chemistry - rates of reactions
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
What is the equation for the rates of a reaction?
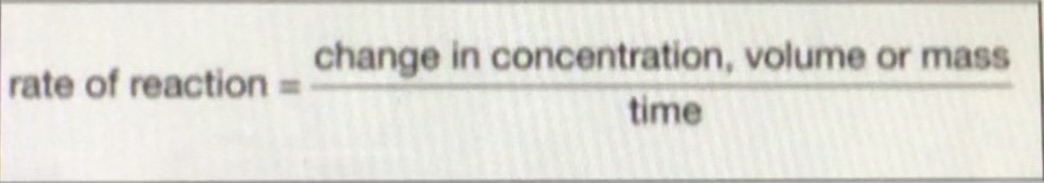
What are the 3 main ways to measure the rate of a reaction?
Loss of mass method
Gas collection method
‘Disappearing cross’ method
Describe the ‘loss of mass’ method:
Conduct the experiment on a balance
This enables you to watch the mass changing as the reaction occurs.
Use a stopwatch to measure the mass lost over time
What types of reactions are suitable for the loss of mass method?
Reactions where a gas is produces because the gas escapes the vessel causing the mass to decrease.
Describe the gas collection method:
Collect gas in a gas syringe to measure the volume of gas given off.
Use a stopwatch to see what volume of gas is given off over what time.
What type of reaction is the gas collection method suitable for?
reactions where a gas is produced.
Describe the ‘disappearing cross’ method
Draw a black x on a white piece of paper.
Place a conical flask on top of the cross
Add your mixture of reactants to the flask.
Look through the top of the flask and time how long it takes for the x to disappear.
What type of reactions is the ‘disappearing cross’ method suitable for?
Reactions that start with solutions and produce a solid.
What is an exothermic reaction?
A reaction which gives out energy to its surrounding.
What is an endothermic reaction?
A reaction which takes in energy from the surrounding.
How do rates of reaction change with time? (model answer)
fastest at the start of the reaction because the concentration of reactants is high so there is more frequent collisions.
The reaction slows down because the concentration of reactant decreases so there are less frequent collisions.
The reaction stops because there are no more reactant particles so there are no more collisions.
What is the activation energy?
The amount of energy needed for a reaction to take place.
What two things do you need to do to increase the rate of reaction?
1) increase the frequency of collisions
2) and/or increase the energy that the reactant have when they collide
how does increasing the surface area of a reactant affect the rate of reaction?
Increases the rate of reaction because there are more particles available to react so there are more frequent collisions.
how does increasing the concentration of a reactant affect the rate of reaction?
Increases the rate of reaction because there are more particles in a given volume so there are more frequent collisions.
how does increasing the pressure of a reactant affect the rate of reaction?
Increases the rate of reaction because there are more particles in a given volume so there are more frequent collisions.
how does increasing the temperature of a reactant affect the rate of reaction?
Increases the rate of reaction because the particles have more kinetic energy, so more particles collide with energy above the activation energy, so there are more frequent successful collisions.
What is a catalyst?
A substance that speeds up a chemical reaction but is not used up in the process.
How does a catalyst work?
Provide an alternative route pathway the reaction that has a lower activation energy.