Mitosis, Cell Cycle and mitosis
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Mitosis
A type of cell division that results in two daughter cells each having the same number and kind of chromosomes as the parent nucleus. Final product is 2 cells that are exactly like the parent cell. (PMAT)
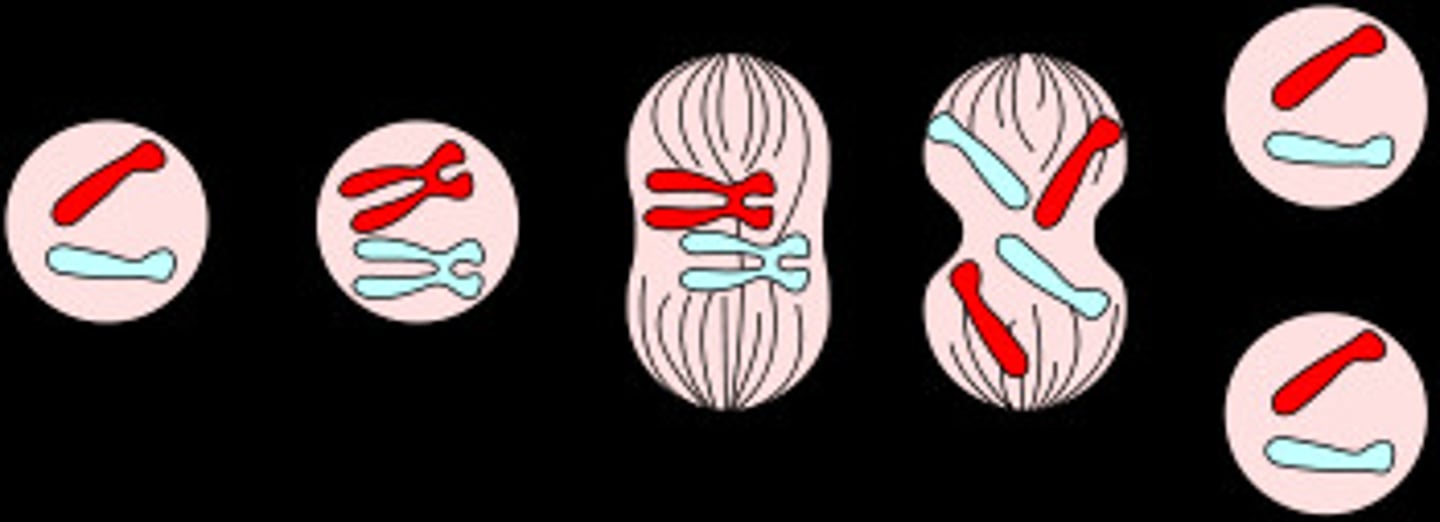
prophase
Chromosomes become visible, nuclear membrane dissolves, spindle fibers forms

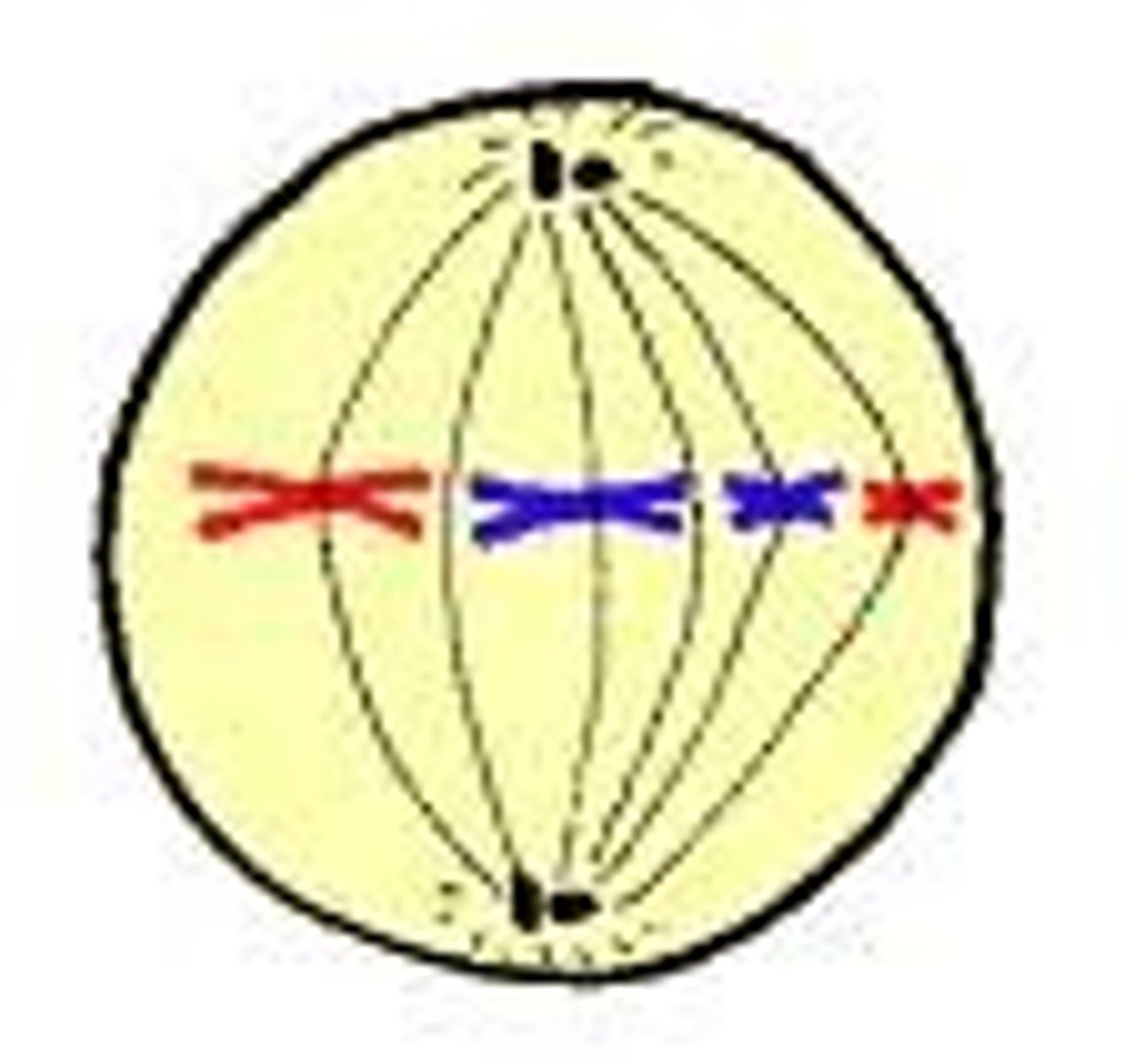
metaphase
Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
anaphase
Phase of mitosis in which the chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell
telophase
Phase of mitosis in which a nuclear membrane reforms around each new set of chromosomes.
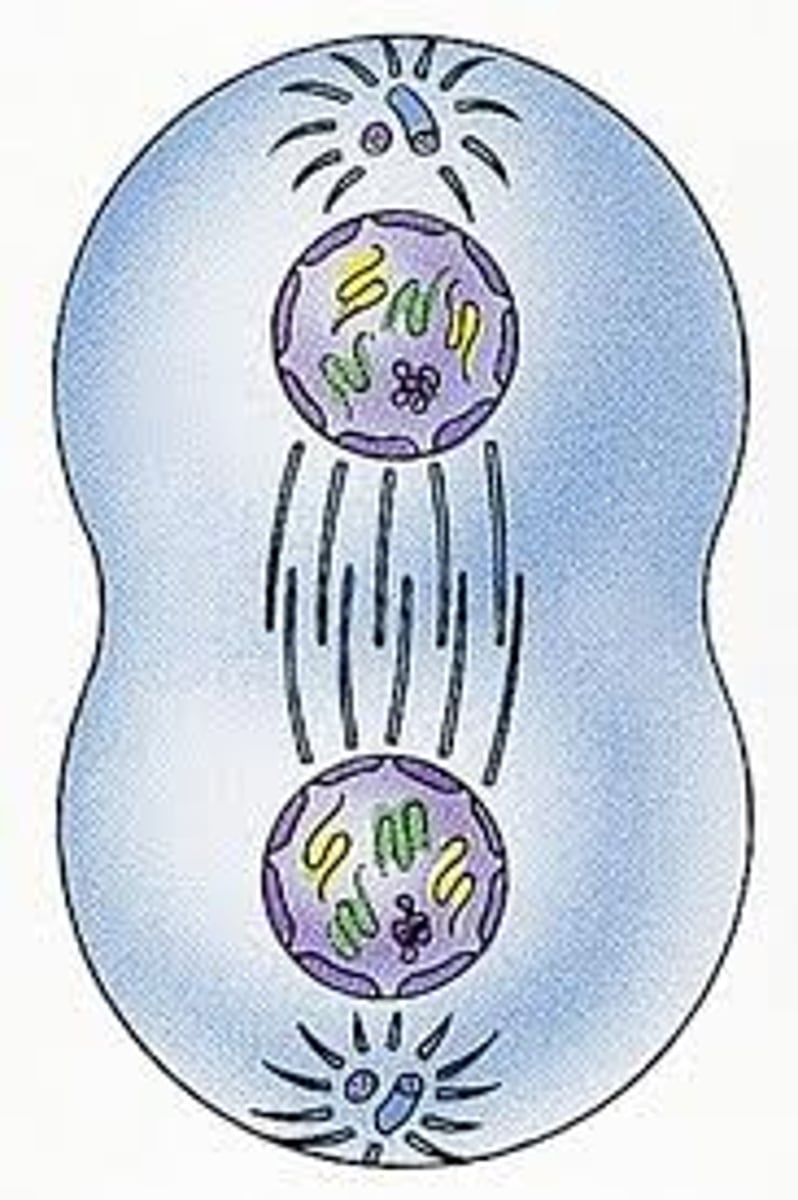
cytokinesis
Division of the cytoplasm during cell division
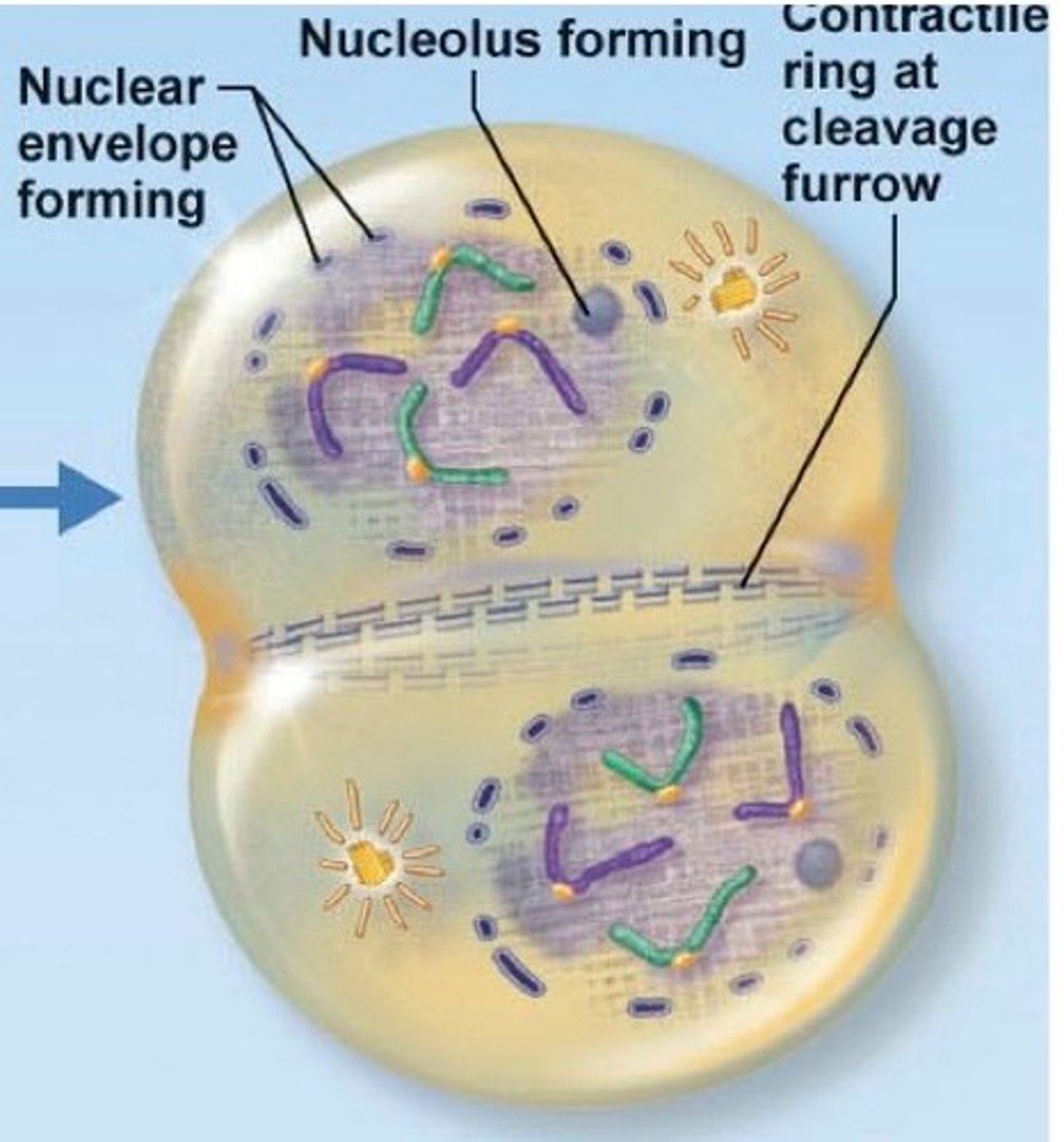
interphase
A period of time in between mitosis during which a cell grows and copies its DNA,
Cell spend most of its time in this phase.
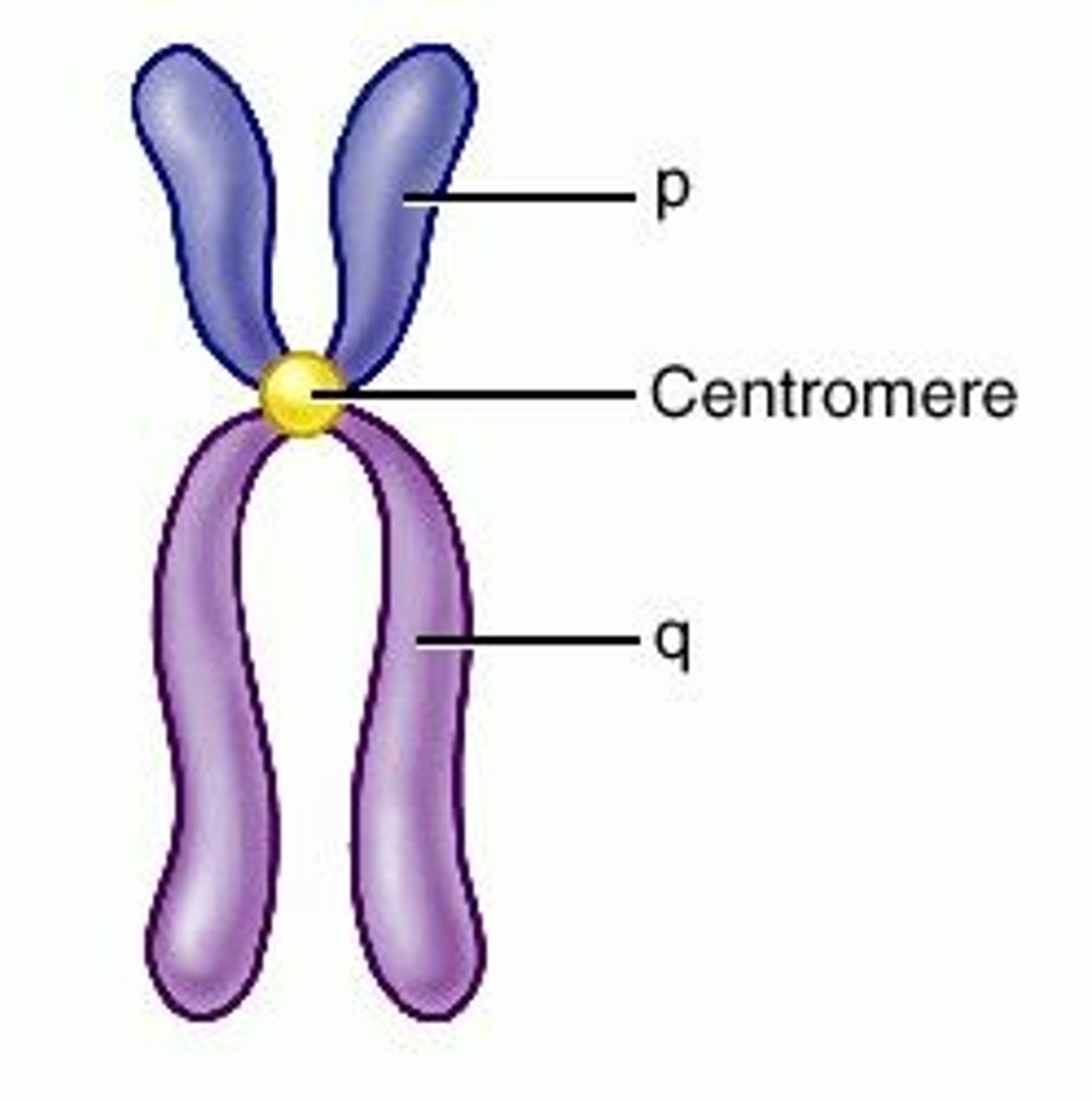
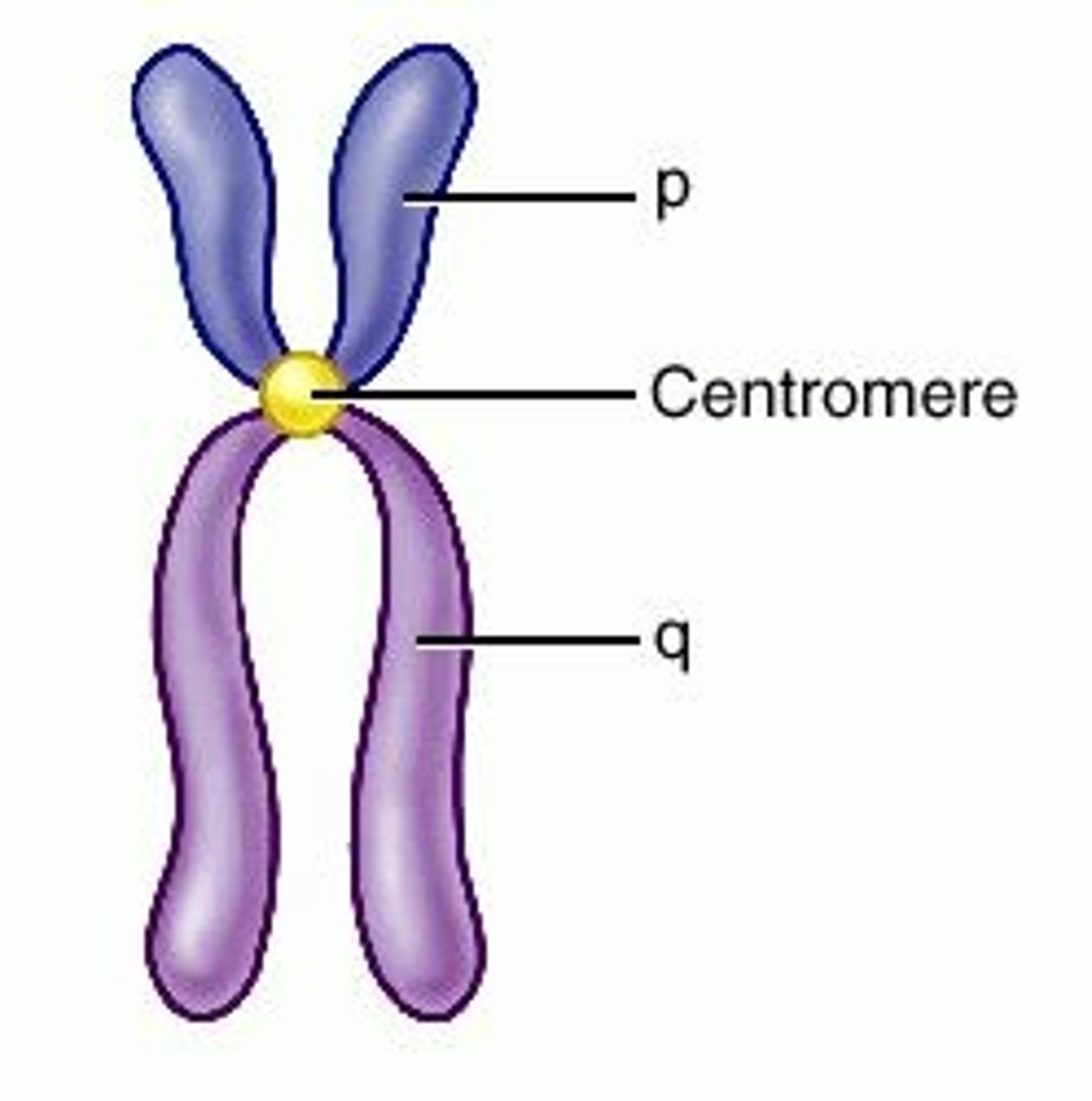
centromere
Area where the chromatids of a chromosome are attached
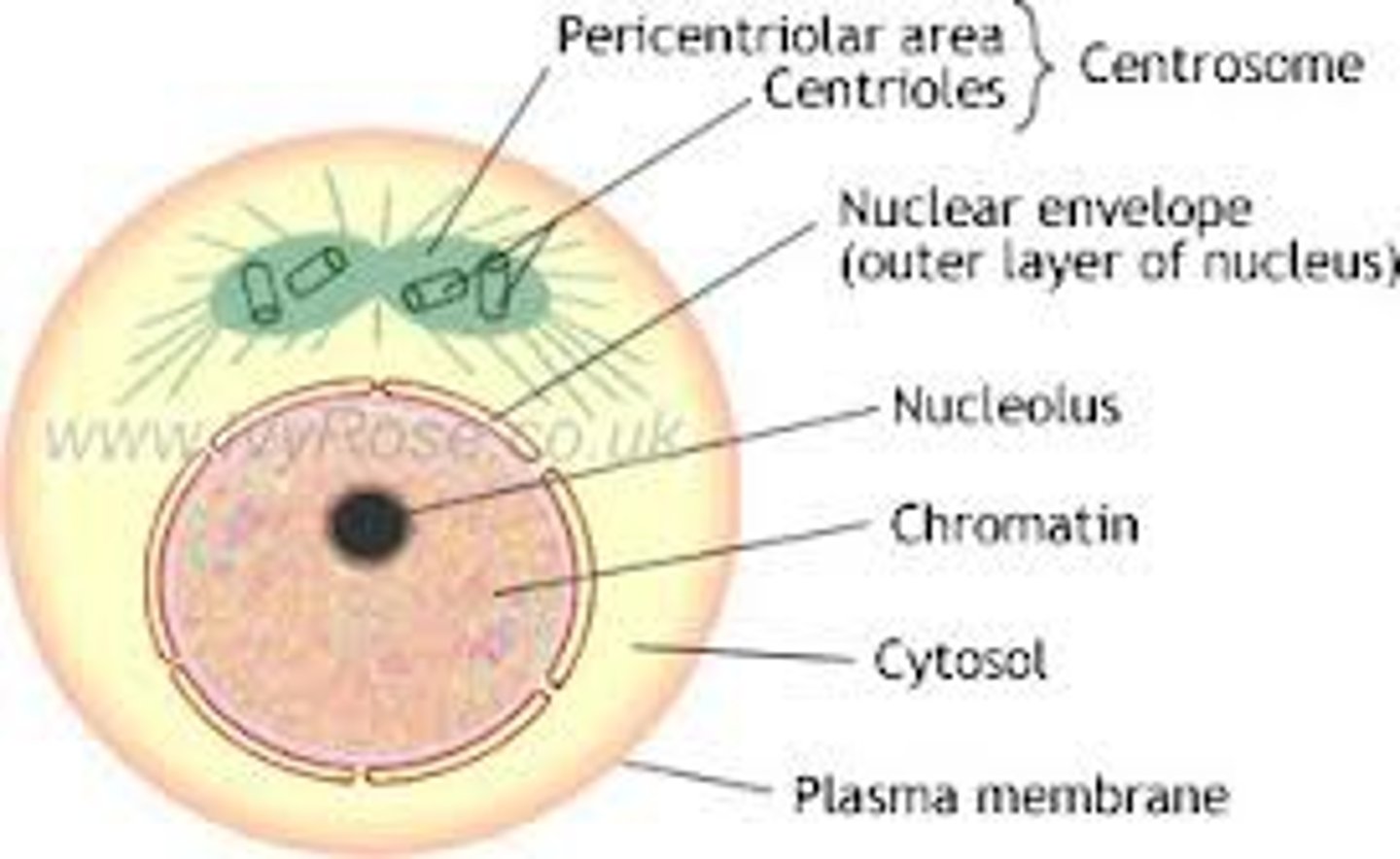
centriole
Cell organelle that aids in cell division in animal cells only by producing spindle fibers.
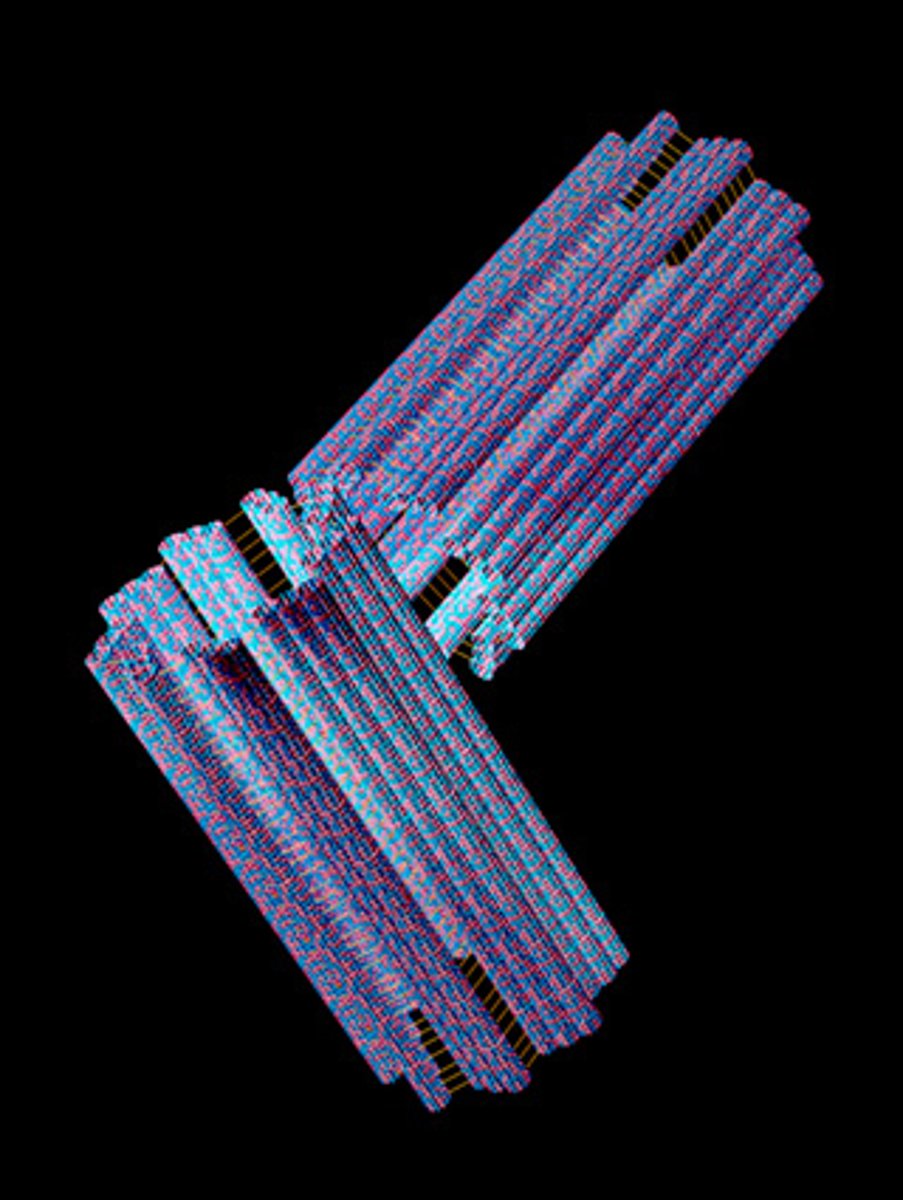
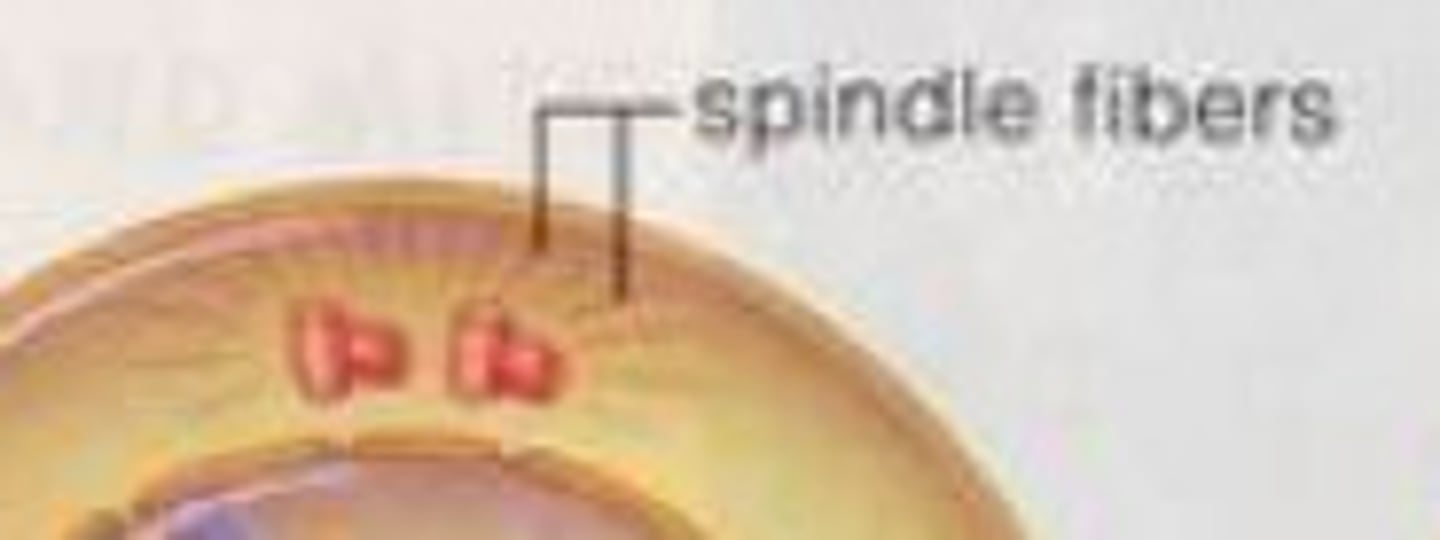
spindle fibers
Helps move chromosomes around the cell and pull apart the cell during replication and are made up of microtubules.
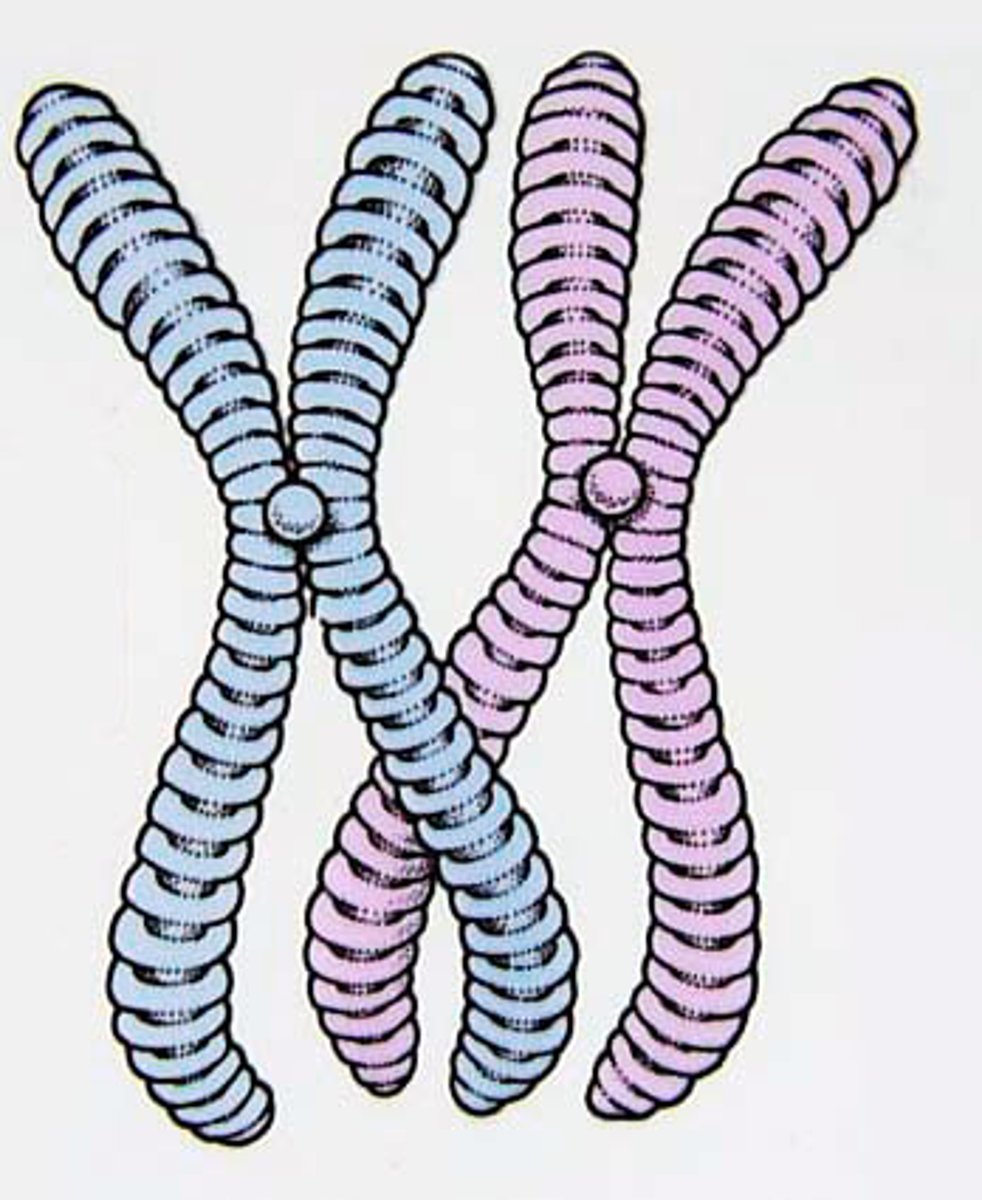
chromosome
A threadlike, gene-carrying structure found in the nucleus. Each chromosome consists of one very long DNA molecule and associated proteins.
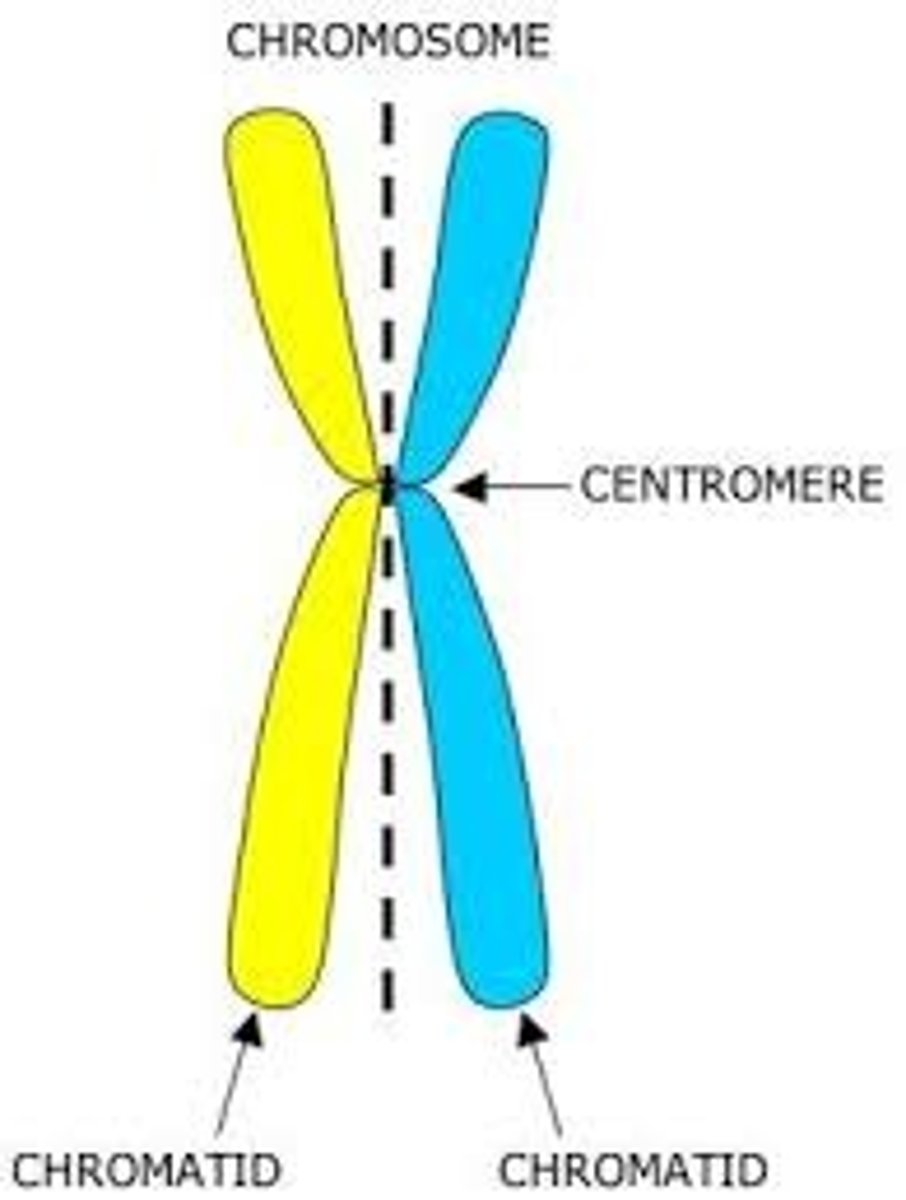
chromatid
one of two identical "sister" parts of a duplicated chromosome
Cell cycle
A regulated, continuous sequence of preparation (interphase) and division (mitosis) in a cell
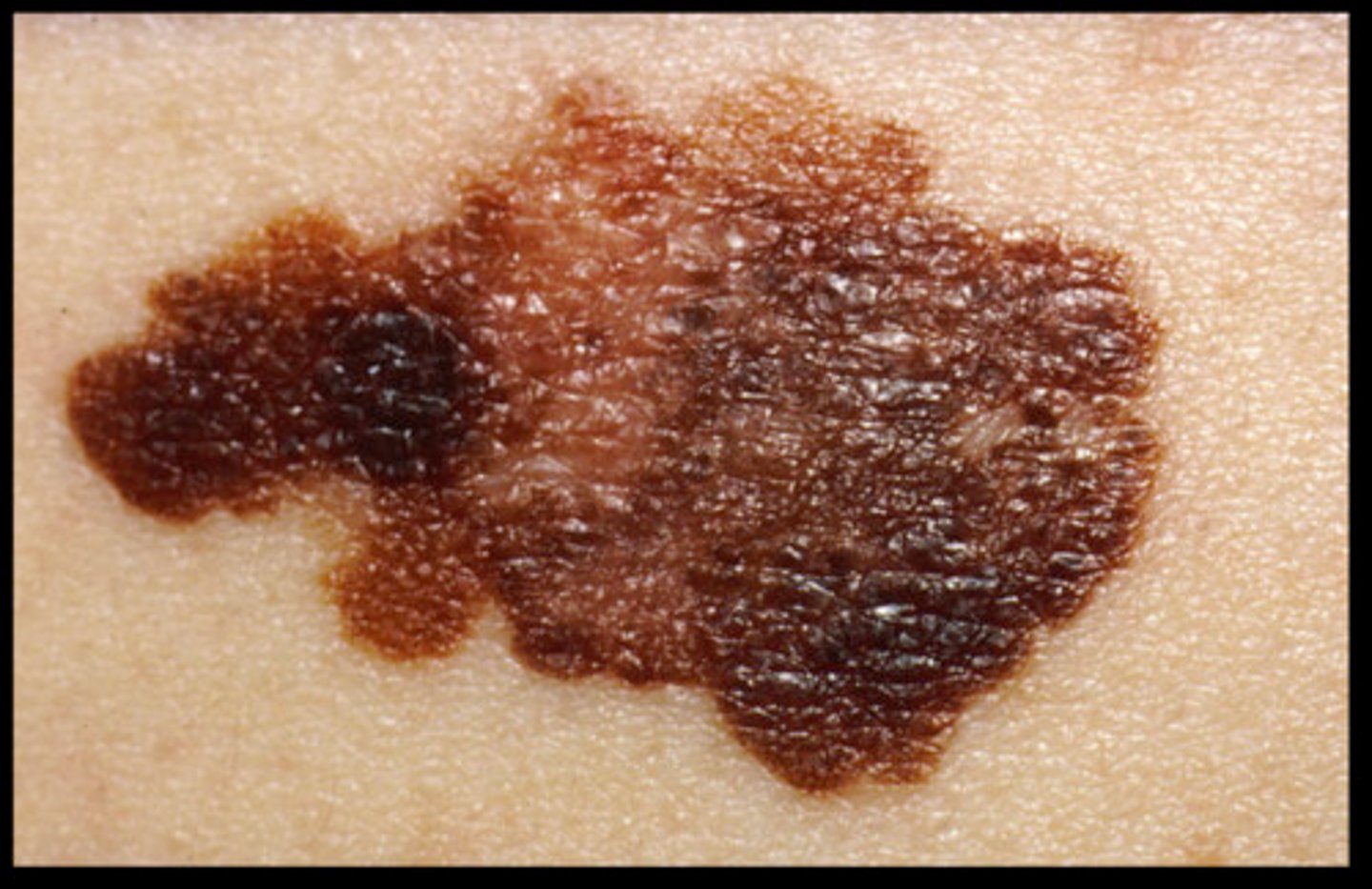
Cancer
Malignant growth or tumor caused by abnormal and uncontrolled cell division.
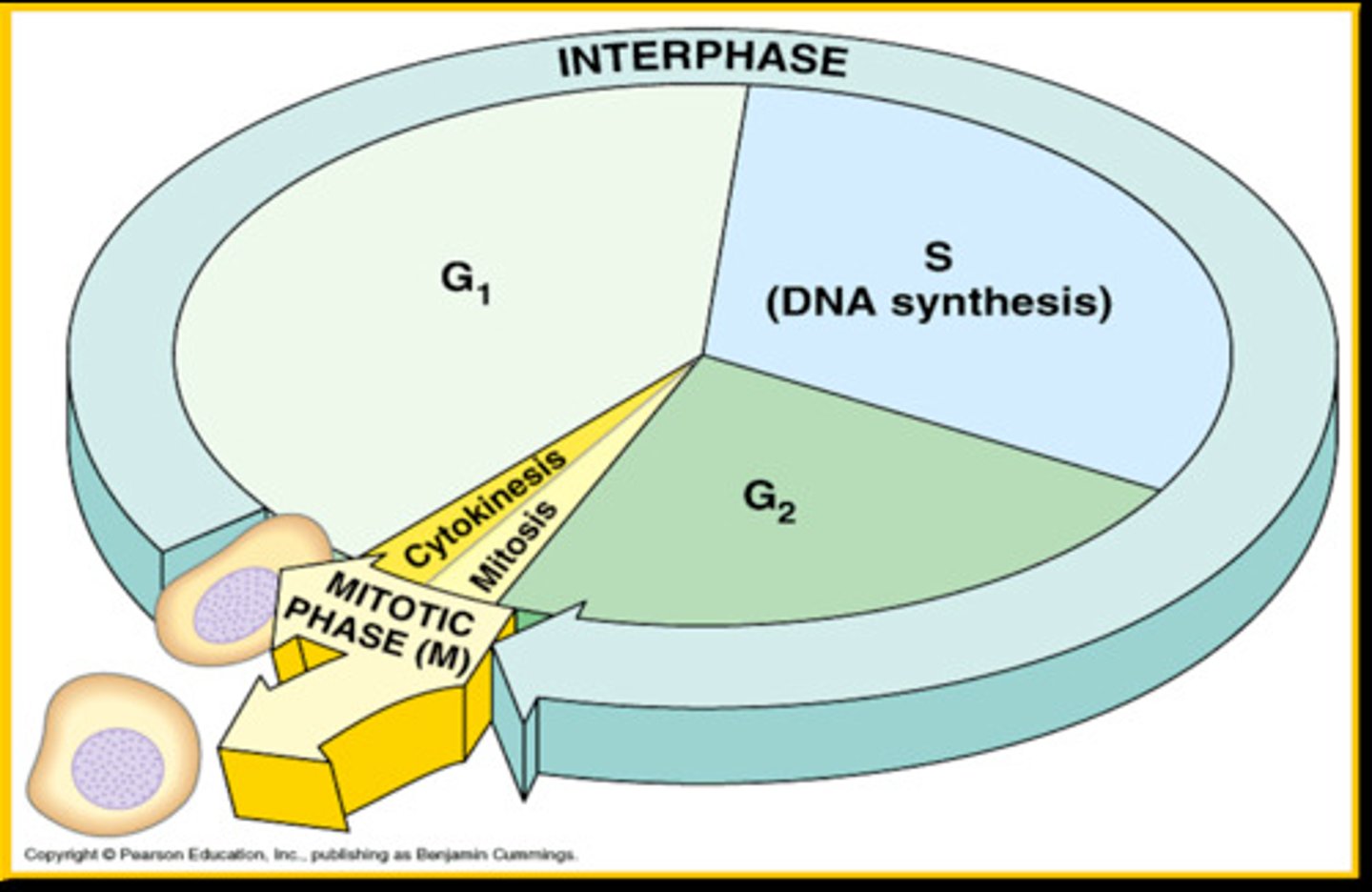
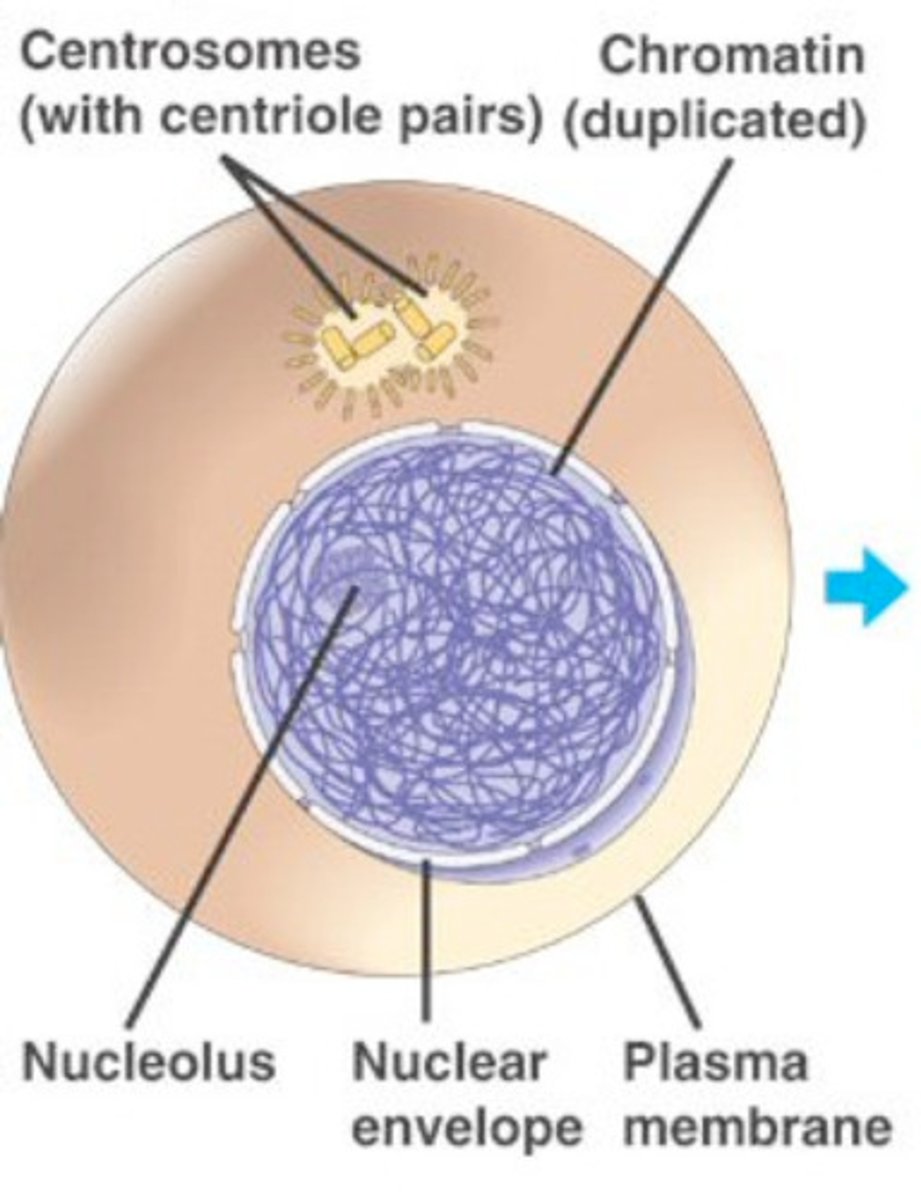
Interphase
Cell grows, performs its normal functions, and prepares for division; consists of G1, S, and G2 phases
G1
In interphase - cell grows rapidly, builds new organelles.
S phase
The "synthesis" phase of the cell cycle; the portion of interphase during which DNA is replicated.
G2
Final preparation phase. Cell checks for DNA errors and begins to form centrosomes.
Prophase
First phase of mitosis in which chromosomes become visible and nuclear membrane disappears

Metaphase
Second phase of mitosis, during which the chromosomes line up across the center of the cell
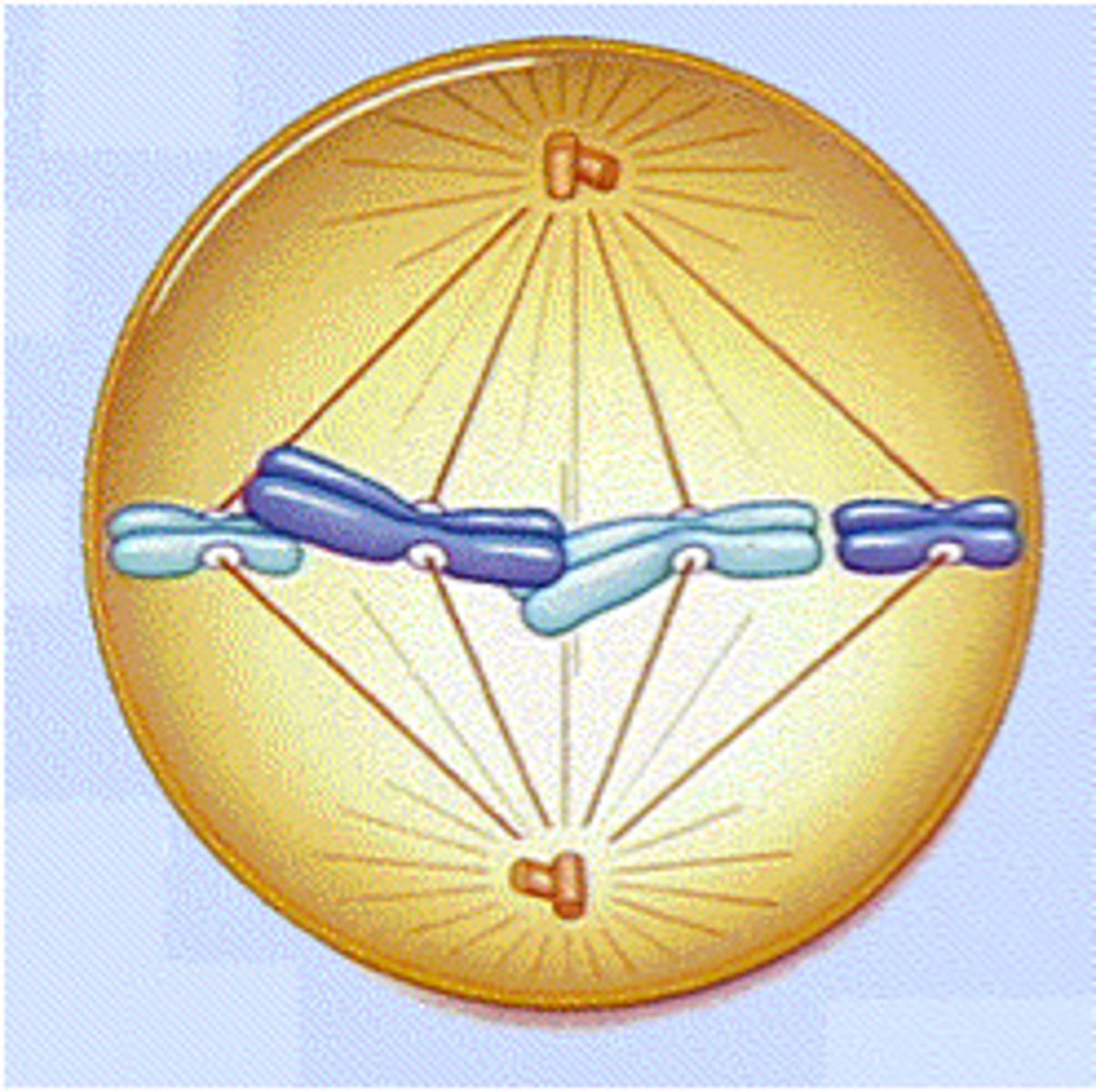
Anaphase
Third phase of mitosis in which sister chromatids are pulled to opposite sides of the cell
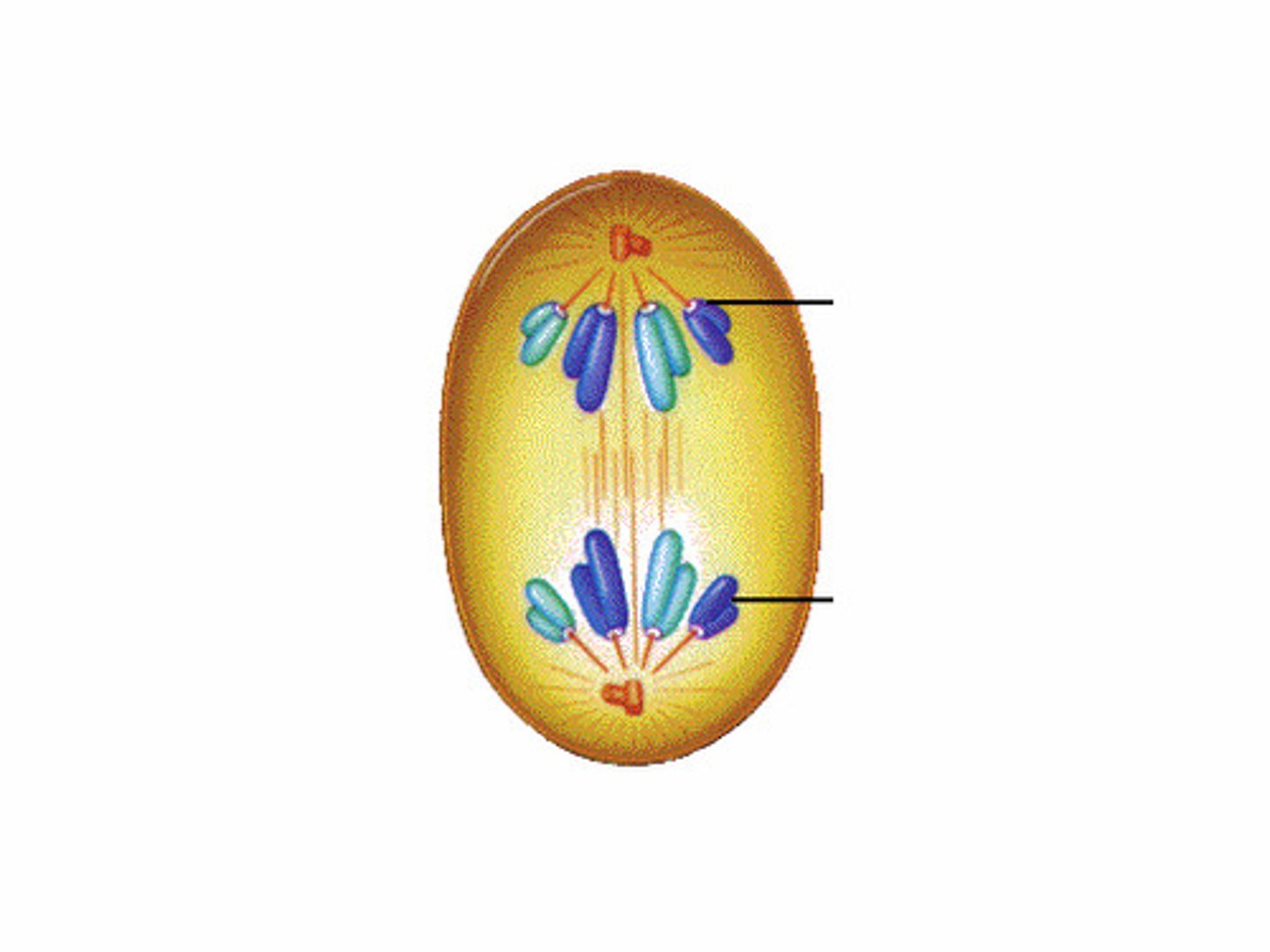
Telophase
The fourth and final stage of mitosis, in which nuclei are forming and cytokinesis has typically begun.
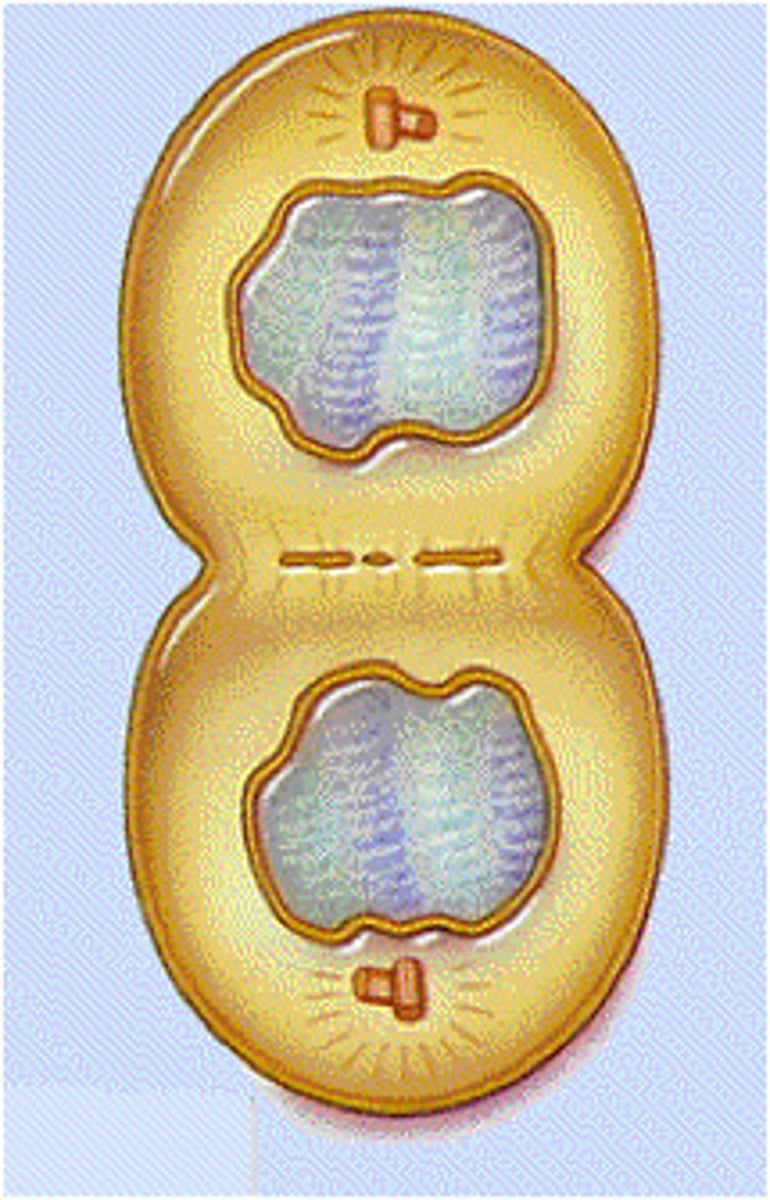
Cytokinesis
Division of the cytoplasm during cell division
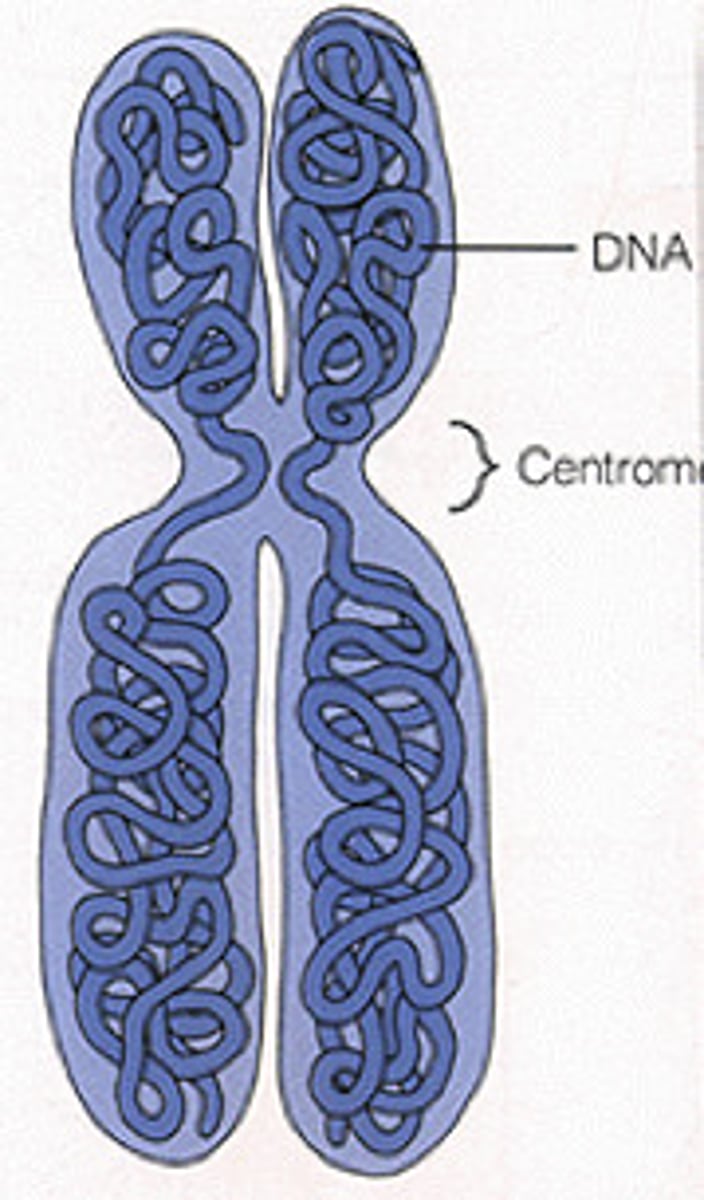
Chromosomes
X-like bodies of tightly coiled chromatin; visible during cell division.
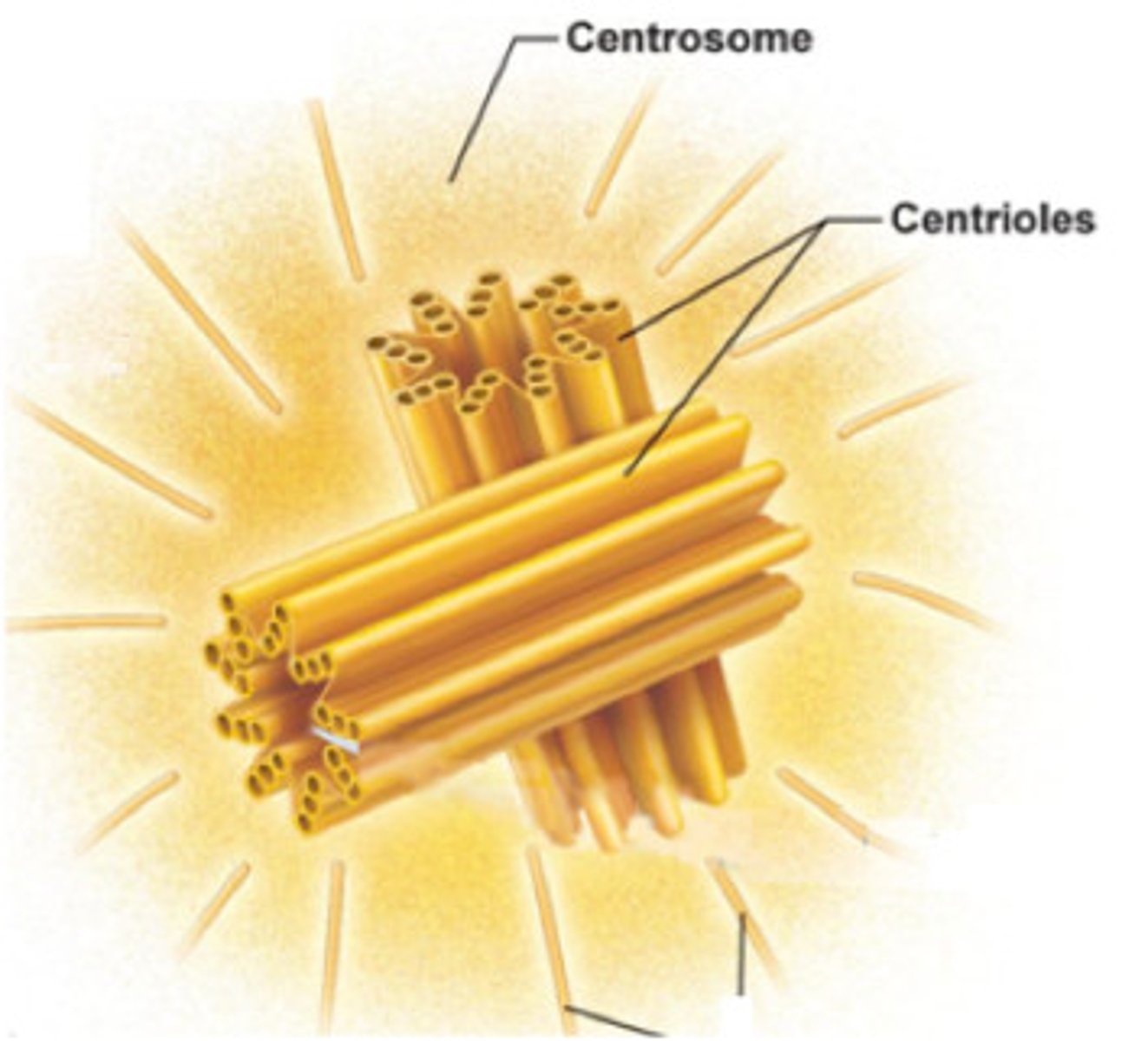
Centrosomes
Areas from which spindle fibers form.
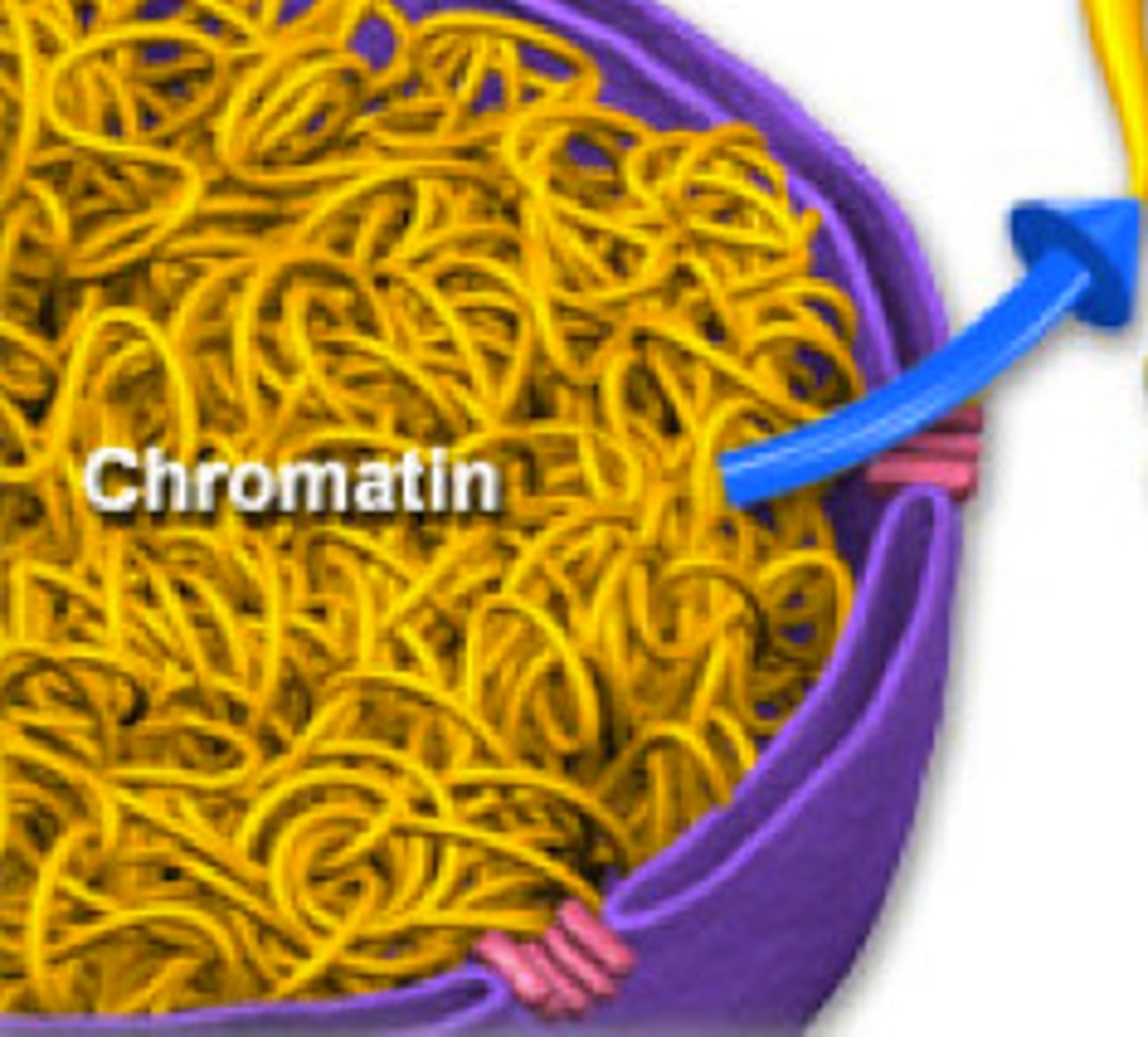
Chromatin
The DNA found in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell. When the cell is not dividing, chromatin exists as a mass of very long, thin fibers that are not visible with a light microscope.
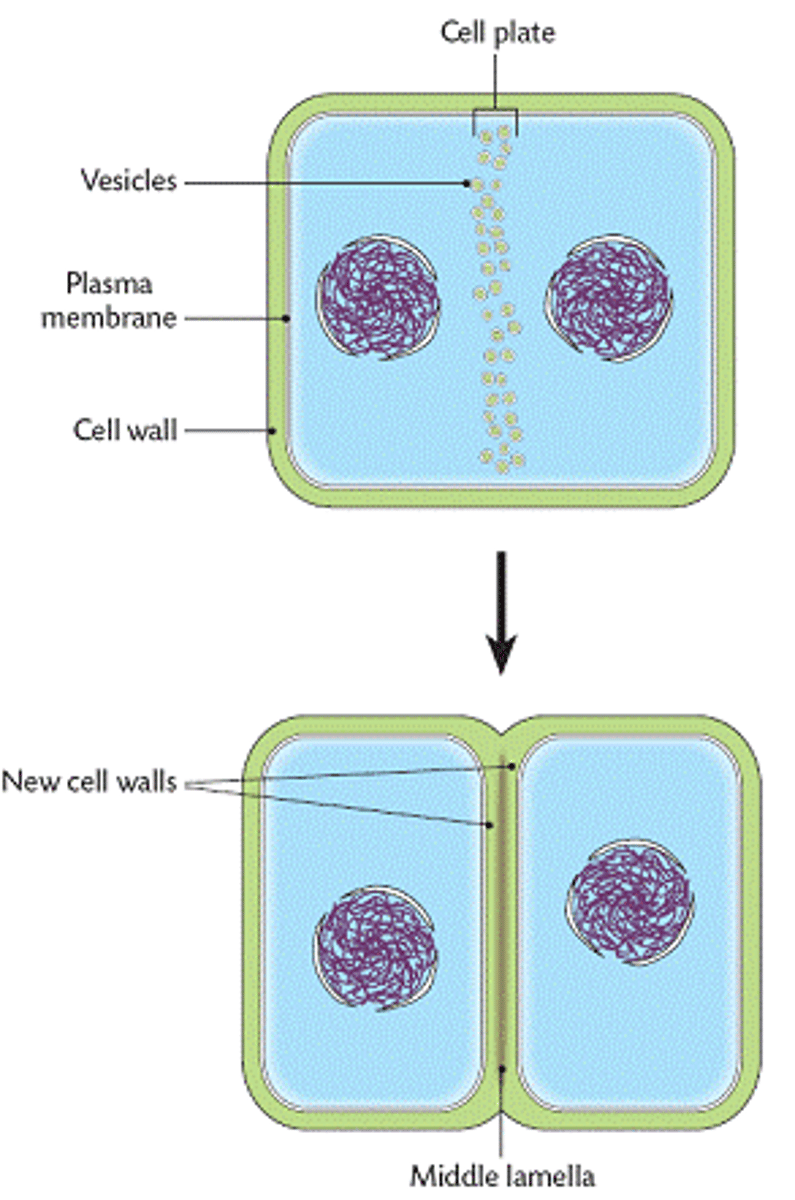
cell plate
In a plant cell, midline of dividing cells. Becomes the cell wall eventually.
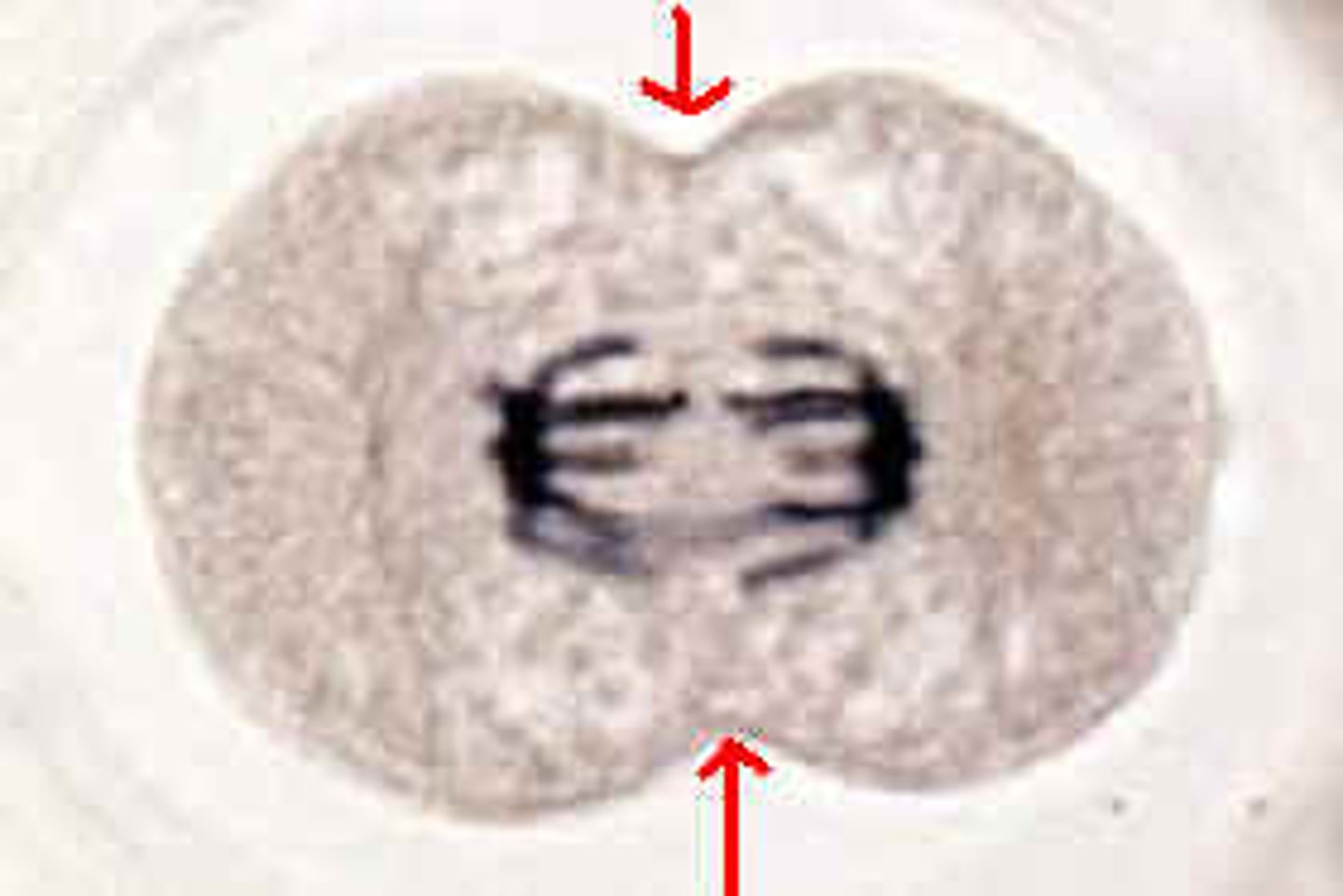
clevage furrow
the division in animal cell cytoplasm caused by the pinching in of the cell membrane
growth factors
Regulatory proteins that ensure that the events of cell division occur in the proper sequence and at the correct rate.
benign tumor
a mass of abnormal cells that remains at the site of origin
malignant tumor
An abnormal tissue mass that can spread into neighboring tissue and to other parts of the body; a cancerous tumor.
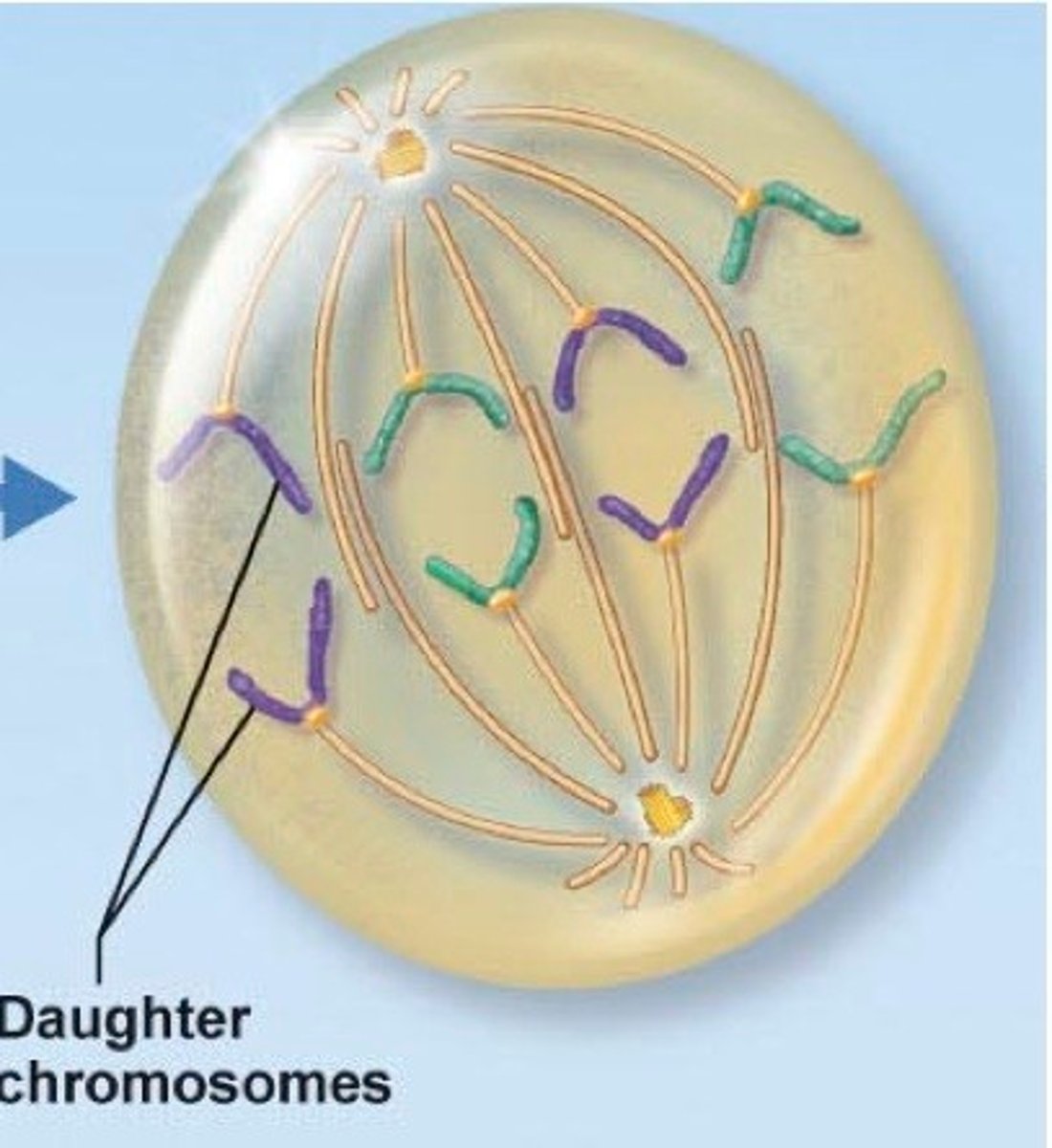
daughter chromosomes
Sister chromatids that are separated by mitosis
Centromere
Region of a chromosome where the two sister chromatids attach