PHYSMOD_ ELECTRICAL CURRENTS FOR MM CONTRACTION
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
DOT
________
means Intact peripheral nerves, including the motor unit and neuromuscular junction
▪ Usually manifests as disuse atrophy
E.g. post-operative weakness, orthopedic
conditions, CNS affectation, etc.
Innervated Muscles
DOT
______
happens due to peripheral nerve injury
manifests as denervation atrophy
Denervated Muscles
DOT
______
Use of ES to produce muscle contractions in innervated muscles
________
Aka Orthotic Substitution
Type of NMES that specifically enhances the control of movement and posture
NMES integrated to functional activities
Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation
Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES)
Muscle Contraction
Volitional
Due to command from ______ neurons
Recruits ____ to ____ motor units
Activates first type ___ muscle fibers
_____ recruitment of motor units
____ onset of muscle fatigue
Due to command from upper motor neurons
Recruits smaller to larger motor units
Activates first type I muscle fibers
Asynchronous recruitment of motor units
Slow onset of muscle fatigue
Muscle Contraction
Electrically-induced
Due to applied electricity stimuli
Recruits larger to smaller motor units
Activates first type II muscle fibers
Synchronous recruitment of motor units
Rapid onset of muscle fatigue
baliktad lang ng volitional
Therapeutic Effects
INC Muscle Strength
______Principle
↑ current, ↑ frequency, ↓ pulse duration ,
INC externally-applied resistance
______ Theory
Targets type II muscle fibers which are reduced
after surgery, immobilization or any pathology
INC Muscle Strength
Overload Principle
↑ current, ↑ frequency, ↓ pulse duration ,
INC externally-applied resistance
Specificity Theory
Targets type II muscle fibers which are reduced
after surgery, immobilization or any pathology
Therapeutic Effects
INC Muscle _____
Increased muscle size ↑ muscle mass usually takes several weeks to occur
Improved motor unit _______
Occur more rapidly
Synchronized recruitment of more motor units
INC Muscle Strength
Increased muscle size ↑ muscle mass usually takes several weeks to occur
Improved motor unit recruitment
Occur more rapidly
Synchronized recruitment of more motor units
Therapeutic Effects
Promotes Muscle _______
Improvement of motor control
Stimulates brain plasticity
Promotes Muscle Re-education
Improvement of motor control
Stimulates brain plasticity
Therapeutic Effects
Prevents _____ Atrophy
Provides externally-induced muscle contraction to prevent muscle wasting
With adequate muscle strength, it serves as a biofeedback to promote muscle contraction
Prevents Disuse Atrophy
Provides externally-induced muscle
contraction to prevent muscle wastingWith adequate muscle strength, it serves as a
biofeedback to promote muscle contraction
Therapeutic Effects
Reduces Muscle ______
Over both agonist
Fatigue the muscle , Relaxation
Reduces Muscle Spasm
Over both agonist
Fatigue the muscle , Relaxation
Therapeutic Effects
Reduces Muscle Spasticity
Over the antagonist
_____ inhibition of agonist muscle
Over both agonist and antagonist muscle
_____ stimulation of agonist then followed by antagonist
Reduces Edema
Through the ________ effect
Reduces Muscle Spasticity
Over the antagonist
Reciprocal inhibition of agonist muscle
Over both agonist and antagonist muscle
Sequential stimulation of agonist then followed by antagonist
Reduces Edema
Through the muscle pumping effect
Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES)
During gait training
Over tibialis anterior during initial contact
Over gastrocnemius during push-off
For idiopathic scoliosis
Over lateral flexors on convex side
During gripping activity
Over wrist extensors
For shoulder subluxation
Over supraspinatus and posterior deltoids
During cycling
LE: Over quadriceps femoris and hamstrings
UE: Over biceps brachii and triceps brachii
Parameters Waveforms:
________
Commonly uses square, balanced, symmetrical,
biphasic PC; some use asymmetrical biphasic PC
_________
Uses medium frequency AC with a frequency of 2500
Hz delivered in 50 bursts per second
_________
Alternating medium-frequency currents, which are
slightly out of phase and amplitude-modulated at low
frequency
Biphasic Pulsed current
Russian current
Interferential current
Electrode placement
Active electrode over the motor point and dispersive electrode about __ inch away on the same muscle following the orientation of the muscle fiber (preferred) [ ____ if on same muscle; ___ if on other area]
Face and smaller muscles of the hand: motorpoint stimulation using probe/motor pen
Motor point between 2 electrodes (_____)
4 electrodes over targeted muscle (_____)
Wider spacing —> _____ stimulation
2 inch away
bipolar → same ; monopolar → other area
bipolar
quadripolar
Wider spacing —> deeper stimulation
PARAMETERS FOR STRENGTHENING
______ Principle & _______ Recruitment
Pulse Duration →
Amplitude →
Ramp Up/Down →
Frequency →
Treatment Duration →
On time: Off Time →
Ratio →
Overload Principle & Selected Recruitment
150-200 μsec (smaller muscles) & 200-350 μsec (larger muscles)
≥50% MVIC; max tolerated muscle contraction
At least 2s
20 pps (smaller mms) ,30 pps (larger mms), 35-50 pps (smooth tetanic) ,50-80 pps (greater strengthening)
10-20min (10-20 reps)
1:5 initially , 1:3 , 1:1
10 sec on: 50 sec off
PARAMETERS FOR MUSCLE ENDURANCE
__ contraction time & _ rest intervals
Pulse Duration →
Amplitude →
Ramp Up/Down →
Frequency →
Treatment Duration →
On time: Off Time →
Ratio →
↑ contraction time & ↓ rest intervals
150-200 μsec (smaller muscles) & 200-350 μsec (larger muscles)
25-50% MVIC
At least 2s
30-50 pps
More repetitions
1:1
NA
PARAMETERS FOR SPASTICITY Motor Level
Pulse Duration →
Amplitude →
Ramp Up/Down →
Frequency →
Treatment Duration →
On time: Off Time →
Ratio →
150-200 μsec (smaller muscles) &
200-350 μsec (larger muscles)
At motor threshold; to visible contraction
0.5-3 sec
35-50 pps
10-60 min
1:1, 3:4
PARAMETERS FOR SPASTICITY Sensory Level
Pulse Duration →
Amplitude →
Ramp Up/Down →
Frequency →
Treatment Duration →
On time: Off Time →
Ratio →
20-100 μsec
Below motor threshold
NA
80-100 pps
10-60 min
NA
PARAMETERS FOR MUSCLE SPASM MOTOR Level
Pulse Duration →
Amplitude →
Ramp Up/Down →
Frequency →
Treatment Duration →
On time: Off Time →
Ratio →
150-200 μsec (smaller muscles) &
200-350 μsec (larger muscles)
At motor threshold; to visible contraction
At least 1 sec
35-50 pps
10-30 min
1:1
(2-5 sec on; 2-5 sec off)
PARAMETERS FOR EDEMA REDUCTION MOTOR Level
Pulse Duration →
Amplitude →
Ramp Up/Down →
Frequency →
Treatment Duration →
On time: Off Time →
Ratio →
150-200 μsec (smaller muscles) &
200-350 μsec (larger muscles)
At motor threshold; to
visible contraction
At least 1 sec
35-50 pps
30 min
1:1 (2-5 sec on; 2-5 sec off)
Duty Cycle Formula
Duty Cycle = [ON ÷ (ON + OFF)] x 100
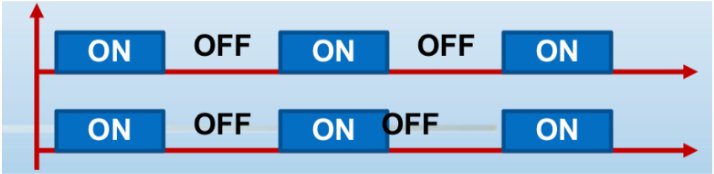
PARAMETERS: STIMULATION MODES
_____________
Channels 1&2 produces ON and OFF times together
Stimulate muscles during on time and off time actively; two channels acting on the same time
Eg. Quadriceps and TAs
Ask the Pt. to extend the knee and bring the toes upwards once you feel the electric sensation
SYNCHRONOUS (CO-CONTRACTION)
PARAMETERS: STIMULATION MODES
____________
While channel 1 is ON, channel 2 is OFF
Application on antagonistic or agonistic muscles; may be done separately if aim is a more focused contraction
Eg. During ON time, ask the Pt. to extend the knee. At OFF time, ask the Pt. to relax the limb
RECIPROCAL
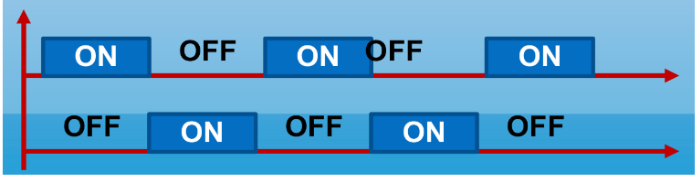
Progressive Training Methods
________
Muscle contraction solely relies on electricity
________
Contraction produced by both the electrical stimulator and the patient
________
Electricity only serves as feedback for contraction
NMES
NMES plus volition
NMES as biofeedback for motion
NMES/FES DOCU
NMES/FES using To <affected muscle> x <pulse frequency> x <pulse duration> x <duty cycle or On & Off time> x <treatment duration> to<rationale>.
DUBI DUBI?
ZAP ZAP