Fail-Safe Defaults
Default configurations should deny access unless explicitly granted. This minimizes potential harm by ensuring that the system is secure even in the absence of active decisions.
Complete Mediation
Every access request must be checked against the security policy, ensuring no bypassing of access control mechanisms.
Open Design
Security should not rely on the secrecy of the design or implementation. Open design allows for external review and ensures security is based on sound principles rather than obscurity.