Lecture 17A: Minor Ailments & Responding to Symptoms in Community Pharmacy | Eye & Ear Health
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Anatomy of the eye
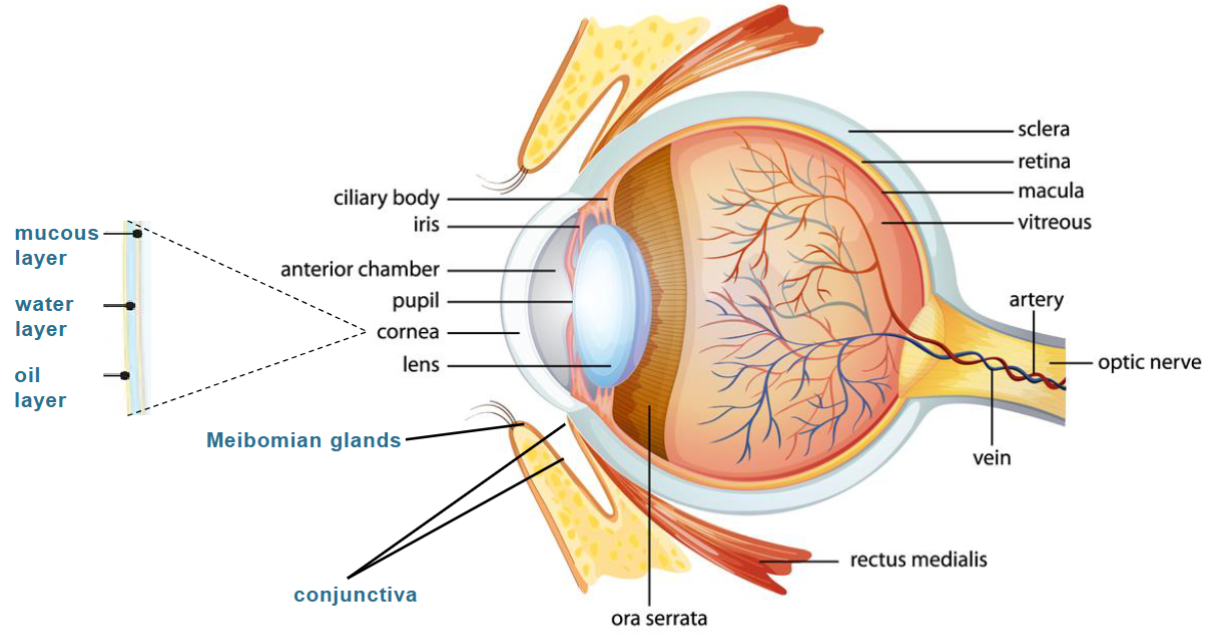
Overview of the eye
Sclera:
White of the eye, protects the eye and keeps its shape
Conjectiva:
Clear tissue covering the white part of the eye and inner eyelids
Cornea:
Transparent dome shaped covering at front of the eye, refracts the light entering the eye onto the lens
Meibomian glands:
Oil glands along the edge of eyelids where the eyelashes are found, the oil extcreted is part of the tear film
Iris:
Coloured part of the eye, controls the amount of light entering the pupil
Lens:
Responsible for ‘fine focusing’ light onto the retina
Pupil:
Circular opening at the center of the iris, through which light passes into the lens of the eye
Cilary body:
Attached to the iris and holds the lens in place
Retina:
Millions of light sensitive cells, light is converted to electric signals sent to the brain which interprets them as an image
Macula:
Small snesitive area of the retina, provides vision for fine work/reading
Red eye
Inflammation of the conjectiva, most common with opthalmic complaint
Can occur alone, or with pain, discharge or altered vision
Take accuarte history to aid diagnosis
Causes can be serious and non serious
Treatment is dependent on cause
Bacterial Conjuctivitis
Inflammation of conjunctiva caused by bacterial infection, usually streptococcus pneumoniae, S. aureus and haemophilus influenzae
Very common, occurs at any age, equally affects men and women
One eye affected a day before the other, contagious
Symptoms: gritty/burning feeling, generalised redness, purulent discharge, eyelids stuck together on waking
Contact lens wearers and immunocompromised people at risk of complications
Management of bacterial conjunctivitis
Usually self limiting, resolves within 5-10 days without treatment
Clean discharge away with cotton wool soaked in cooled boiled water
Avoid wearing contact lenses until resolved
Sever symptoms: Chloramphenicol 0.5% eye drops (P), 1 drop 2 hourly for 2 days then 4 hourly, 5 day course
Chloramphenicol 1% eye ointment (P) apply 4 times a day, preferred in younger children
Chloramphenicol not licensed OTC for children under 2 years
Self care: use separate towels, wash hands thoroughly
Allergic Conjunctivitis
Inflammation of the conjenctiva caused by allergens
Affects both eyes, not contagious, occurs seasonally or with allergen exposure
Symptoms: itchy, watery eyes, generalised redness
Associated with snezzing, itchy throat
Management of allergic conjunctivitis
Avoidance of the allegen would alleviate symptoms
Topical mast cell stabilisers e.g. Sodium cromoglicate 2% eye drops (P) 1-2 drops up to 4 times a day, slower acting, may sting
Oral antihistamine e.g. loratadine 10 mg tablets (GSL/P) 1 daily, cetirizine 10 mg tablets (GSL/P) 1 daily
Self care: avoid allergens if possible, avoid eye rubbing
Dry eyes
Can be caused by reduction of tear production, alteration in tear composition, increased evaporation of tears from the eye or increased tear drainage
Medication induced e.g. diuretics, antihistamines
Common with increasing age, especially in women
Usually affects both eyes
Symptoms: eyes look normal but burn/feel gritty, irritataed, vision unaffected
Often associated with blepharitis
Management of dry eyes
Chronic condition - no cure
Reduce use of contact lenses
Avoid long periods without blinking - staring at a screen
Avoid antihistamines - exacerbate dry eyes
Artificial tears e.g. Hypromellose 0.3% eye drops (P), Viscotears 0.2% eye gel (P), Hylo forte 0.2% eye drops
Subconjunctival Haemorrhage
Spontaneous rupture of a blood vessel under the conjunctiva
Can be triggered by coughing
More common in older people - use of aspirin, anticoagulants
Symptoms: a portion or a large part of the white of the eye becomes bright red, no pain, vision is unaffected
May look alarming
Manageement of subconjunctival haemorrhage
Symptoms resolve without treatment within 10-14 days
Give reassurance
Measure blood pressure
Safety-net (pain, vision changes)
Stye
Bacterial infection (often staphylococcus) of eyelash follicle or oil gland
Fairly common, may experience 1-2 times in the lifetime
Symptoms: small painful red lump on the outer eyelid, sensitive to touch
May be associated with bacterial conjunctivitis
Blepharitis may increase risk of stye
Management of stye
Self limiting, resolves within a few days or weeks without treatment
Antibiotic use including topical, isn’t recommendedWarm compress 10-15 minutes, 3-4 times daily to encourage the drainage of pus
Avoid puncturing or squeezing the stye
Avoid makeup and contact lenses
Blepharitis
Chronic inflammation affecting the margin of the eyelids, vaused by bacteria staphylococci or seborrhoeic dermatitis
Common, usually develops in middle age
Symptoms: stickiness and yellow scales at roots of eye lashes, worse in the morning
Commonly associated with dry eyes, seborrhoeic dermatitis and rosacea
Management of blepharitis
Chronic condition - no cure, aim to reduce flare ups
Long term lid hygiene - solution/wipes to cleanse eyelids e.g. Blephaclean, Blephasol
Warm compress for 5-10 mins once or twice daily
Chloramphenicol 1% eye ointment (P) if lid hygiene not sufficient
Refer
Visual disturbance
Photophobia
True eye pain
Trauma/foreign body
Baby under 4 weeks with red eye
Irregular pupil/non-reactive to light
Previous serious eye disease
Administration of eye drops
Wash hands
If required clean the eye(s) with boiled and cooled water and a tissue, if they are sticky/watery
Remove the lid from the bottle
Lie down or sit and tilt head backwards to look at the ceiling
Form pocket between the eye and the lower eyelid by gently pulling down the lower eyelid with a finger
Look upwards
With other hand, hold bottle close to eyelid as possible, ensure tip of bottle does not touch any part of the eye or finger
Squeeze the bottle to insert one drop into the lower eyelid and close the eye for a moment
Wipe away any excess drops with a clean tissue
Apply slight pressure for about 30 seconds to the inner corner of the eye (this prevents drops entering the tear duct and into the back of the throat)
Replace the lid on the bottle
Discard bottle after 4 weeks of opening
Administration of eye oitment
Administration is the same as eye drops however place 1cm of ointment along the inside of the lower eyelid, starting nearest the nose to outer edge
Close the eye and blink to help spread the eye ointment over the eyeball
When using ointment, vision may become blurry but will soon clear by blinking
Anatomy of the ear
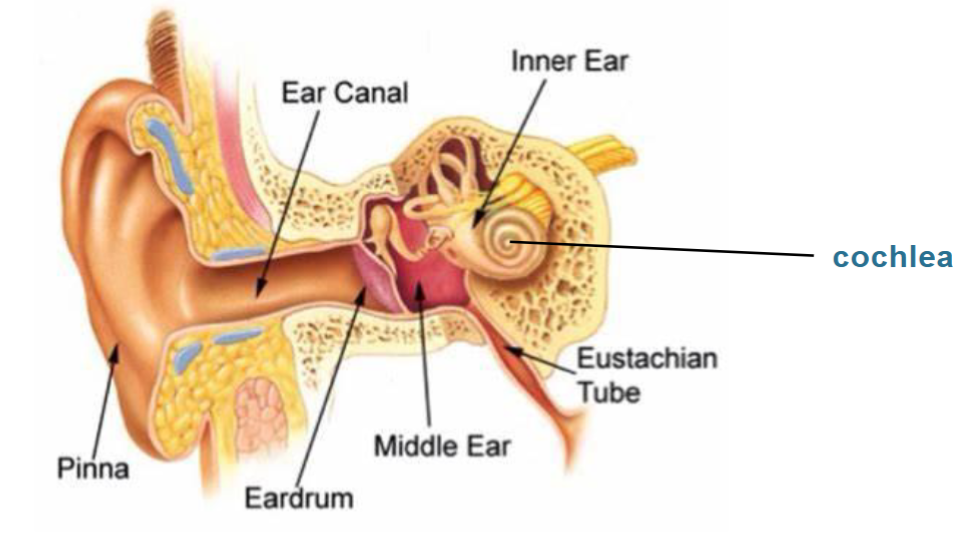
Overview of the ear anatomy
Outer ear:
Pinna – mainly made up of cartilage, has a firm elastic consistency, assembles sound waves and directs them down the ear canal
Ear canal – 2/3 covered with tiny hairs, 1/3 smooth skin with glands that produce cerumen/ear wax
Tympanic membrane/Ear drum – thin piece of skin at the end of the canal, vibrates in response to sound waves, initial conduction of sound
Middle ear:
Cavity linked with nose through Eustachian tube, helps to keep ear pressure consistent. Consists of 3 tiny bones; Malleus, Incus and Stapes, which increase the strength of the vibrations from the ear drum before they move towards the cochlea
Inner ear:
Cochlea – snail shell shaped, filled with fluid. Sound vibrations from the tiny bones are passed to fluid of cochlea, sound vibrations are converted to electrical impulses by tiny hairs, that are transmitted to the brain, this becomes the sound we hear
Otic health
Affected ears
Discharge
Pain/discomfort
Changes to hearing
Associated symptoms
Duration of symptoms
Treatment tried
Visual checki in/behind
Ear wax
Ear wax is made up of dead skin cells, cerumen (wax like substance) and sebum which is naturally eliminated by jaw movement
Ear wax cleans the ear and protects against infections and dirt, when impacted becomes a concern
Causes include use of cotton buds, hearing aids
More common in elderly
Symptoms: gradual hearing loss, discomfort, ear feels full/blocked
Management of ear wax
Remove earwax if ear wax is totally blocking ear canal and is symptomatic or need to visualise tympanic membrane
Ear drops used to soften wax and facilitate removal
Cerumenolytic agents e.g. olive oil (GSL), sodium bicarbonate 5% (P), urea hydrogen peroxide 5% (P) - safe and effective
Avoid inserting cotton buds
No evidence to support use of ear candles
May require ear syringing or microsuction, may not be provided by GP surgeries
Otitis externa
Inflammation of the skin of the external ear canal, caused by bacteria such as pseudomonas aeruginosa or staphylococcus aureus
Common in all ages, more so in females
Risk factors – swimming, use of hearing aids/headphones, trauma
Symptoms: Ear discomfort/pain/itch, discharge, moving pinna worsens pain,
Associated with contact dermatitis, psoriasis, skin infections
Management of otitis externa
Manage underlying causes/risk factors
Mild infection: Acetic Acid (EarCalm) ear spray (P), 1 spray 3 times a day
Moderate/severe infection: Topical antibiotics +/- corticosteroid e.g. Gentisone HC ear drops (POM), Cilodex ear drops (POM)
Self care:
Avoid ear trauma, avoid swimming/water sports for 7-10 days
It is not contagious
Keep ears clean and dry, pain relief – paracetamol or ibuprofen
Administration of ear drops
Wash hands
Clean and dry ear if needed, with a face cloth
Warm the ear drops by holding the bottle in the hand for a few minutes
Remove the lid from the bottle
Lie down on your side or tilt the head, so the affected ear points towards the ceiling
Pull top of affected ear up and back to straighten the ear canal
Insert required number of drops into the ear canal
Stay lying down or keep head tilted for 5-10 minutes, massage in front of the ear (to allow drops to stay in the ear and run down the ear canal)
Wipe away any excess solution with a clean tissue
Replace lid on the bottle
Discard bottle after 4 weeks of opening
Refer
Ear pain in young children
Pain from middle ear
Foreign body in ear
Mastoiditis - redness, swelling, tenderness and pain behind ear
Persistent or sedden hearing loss
Trauma-related deafness
Dizziness or tinnitus