CH 12: Virus Infection and Viral Genomes Overview
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
Virus
Noncellular particle with a genome and capsid.
Bacteriophages
Viruses that infect bacterial cells.
Virus-First Model
Ancient viruses predated cellular organisms.
Reduction Model
Viruses evolved from parasitic cells through genome reduction.
Escape Model
Viruses arose from cellular components that escaped.
Host Range
Specific group of host species a virus infects.
Transmission
Process of reaching and infecting new hosts.
Tissue Tropism
Range of tissue types a virus can infect.
Broad Tropism
Virus infects many tissue types.
Narrow Tropism
Virus infects specific tissue types.
Antiviral Agents
Chemicals designed to combat viral infections.
Viral Genomes
Composed of either DNA or RNA.
Baltimore Model
Classifies viruses based on genome type and structure.
Group I
Double-stranded DNA viruses.
Group II
Single-stranded DNA viruses.
Group III
Double-stranded RNA viruses.
Group IV
Single-stranded RNA viruses, directly translated.
Group V
Single-stranded RNA viruses, require complement synthesis.
Group VI
Retroviruses, RNA reverse-transcribing viruses.
Group VII
Pararetroviruses, DNA reverse-transcribing viruses.
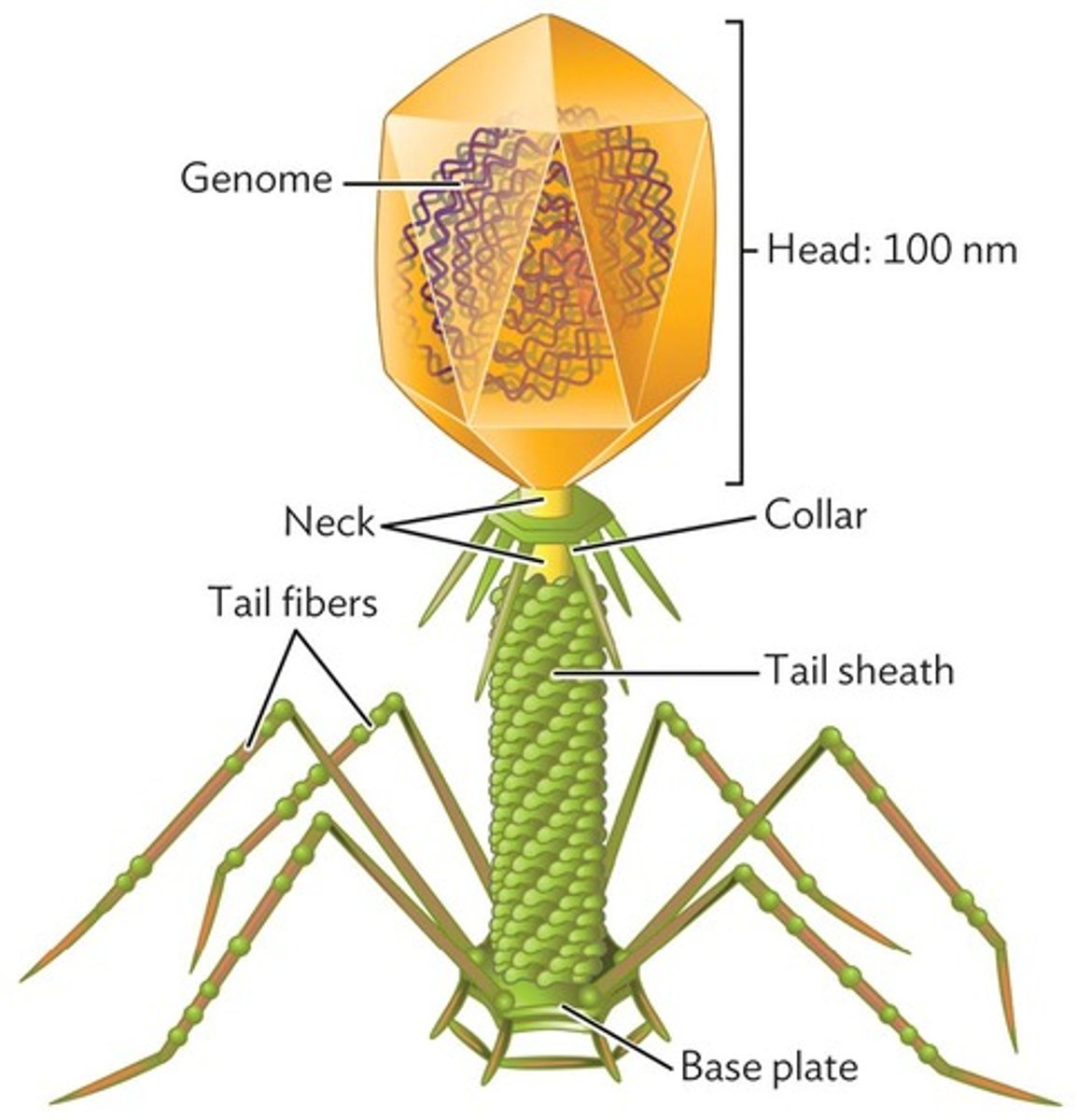
Capsid
Protein package enclosing a viral genome.
Icosahedral Capsid
Radial symmetry, 20 triangular faces.
Filamentous Viruses
Helical symmetry, flexible filament structure.
Complex-Tailed Bacteriophages
Icosahedral head with a tail for injection.
Amorphous Viruses
No symmetrical form, flexible core wall.
Viral Envelope
Membrane derived from host cell structures.
Spike Proteins
Aid viral attachment during host cell infection.
Tegument Proteins
Expressed during infection, aid viral replication.
Viral Genome Size
Varies greatly; RNA can be very small.
Retroviruses
Small genomes maximize virion production efficiency.
Avian Leukosis Virus (ALV)
Has three protein-encoding genes: gag, pol, env.
Double-Stranded DNA Viruses
Large genomes encoding numerous cellular-like proteins.
Herpes Simplex Virus
152 kilobases, encodes over 70 gene products.
Viroids
Infectious agents with circular RNA genomes.
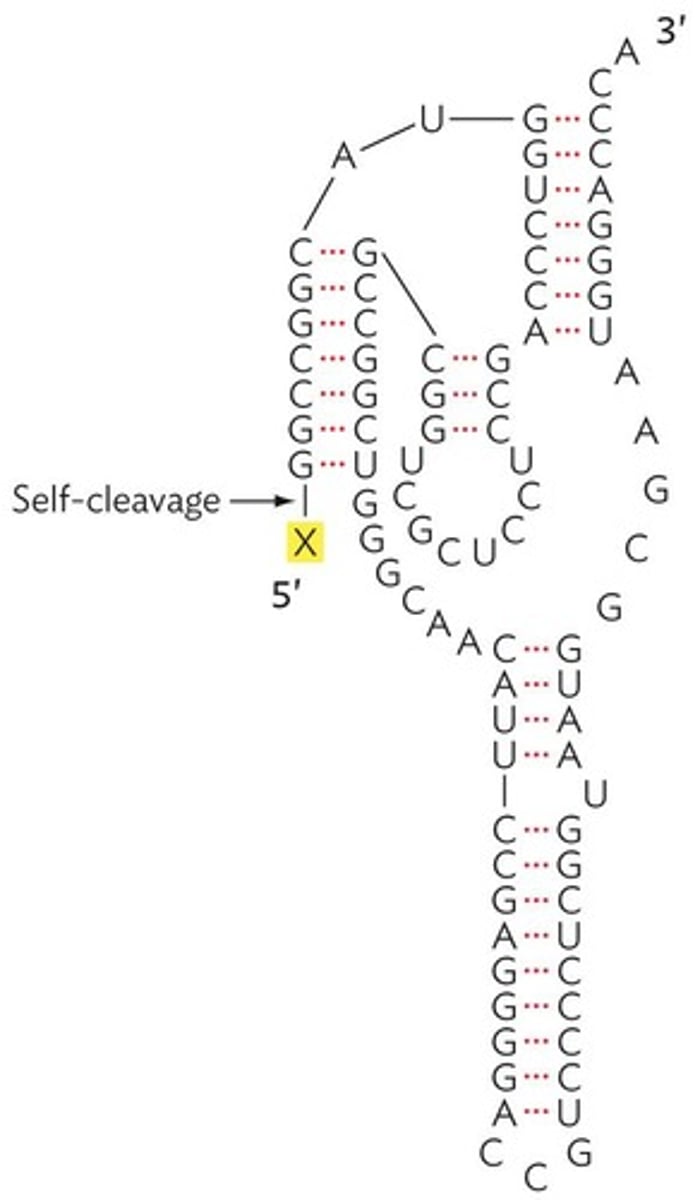
Hepatitis Delta Ribozyme
RNA portion that catalyzes its own cleavage.
Prions
Infectious proteins with no nucleic acid.
PrPC
Normal protein that misfolds into infectious form.
PrPSc
Abnormal prion form that aggregates and kills cells.

Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease
Neurodegenerative disease caused by prions.
Lytic Lifecycle
Immediate viral replication producing many progeny.
Lysogenic Lifecycle
Viral DNA integrates into host DNA as prophage.
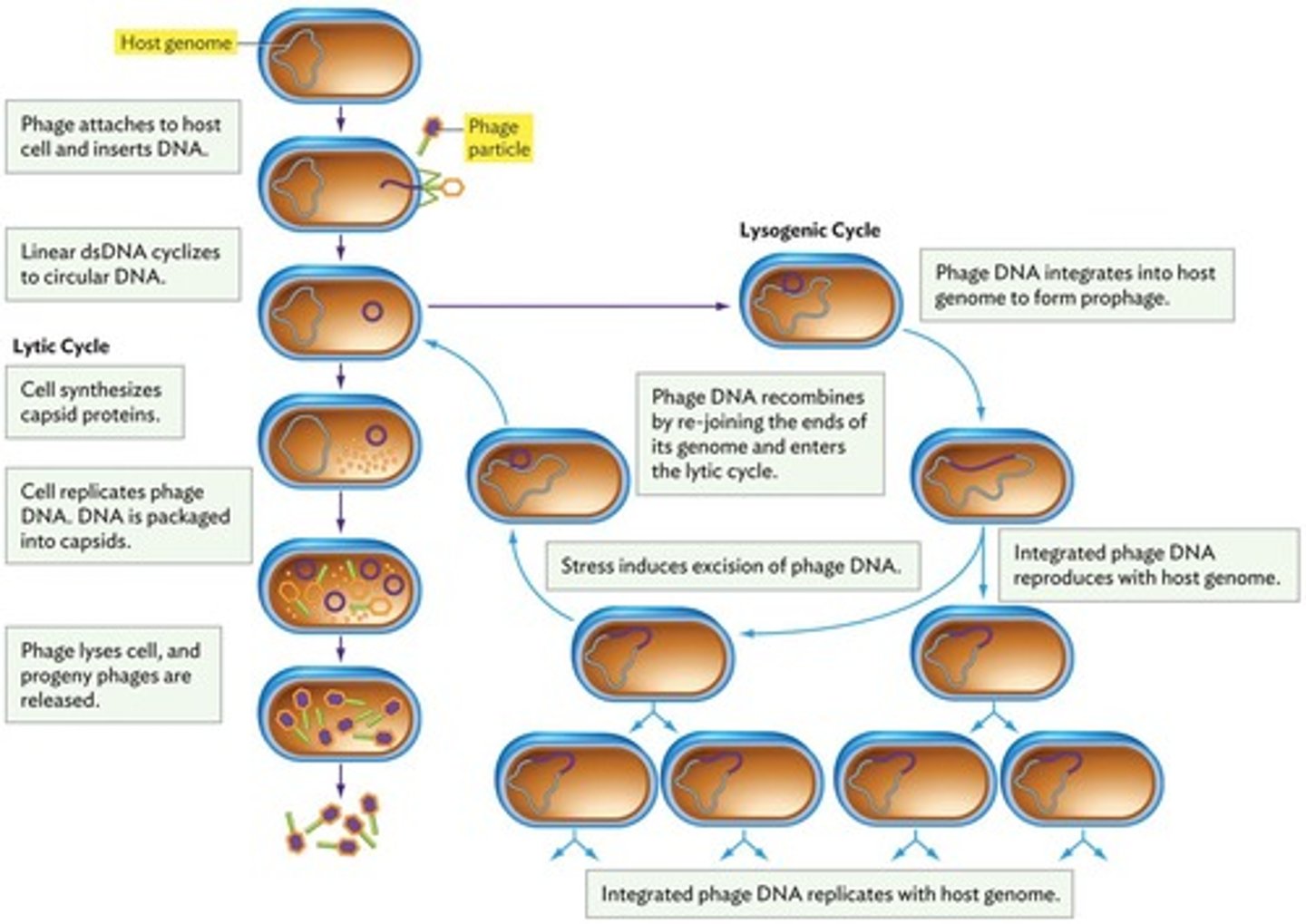
Adsorption
Virus binds to specific host cell receptors.
Penetration
Virus injects nucleic acid into host cell.
Replication
Host cell produces viral components.
Maturation
Assembly of new virus particles.
Release
Host cell lyses, releasing infectious particles.
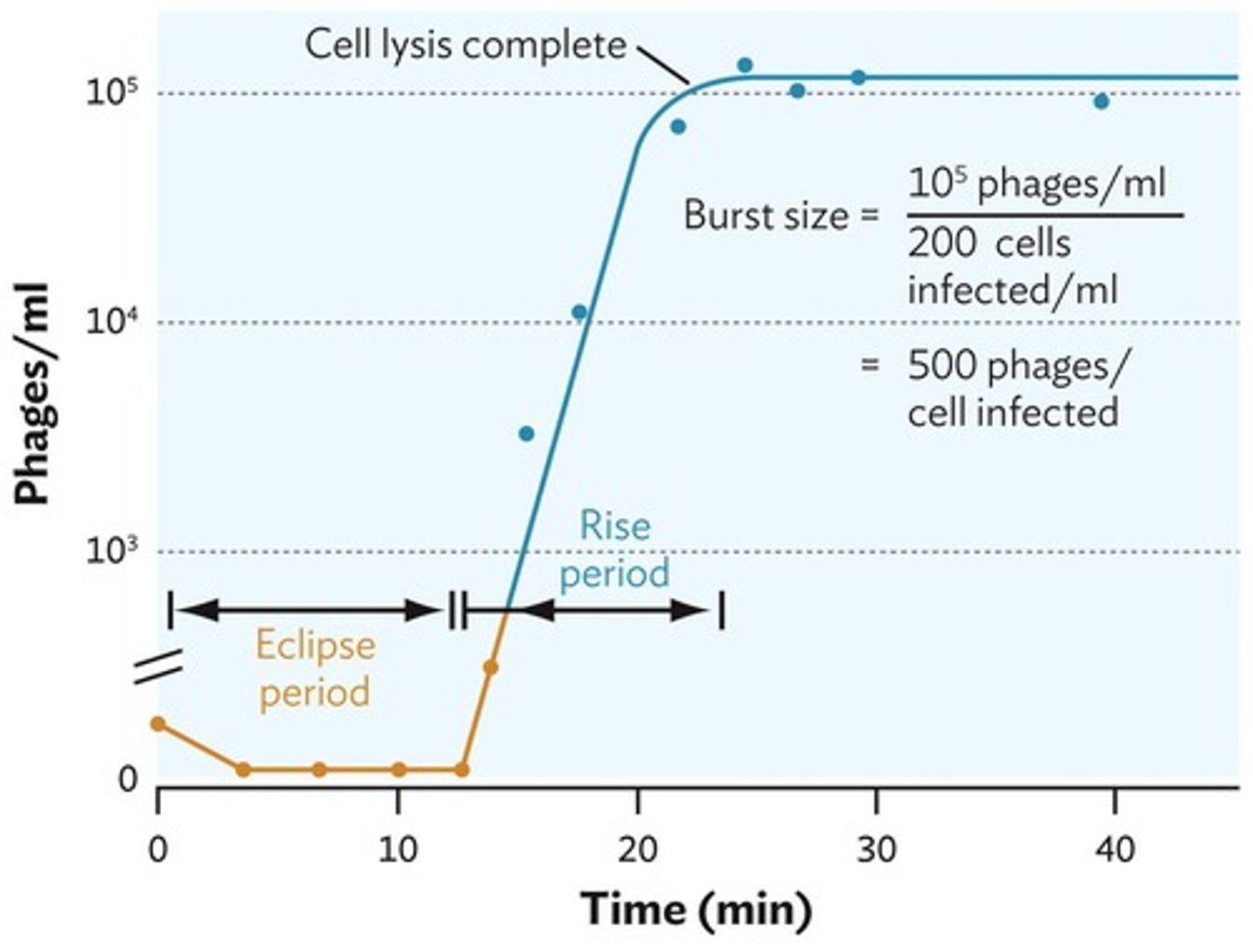
Burst Size
Number of virus particles released per cell.
Multiplicity of Infection (MOI)
Every host cell infected by viruses.
Eclipse Period
Phase where viruses are undetectable in medium.
Rise Period
Phase where phage particles begin to appear.
Antigenic Drift
Accumulation of mutations evading host antibodies.
Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
Infects basal epithelial cells, can cause cancer.
Gardasil Vaccine
Prevents certain strains of HPV effectively.
Icosahedral viruses
Small viruses, twice ribosome size, non-enveloped.
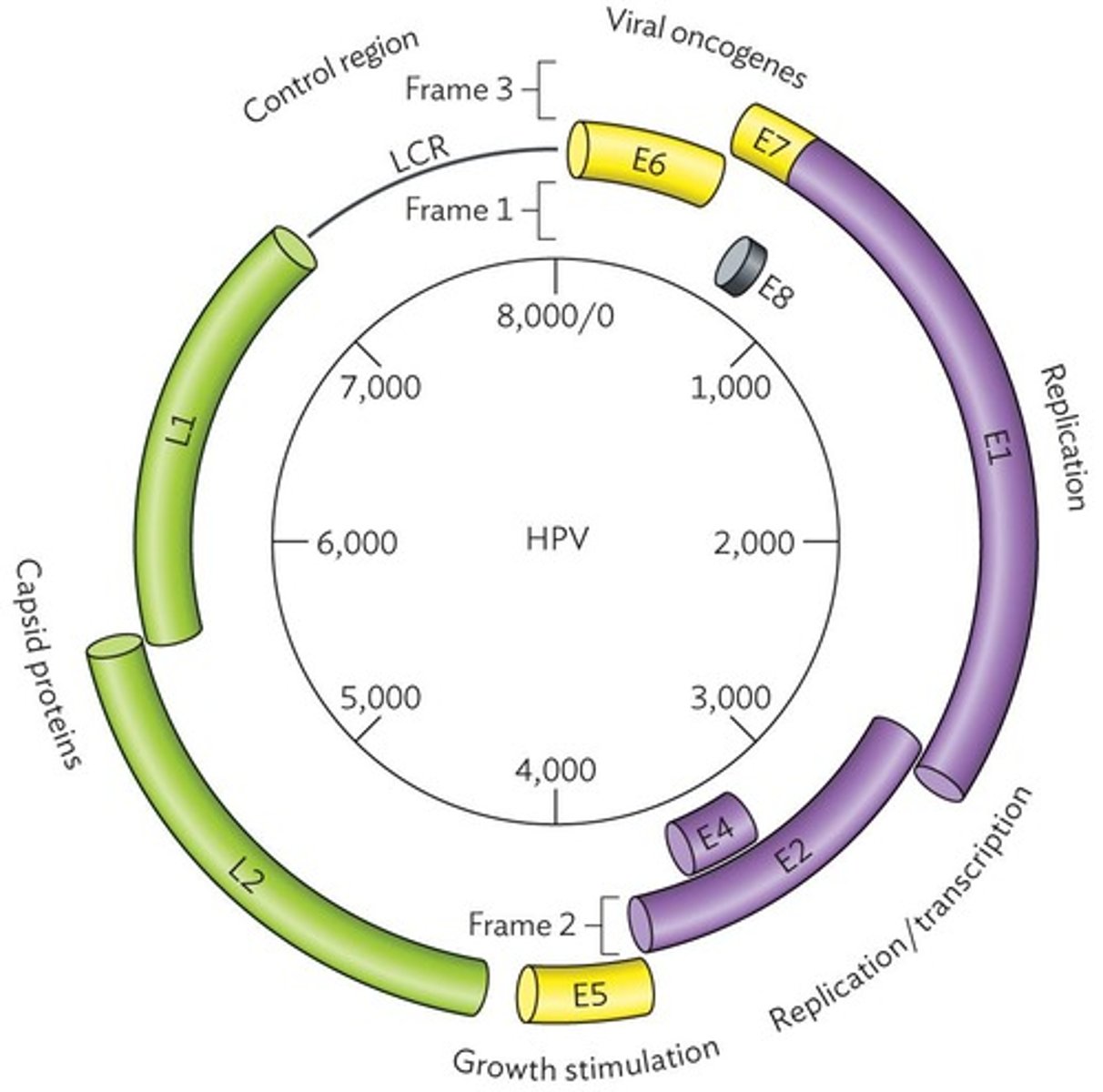
ds-DNA
Double-stranded DNA, circular structure.
Base pairs
8,000 base pairs encode eight genes.
Open reading frames
Multiple frames allow overlapping gene expression.
HPV integration
HPV integrates into host genome, causing cancer.
Oncogenes
Genes that promote cancer development.
Influenza A virus
Orthomyxovirus causing respiratory infections.
Antigenic drift
Minor mutations in envelope proteins.
Antigenic shift
Major genetic reassortment from different strains.
Virion structure
Asymmetrical, amorphous, no fixed capsid.
RNA segments
Eight segments required for influenza infection.
Hemagglutinin (HA)
Protein involved in virus entry into cells.
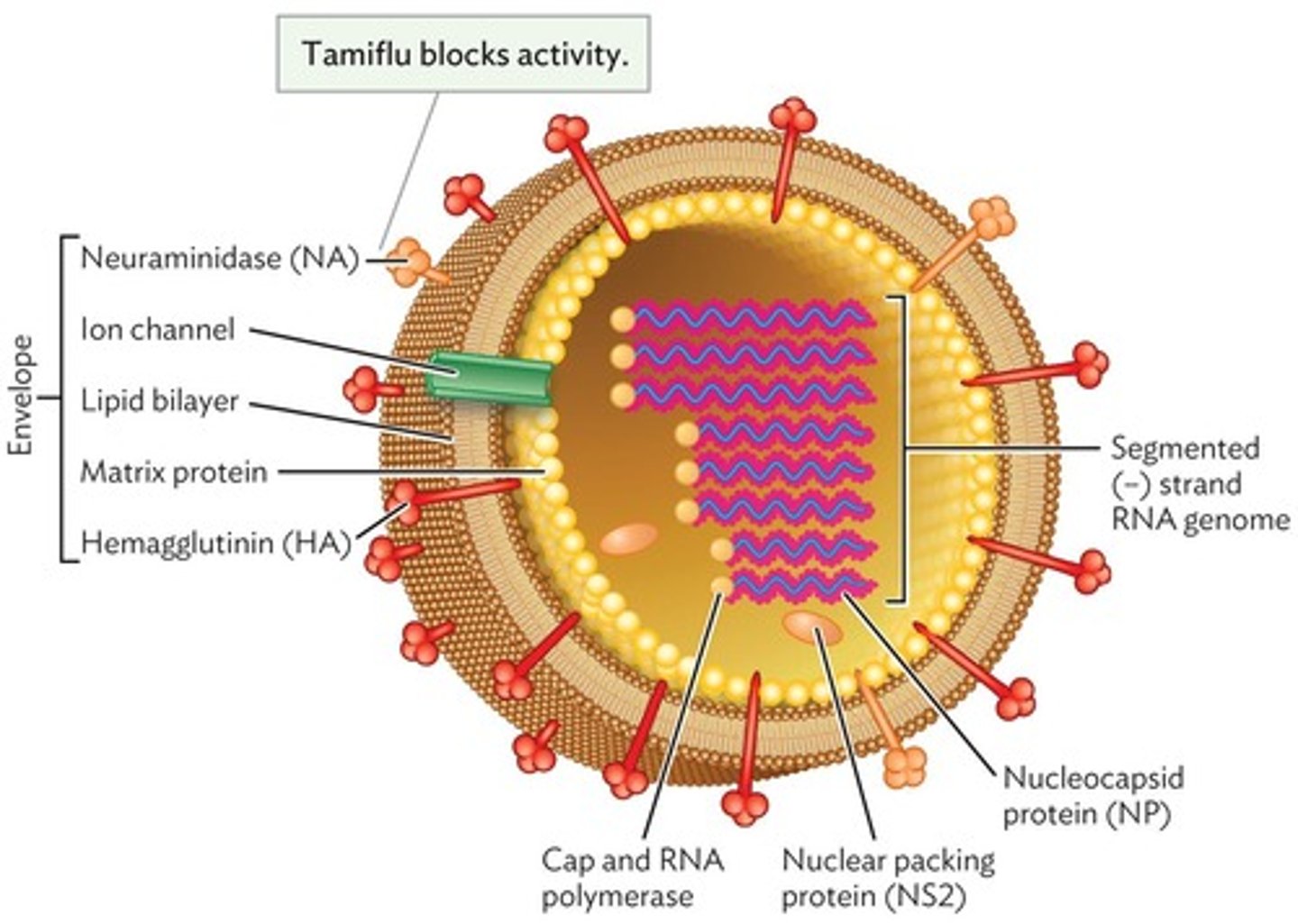
Neuraminidase (NA)
Protein facilitating viral release from host cells.
Defective particles
Majority of influenza particles are non-infectious.
Virion production
Infected cells can produce over 10,000 virions.
H5N1 avian influenza
Current outbreak affecting birds and potentially mammals.
Bird flu impact
Killed nearly 60 million birds in 49 states.
Influenza susceptibility
Elderly and young are most affected during epidemics.
Genome reassortment
Influenza maximizes gene mixing to evade immunity.
Influenza mortality
Causes approximately 36,000 deaths annually in the US.
Egg price increase
Average price rose $2.60 due to bird flu.
Virus transmission potential
Concerns about bird flu jumping to humans.
Pandemic
Widespread disease affecting global human population.
Influenza Virus Strain
Variant of virus causing flu, potentially zoonotic.
Avian H5N1 Flu
Bird flu strain with high human mortality rate.
Mortality Rate
Percentage of deaths in infected population.
1918 Influenza Pandemic
Deadly flu outbreak killing 20% of global population.
CDC Statistics
Data on disease prevalence and impact from CDC.
H5N1 Transmission
Spread occurs through contact with infected poultry.
HIV
Retrovirus causing acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS).
Lentivirus
Slow-progressing retrovirus affecting immune system.
Global HIV Prevalence
Approximately 33 million people living with HIV.
AIDS Mortality
3 million deaths annually due to AIDS.
Initial AIDS Case
First reported case in the US was 1981.
HIV Infection Rate
1 in 100 adults infected, equal among genders.
High-Risk Behavior
Includes unprotected sex and needle sharing.
CD4+ T Lymphocytes
White blood cells crucial for immune response.
Clinical Latency
Phase of slow T cell loss in HIV infection.
Opportunistic Infections
Infections taking advantage of weakened immune system.
HIV Structure
Includes capsid, envelope, and spike proteins.
Reverse Transcriptase
Enzyme converting viral RNA into DNA.
HIV Treatment
Combination of antiviral drugs to manage infection.
HIV Genome
Contains gag, pol, and env genes for replication.
gag Gene
Encodes capsid and matrix proteins in HIV.
pol Gene
Encodes reverse transcriptase and integrase enzymes.
env Gene
Encodes envelope proteins for HIV virion.