QCAA Biology QCAA Unit 3 Topic 1
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Biodiversity
Biodiversity is the variety of life on earth and takes into account in how many different species work together in an ecosystem
Species
Species is a group of organisms that share a gene pool and is able to breed and produce offspring as long as there is no physical barrier.
What are the types of biodiversity
Genetic: range of different genes within species
Species: range of different species in an ecosystem
Ecosystem: range of different ecosystem in a particular location
Consequences of low biodiversity
Inbreeding, over predation, ecosystem breakdown and vulnerability to disease.
Ecosystem
Ecosystem includes biotic and abiotic factors and they tend to be fairly uniform. An ecosystem is linked to the cycling of nutrients and raw materials within it. Energy transforms from light to chemical energy through the process called photosynthesis then transferred between organisms via linked food webs then to body heat.
Measures of biodiversity
Species richness, species abundance, percentage cover and SDI
Abbundance
The amount of different species in an ecosystem
Species interactions
Predation, competition, symbiosis and disease
Abiotic factors
Weather, wave action, temperature, humidity, acidity, oxygenation…
Biotic Factors
Animals, plants, bacteria, fungi, protist…
Sampling Methods
Quadrats, point sampling, transect, belt transects.
Sampling Techniques
Random, systmatic, stratafied.
Spatial Scale
the way the size of ecosystem is measured with; ex. the foot of a mountain to the peak
Temporal Scale
the way an ecosystem is measured over time; ex. measuring the same 10 quadrats each month.
Effect of environmental factors
Environmental factor can limit the distribution and species abundance in an ecosystem as organisms has their own tolerance limit and range that restricts them from whey they could live. Some factors include habitat, pH and temperature.
Formula: Relative Species Abbundance
(no. of species being measured / no. of organisms) x 100
Formula: Simpsons Diversity Index
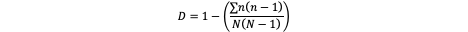

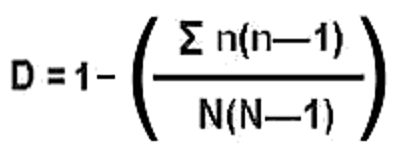
Formula: Percentage Frequency
(no. of quadrats containing the species / no. of quadrats sampled) x 100
Ecological Niche
An ecological niche is the role and space an organism plays in its environment, including all interactions with biotic and abiotic factors.
Keystone Species
A species that plays a unique and crucial role in the way which an ecosystem functions.
Gauzes Law/ Competitive Exclusion Law
No two species can occupy the same ecological niche; one species will be better fit for the niche, and will outcompete the other species.