Macroeconomics UNIT 1 MULTIPLE-CHOICE SAMPLE QUESTIONS
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
The crucial problem of economics is...
allocating scarce productive resources to satisfy unlimited wants.
When one decision is made, the next best alternative not selected is called...
opportunity cost.
Which of the following is true if the production possibilities curve is a curved line concave to the origin?
As more of one good is produced, increasing amounts of the other good must be given up.
Which of the following will not change the demand for oranges?
A change in the price of oranges
To be considered scarce, an economic resource must be...
limited and desirable, but not free.
If there is an increase in demand for a good, what will most likely happen to the price and quantity of the good exchanged?
Price and Quantity Increase
Which of the following goods would be considered scarce? (A) Education (B) Gold (C) Time
Education, gold, and time
An increase in the price of gasoline will cause the demand curve for tires to shift in which direction?
To the left, because gasoline and tires are substitutes
Which of the following indicates that the macroeconomy is achieving its economic goals?
Economic growth
In which way does a straight-line production possibilities curve differ from a concave production possibilities curve?
A straight-line production possibilities curve has a constant opportunity cost.
The law of increasing opportunity cost is reflected in the shape of the...
production possibilities curve concave to the origin.
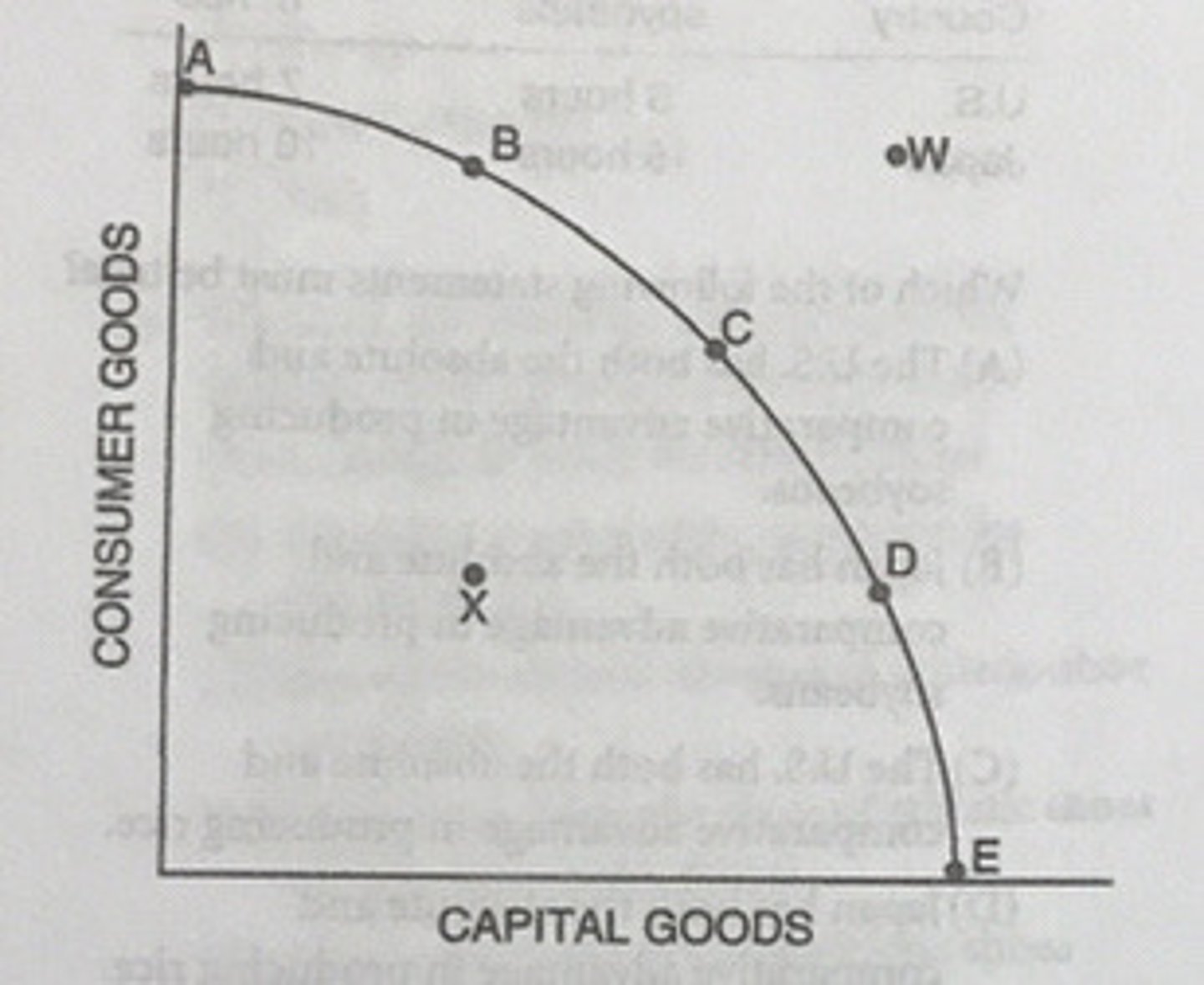
If the country is currently producing at Point C, it can produce more computers by doing which of the following?
Moving to Point D
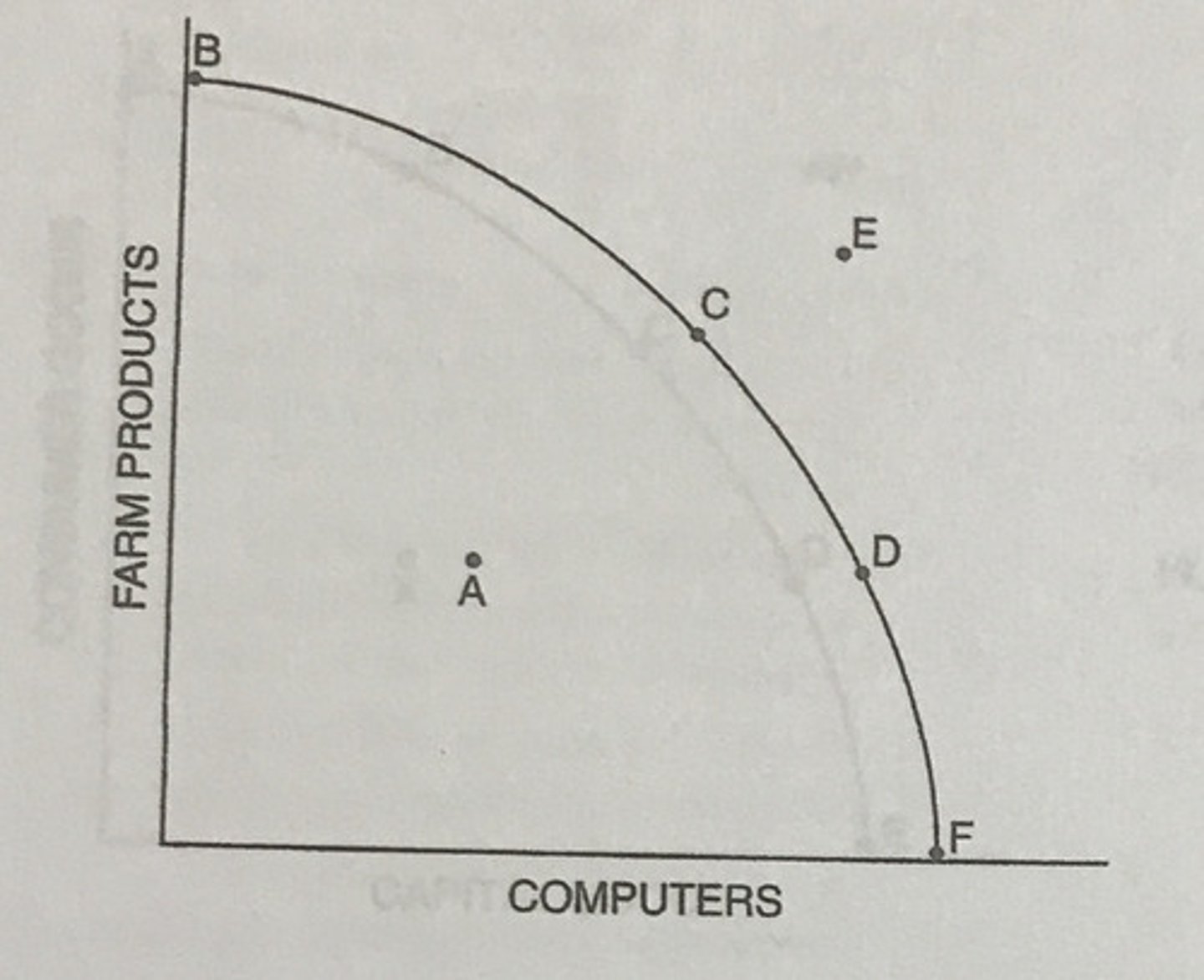
Which of the following statements about the production possibilities curve is true?
The relative positions of Points C and D reflect production alternatives rather than relative prices.
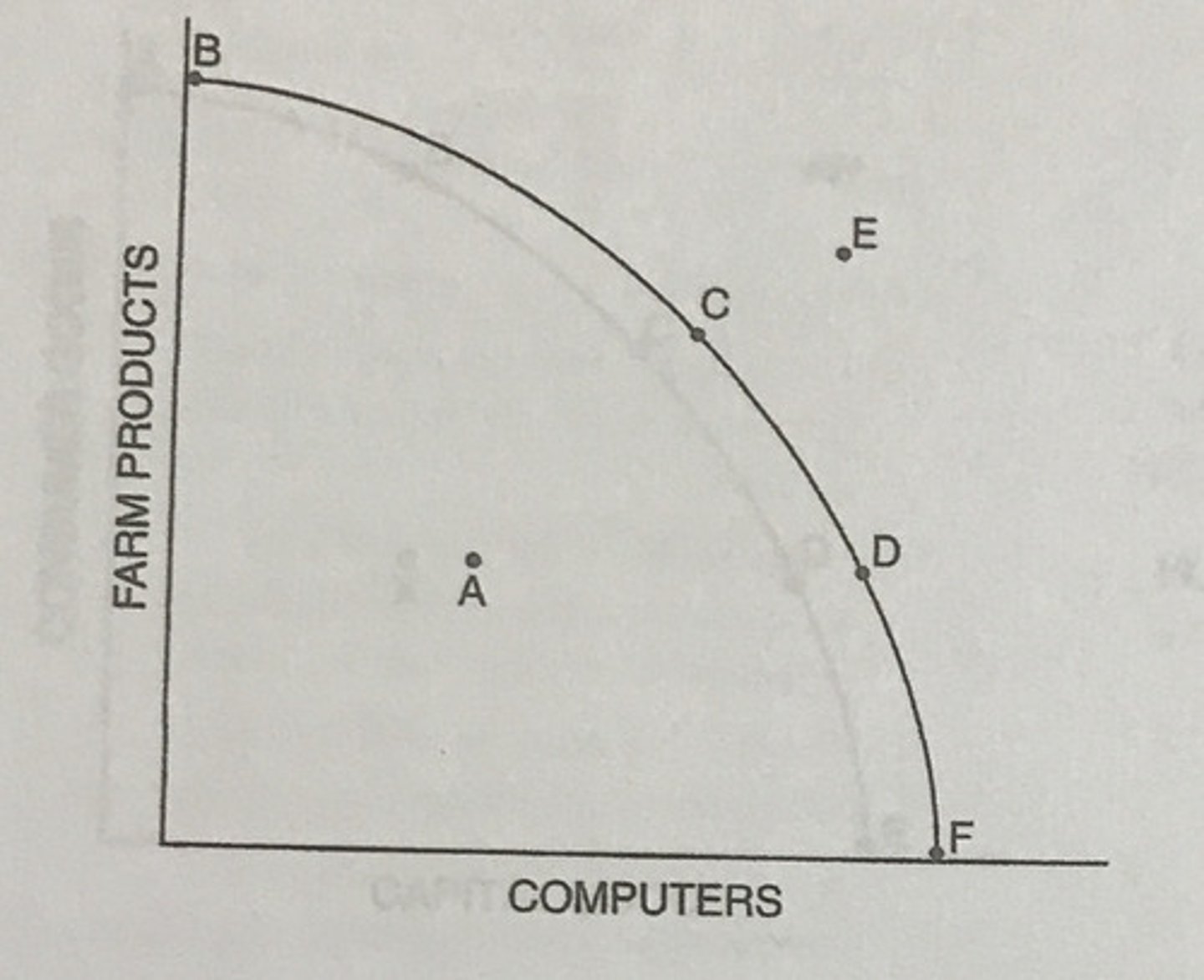
How might Point E be attained?
If improvements in technology occurred in either the computer sector or the farm products sector
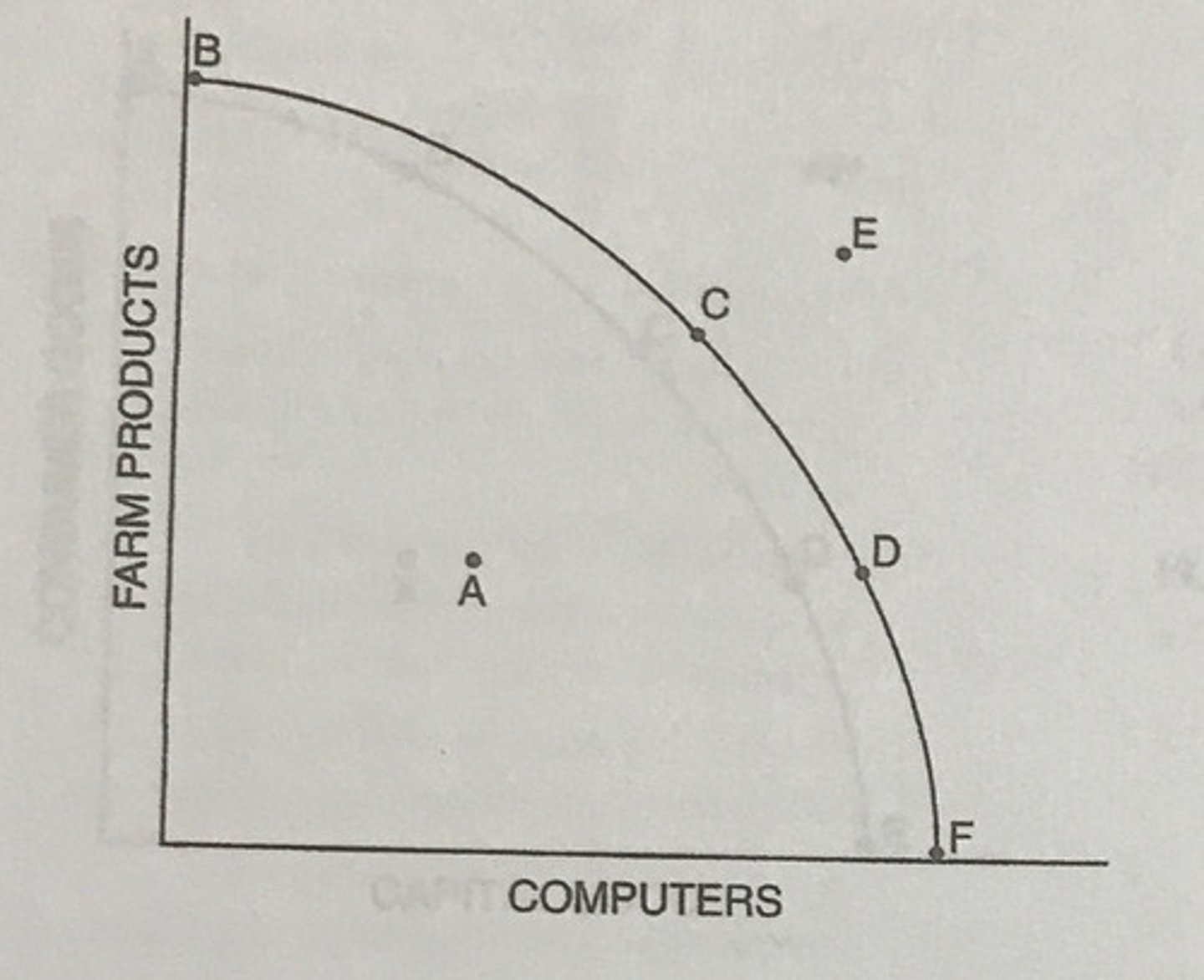
The production possibilities curve of the country would most likely shift to the right if the country were currently producing at which of the following points?
Point D
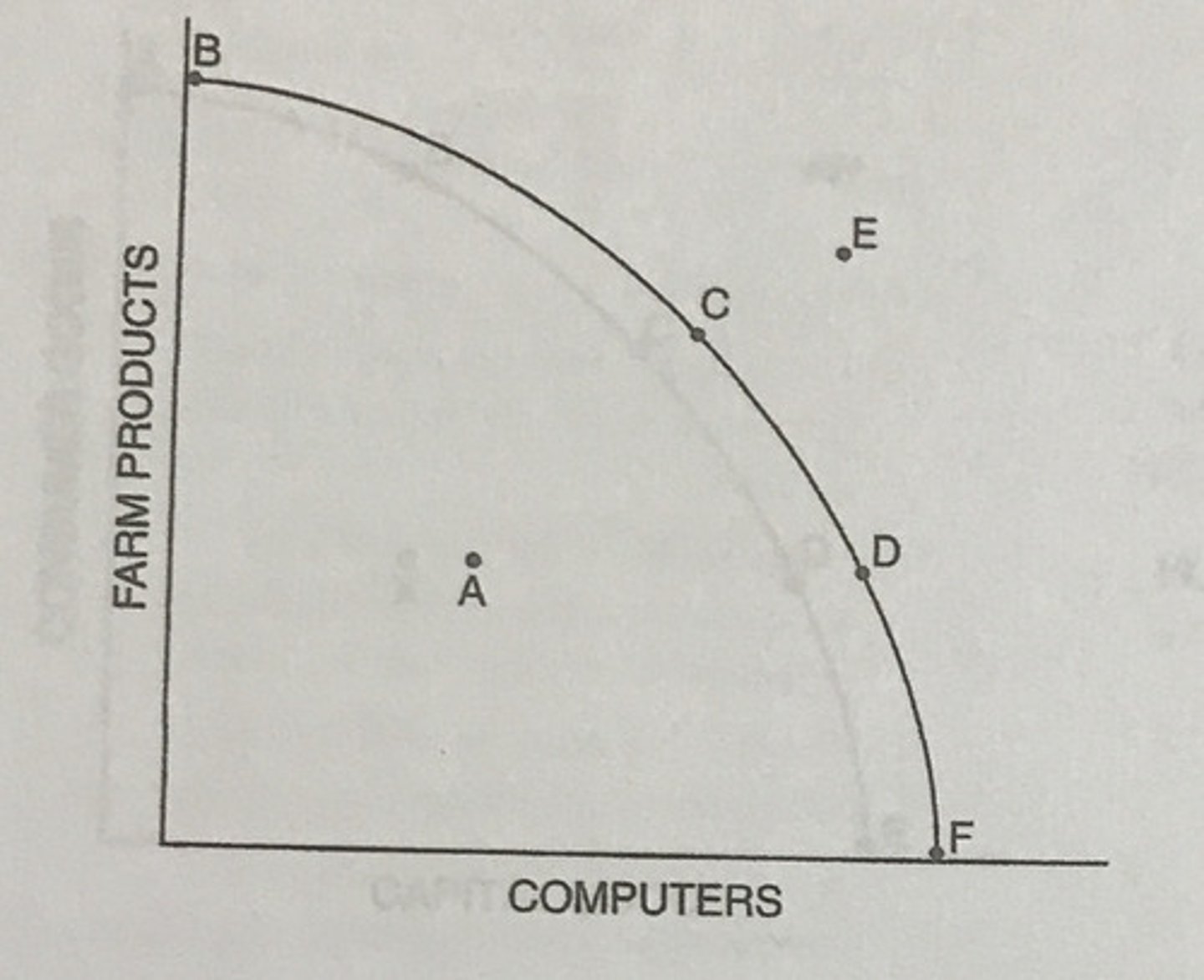
If the country is currently producing at Point C, it can produce more capital goods by moving in the direction of...
Point D
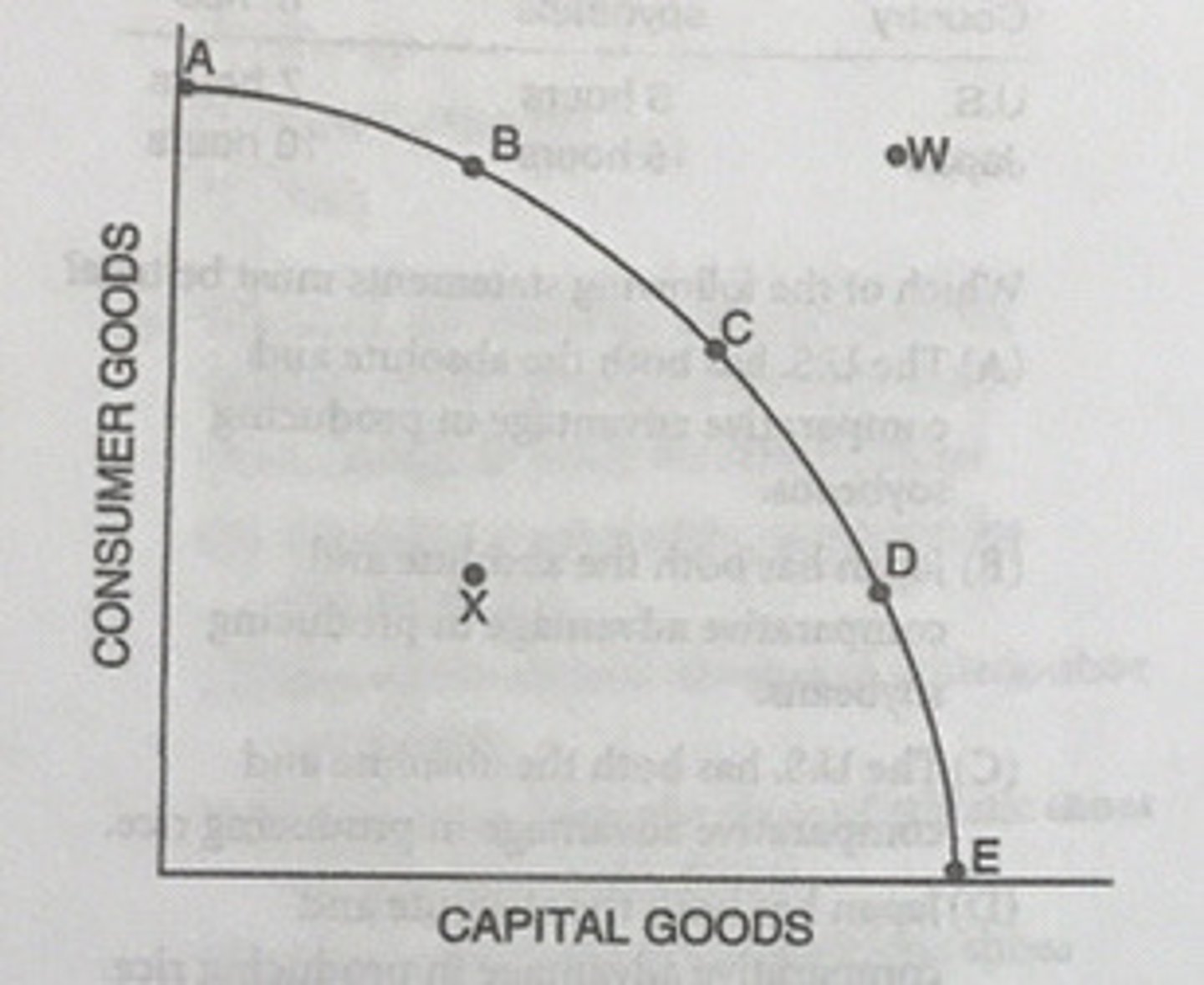
If the country moves from Point C to Point D, future economic growth will...
increase.
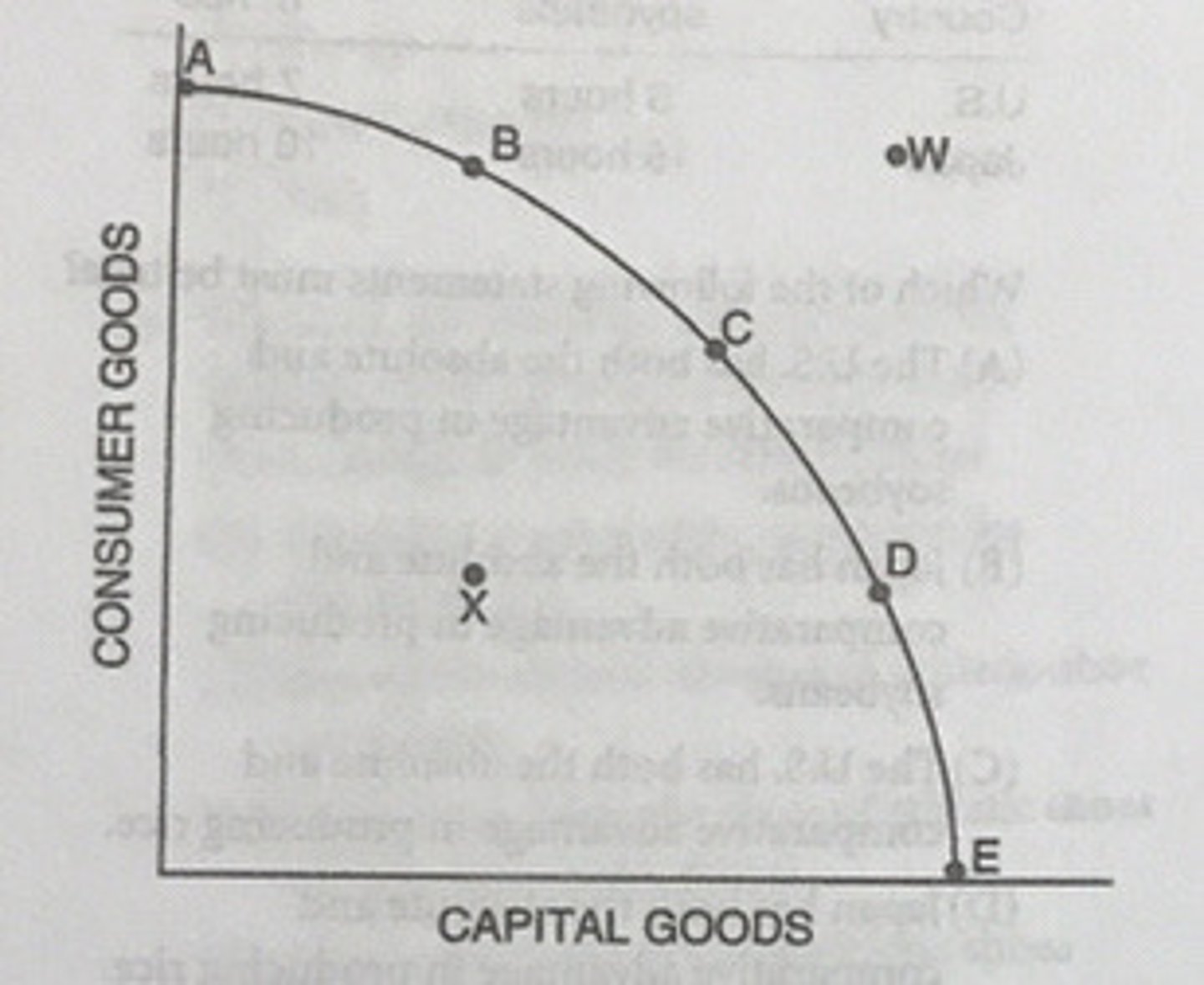
Which of the following is most likely to cause the production possibilities curve to shift outward toward Point W?
Improving the technology for the production of either consumer or capital goods
The opportunity cost of producing an additional unit of product J is...
the amount of product K that could have been produced with the resources used to make the unit of J.
Which of the following would cause a leftward shift of the production possibilities curve
A decrease in working age population
Which of the following would cause an outward or rightward shift in the production possibilities curve?
An increase in capital equipment
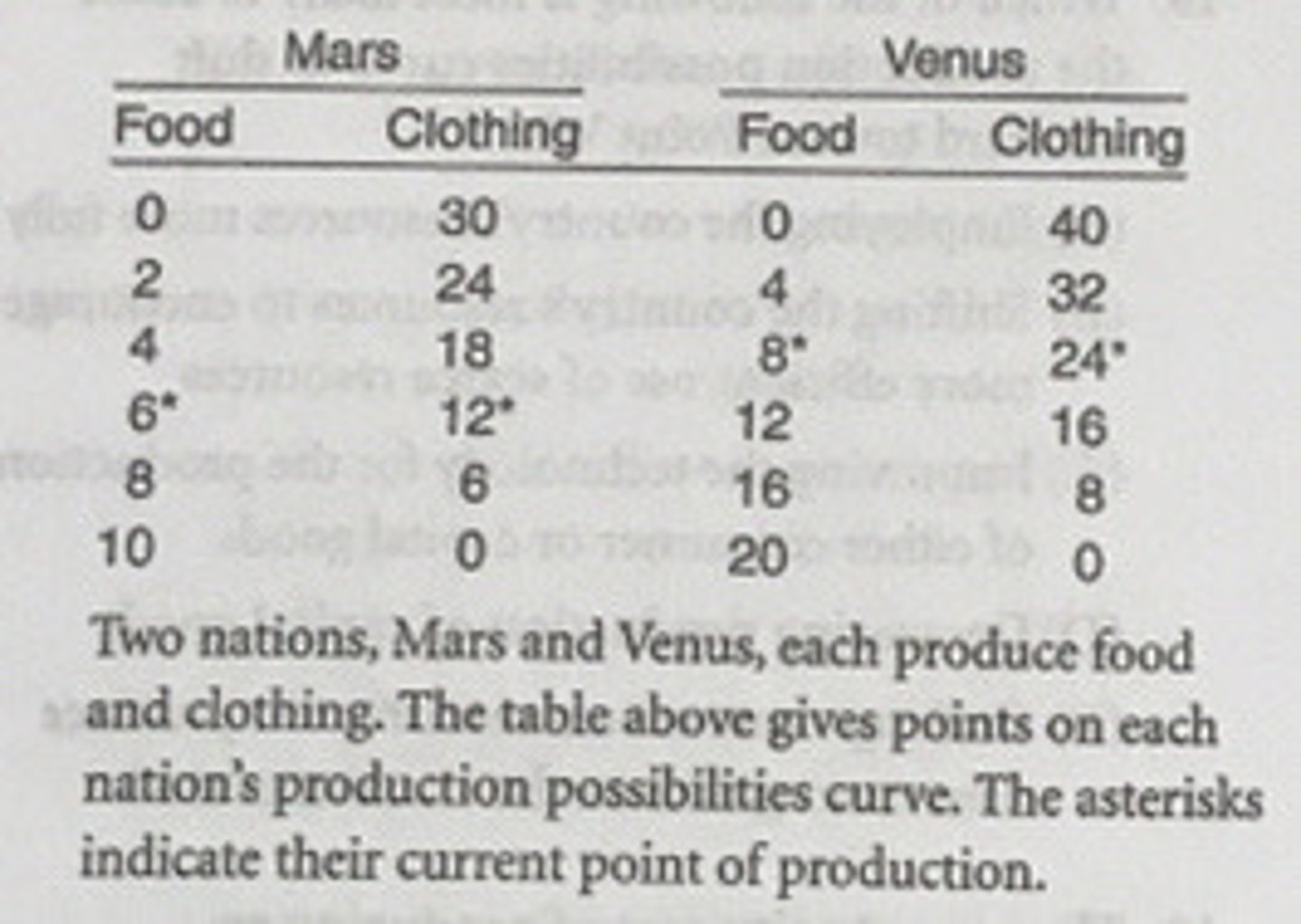
In Mars, the opportunity cost of obtaining the first two units of food is how many units of clothing?
6
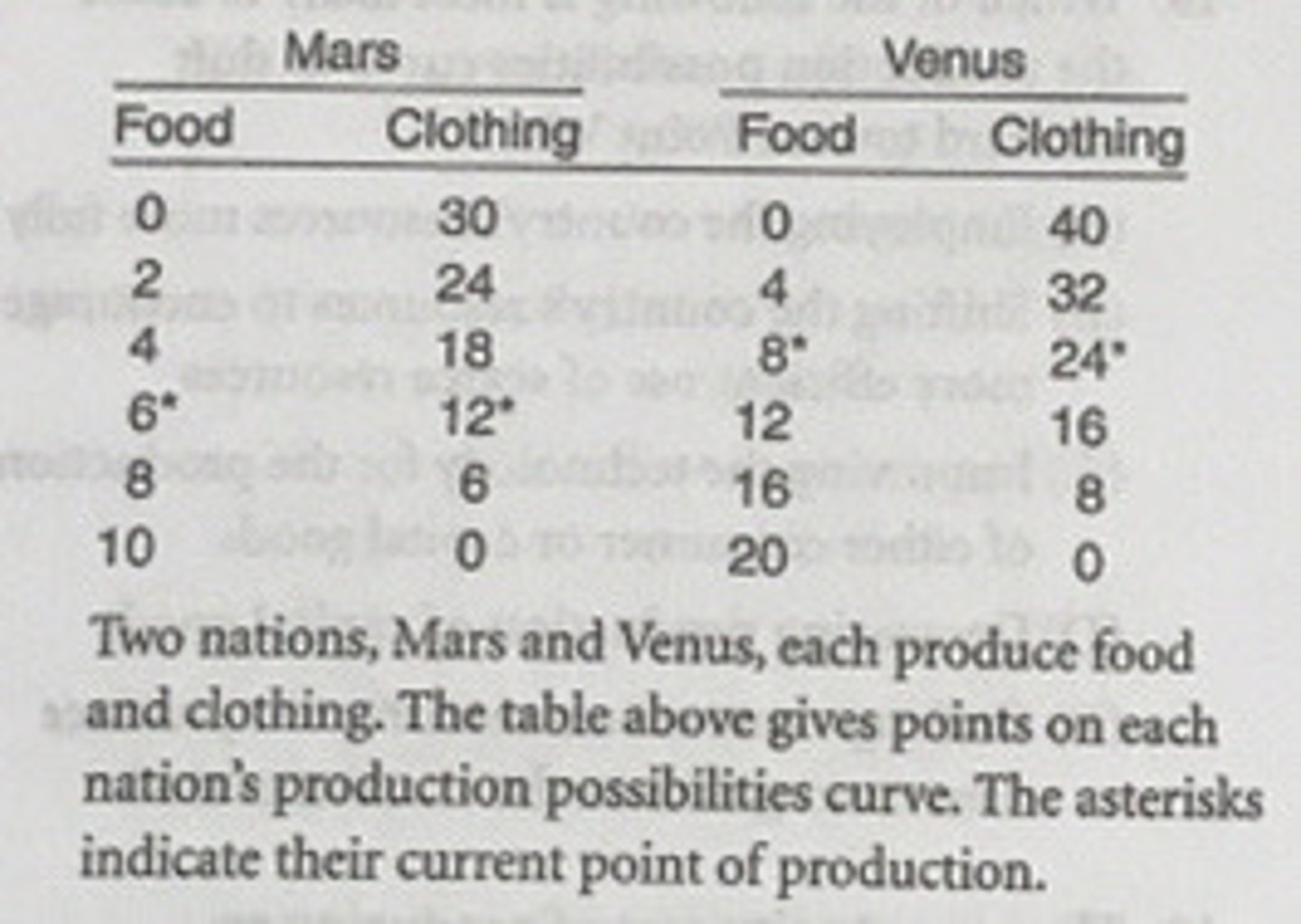
In Venus, the opportunity cost of the first unit of...
food is two units of clothing.
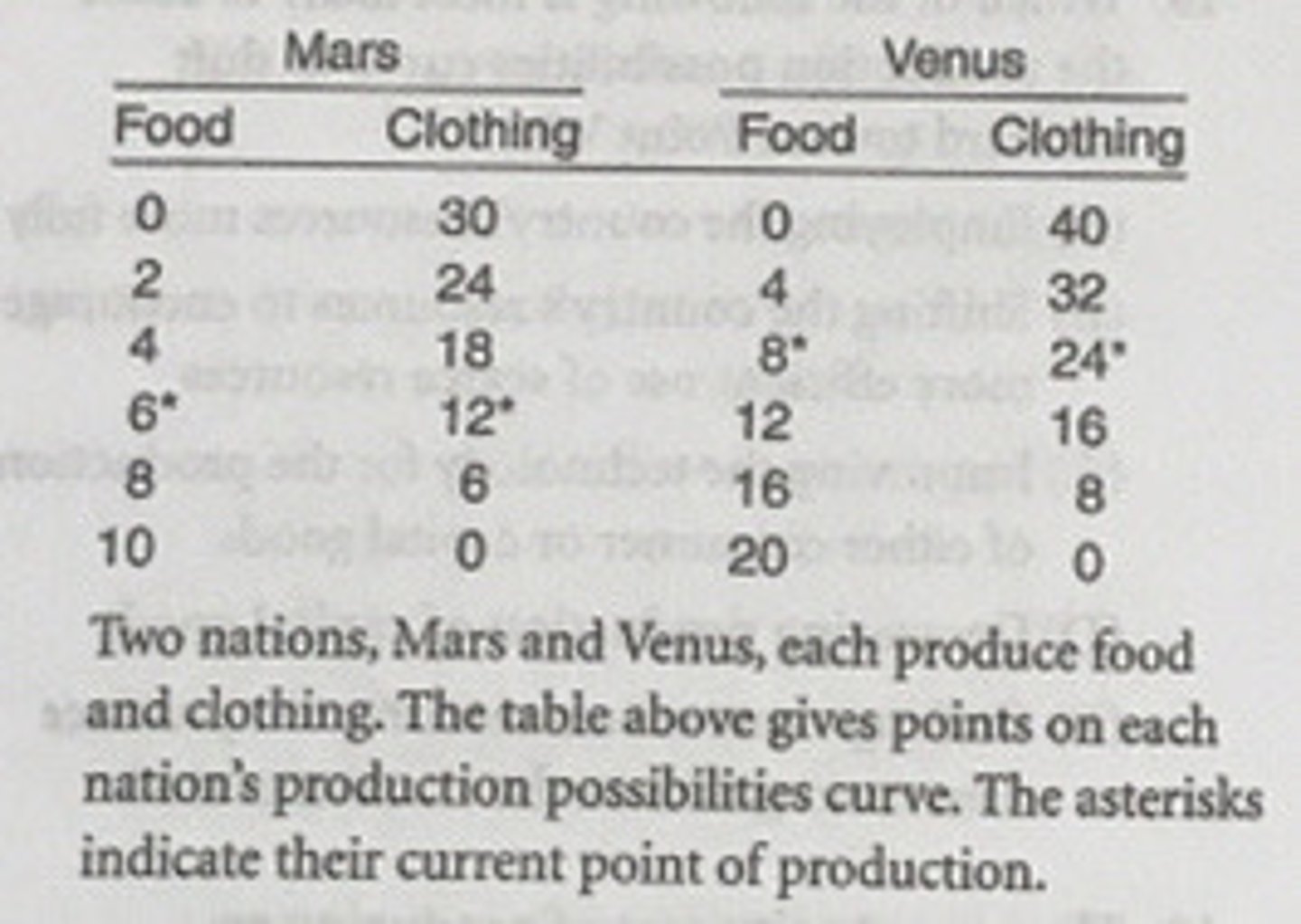
According to the theory of comparative advantage, a good should be produced where...
its opportunity costs are least.
Which of the following statements is correct based on the concept of comparative advantage?
Mars should specialize in the production of clothing.
Which of the following statements must be true?
The U.S. has both the absolute and comparative advantage in producing soybeans.

Unemployment
Trough
A decrease in the price of athletic shoes
Assume that the demand for apples is downward sloping. If the price for apples falls from $0.80 a pound to $0.65 per pound, which of the following will occur?
A larger quantity of apples will be demanded.