Animal Health and Disease Exam 3
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
The modified live virus vaccine against Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus is:
Ideal for calves since it stimulates a strong immune response even with one dose, but NOT for cows since it can induce abortions or cause chronic infection on the fetus
The adjuvant Alum enhances Th17 responses
false
Adjuvant
a substance added to a vaccine which enhances the immune response to an antigen via mimicking PAMPs to trigger and train the immune system
Category III vaccines are:
Live recombinant organism
Category I vaccine
antigens generated by gene cloning, LIMITATION: requires 1000x more antigen to match protection of killed virus vaccine, pure proteins are often poor immunogens, may not be properly folded, not effectively delivered to antigen presenting cells
process of gene cloning
This process involves isolating the DNA coding for an antigen from a pathogen, then inserting this DNA into a bacterium or yeast to express a protein. This recombinant protein is produced in large quantities, generating antigens.
mosaic vaccine
This type of vaccine combines multiple key epitopes into a single, artificial protein. It is designed to stimulate a stronger, broader immune response than gene cloning
category II vaccine
a type of vaccine in which molecular genetic techniques allow for gene editing of an organism to make it irreversibly attenuated (VIRULENC GENE IS REMOVED)
attenuation
weakening a pathogenic organism by removing its virulence factor
live recombinant organism
category III vaccine: genes coding for protein antigens are clined into live recombinant organisms used as vaccine vectors. The LIVE VECTOR ORGANISM (not purified protein) is used to immunize. ADVANTAGES: no reversion to virulence, safe across species, strong immunity without risk of disease.
category IV vaccines
nucleic acid vaccines
traits of nucleic acid vaccines
category IV, an increasingly popular method of vaccination involving injection (NOT of protien antigen) of PURE DNA or RNA that encode vaccine antigens. These are (technically) NOT vaccines, they turn an animal’s cells into vaccine FACTORIES that produce large amounts of viral antigens. MUST be delivered directly into animals cells. Once inside the cytoplasm, the RNA is released and efficiently translated into a protein that is processed and expressed on the cell surface.
depot adjuvants
a type of adjuvant characterized by removal of antigen, prolonged immune response
particulate adjuvants
a type of adjuvant which leads to enhanced antigen presentation, enhanced cytokine production by antigen-presenting cells, enhanced Th cell responses and enhanced cell-mediated immunity
immunostimulatory adjuvants
a type of adjuvant which stimulates TLRs (toll-like receptors), enhances cytokine production by antigen-presenting cells, enhanced Th cell responses and enhanced antibody production/cell-mediated immunity
Category I vaccines are:
antigen generated by gene cloning
In mRNA vaccines, the RNA is commonly delivered within stable lipid nanoparticles that are endocytosed by dendritic cells and macrophages once injected.
true
Nucleic acid vaccines work by delivering genetic material—such as mRNA—that encodes a pathogen-derived protein, which the host cells then produce to stimulate an immune response.
true
The adjuvant Alum promotes antigen processing and presentation, and promotes DC homing to the lymph nodes:
true
Some characteristics of passive immunization are:
produces temporary immunity by transferring antibodies from a resistant to a susceptible animal
Self-replicating mRNA vaccines include genetic instructions not only for the antigen of interest but also for a replicase enzyme, allowing the mRNA to amplify itself inside host cells and enhance antigen expression.
true
Adjuvants are used to maximize the effectiveness of vaccines, and are specially important in killed vaccines
true
What viruses need to enter the host cell
A receptor that is normally host specific
Antibody mediated immunity is more important than cell mediated immunity to fight viral infections
false
cell-mediated immunity
a type of the adaptive immune system which mainly operates intracellularly, involving T cells directly attacking infected cells or activating other immune cells
antibody-mediated (humoral) immunity
a type of the adaptive immune system which mainly operates extracellularly and relies on antibodies produced by B cells to neutralize pathogens or mark them for destruction
which of the following is a function of interferons
signal neighboring cells to put up barriers
what is the “S phase”
A phase in the host cell cycles that the virus uses to replicate by forcing the host cell to enter S phase and gain access to DNA polymerases
Type II Interferons like Interferon gamma are produced exclusively by epithelial cells
false
what is ADCC
antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity
Intermediate adapted viruses
Require new vaccines frequently due to its antigenic variation.
Which of the following is the correct step order of a DNA virus replication:
Infectious virus DNA —> new viral DNA —> viral RNA —> viral protein —> virus assembly
Antibodies can prevent invasion of a virus by:
Blocking the adsorption of virions to target cell, Stimulating virus phagocytosis, Triggering complement activation to lyse viruses
Type I Interferons like Interferon alpha and beta are produced by most nucleated cells
true
type I interferon
this type of interferon is primarily produced by leukocytes and fibroblasts infected with viruses and involved types alpha, beta and gamma
type II interferon
this type of interferon is produced by T-cells and natural killer cells
What is antibody dependent enhancement in the context on viral infections?
A mechanism use by viruses to gain access to immune cells and remain undetected by the immune system
What mechanisms of immune evasion does viruses have?
Block interferon activity, Interfere with MHC loading to cell surface and reduce antigen presentation, Promote immunodeficiencies in T cells reducing cell mediated immunity
Allergies largely result from inappropriate humoral immune responses that result in IgE production leading to aggressive inflammatory responses to allergens.
true
What are virulence factors in bacterial pathogens
Bacterial genes in highly evolved bacterial pathogens that encode proteins that help with host infection
Unlike bacteria, parasites are more complex prokaryotes
False
What type of organism are parasites? (prokaryote or eukaryote)
eukaryote
Malaria can use decoy antigens to trick the immune system into building a memory response against proteins that are not essential for malaria parasite survival
True
Parasites are more complex organisms than virus and bacteria, and have evolved sophisticated mechanisms to evade the immune system such as:
Hide inside cells that don't express MHCI, Antigenic variation by changing the proteins they express in cell surface, Migrate between tissues at different stages of their cycle
Cell mediate immune responses are usually not very effective in controlling viral infections
false
Antibodies may aid in killing infected cells using complement or antibody-dependent cell–mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC)
true
antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC)
A process where immune cells kill target cells that have been coated with antibodies
Cytotoxic T cells driven immune responses are only important for extracellular bacterial infections
false
Why is the S Phase important for DNA virus replication?
Many DNA viruses rely on the host’s DNA replication machinery (DNA polymerase, dNTPs, replication factors) — can FORCE a host cell into S phase to access cellular enzymes that replicate DNA
What is the difference between DNA and RNA viruses?
RNA viruses do not need to use the host’s DNA during replication. Instead, they replicate their genomes ENTIRELY in the cytoplasm
antigenic variation
the ability of viruses to change their surface proteins (antigens) over time (multiple mutations permit the generation of many closely related but DISTINCT viruses that “evade” previously formed memory immune responses (think, different variations of the flu each year))
Pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) (Innate immune responses to bacteria)
Receptors like TLRs, and NOD-like receptors, recognize conserved bacterial molecules (e.g., LPS,
peptidoglycan, flagellin)
•Trigger cytokine release, inflammation, and recruitment of immune cells
types of Phagocytic cells (Innate immune responses to bacteria)
Neutrophils & Macrophages, rapidly engulf and destroy bacteria through Phagocytosis, and
Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species (ROS/RNS)
complement system (Innate immune responses to bacteria)
Tags bacteria with C3b for phagocytosis (opsonization)
•Forms membrane attack complex (MAC) to lyse Gram-negative bacteria
•Releases C3a and C5a, which promote inflammation and recruit leukocytes
What B cell type degranulates and expulses parasites?
IgE
Why does IgE react to parasites?
Helminths are too large for phagocytosis
How does IgE deal with parasites?
Immune system shifts toward IgE-mediated degranulation and expulsion (NOT destruction), IgE binds to FceRI receptors on mast cells, basophils and eosinophils. Cross-linking by helminth antigens triggers rapid release of granules —> worm damage and expulsion
What does IgE arm mast cells and basophils to do with parasites?
release proteases that degrade epithelial tight junctions, increase fluid efflux and intestinal permeability, secrete histaming, chitinases, and leukotrienes
parasite methods of immune evasion
antigenic variation (switching expression of surface protein), sequestration (hiding from immune surveillance, adherence to vascular endothelium in tissues) ((MALARIA)), avoiding antibody and complement via LIVER STAGE (sporozoites invade hepatocytes and replicate undetected) and BLOOD STAGE (merezoites reside within RBCs which LACK MHC I), also immune modulation (dampening hosts responses by inducing IL-10 and TGF-B which suppress proinflammatory cytokines and inhibit Th1 and cytotoxic responses
active immunization
involves administering antigen to an animal so that it responds by mounting an adaptive OR immune response. Reimmunization or exposure to infection in the same animal will result in a secondary response and greatly enhanced immunity. The disadvantage is that protection is not conferred immediately. However, once established, active immunity is long-lasting
traits of modified live viruses
infect host cells and undergo replication, the infected cells then process the endogenous antigen, and viruses trigger a type 1 immune response dominated by CD8+ cytotoxic T cells. While proactive, this approach may be hazardous since vaccine viruses themselves cause sickness or persistent infection
Category I vaccines
Vaccines that contain inactivated recombinant organisms or purified antigens derived from recombinant organisms (require MUCH more antigen to match protection of killed virus vaccine)
Category II vaccines
Vaccines containing live organisms that contain gene deletions or heterologous marker genes
traits of Category III vaccines
Vaccines that contain live expression vectors expressing heterologous genes for
immunizing antigens or other stimulants
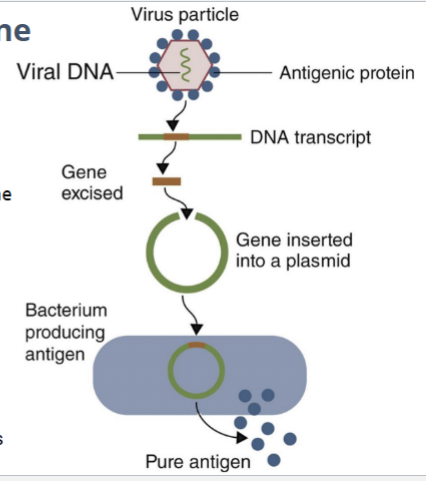
Which category of vaccine does this image represent?
Category I
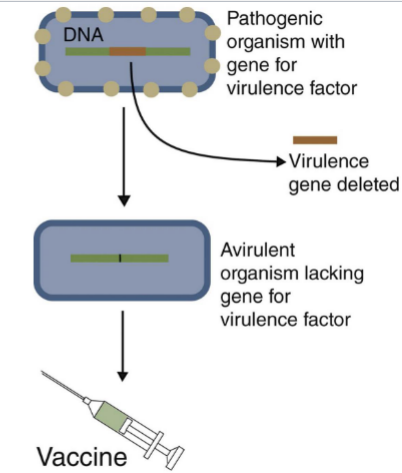
Which category of vaccine does this image represent?
Category II
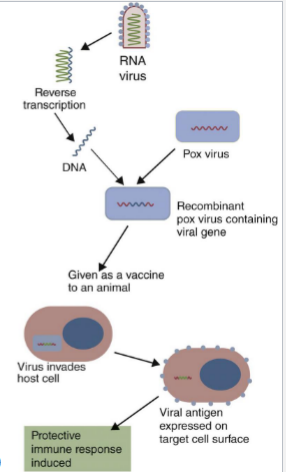
Which category of vaccine does this image represent?
Category III
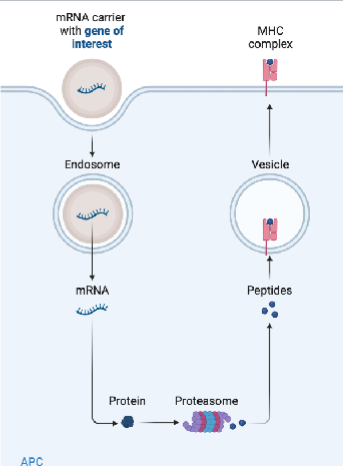
Which category of vaccine does this image represent?
Category IV
Category I
Antigens generated by gene cloning
Category II
Genetically attenuated organisms
Category III
Live recombinant organisms
Category IV
Nucleic acid vaccines