ECON 248 15.1 How Monetary Policy Influences Aggregate Demand
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
The purpose of () is to control money and interest rates in order to avoid () and () shifts in Real GDP and unemployment rates.
Monetary Policies, Inflation, Sudden
A strategy where a central bank commits to specific inflation target, explaining how it will reach that target.
Inflation Targeting
Monetary policy in Canada involves using () and () to influence aggregate planned expenditures and aggregate demand.
Overnight Rate, Cash Management Operations(Open Market Operations)
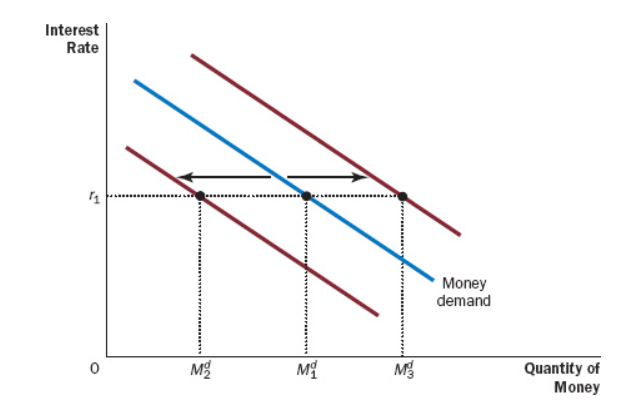
An increase in money supply would reduce () and cause aggregate demand to shift to the ().
Equilibrium Interest Rate, Right
A lower interest rate causes a lower ().
Real Exchange Rate
Monetary policies have greater impact on () in a () than () due to the former being able to act as a ().
Aggregate Demand, Flexible Exchange Rate Systems, Fixed Exchange Rate Systems, Monetary Policy Transmission Channel
An increase in the () decreases money supply since commercial banks will less likely to loan from a central bank with high interest.
Bank Rate
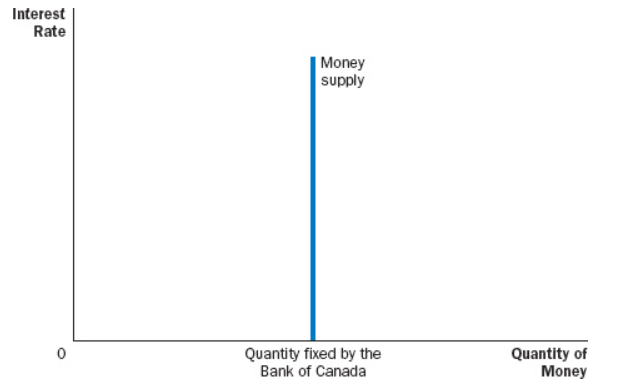
A method to increase money supply is when a central bank buys () or () in an () or ().
Bonds, Foreign Currency, Open Market Operation, Foreign Currency Market Operation
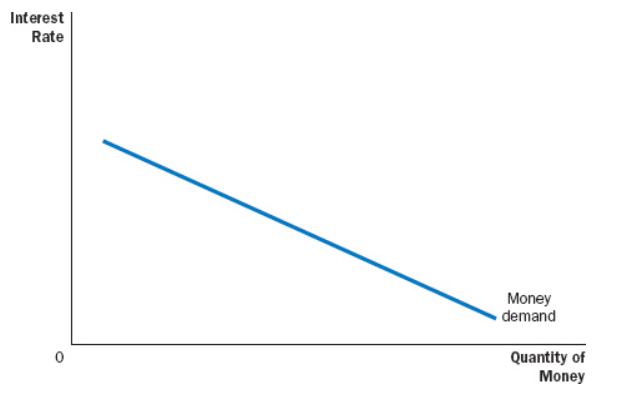
The main factor which affects money demand emphasized by liquidity preference theory is ().
Interest Rate
When the dollar value of transactions increases either due to an increase in prices of GDP, then the demand curve for money shifts ().
Right