Biology EOC Test Study Guide: Key Concepts and Goals
1/412
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
413 Terms
Scientific Investigations
A systematic approach to understanding scientific inquiry through experiments and observations.
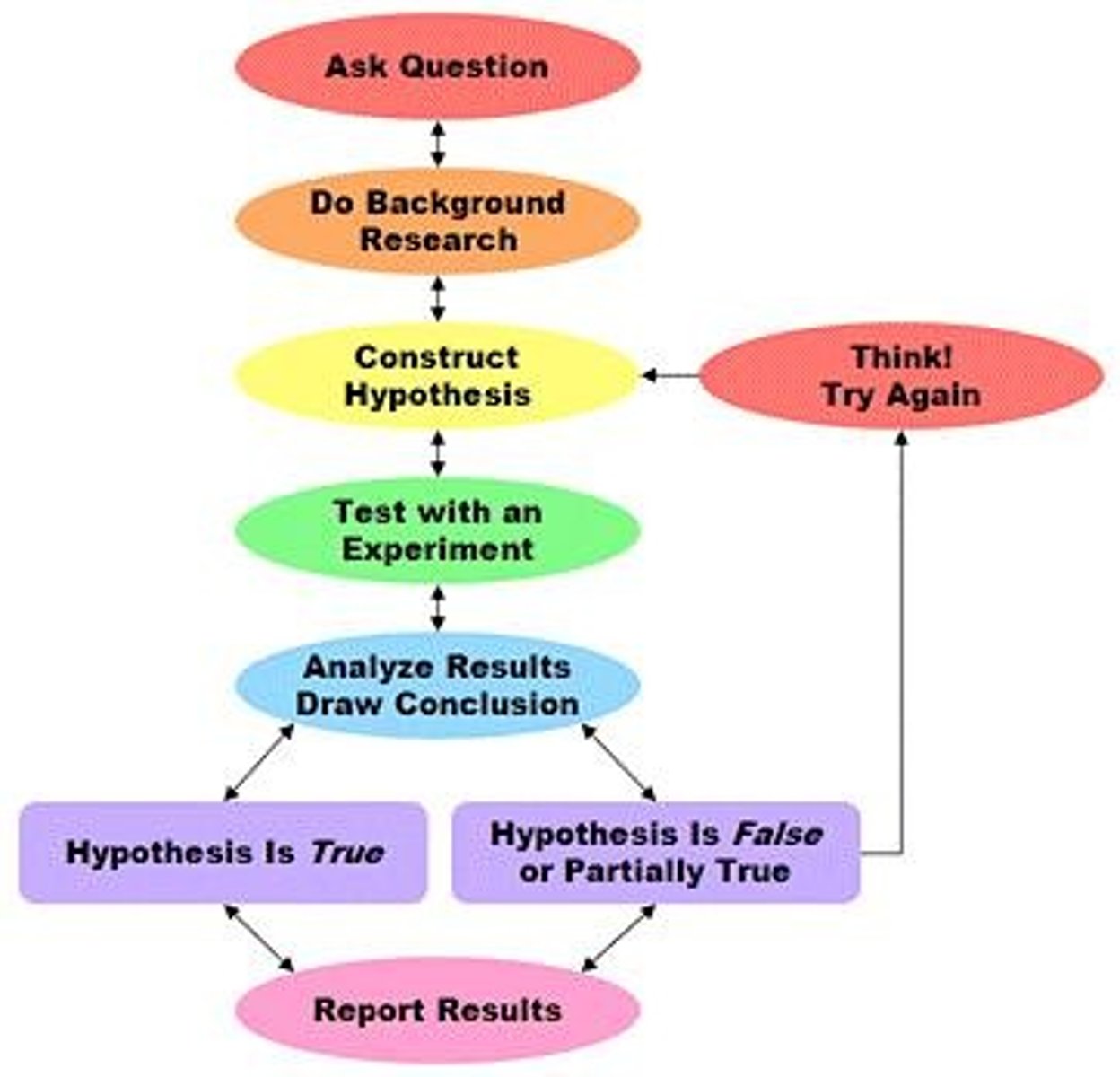
Hypothesis
Tentative explanation for an observation, phenomenon, or scientific problem that can be tested by further investigation.
Variable
To vary or change.
Independent Variable
A manipulated variable in an experiment or study whose presence or degree determines the change in the dependent variable.
Dependent Variable
The observed variable in an experiment or study whose changes are determined by the presence or degree of one or more independent variables.
Control
A standard against which other conditions can be compared in a scientific experiment.
Sources of Error in Experiments
Factors that can lead to inaccuracies in experimental results, including instrumental error, personal error, sampling error, replication error, experimental design, and measurement error.
Instrumental Error
Error due to lack of calibration of instruments.
Personal Error
Error due to inaccurate observations made by the researcher.
Sampling Error
Error that occurs when the sample size is too small or not random.
Replication Error
Error due to lack of consistency and accuracy in repeated experiments.
Basic Steps for an Experiment
1. Plan the research, 2. Design the experiment, 3. Summarize observations, 4. Reach consensus on observations, 5. Document and present results.
Types of Observations
Qualitative observations are described by words or terms, while quantitative observations are numerical values derived from counts or measurements.
Qualitative Observations
Described by words or terms rather than numbers, including subjective descriptions in terms of variables such as color, shape, and smell.
Quantitative Observations
Numerical values derived from counts or measurements of a variable, often requiring instruments for recording.
Organic Molecules
Organic compounds that contain carbon and are found in all living things.
Structure and Functions of Organic Molecules
Includes carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids.
Cell as a Living System
Refers to the cell's ability to maintain homeostasis, cellular transport, and energy use and release in biochemical reactions.
Bioenergetic Reactions
Include aerobic and anaerobic respiration and photosynthesis.
Structure and Function of Enzymes
Enzymes are crucial in biological systems for facilitating biochemical reactions.
Carbohydrates
Major source of energy and include sugars and starches.
Proteins
Nitrogen-containing compounds made up of chains of amino acids.
Lipids
Water-insoluble (fats and oils) made up of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen; composed of glycerol and fatty acid.
Nucleic Acids
Direct the instruction of proteins and contain genetic information an organism receives from its parents.
Unicellular
Organism that exists as a singular, independent cell.
Multicellular
Organism that exists as specialized groups of cells organized into tissues that perform the same function.
Chloroplast
Capture solar energy for photosynthesis (plant cells, some algae).
Golgi Body
Package, distribute products.
Lysosomes
Digest excess products and food particles.
Mitochondria
Transform energy through respiration.
Nucleus
Contains DNA which controls cellular activities.
Ribosome
Produce proteins.
Vacuole
Store substances.
Cell (plasma) membrane
Phospholipid bilayer that protects and encloses the cell; controls transport; maintains homeostasis.
Prokaryote
Has nuclear material in the center of the cell, but is not enclosed by a nuclear membrane; no membrane-bound organelles; found in bacteria and blue-green bacteria.
Eukaryote
Contain a clearly defined nucleus enclosed by a nuclear membrane and membrane-bound organelles; found in plants, animals, fungi, and protists.
Cell wall
Rigid second layer that protects and encloses the cell (plant cells and some bacteria).
Cytoplasm
Fluid-like substance that contains various membrane-bound structures (organelles) that perform various functions.
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Site of chemical reactions; ROUGH contains ribosomes, SMOOTH is for lipid production.
Cytoskeleton
Provides internal structure; includes microfilaments (fibers) and microtubules (cylinders).
Passive Transport
Movement of substances across the plasma membrane without the use of the cell's energy (with the concentration gradient).
Diffusion
Movement of substances across the plasma membrane from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
Osmosis
Diffusion of water across the plasma membrane from areas of high concentration to areas of lower concentration.
Facilitated Transport
A carrier molecule embedded in the plasma membrane transports a substance across the plasma membrane following the high-to-low concentration gradient.
Active Transport
Movement of substances across the plasma membrane that requires the use of the cell's energy and carrier molecules; substances are moving from an area of low concentration to an area of higher concentration (against the concentration gradient).
Endocytosis
Large particles are brought into the cell.
EXOCYTOSIS
large particles leave the cell
HOMEOSTASIS
internal equilibrium; the plasma membrane regulates what enters and leaves the cell; a selectively permeable membrane only allows certain substances to pass through
HYPOTONIC
water moves in; cell bursts
HYPERTONIC
water moves out; cell shrivels
ISOTONIC
no net movement; cell maintains equilibrium
HOMEOSTASIS (self-regulating mechanism)
Self-regulating mechanism that maintains internal conditions (with individual cells and within organs, systems)
Example of HOMEOSTASIS
body temperature, respiration, nutritional balance, etc.
Cell Communication
Cells communicate their needs to each other mainly through their cell membranes by releasing chemical messengers
Hypothalamus Role in Homeostasis
The hypothalamus sends neural and chemical signals to other glands, tissues, organs, and organ systems to adjust the internal environment.
Changing Internal Environment
Homeostasis needs to change along with our activities, both day and night.
Process of Homeostasis
This constantly changing internal environment is the process of homeostasis.
Negative Feedback
Glucose / Insulin levels in cells
Positive Feedback
Blood platelets / Blood clotting
Biochemical Reactions
Chemical bonds are formed and broken within living things creating chemical reactions that impact the ability to maintain life and carry out life functions.
Cellular Respiration
Food molecules are converted to energy; there are three stages to cellular respiration; the first stage is called glycolysis and is anaerobic (no oxygen is required); the next two stages are called the citric acid cycle and the electron transport chain and are aerobic (oxygen is required).
Cellular Respiration Equation
C6H12O6 + 6O2 ⇒ 6CO2 + 6H2O + ENERGY (36 ATP)
Photosynthesis
Plant cells capture energy from the Sun and convert it into food (carbohydrates); plant cells then convert the carbohydrates into energy during cellular respiration.
Photosynthesis Equation
6CO2 + 6H2O + ENERGY(from sunlight) ⇒ C6H12O6 + 6O2
ATP
ATP is a molecule that stores and releases the energy in its bonds when the cell needs it; removing a phosphate group (P) releases energy for chemical reactions to occur in the cell and ATP becomes ADP.
ATP Reaction
ATP ⇔ ADP + P + ENERGY
Fermentation
When cells are not provided with oxygen in a timely manner, this process occurs to continue producing ATP until oxygen is available again; glucose is broken down; there are two types of fermentation.
Lactic Acid Fermentation
Glucose ⇒ Lactic Acid + 2ATP
Alcoholic Fermentation
Glucose ⇒ CO2 + Alcohol + 2ATP
Aerobic Respiration
Requires the presence of oxygen; release of energy from the breakdown of glucose (or another organic compound) in the presence of oxygen; energy released is used to make ATP, which provides energy for bodily processes; takes place in almost all living things.
Anaerobic Respiration
Occurs in the absence of oxygen; breakdown of food substances in the absence of oxygen with the production of a small amount of energy; produces less energy than aerobic respiration; often called fermentation; seen as an adaptation for organisms that live in environments that lack oxygen.
Comparison of Cellular Respiration, Photosynthesis and Chemosynthesis
Cellular Respiration: Food Broken Down, Energy from Glucose Released, Carbon Dioxide given off, Oxygen taken in, Produces Carbon Dioxide and Water, Does not require Light, Occurs in ALL Living Cells, Organisms often called Heterotrophs.
Photosynthesis
Food Synthesized, Energy from Sun stored in Glucose, Carbon Dioxide taken in, Oxygen given off, Produces Sugars (Glucose) from PGAL, Requires Light, Occurs only in presence of Chlorophyll, Organisms called Autotrophs.
Chemosynthesis
Food Synthesized, Energy from Methane or Inorganic Material (ex: H gas or Hydrogen sulfide), Organisms often called chemotrophs, Organisms called extremophiles, Live in environments without oxygen, Anaerobic Bacteria, Habitats: hydrothermal vents.
Enzymes
Enzymes are special proteins that regulate nearly every biochemical reaction in the cell. Different reactions require different enzymes.
Functions of Enzymes
Provide energy to cells, Build new cells, Aid in digestion, Break down complex molecules ("substrate" = reactant), Catalysts (speed up chemical reactions without being used up or altered).
Factors Affecting Enzymes
pH, temperature, and quantity.
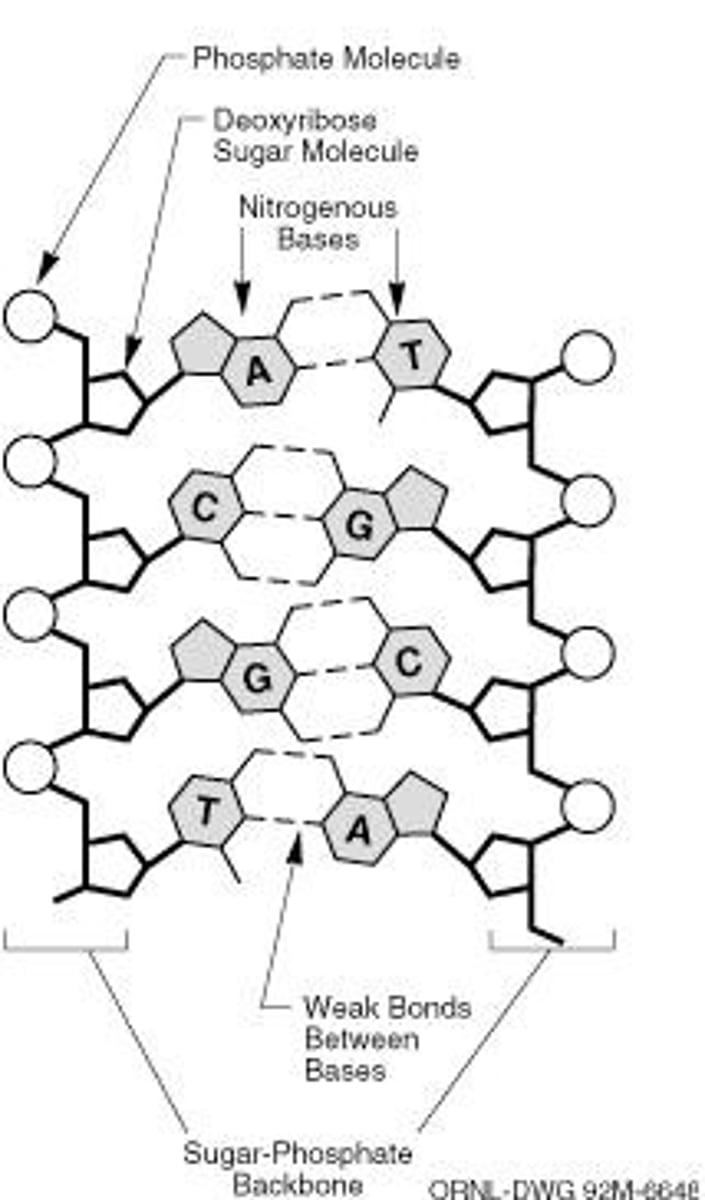
Molecular Basis of Heredity
The study of how genetic information is transmitted from one generation to the next.
DNA Replication
The process by which DNA makes a copy of itself before cell division.
Protein Synthesis
The process by which cells generate new proteins, involving transcription and translation.
Transcription
The process of copying a segment of DNA into RNA.
Translation
The process of translating the sequence of an mRNA molecule to a sequence of amino acids during protein synthesis.
Gene Regulation
The mechanisms that control the expression of genes.
Sexual Reproduction
A mode of reproduction that involves the fusion of haploid sex cells from two parents.
Asexual Reproduction
A mode of reproduction where a single parent produces one or more identical offspring.
Patterns of Inheritance
The ways in which traits are passed from parents to offspring.
Dominant Traits
Traits that are expressed in the phenotype even when only one copy of the allele is present.
Recessive Traits
Traits that are expressed in the phenotype only when two copies of the allele are present.
Intermediate Traits
Traits that are expressed as a blend of the two alleles present.
Multiple Alleles
A situation in which three or more alleles exist for a particular gene.
Polygenic Inheritance
A type of inheritance where multiple genes determine the phenotype of a trait.
Sex-Linked Traits
Traits that are associated with genes located on sex chromosomes.
Independent Assortment
The principle that alleles for different traits are distributed to sex cells (& offspring) independently of one another.
Test Cross
A genetic cross between a homozygous recessive individual and an individual with an unknown genotype.
Pedigrees
A diagram that shows the occurrence of a genetic trait in several generations of a family.
Punnett Squares
A diagram used to predict the outcome of a genetic cross.
Human Genome Project
An international scientific research project aimed at mapping all the genes of the human genome.
Applications of Biotechnology
The use of biological processes, organisms, or systems to develop products and technologies.
Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection
The theory that species evolve over time through the process of natural selection.
Fossil Evidence
Physical remains of organisms from the past that provide evidence for evolution.