THE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Urethra
Identity this male reproductive system (marked with 1)
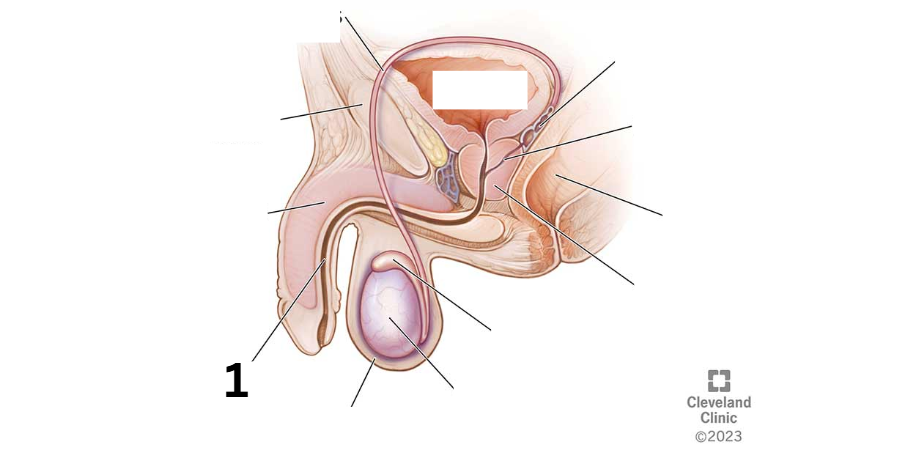
Penis
Identity this male reproductive system (marked with 2)
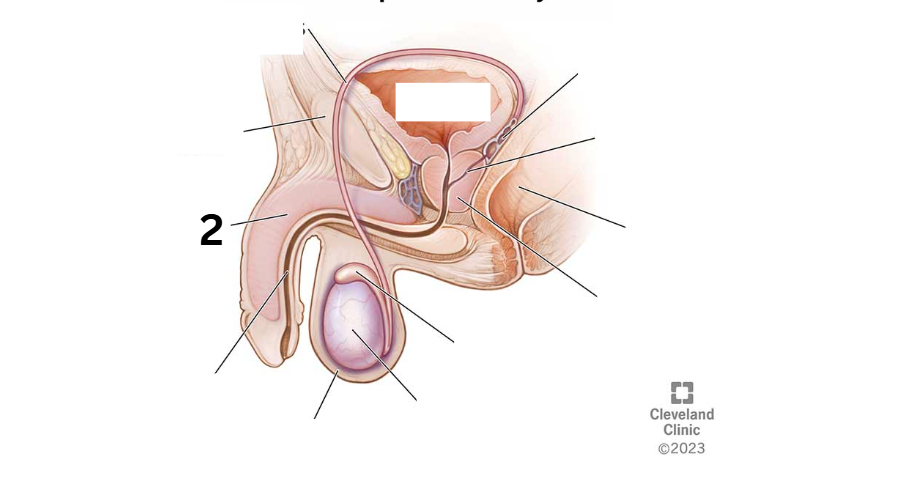
Pubic bone
Identity this male reproductive system (marked with 3)
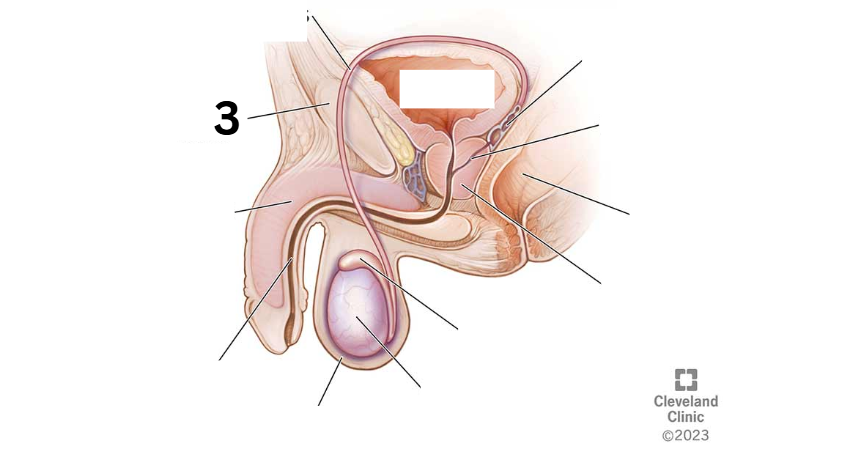
Vas deferens
Identity this male reproductive system (marked with 4)
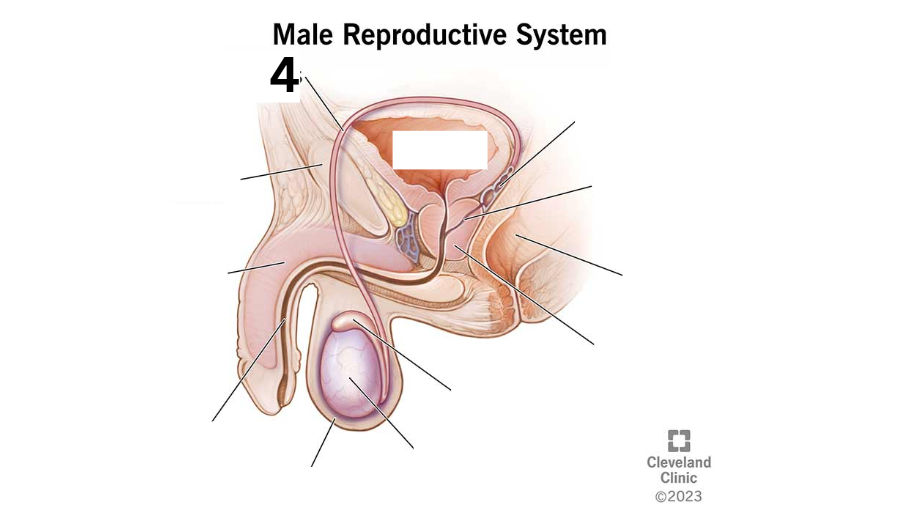
Bladder
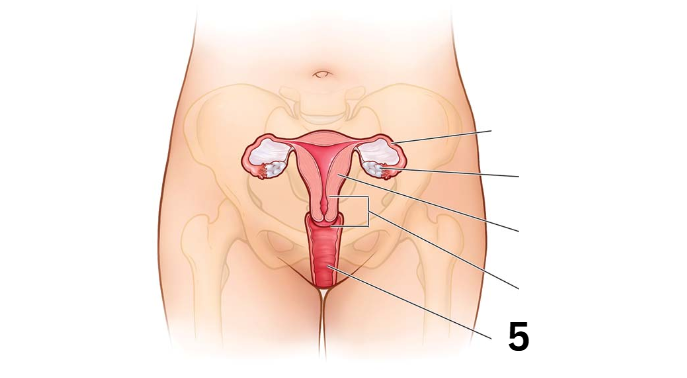
Identity this male reproductive system (marked with 5)
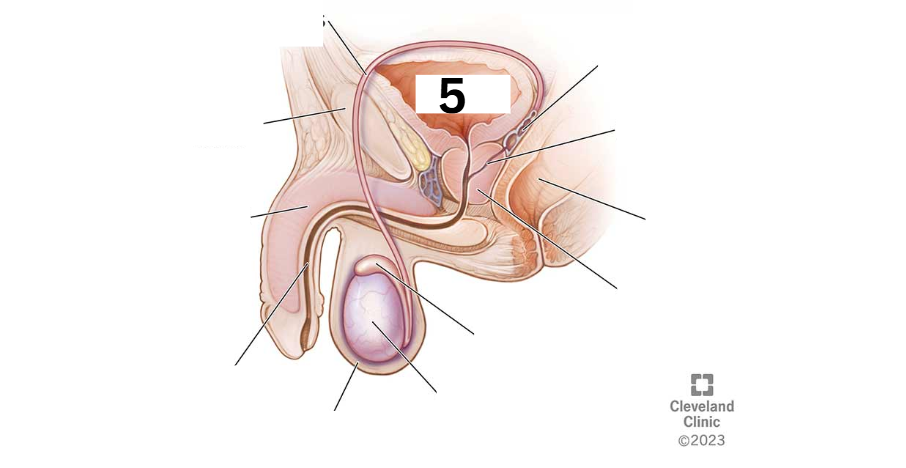
Seminal vesicle
Identity this male reproductive system (marked with 6)
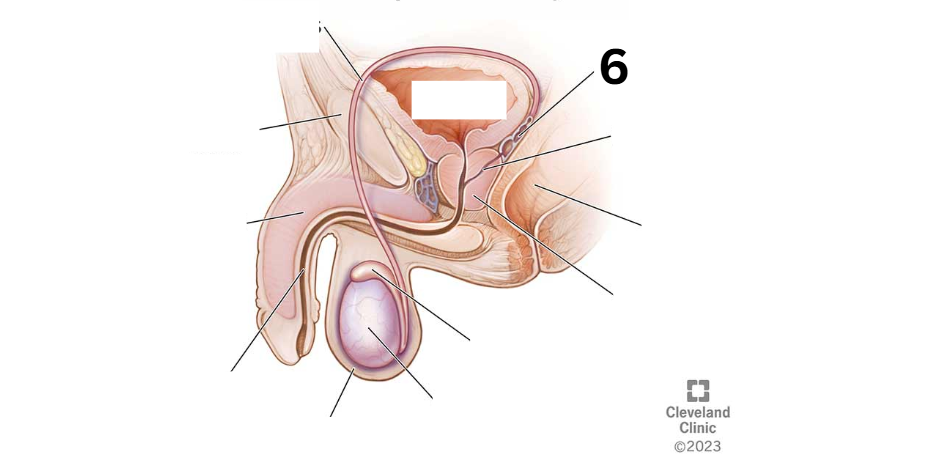
Ejaculatory duct
Identity this male reproductive system (marked with 7)
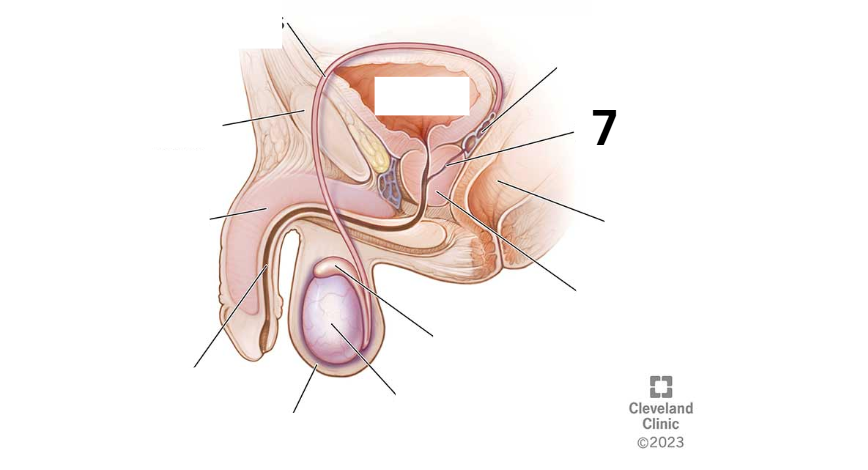
Rectum
Identity this male reproductive system (marked with 8)
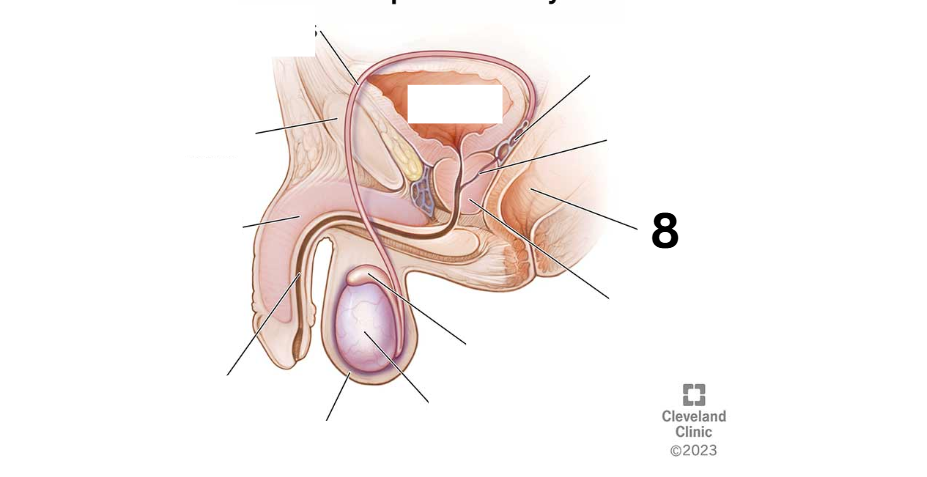
Prostate
Identity this male reproductive system (marked with 9)
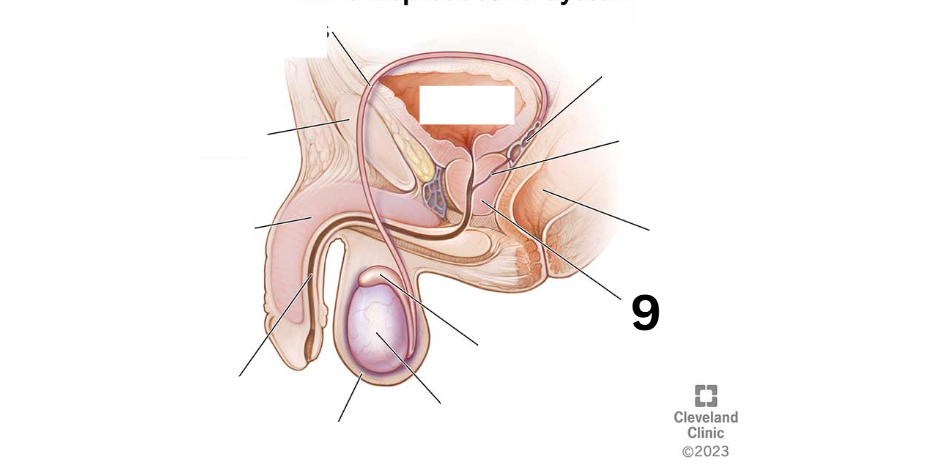
Epididymis
Identity this male reproductive system (marked with 10)
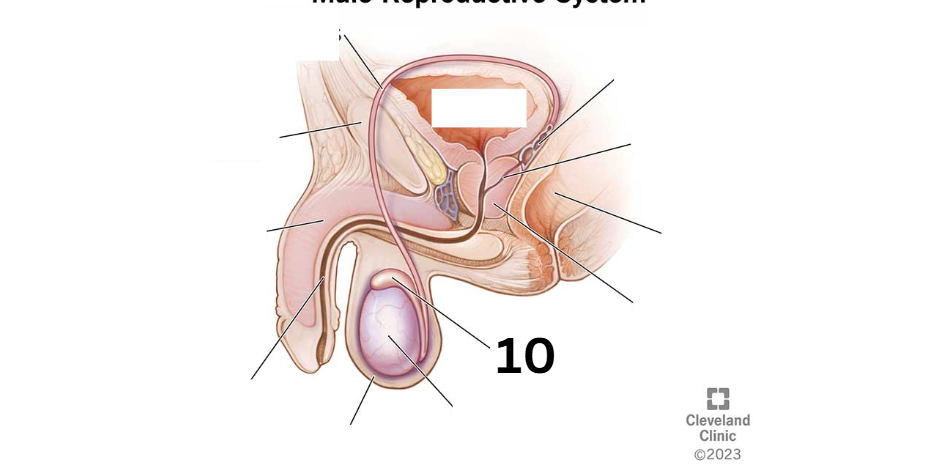
Testicle
Identity this male reproductive system (marked with 11)
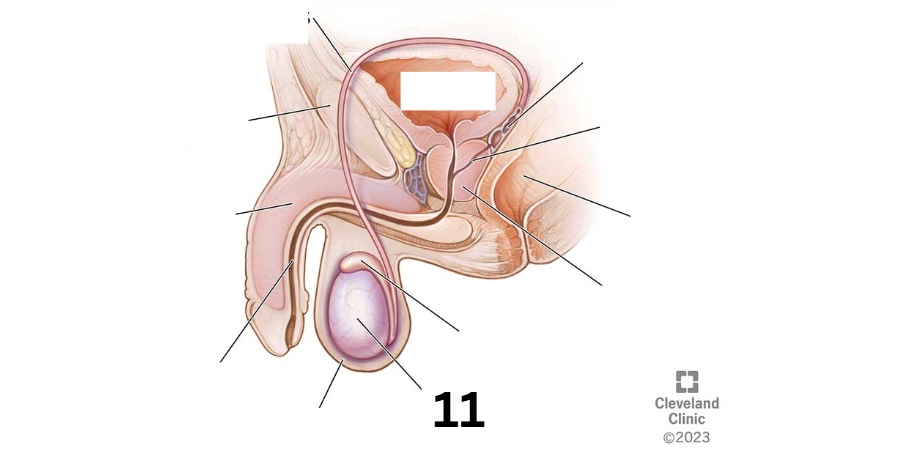
Scrotum
Identity this male reproductive system (marked with 12)
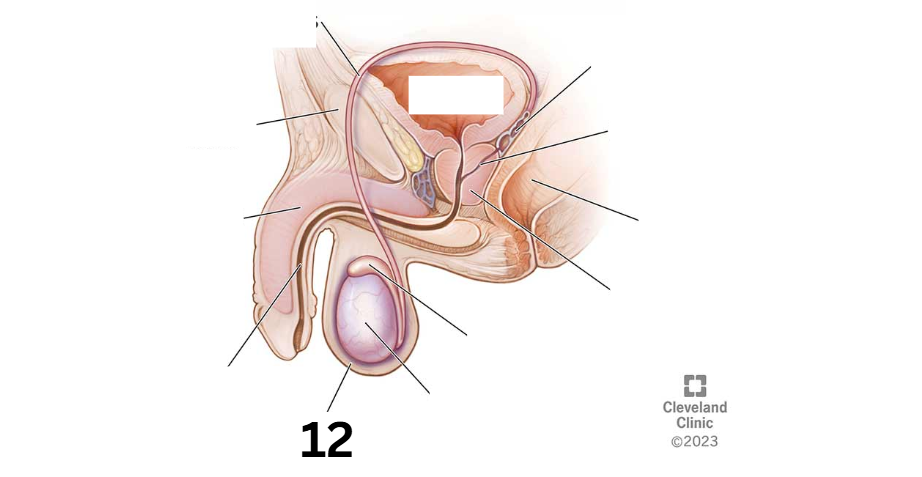
Fallopian tube
Identity this female reproductive system (marked with 1)
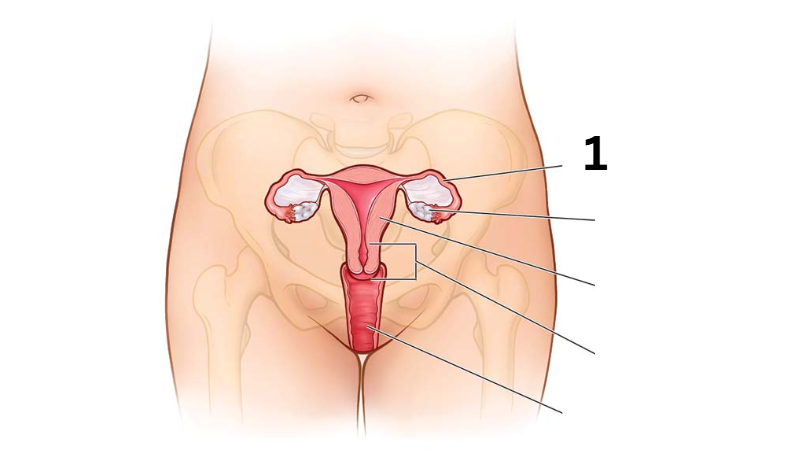
Ovary
Identity this female reproductive system (marked with 2)
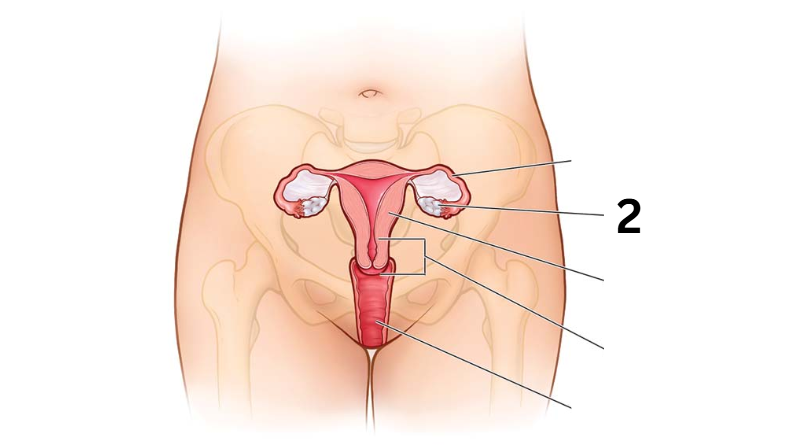
Uterus
Identity this female reproductive system (marked with 3)
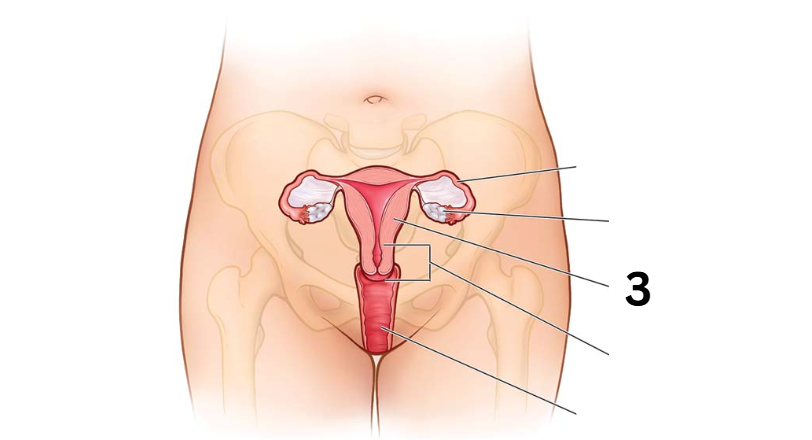
Cervix
Identity this female reproductive system (marked with 4)
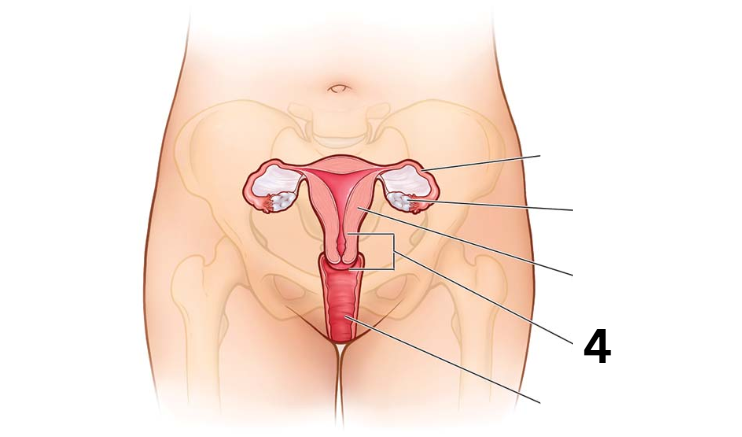
Vagina
Identity this female reproductive system (marked with 5)
Mons pubis
Identity this female reproductive system (marked with 6)
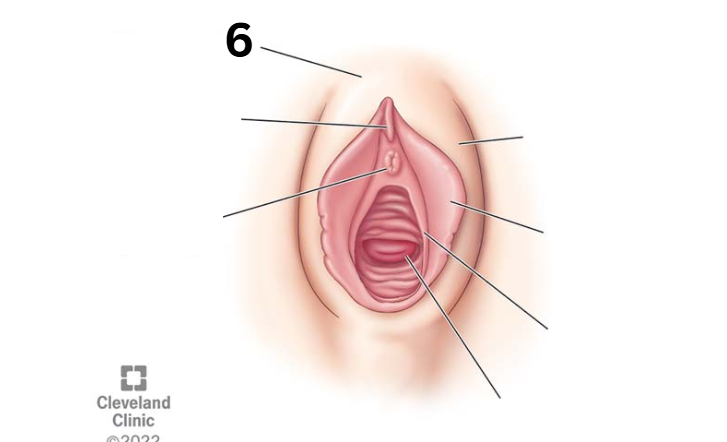
Clitoris
Identity this female reproductive system (marked with 7)
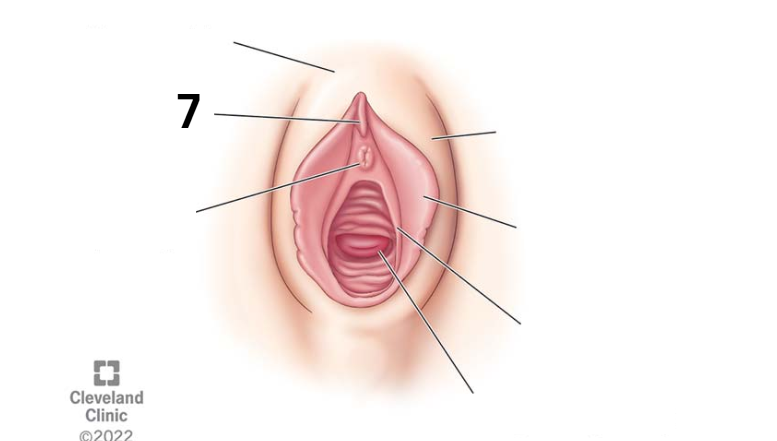
Urethral opening
Identity this female reproductive system (marked with 8)
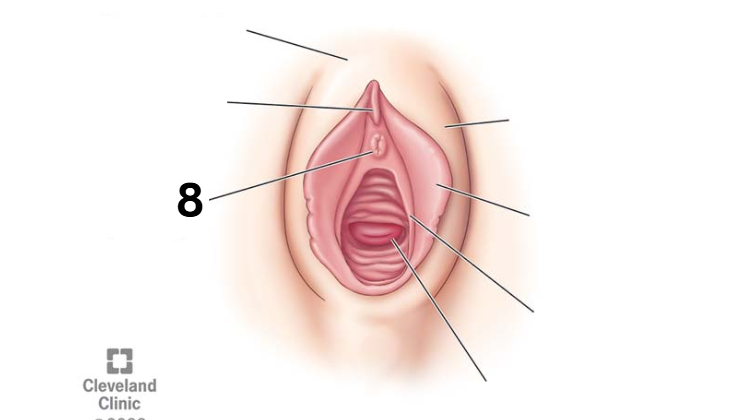
Labia majora
Identity this female reproductive system (marked with 9)
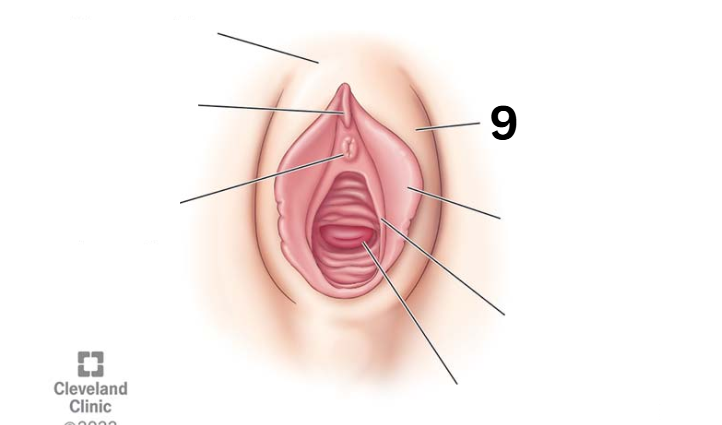
Labia minora
Identity this female reproductive system (marked with 10)
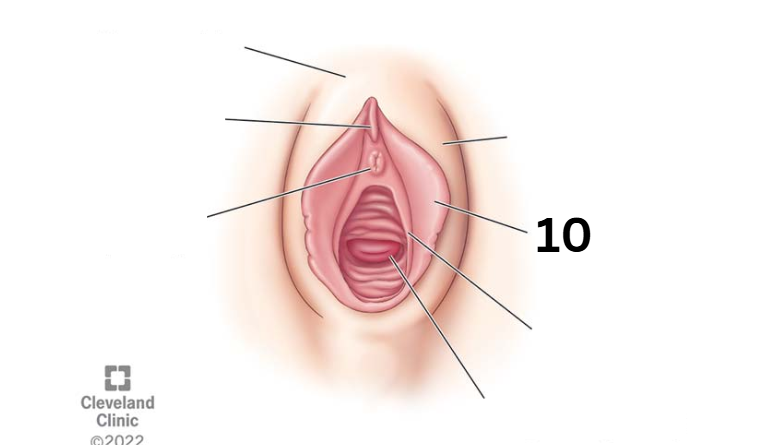
Hymen
Identity this female reproductive system (marked with 11)
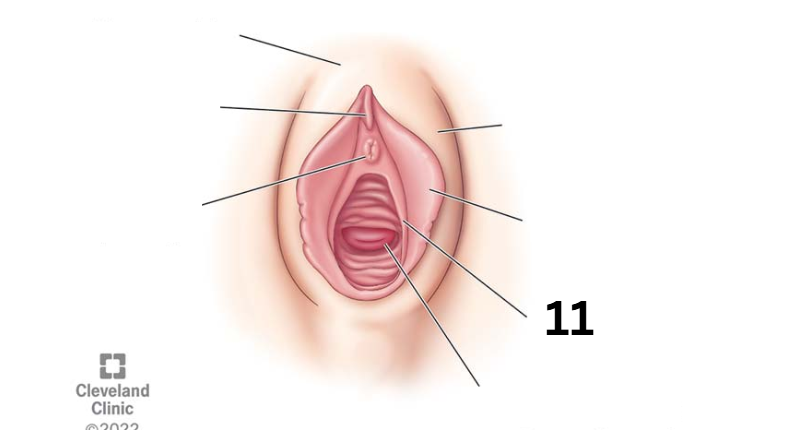
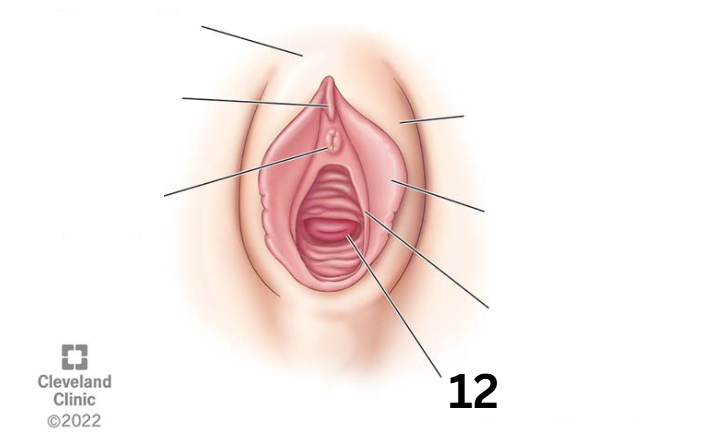
Vaginal opening
Identity this female reproductive system (marked with 12)
Abstinence
This contraceptive refers to the complete avoidance of sexual intercourse, making it the only method that is 100% effective in preventing pregnancy and STDs
Calendar method
This contraceptive involves tracking the menstrual cycle to predict ovulation, aiming to avoid intercourse during the fertile window. It requires careful tracking and is less effective if cycles are irregular
Basal body temperature method
This contraceptive involves tracking daily temperature daily, as slight temperature increase indicate ovulation. Couple avoid intercourse during ovulation
Cervical mucus method
This contraceptive observes changes in cervical mucus consistency, which becomes clearer and stretchier during ovulation. Couples avoid intercourse when fertile mucus is observed
Sympto-thermal method
This contraceptive combines BBT, cervical mucus observation, and sometimes other physical symptoms (e.g. ovulation pain) to predict fertility
Coitus interruptus (withdrawal)
A type of contraceptive where the male partner withdraws before ejaculation to prevent sperm from entering the vagina. This method requires precise timing and is not highly reliable
Condom
This contraceptive uses a barrier method worn over the penis or inside the vagina to prevent sperm from entering the uterus. It also protects against most STDs
Cervical cap
This contraceptive uses a small, flexible cap inserted over the cervix to block sperm from entering. It must be used with spermicide for effectiveness and left in place after intercourse
IUD
This contraceptive uses a t-shaped device inserted into the uterus by a healthcare provider. It release hormones or uses copper to prevent sperm from fertilizing the egg and can last from 3-10 years
Vaginal ring
This contraceptive uses a small, flexible ring inserted into the vagina that releases hormones to prevent ovulation. Its worn for three weeks each month, then removed for a week
Patch
This contraceptive is applied to the skin that releases hormones to prevent ovulation. It is worn for three weeks and removed for a week to allow menstruation
Subdermal implants
This contraceptive uses small rods placed under the skin of the upper arm that release hormones to prevent ovulation. They can last up to 3-5 years
HIV/AIDS
It is a type of STD that attacks the immune system, leading to immune deficiency (AIDS) if untreated. It is primarily transmitted through unprotected sexual contact, sharing needles, or from mother to child during birth or breastfeeding
Genital Herpes
This STD is a viral infection leads to sores and blisters on the genitals or mouth. It is highly contagious and can be spread through skin to skin contact
Gonorrhea
This type of STD is a bacterial infection that affects the mucous membranes of the genital tract, rectum, and throat. Symptoms include pain and discharge, but it can be asymptomatic. It is treatable with antibiotics
Syphilis
This type of STD is a bacterial infection that progresses in stages if untreated, starting with sores and rashes, potentially leading to severe organ damage. It is curable with antibiotics in early stages